Shock
Question 1. Write Classification And Uses Of Drugs In Shock.
Or
Describe Drugs Use To Manage Acute Anaphylactic Shock.
Answer:
Shock is a state of acute circulatory failure associated with moderate perfusion of vital tissue.
Classification And Uses Of Drugs Used In Shock
- Sympathomimetic amines: Noradrenaline, adrenaline, dopamine, and dobutamine.
- These above drugs maintain perfusion of vital organs by increasing myocardial contractility, increasing cardiac output, constricting vessels, and venules, and dilating arterioles in vital organs.
- Alpha adrenoceptor blocking agents, i.e. Phenoxybenzamine are used in surgical shock after loss of adequate fluid volume by reducing vasoconstriction by reflex release of noradrenaline.
- Oxygen: It is used in patients in cardiogenic shock, to reduce cyanosis due to arterial hypoxemia.
- Dextran and other plasma expanders: High molecular weight dextran and low molecular weight dextran are used in hypovolemic shock. They increase plasma volume temporarily and draw fluid in vascular space and improve blood flow.
- Glucagon: It increases myocardial contractility and improves hemodynamic status.
- Corticosteroids: They are used in anaphylactic shock, septic shock, and shock due to acute adrenal insufficiency.
Question 2. Discuss The Management Of A Case Of Anaphylactic Shock.
Or
Give The Description Of Drugs For Anaphylactic Shock.
Or
Write In Short On Anaphylactic Shock.
Or
Write Drug Treatment Of Anaphylactic Shock.
Or
Write In Short Treatment Of Anaphylactic Shock.
Or
Write Management Of Anaphylactic Shock.
Or
Write A Short Note On Anaphylactic Shock.
Answer:
Anaphylaxis is an acute allergic reaction in a sensitized individual on exposure to an antigen. It is mediated by IgE antibodies. The clinical features are bronchospasm, hypotension, laryngeal edema, urticaria, etc.
Treatment Of Anaphylactic Shock
- Summon ambulance
- Always check whether respiratory distress is due to other causes
- Assess the degree of cardiovascular collapse by checking pulse and blood pressure
- Assess the degree of airway obstruction
- Stop the administration of the drug
- The patient should be kept supine
- Assess breathing difficulty by checking for stridor, wheezing
- Administer oxygen to the patient with a face mask
- Give antihistamine chlorpheniramine maleate 10 mg
- Administer hydrocortisone 100 to 200 mg IV
- Monitor consciousness, airway, breathing, circulation, pulse, blood pressure
- Raise legs if blood pressure is low
- Adrenaline 1:1000, 0.5 ml IM is given immediately.
- Repeat IM adrenaline every 5 minutes while waiting for the ambulance
- Administer 100% oxygen.
- CPR if cardiac arrest occurs.
- If the BP fall is rapid, 1:10,000 adrenalin may be infused IV slowly.
Question 3. Describe Briefl Use Of Various Drugs In Treatment Of Cardiovascular Shock. Point Out The Possible Mechanism Of Action Of Each Drug You Mention.
Answer:
Cardiogenic shock can be due to acute heart failure in myocardial infarction, acute myocarditis, and severe tachycardia.
Treatment Of Cardiogenic Shock
- For Relief Of Pain:
- Sublingual nitroglycerine 0.4 mg every 5 min till the pain is relieved.
- IV morphine 10 mg.
- 100% oxygen by face mask to reduce free radicals.
- Aspirin 75 to 150 mg is used and causes inhibition in prostaglandin synthesis and hence acts as an analgesic.
- Thrombolytic therapy: Streptokinase is used as an anticoagulant.
- To maintain blood volume IV flid 5% dextrose increases reduced plasma volume and RBC dilution.
- Ionotropic drugs: Dopamine and dobutamine increase cardiac contractility and peripheral vasoconstriction, restoring blood to vital organs.
- Vasodilator nitroglycerine is used which causes the generation of nitric oxide and hence vasodilatation.
Question 4. Explain The Pharmacological Basis For Adrenaline Used In Anaphylactic Shock.
Or
Explain Why Adrenaline Is The Drug Of Choice In Anaphylactic Shock.
Or
Write A Short Note On The Use Of Adrenaline In Anaphylactic Shock.
Answer:
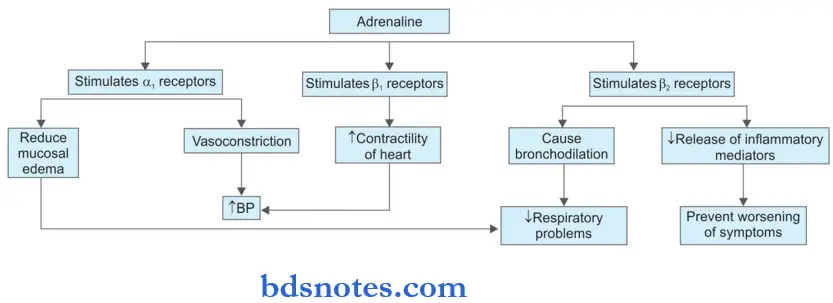
- Adrenaline is the ‘physiological antagonist of histamine.
- Actionofadrenaline onbeta2 receptors are responsible for causing bronchodilatation which counters the bronchospastic action of histamine.
- Adrenaline maintains blood pressure by its action on α1 and β1 receptors.
- Action on α1 receptors is responsible for vasoconstriction which is also responsible for reducing the mucosal edema in airways.
- β2 receptors are present on the mast cells also and when activated by adrenaline cause inhibition of the release of inflammatory mediators.
Question 5. Write An Essay On Antishock Drugs.
Answer:
Following are the antishock drugs:
1. Sympathomimetic Amines
- These drugs maintain perfusion of the vital organs by one or more of the following mechanisms:
- Increasing myocardial contractility, which increases cardiac output provided the venous return is adequate.
- Constricting the capacitance vessels, and venules and preventing the pooling of blood in the veins.
- Dilating arterioles in the vital organs.
- The various sympathomimetics used in the treatment of shock are:
- Noradrenaline: It raises the perfusion pressure and the cardiac output in the patient of shock with very low peripheral resistance.
- Adrenaline: It is used mainly in the treatment of anaphylactic shock.
- Dopamine: It is employed in the management of cardiogenic shock, septic shock, and traumatic shock, alone or in combination with an alfa adrenoceptor-blocking agent. It stimulates the heart and increases cardiac output by acting on cardiac beta receptors and improves renal and mesenteric blood flow by acting on dopamine receptors.
- Dobutamine: It acts mainly on beta receptors with fewer vascular effects. It is used for short-term therapy of severe CCF and in patients following cardiac surgery, to increase cardiac output.
Other sympathomimetic agents used are metaraminol, methoxamine, phenylephrine, and isoprenaline.
2. Alfa-Adrenoceptor Blocking Agents.
- Phenoxybenzamine is used in surgical shock, after adequate replacement of fluid volume. It reduces the vasoconstriction produced by the reflux release of noradrenaline and
- Prevents the harmful effects of vasoconstriction on microcirculation.
- Permits rapid administration of IV fluid without increasing central venous pressure.
- Oxygen: It is used in patients in cardiogenic shock, to reduce cyanosis due to arterial hypoxemia.
- Dextran and other plasma expanders: High molecular weight dextran and low molecular weight dextran are used in hypovolemic shock. They increase plasma volume temporarily and draw fluid in vascular space and improve blood flow.
- Glucagon: It increases myocardial contractility and improves hemodynamic status.
- Corticosteroids: They are used in anaphylactic shock, septic shock, and shock due to acute adrenal insufficiency.
Question 6. What Is Shock? Enumerate Various Types Of Shock.
Answer:
Shock is a state of acute circulatory failure associated with moderate perfusion of vital tissue.
- Various Types Of Shock
- Hypovolemia shock
- Cardiogenic shock
- Distributive shock
- Obstructive shock.
Question 7. Write A long answer on The treatment of shock.
Answer:
Following is the treatment for shock:
Basic Management
- Oxygen should be given which is 4 to 6L/min.
- Crystalloids, i.e. normal saline or ringer lactate should be given 20 ml/Kg over 5 min by IV route.
- If there is no improvement, repeat.
- If still there is no improvement and CVP should be <10 mm Hg, colloids or whole blood can be started.
In Cardiogenic Shock
- Dobutamine should be infused IV 5 to 15 mg/Kg/min
In Septic Shock
- Inj. Ceftriaxone 2 g IV is given twice a day.
- Inj. Amikacin 5 mg/Kg IV is given thrice a day
- Inj. Vancomycin 7 mg/Kg IV is given twice daily.
In Anaphylactic Shock
- Inj. Adrenaline (1:1000) 0.5 ml by IM route
- Inj. Diphenhydramine 1 mg/Kg slow IV
- Inj. Hydrocortisone 5 mg/Kg IV

Leave a Reply