Sedative And Hypnotics
Question 1. What Are Sedatives And Hypnotics? Classify Hypnotics. Describe Pharmacological Actions, Therapeutic Uses, And Toxicity Of Phenobarbitone. Mention important indications.
Answer:
A sedative is a drug that reduces excitement and calms the patient without producing sleep but drowsiness may be present.
- Hypnotic is a drug that produces sleep resembling natural sleep.
- Sedatives and hypnotics depress CNS.
Classification Of Hypnotics
- Barbiturates:
- Long-acting: Phenobarbitone, Mephobarbitone
- Short acting: Pentobarbitone, Butobarbitone
- Ultrashort acting: Thiopentone sodium, Methohexitone.
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question And Answers
- Benzodiazepines:
- Newer nonbenzodiazepines hypnotic: Zopiclone, Zolpidem, Zaleplon.
Phenobarbitone
Phenobarbitone Pharmacological Action
- Phenobarbitone depresses all excitable tissues. The CNS is most sensitive and the effect is dose-dependent with an increase in dose there is sedation → sleep → anesthesia → comma
- Phenobarbitone has anticonvulsant action
- Respiration: An increase in dose cause depression in the respiratory center.
- CVS: At hypnotic doses, there is a slight fall in BP and a decrease in heart rate.
- Kidney: Phenobarbitone anesthesia results in decreased urinary output.
- Phenobarbitone induces microsomal enzymes and increases the rate of their own metabolism as well as for other drugs.
Phenobarbitone Therapeutic Uses/Indications
- Phenobarbitone is used in epilepsy.
- Phenobarbitones are used as hypnotics.
- It can be used as an adjuvant drug during psychiatric uses.
- During neonatal jaundice, phenobarbitone acts on glucosyl transferase which causes metabolization and excretion of bilirubin.
Toxicity Of Phenobarbitones
- Poisoning of phenobarbitones is caused due to over dosages.
- The sign and symptoms are drowsiness, restlessness, hallucination, hypotension, respiratory depression, convulsions coma, and death.
Treatment Of Toxicity Of Phenobarbitone
- Maintain airway, breathing, and circulation.
- Electrolyte balance should be maintained.
- Gastric lavage: After stomach wash, activated charcoal is administered which enhances the elimination of phenobarbitone.
- Endotracheal intubation should be performed before gastric lavage to protect the airway in unconscious patients.
- Alkaline diuresis: IV sodium bicarbonate alkalinizes urine. In alkaline urine, phenobarbitone exists in an ionized form, so they are not resorbed by passing through the renal tubule and are rapidly excreted in the urine.
- In severe cases, hemodialysis is employed.
Question 2. Mention contraindications of phenobarbitones.
Answer:
Contraindications Of Phenobarbitones
- It is contraindicated in liver and kidney disease.
- It is contraindicated in severe pulmonary insufficiency, For Example. emphysema.
- It is contraindicated in obstructive sleep apnea.
- It is contraindicated in acute intermittent porphyria.
Question 3. Write Note On Alprazolam.
Answer:
Alprazolam is a benzodiazepine and lies under the category of hypnotics.
- Alprazolam is a highly potent benzodiazepine that in addition has mood-elevating action in mild depression.
- Alprazolam is effective in anxiety associated with depression.
- The response of the drug is good in panic disorders and severe anxiety and autonomic symptoms.
- The drug produces less drowsiness.
- Alprazolam is a nighttime hypnotic with few residual effects the next day.
- Alprazolam produces metabolite.
- It is given in a dose of 0.25 to 0.5 mg.
- Discontinuation after regular use has produced a relatively marked withdrawal phenomenon.
Question 4. Write A Note On Diazepam Action And Uses Or Therapeutic Uses Of Diazepam. Discuss The Mechanism Of Action Of Diazepam
Or
Write A Short Note On Diazepam.
Answer:
Benzodiazepine lies in the category of benzodiazepines.
Diazepam Mechanism of Action
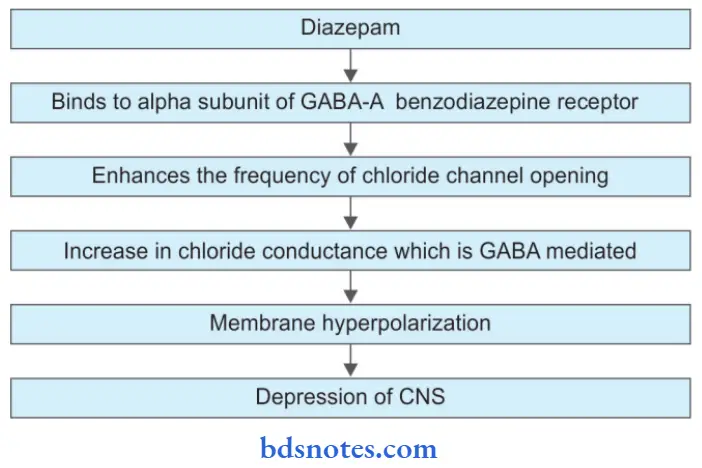
Diazepam Pharmacological Actions
- Hypnotic action: At larger doses diazepam produces sleep, decreases awakenings during sleep, increases total sleep time, and shorter REM (rapid eye movement) sleep.
- Analgesic action: IV diazepam causes analgesia.
- Anticonvulsant action: Diazepam increases the seizure threshold and acts as an anticonvulsant.
- Diazepam decreases nocturnal gastric secretion and respiratory tract, and BP may be lowered.
Diazepam Adverse Effects
At a hypnotic dose, it causes dizziness, vertigo, ataxia, disorientation, amnesia, and impaired psychomotor skills.
Diazepam Uses
- It is used as a hypnotic for insomnia.
- As muscle relaxant.
- For pre-anesthetic medication.
- Alcohol withdrawal patient.
- Along with analgesics NSAID, Spasmolytics, anti-ulcer, and other drugs.
Question 5. Write In Brief About The Advantages Of Benzodiazepines As Sedative And Hypnotics.
Answer:
- Benzodiazepines do not affect respiration or cardiovascular function.
- Benzodiazepines have particularly no action on another body system.
- Benzodiazepines cause less distortion of sleep architecture, and the rebound phenomenon on discontinuation of regular use is less marked.
- Benzodiazepines do not enter the disposition of other drugs by microsomal induction.
- They have lower abuse liability, tolerance is mild.
- A specific benzodiazepine antagonist flumazenil has been developed which can be used in case of poisoning.
Question 6. Explain Why Lorazepam Is Used In The Treatment Of Insomnia.
Answer:
Lorazepam is used in the treatment of insomnia because it is a slowly eliminated drug due to this property of lorazepam rebound insomnia and withdrawal symptoms are least marked.
Q.7. Classify Hypnosedatives. Describe Diazepam Under The Following Headings:
1. Precautions
2. Adverse Effects
Or
Write In Brief On Uses And Adverse Effects Of Diazepam.
Answer:
Classification Of Hypnosedatives
1. Barbiturates:
- Long-acting: Phenobarbitone
- Short-acting: Pentobarbitone
- Ultrashort acting: Thiopentone sodium.
2. Benzodiazepines
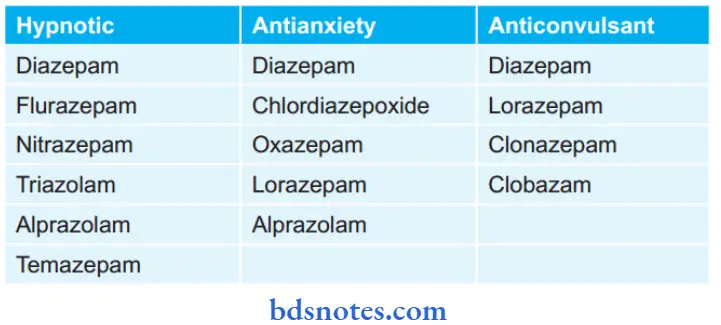
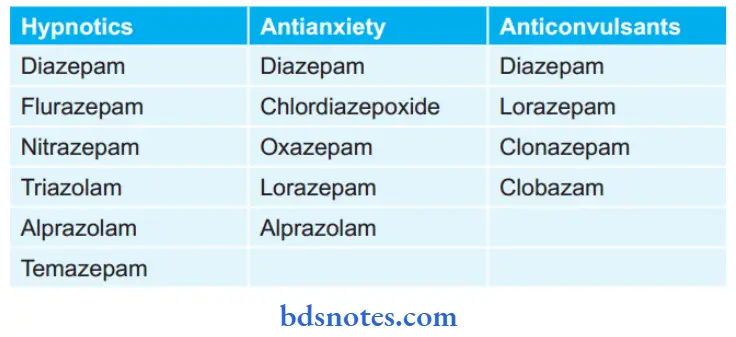
- Hypnotics: diazepam, flrazepam, nitrazepam, alprazolam, temazepam, triazolam
- Antianxiety: diazepam, chlordiazepoxide, oxazepam, lorazepam, alprazolam
- Anticonvulsant: diazepam, clonazepam, clobazam.
3. Newer Non-benzodiazepine hypnotics: Zopiclone, Zolpidem, Zaleplon.
Precautions In Taking Diazepam
- Diazepam should not be taken with alcohol as it gets synergies with the alcohol and causes excessive impairment.
- Its use with sodium valproate leads to psychotic symptoms.
- It should not be taken with cimetidine, isoniazid, and oral contraceptives as these drugs retard the metabolism of diazepam.
Adverse Effects Of Diazepam
The following are the common adverse effects:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Blurred vision
- Amnesia
- Disorientation
- Xerostomia
- Drug tolerance and drug dependence
- After long-term use, its withdrawal leads to tremors, insomnia, restlessness, nervousness, and loss of appetite.
- Its usage during labor can lead to respiratory depression and hypotonia in newborns.
Question 8. Classify Benzodiazepines. Write Their Mechanism Of Action And Uses. What Are The Advantages Of Non Benzodiazepines Hypnotics Over Benzodiazepines.
Answer:
Classifiation Of Benzodiazepines
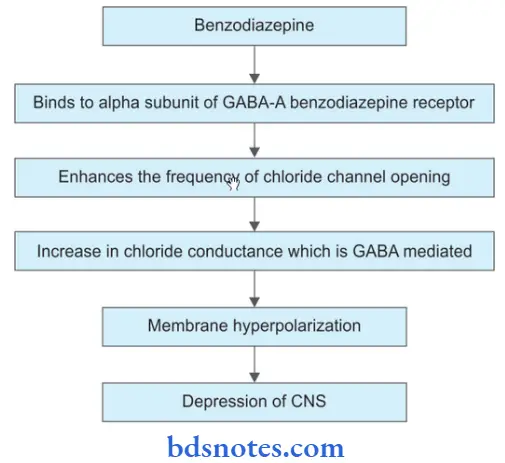
Benzodiazepines Mechanism Of Action
Benzodiazepines Uses
- Benzodiazepines are used in the treatment of short-term insomnia.
- Benzodiazepines are used as anticonvulsants. IV diazepam control life-threatening seizures in status epilepticus, tetanus, drug-induced convulsions, etc.
- Benzodiazepines are used in diagnostic endoscopies as well as minor operative procedures as their IV administration leads to sedative – amnesic – analgesic and muscle relaxant properties.
- Benzodiazepines are used in pre-anesthetic medication due to sedative–amnesic and anxiolytic effects.
- They are used in general anesthesia combined with other CNS depressants.
- Some of benzodiazepines have selective anti-anxiety action at low doses. Anti-anxiety action is due to their action on the limbic system.
- Benzodiazepines act as muscle relaxant. These drugs decrease skeletal muscle tone by inhibiting polysynaptic reflexes in the spinal cord. It is useful in spinal injuries, tetanus, and cerebral palsy and to reduce spasms in a joint injury.
- Benzodiazepines are used in alcohol withdrawal symptoms.
- Benzodiazepines are used in conscious sedation.
Advantages Of Non-Benzodiazepine Hypnotics Over Benzodiazepines
Advantages of non-benzodiazepine hypnotics over benzodiazepine hypnotics are:
- Non-benzodiazepine hypnotics do not cause a hangover while benzodiazepines cause less hangover.
- Non-benzodiazepine hypnotics do not result in distortion of sleep architecture while benzodiazepines cause less distortion of sleep architecture.
- Non-benzodiazepine hypnotics are non-addictive while benzodiazepines are addictive.
- Non-benzodiazepine hypnotics show no rebound insomnia after discontinuation while benzodiazepine hypnotic leads to rebound insomnia after discontinuation.

Leave a Reply