Q. What is erythropoesis and where does it occurs? Give stages of Ertythropoiesis and requirement of each stage.
Answer:
Erythropoiesis:
- Erythropoiesis is the process which involves the origin, development and maturation of erythrocytes.
Site of erythropoiesis:
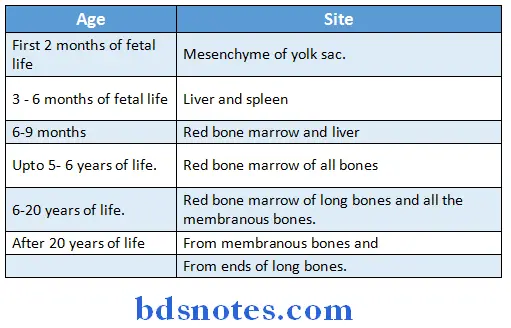
Erythropoiesis Requirements:
- Oxygen – for regulation of erythropoiesis.
- Nutrients.
- Carbohydrates – for energy supply.
- Fats for cell membrane.
- Proteins for globin formation.
- Minerals.
- Iron, manganese, copper, cobalt and nickel help in ‘heme’ formation.
- Calcium – increases iron absorption.
- Vitamins.
- Vit B12 and folic acid helps in maturation of RBC
- Hormones.
- Erythropoietin – stimulates RBC production
- Thyroxine – Accelerate the process.
- Sex hormones – androgen stimulates and oestrogen depress the formation of erythropoietin.
- Glucocorticoid-stimulates secretion of erythropoietin from kidney.
- Growth – hormone – stimulates erythropoietin secretion.
- Neural-stimulation of the hypothalmus causes an increase in RBC.
Question. Describe the morphology of red blood corpuscles. Briefly outline the stges in erythropoiesis. Mention two factors that affects erythropoiesis.
Answer:
Morphology of red blood corpuscles (RBC):
- RBC is a circular, biconcave, non-nucleated disc.
- Its cell membrane contains circular pores below which lies a contractile layer of lipoprotein – spectrin.
- It maintains the shape and flexibility of RBC membrane and contains antigen.
- RBC has a special type of cytoskeleton which is made up of actin and spectrin.
- Both are anchored to transmembrane protein called ankyrin.
Red Blood Corpuscles Size:
- Diameter -7.2 μ
- Thickness – At the periphery 2.2 μ, At the center – 1 μ.
- Surface area – 120 sqm
- Volume-85-90 cum.
Stages of Erythropoiesis:
1. Proerythroblast.
- It is very large in size occupying almost whole of the cell with diameter 20 μ
- Nucleus is large containing 2-3 nucleoli.
- The cytoplasm is basophilic.
- The proerythroblast multiplies several times to form early normoblast.
2. Early normoblast.
- The cell decreases to diameter of about 15 μ.
- It contains no nucleoli and condensed chromatin.
- It develops into intermediate normoblast.
3. Intermediate normoblast.
- Diameter is of 10 – 12 μ.
- Chromatin is condensed and haemoglobin starts appearing.
- Due to basophilic cytoplasm and acidophilic hemoglobin.
- The cell is called polychromophilic erythroblast.
- It develops into late normbolast.
4. Late normoblast.
- The diameter becomes 8 – 10 μ
- Nucleus is very small with chromatin dot giving cart wheel appearance.
- Cytoplasm becomes acidophilic so the cell is called orthochromic erythroblast.
- Next the nucleus becomes pinpoint called pyknosis.
- It develops into reitculocyte.
5. Reticulocyte Immature RBC.
- It is non-nucleated, basophilic in nature.
- Cytoplasm contains remnants of disintegrated organelles.
6. Matured erythrocyte.
- It is biconcave with diameter of 7.2 μ.
- It contains hemogolobin and is non-nucleated.
Factors effecting erythropoiesis:
1. General factors.
- Erythropoietin.
- Thyroxine.
- Hemopoietic growth factors.
- Vitamins Vit. B, C, D and E.
2. Maturation factors.
- Vitamin B12.
- Intrinsic factor of castel.
- Folic acid.
3. Factors necessary for haemoglobin formation.
- Amino acids
- Iron
- Copper
- Cobalt and nickel.
- Vitamins Vit. C, riboflavin, nicotinic acid and pyridoxine.
Erythropoiesis Regulation
- Factors regulating erythropoiesis are:
-
- General factors
- Erythropoietin
- Thyroxine
- Haemopoetic growth factor
- Vitamins B, C, D & E
- Maturation factors
- Vitamin B12
- Intrinsic factor of Castel
- Folic acid
- Factors necessary for haemoglobin formation
- Amino acids
- Iron
- Copper
- Cobalt and nickel
- Vitamins Vit C, riboflavin, nicotinic acid and pyridoxine
- General factors
Question. Name two factors that regulate erythropoiesis.
Answer:
1. Erythropoiesis General factors
- Erythropoietin
- Thyroxine
- Haemopoetic growth factor
- Vitamins B, C, D & E
2. Erythropoiesis Maturation factors
- Vitamin B12
- Intrinsic factor of Castel
- Folic acid
3. Erythropoiesis Factors necessary for haemoglobin formation
- Amino acids
- Iron
- Copper
- Cobalt and nickel
- Vitamins Vit C, riboflavin, nicotinic acid and pyridoxine
Leave a Reply