Question 1. Give the development of retina
Answer:
Retina Origin:
- The retina is derived from the layers of optic nip
- Posterior part
- It becomes thick
- It forms retina proper
- Anterior part
- It remains thin
- It forms an epithelial covering for the ciliary body & iris
- Posterior part
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
Retina Optic cup:
- Its different parts develops retina
- Outer wall of the posterior part
- Its cells form pigmented layers
- Inner wall
- It differentiates into
- Matrix layer
- It forms rods & cones
- Mantle layer
- It forms the bipolar cells, the ganglion cells & other neurons of the retina
- Marginal layer
- Form the layers of nerve fibres
- These fibres grow into the optic stalk by passing through tire coordinal fissure
- The optic stalk is then converted into the optic nerve
- Matrix layer
- It differentiates into
- Outer wall of the posterior part
Question 2. Central Artery of Retina
Answer:
- This is an end artery
- In the optic disc, it divides into
- Upper branch
- Lower branch
- Structures Supplied By It:
- Deeper layers of the retina upto the bipolar cells
- The rods & cones are supplied by diffusion from the capillaries of the choroid
Central Artery of Retina Branches:
- Each upper & lower branch gives off nasal & temporal branches
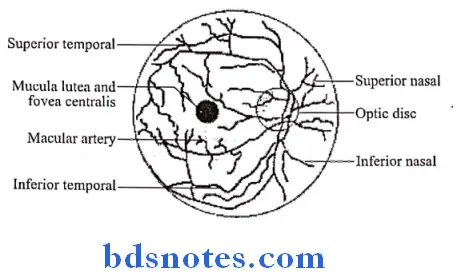
Central Artery of Retina Clinical anatomy:
- It is only arterial supply to most of the retina
- If this artery is blocked, there is sudden blindness
Question 3. Give the nerve supply to iris.
Answer:
- Iris is innervated more specifically by postganglionic sympathetic nerves arising from the superior cervical ganglion as the sympathetic root of ciliary ganglion.
- From there, they travel via the internal carotid artery through the carotid canal to foramen lacerum.
- They then enter the middle cranial fossa above foramen lacerum, travel through the cavernous sinus in tire middle cranial fossa and then travel with the ophthalmic artery in the optic canal or on the ophthalmic nerve through the superior orbital fissure.
- From there, they travel with the nasociliary nerve and then the long ciliary nerve.
- They then pierce the sclera, travel between sclera and choroid to reach the iris dilator muscle.
- They will also pass through ciliary ganglion and travel in short ciliary nerves to reach the iris dilator muscle.

Leave a Reply