Skeletal Muscle Relaxants
Question 1. Classify Skeletal Muscle Relaxants And Write Therapeutic Uses.
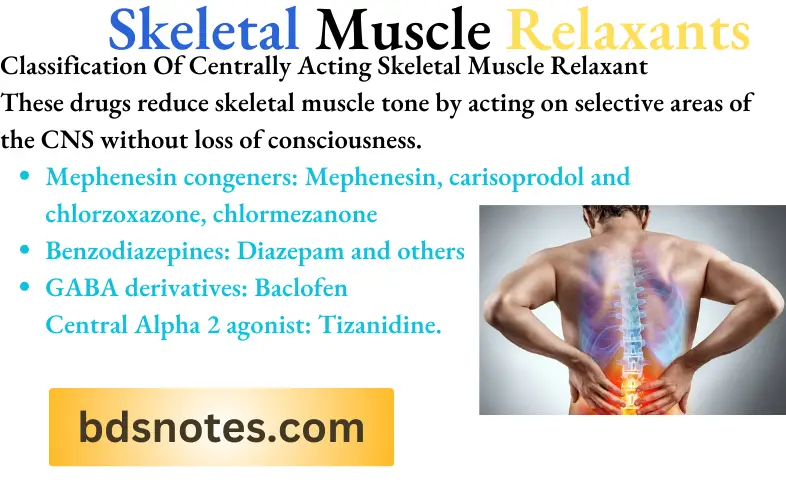
Classification And Uses Of Skeletal Muscles Relaxants.
Answer:
Skeletal muscle relaxants are both centrally-acting muscle relaxants and peripherally-acting muscle relaxants.
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question And Answers
Classification Of Peripherally Acting Muscle Relaxant
1. Neuromuscular Blocking Agents:
- Non-depolarizing (Competitive) blockers.
- Long acting: d-Tubocurarine, Pancuronium, Doxacurium, Pipecuronium.
- Intermediate acting: Vecuronium, Atracurium, Cisatracurium, Rocuronium, Rapacuronium.
- Short Acting: Mivacurium.
- Depolarizing blockers.
- Succinylcholine, Decamethonium.
- Directly acting agents: Dantrolene sodium, Quinine.
Therapeutic Uses Of Centrally Acting Skeletal Muscle Relaxant
- During acute muscle spasms, diazepam or other muscle relaxant are combined with analgesics.
- Torticollis, backache, and neuralgia are cured by using these drugs.
- These are used in spastic neurological disorders like hemiplegia and paraplegia.
- During tetanus IV diazepam is given.
- During electroconvulsive therapy, diazepam may be void to suppress convulsions.
- Orthopedic manipulations may be performed under diazepam influence.
Therapeutic Uses Of Peripherally Acting Skeletal Muscle Relaxant
- As an adjuvant to general anesthetics
- They are used to promote skeletal muscle relaxation during abdominal surgery and in dentistry for the setting of mandibular fractures.
- They are used in severe cases of tetanus and status epilepticus.
Question 2. Write The Therapeutic Uses And Adverse Effects Of Succinylcholine.
Answer:
It is a peripherally acting skeletal muscle relaxant.
Succinylcholine Therapeutic Uses
- It is the most commonly used skeletal muscle relaxant for passing the tracheal tube.
- It is employed for brief procedures, i.e. endotracheal intubation, laryngoscopy, bronchoscopy, esophagoscopy, reduction of fracture and dislocation, etc.
- Convulsion and trauma from electroconvulsive therapy can be avoided by the use of muscle relaxants without decreasing therapeutic benefits. Succinylcholine is most
commonly used. - It is used as an adjuvant for general anesthesia.
Succinylcholine Adverse Effects
- It causes an increase in intraocular pressure.
- It causes an increase in postoperative muscle pain.
- Neuromuscular block by succinylcholine may be prolonged causing apnea in patients with atypical plasma cholinesterase.
- Aspiration of gastric content may occur.
- Presence of hyperkalemia.
- Presence of sinus bradycardia.
- Malignant hyperthermia can occur when succinylcholine is used with halothane in genetically susceptible individuals.
Question 3. Write A Short Note On Succinylcholine.
Answer:
Succinylcholine is a peripherally acting skeletal muscle relaxant
- It is depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent.
- The structure of succinylcholine resembles two molecules of acetylcholine linked together.
- Succinylcholine is the fastest and the shortest-acting muscle relaxant.
- Succinylcholine is the choice of drug for endotracheal intubation.
Succinylcholine Pharmacokinetics
- It is administered intravenously.
- Succinylcholine is rapidly hydrolyzed by pseudocholinesterase, so it has a shorter duration of action, i.e. 3 to 8 min.
Succinylcholine Mechanism Of Action
- Succinylcholine has an affinity with nicotinic cholinoceptors.
- They depolarize muscle endplates by opening Na+ channels and initially produce Switching and fasciculations.
- These drugs do not dissociate rapidly from the receptors → Induce prolonged partial depolarization of the region around muscle endplate → Inactivation of Na+ channels AC h released from motor nerve ending is unable to generate propagated muscle action potential → Flaccid paralysis.
- In other words, a zone of inexcitability is created around the endplate preventing activation of muscle fier.
Succinylcholine Contraindications
- In nerve injuries like hemiplegia, paraplegia.
- In muscle injuries like burns, crush injuries, etc.
- In patients with atypical pseudocholinesterase.
Question 4. Write Pharmacological Basis Of Use Of Succinylcholine As A Skeletal Muscle Relaxant.
Answer:
Succinylcholine reacts with NM receptors of the motor endplate, opens the sodium channel, and causes its depolarization which then spreads and produces
repetitive excitation of muscle motor units that result in transient muscle fasciculations.
Both succinylcholine, i.e. metabolized by acetylcholine esterase, and acetylcholine released during action potential bind to NM receptors at the motor endplate which is already depolarized.
As a result, the depolarized membrane remains persistently depolarized and in the absence of any repolarization, it becomes unresponsive to additional impulses. In this way, succinylcholine acts as a skeletal muscle relaxant.
Question 5. Write Short Note On Muscle Relaxants.
Answer:
Skeletal muscle relaxants act peripherally at the neuromuscular junction or muscle fier itself or centrally in the cerebrospinal axis to reduce muscle tone and/or cause paralysis.
Skeletal muscle relaxants are both centrally-acting muscle relaxants and peripherally-acting muscle relaxants.
Important Features Of Peripherally Acting Muscle Relaxants
- They lead to muscle paralysis and loss of voluntary movements.
- These drugs block neuromuscular transmission.
- The central nervous system is spared and shows no effect.
- It should always be given IV
Important Features Of Centrally Acting Muscle Relaxants
- They decrease muscle tone without decreasing voluntary power.
- They selectively inhibit polysynaptic reflexes in the central nervous system.
- They can cause some central nervous system depression.
- They can be given orally or parenterally.

Leave a Reply