The Lymphoid System
Question 1. Write short notes on the types and staging of Hodgkin’s disease.
Answer:
Types of Hodgkin’s Disease.
- Classic Hodgkin’s Disease:
- Nodular Sclerosis Hodgkin’s Disease: Morphology shows a nodular pattern. The broadband of fibrosis divides the node into nodules. The capsule is thick. Lacunar type Reed-Sternbergcell which has a monolobated or multilobated nucleus and a small nucleolus with abundant and pale cytoplasm.
- Mixed Cellularity Hodgkin’s Disease: Infiltrate is diffuse. Reed Sternberg Cells are of classic type. It affects abdominal lymph nodes and the spleen.
- Lymphocyte-Depleted Hodgkin’s Disease: The infiltrate is diffuse and often appears hypocellular. A large number ofReed-Sternbergcells and bizarre sarcomatous variants are present.
- Lymphocyte-Rich Classic Hodgkin’s Disease: In this Reed-Sternberg cells of classic and lacunar variety is observed with background infiltrate of lymphocytes.
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin’s Disease: In this variant of Reed-Sternberg cells the lymphocytic and histiocytic cells or popcorn cells are seen within a background of inflammatory cells, predominantly benign lymphocytes.
Read And Learn More: Pathology Question And Answers
Staging of Hodgkin’s Disease
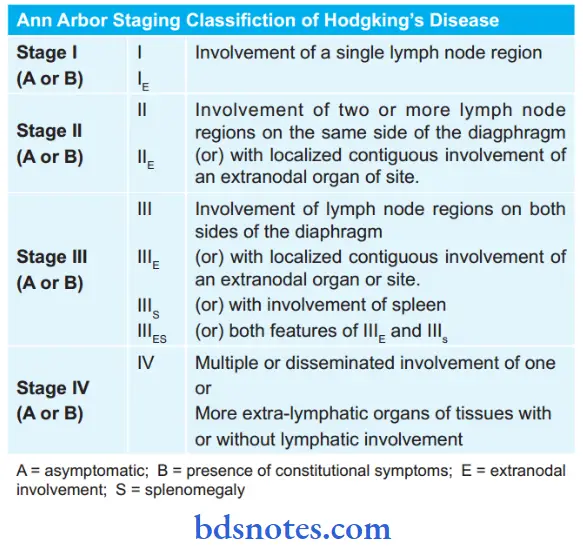
Question 2. Write a short note on Hodgkin’s Disease.
Answer:
Thomas Hodgkin first describes Hodgkin’s disease in 1832. It is a malignant lymphoma.
Hodgkin’s Disease Predisposing Factors
- Epstein Barr virus is involved in causing the disease.
- Patients with HIV infection have a higher incidence.
- Genetic predisposition can be present.
Hodgkin’s Disease Clinical Features
- It occurs in young adults and males are more commonly affected.
- There is a painless enlargement of one or more cervical lymph nodes
- Lymph node enlargement occurs in the cervical area, axilla, inguinal area, and Waldeyer’s ring.
- Nodes are firm and rubbery in consistency
Hodgkin’s Disease Histology
- Nodular Sclerosis Hodgkin’s Disease
- Morphology shows a nodular pattern.
- Broadbands of fiers divide nodes into nodules
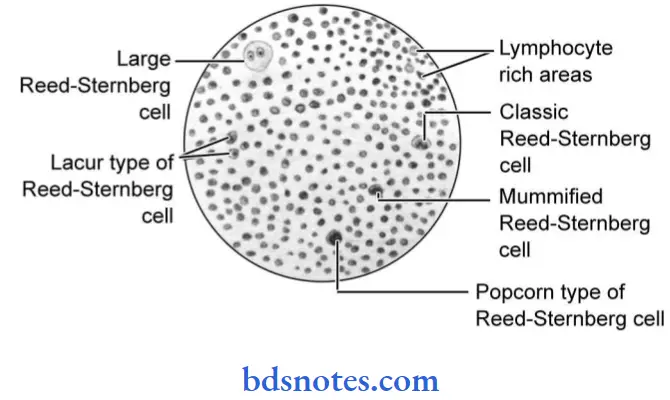
- The characteristic cell is a lacunar-type Reed-Sternberg cell which has conglobated, multilobate nucleus and a small nucleolus with abundant and pale cytoplasm.
- Mixed Cellularity Hodgkin’s Disease
- Infiltrate is usually diffuse
- Reed-Sternberg cells are of classic type, i.e. large with bilobate, double or multiple nuclei, and a large eosinophilic inclusion like the nucleolus.
- Lymphocyte-Depleted Hodgkin’s Disease
- Infiltrate is diffuse and often appears hypocellular.
- A large number of Reed-Sternberg cells and bizarre sarcomatous variants are present.
- It is associated with older age and HIV positivity.
- Lymphocyte-Rich Classic Hodgkin’s Disease
- Reed-Sternberg cells of the classic or lacunar type are observed with background infiltrate of lymphocytes.
- Nodular LymphocytePredominant Hodgkin’s Disease
- In this typical Reed-Sternberg Cell is not seen, instead a variant of Reed-Sternberg Cell the lymphocytic and histiocytic cells or popcorn cells are seen within the background of inflammatory cells which are predominantly benign lymphocytes.

Leave a Reply