The Temporomandibular Joints, Teeth, And Muscles, And Their Functions
Question 1. Describe the structure and functions of muscles of mastication. Deglutition/stages of deglutition. (or) Lateral pterygoid muscle. (or) Masseter muscle. (or) Muscles of mastication.
Answer:
Muscles of mastication:
- Masseter muscle:
- It is quadrilateral in shape.
Muscles of mastication Extend:
- From the zygomatic arch to the ramus and body of the mandible.
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
Muscles of mastication Insertion:
- Extends from the second molar to the posterior lateral surface of the ramus.
Muscles of mastication Structure:
- The masseter muscle is partly covered by the platysma and risorius muscle and to a variable degree with the parotid gland tissue.
- The superficial part of the muscle is separated from the deeper layer at the posterior upper part of the muscle.
Muscles of mastication Nerve supply:
- Massetric nerve – a branch of the anterior division of the mandibular nerve.
Muscles of mastication Actions:
- Elevates mandible to close the mouth to bite.
Temporalis Structure:
- It is fan-shaped.
- It has three component parts.
Temporalis Origin: It originates in the temporal fossa.
- Insertion:
- Anterior border and the mesial surface of the coronoid process of the mandible.
- Along the anterior border of ascending ramus.
Temporalis Functions:
- The anterior part is active in clenching.
- The posterior part retracts the protruded mandible.
- The Temporalis muscle also helps in side-to-side grinding movement.
Temporalis Nerve supply:
- 2 deep temporal branches of the mandibular nerve.
Lateral pterygoid Structure:
- It is short and conical in shape.
- It has upper and lower heads.
Lateral pterygoid Origin:
- Upper smaller head
- Infratemporal surface
- Crest of the greater wing of the sphenoid.
- Lower larger head.
- The lateral surface of the lateral pterygoid plate.
Lateral pterygoid Insertion:
- Pterygoid fovea.
- Anterior margin of articular disc and capsule of the temporomandibular joint.
Lateral pterygoid Actions:
- Depress mandible to open mouth
- Protrude the mandible.
- Contralateral abduction.
- The superior head is active during chewing and clenching of the teeth and stabilizes the condylar head during mandibular closing.
- The inferior head assists in the translation of the condyle during jaw opening.
Lateral pterygoid Nerve supply:
- The branch from the anterior division of the mandibular nerve.
Medial Pterygoid Structure:
- It is quadrilateral
- It has a small superficial and a large deep head.
Medial Pterygoid Origin:
- Superficial head
- From maxillary tuberosity
- Deep head.
- From the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate.
Medial Pterygoid Insertion:
- Medial surface of angle of the mandible.
- Ramus upto mandibular foramen.
Medial Pterygoid Actions:
- Elevation and lateral positioning of the mandible
- Protrudes the mandible.
Medial Pterygoid Nerve supply:
- Branch of the main trunk of the mandibular nerve.

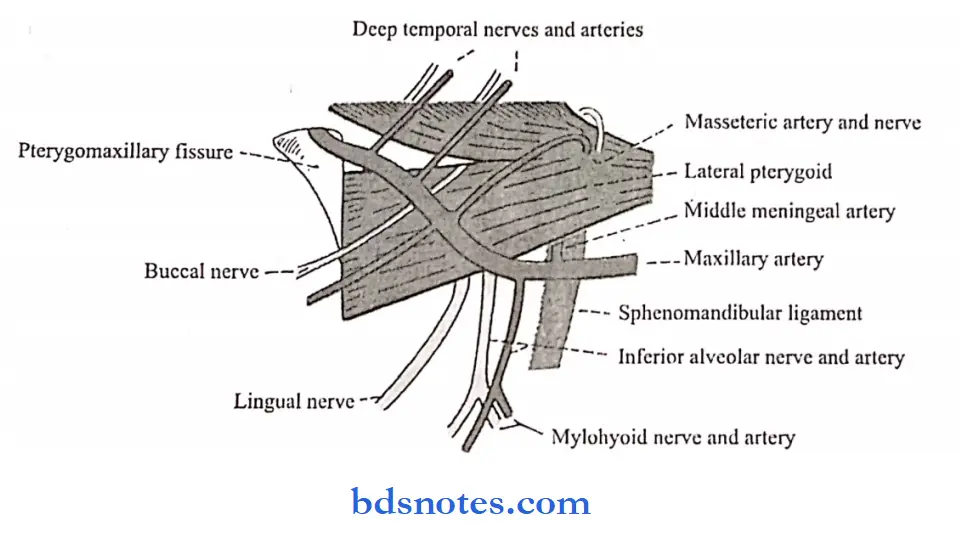
Question 2. Enumerate the ligaments and functions of TMJ.
Answer:
Ligaments:
1. Fibrous capsule:
- Attached above to the articular tubercle, mandibular fossa, and below to the neck of the mandible.
2. Lateral/temporomandibular ligament:
- Attached above to the articular tubercle.
- Below to the posterolateral aspect of the neck of the mandible.
- It reinforces and strengthens the capsular ligament.
3. Sphenomandibular ligament:
- It is an accessory ligament.
- It arises from the spine of the sphenoid and from the petrotympanic fissures and ends at the lingula of the mandible.
- It is a remnant of Meckel’s cartilage.
4. Stylomandibular ligament:
- It is also an accessory ligament.
- It is attached above the lateral surface of the styloid process and below to the angle and ramus of the mandible.


5. Otomandibular ligaments:
- These are discomalleolar and tympano mandibular ligaments.
- They connect callers to the TMJ disk and to the sphenomandibular ligaments.
Temporomandibular Joints Functions:
1. Protraction/forward movement of the mandible.
- During this movement the articular disc of the TMJ glides forward over the upper articular surface, the head of the mandible moving with it.
2. Retraction of mandible:
- During this, the articular disc glides backward over the upper articular surface.
3. Slight opening of the mouth.
- The head of the mandible moves on the undersurface of the disc.
4. Wide opening of the mouth.
- It is followed by protraction.
5. Chewing movements/side-to-side movements of the mandible.
Question 3. Enumerate the stages of deglutition and describe each stage.
Answer:
Deglutition:
1. Deglutition First stage – oral stage:
- The anterior part of the tongue is raised and pressed against the hard palate by the intrinsic muscle of the tongue.
- The movement takes place from the anterior to the posterior side.
- This pushes the food bolus into the posterior part of the oral cavity.
- The soft palate closes down and helps to form the bolus.
- The hyoid bone is moved upwards and forwards.
- The posterior part of the tongue is elevated upwards and backward.
- This pushes the bolus through the oropharyngeal isthmus to the oropharynx.
2. Deglutition Second stage – pharyngeal stage:
- The food is pushed from the oropharynx to the lower part of the laryngopharynx.
- The nasopharyngeal isthmus is closed by elevation of the soft palate.
- This prevents the food bolus from entering the nose.
- The inlet of the larynx is closed, this prevents.
- The food bolus from entering the larynx.
- The larynx and pharynx are elevated.
- The bolus is pushed down over the posterior surface of the epiglottis.
3. Deglutition Third stage-Oesophageal stage:
- Food passes from the lower part of the pharynx to the esophagus.
- It is brought about by the inferior constrictor of the pharynx.
Question 4. Articular capsule.
Answer:
- The TMJ is enclosed in it.
Articular capsule Attached to:
- Borders of the articulating surfaces of the mandibular fossa.
- The eminence of the temporal bone.
- The neck of the mandible.
Articular capsule Consists of:
- Internal synovial layer.
- The outer fibrous layer contains veins, nerves, and collagen fibers.
Articular capsule Nerve supply:
- Trigeminal nerve.
Articular capsule Blood supply:
- Maxillary, temporal, and masseteric arteries.
Question 5. Articular disc.
Answer:
- It is an oval fibrous plate that divides TMJ into compartments.
Articular disc Compartments:
- Upper compartments permit gliding movements
- Lover compartment – permits rotatory as well as gliding movements.
Articular disc Surfaces:
- Superior surface – concavoconvex.
- Inferior surface – concave.
Articular disc Composed of:
- Anterior extension
- Anterior thick band
- Intermediate zone
- Posterior thick band
- Bilaminar region.
Question 6. Neural control of deglutition.
Answer:
- Deglutition is triggered by afferent impulses
- These impulses arise from
- Oral mucous membrane and pharynx
- Posterior pharyngeal wall;
- Soft palate and
- Epigoltis.
- These impulses travel in trigeminal glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves.
- This stimulates a group of nerve cells located in the floor of the ventricle.
- The efferent fibers pass through motor fibers of hypoglossal) nerves to the pharyngeal musculature and the tongue.

Leave a Reply