The Immune Response
Question 1. Write brief on cellular immunity.
Answer:
It is also known as cell-mediated immunity.
- Cellular immunity is the specific acquired immune response mediated by sensitized T cells.
- Bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi are intracellular pathogens which get to multiply in host cells.
- Antibodies are not active against such pathogens,
immunity against these pathogens is mediated by T lymphocytes.
The such an immune response which involves the interaction of cells of the immune system with antigens is known as cell-mediated immunity.
Read And Learn More: Microbiology Question And Answers
Induction of Cell-Mediated Immunity
- T cells possess various specifi T cell receptors on their surface for antigen.
- The binding of antigen with this receptor on T-lymphocyte initiates cellular immunity.
- As antigen reacts with the T cell, it undergoes proliferation and a sequence of morphological and biochemical events occur and the cell transforms into a larger blast cell, which is known as blast transformation.
- This above interaction leads to blast transformation, clonal proliferation, and differentiation which results in generation of Th and Ts cells, cytotoxic T cells, lymphokine-producing T cells, and memory cells.
Role of Cellular Immunity
- It provides immunity against infectious diseases caused by obligate and facultative intracellular pathogens.
- It has an important role in delayed hypersensitivity.
- It has an important role in transplantation immunity and graft-versus-host reaction
- It has an important role in immunological surveillance and also provides immunity against cancer.
- It has a role in the pathogenesis of certain autoimmune diseases i.e thyroiditis, etc.
Question 2. Write a short note on cellular and non-cellular components of cell-mediated immunity.
Answer:
Cellular Component of Cell-Mediated Immunity
T-lymphocytes are the cellular components of cell-mediated immunity.
The antigen is presented by antigen-presenting cells to Tlymphocytes. T-lymphocytes recognize antigens through T cell receptors. These sensitized T lymphocytes undergo blast transformation, clonal proliferation, and differentiation in memory cells and effector cells. Activated lymphocytes release lymphokines which leads to manifestations in cell-mediated immunity.
Non-cellular Components
The non-cellular components are:
- Lymphokines
- Cytokines.
1. Lymphokines
- Migration inhibiting factor: Inhibits migration of normal macrophages.
- Macrophage activating factor: Restrict macrophage movement and increase phagocytize activity.
- Macrophage chemo tactic factor: Stimulate chemotaxis of macrophages.
- Macrophage stimulating factor: Stimulate macrophage migration to the action site.
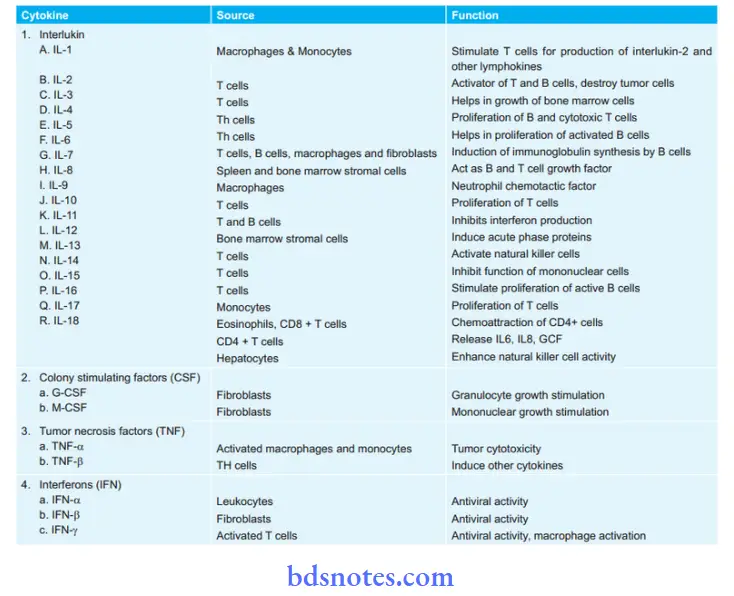
2. Cytokines:

Leave a Reply