Scalp Temple And Face
Question 1. Describe the scalp under the following headings:
- Definition,
- Layers,
- Arterial supply,
- Venous drainage,
- Nerve supply and
- Applied anatomy.
Answer.
The soft-tissue structures covering the vault of the skull form the scalp. The boundaries of the scalp are as follows.
Anteriorly: Superciliary arches of the frontal bone.
Posteriorly: Superior nuchal lines of the occipital bone.
On each side: Superior temporal line.
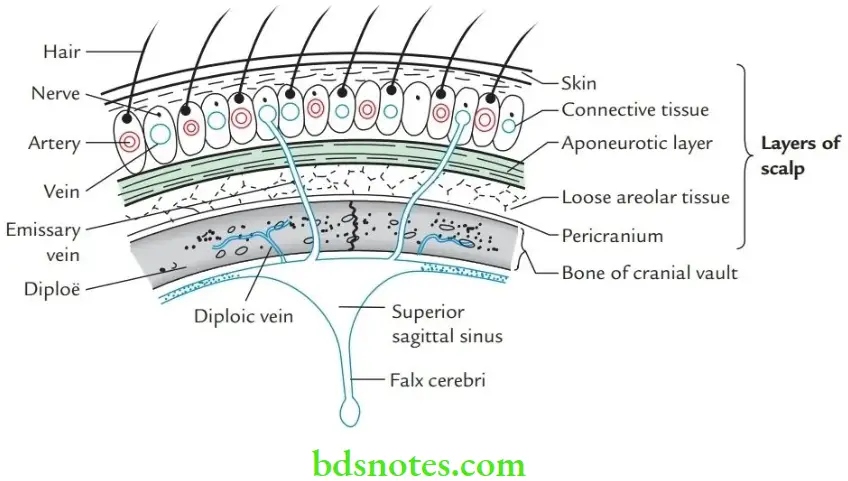
Layers of scalp The scalp consists of five layers, which can be easily remembered by the initial letter of each layer, i.e. SCALP.
- S: Skin
- C: Connective tissue
- A: Aponeurosis (epicranial aponeurosis)
- L: Loose areolar tissue
- P: Pericranium (outer periosteum)
Mnemonic: SCALP
Scalp Temple Arterial supply Each lateral half of the scalp is supplied by five arteries:
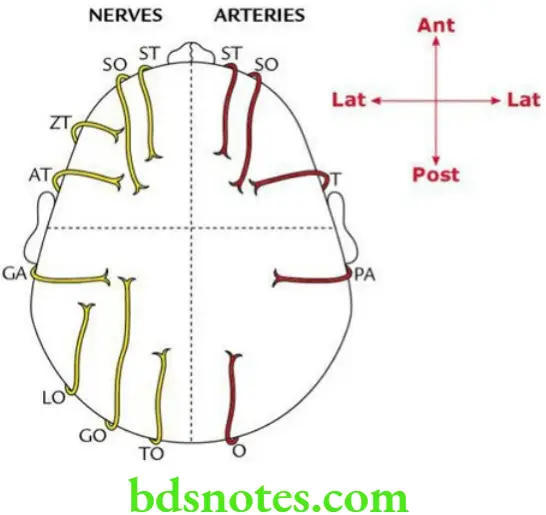
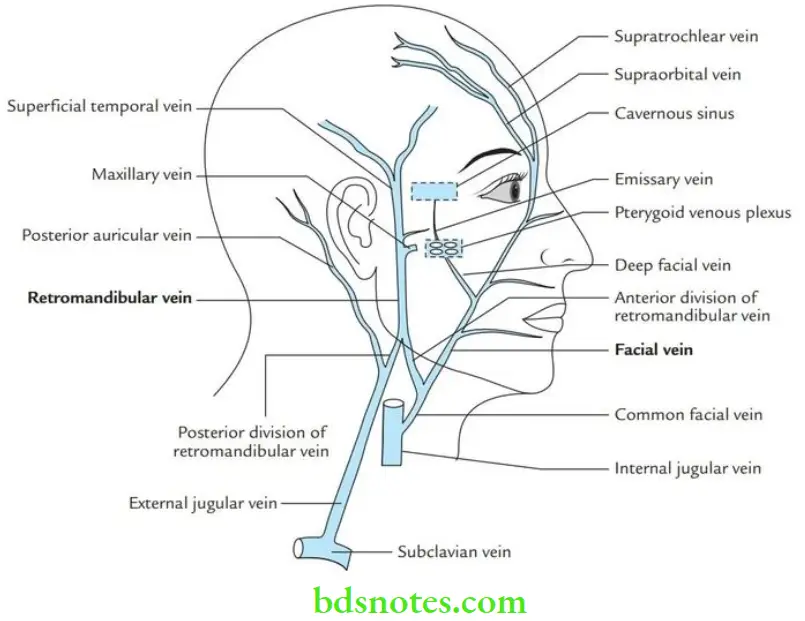
Venous drainage Each lateral half of the scalp is supplied by five veins:
- Three in front of the auricle
- Supratrochlear vein
- Supraorbital vein
- Superficial temporal vein
- Two behind the auricle
- Posterior auricular vein
- Occipital vein
Nerve supply Sensory Each lateral half of the scalp is supplied by eight nerves:
- Four in front of the auricle (i.e. anterior quadrant)
- Four behind the auricle (i.e. posterior quadrant)
- Great auricular, GA (C2, C3)
- Lesser occipital, LO (C2, C3)
- Greater occipital, GO (C2)
- Third occipital, TO (C3)
Motor Each lateral half of the scalp is supplied by two nerves – one in front of the auricle and one behind the auricle.
- In front of the auricle
- Temporal branch of the facial nerve
- Behind the auricle
- Posterior auricular branch of the facial nerve
Scalp Temple Applied anatomy Wounds of the scalp bleed profusely because:
- Walls of torn vessels fail to retract because they adhere to the dense connective tissue.
- It is profusely supplied with blood.
- Wounds of the scalp heal quickly because of profuse blood supply.
- The scalp is the most common site of sebaceous cysts because it contains a maximum number of sebaceous glands as compared to anywhere else in the body.
- A dangerous layer of the scalp: The layer of loose areolar tissue (i.e., the fourth layer of the scalp) is called the dangerous layer of the scalp because if the pus collects in this layer, the infection from here may travel through emissary’s veins into the intracranial dural venous sinuses causing their thrombosis and associated meningitis.
- Black eye: If blood collects in the fourth layer of the scalp due to trauma on the head. It tracks anteriorly in the subcutaneous tissue of eyelids for a couple of days where it clots. As a result, the eyelids appear black (black eye).
Read And Learn More: Selective Anatomy Notes And Question And Answers
Question 2. Give the origin, insertion, nerve supply and actions of the occipitofrontalis muscle.
Answer.
The occipitofrontalis muscle along with epicranial aponeurosis forms the third layer of the scalp. This muscle consists of four bellies: two occipital bellies and two frontal bellies.
Occipitofrontalis Muscle Origin
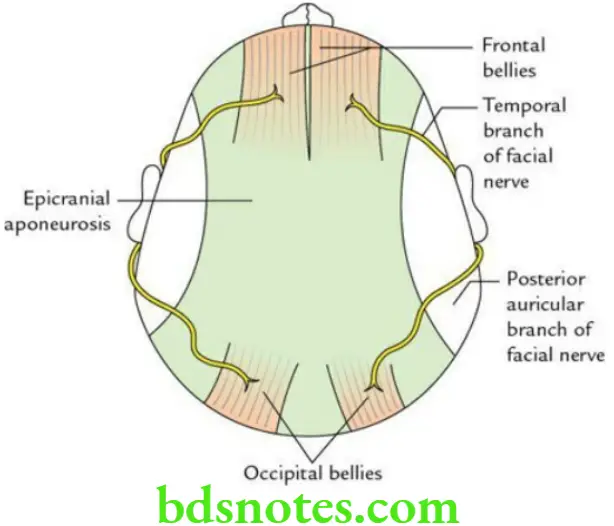
Occipitofrontalis Muscle Occipital bellies: From lateral two-third of superior nuchal lines of the occipital bone.
Frontal bellies: From subcutaneous tissue of eyebrows and root of the nose where it blends with orbicularis oculi muscle.
Insertion Into epicranial aponeurosis (galea aponeurotica).
Nerve supply Posterior auricular and temporal branches of the facial nerve.
Occipitofrontalis Muscle Actions
- Moves the scalp forward and backwards by alternate contractions of frontal and occipital bellies.
- Occipital bellies draw the epicranial aponeurosis backwards, allowing the frontal bellies to contract, and cause transverse wrinkles in the skin of the forehead.
Question 3. Write a short note on the superficial temporal artery.
Answer.
- It is the smaller terminal branch of the external carotid artery. It begins in the parotid gland behind the neck of the mandible.
- It runs vertically upwards across the root of the zygoma in front tragus. About 5 cm above the zygoma, the artery divides into terminal anterior and posterior branches which supply the temporal fossa and scalp.
Superficial Temporal Artery Branches
- The transverse facial artery arises within the parotid gland and runs forward over the masseter muscle. It supplies TMJ, parotid gland and masseter muscle.
- Anterior auricular branch: It supplies the lateral surface of the auricle and part of the external auditory meatus.
- Middle (deep) temporal artery: It pierces the temporal fascia to supply the temporalis muscle.
- The zygomatic-orbital branch runs towards orbit along the upper border of the zygomatic arch.
- The anterior terminal branch runs forward towards the frontal tuberosity to supply soft tissues of the region. It often becomes noticeably tortuous in old age.
- The posterior terminal branch runs upwards, backwards and towards the occipital region to supply the soft tissues in the region.
Question 4. Give the origin, insertion, nerve supply and actions of the platysma.
Answer.
The platysma is a thin, quadrilateral, broad sheet of muscle in the superficial fascia of the side of the neck.
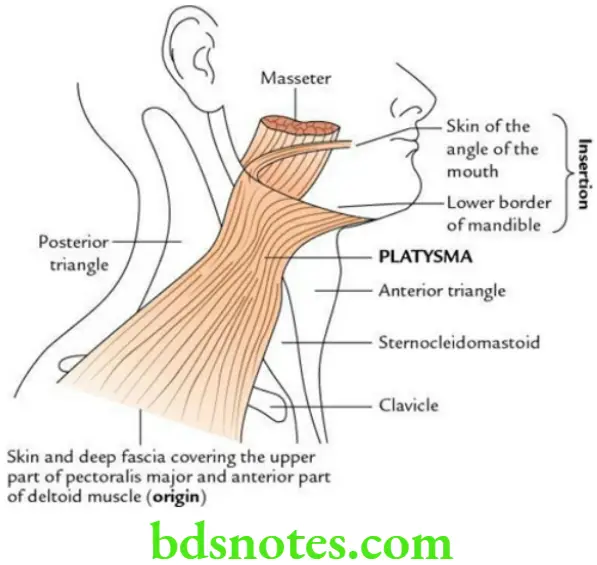
Platysma Origin From skin and deep fascia covering the pectoralis major and anterior part of the deltoid.
Platysma Insertion Into the lower border of the mandible and angle of mouth.
Platysma Nerve is supplied By the cervical branch of the facial nerve.
Platysma Actions
- Forms wrinkles in the skin of the neck
- Releases pressure of the skin on the underlying superficial veins of the neck to help in venous return
- Draws the angle of the mouth downward and laterally as seen clearly in the faces of marathon runners.
Question 5. Enumerate the characteristic features of the muscles of facial expression.
Answer.
- Lie in the superficial fascia
- Develop from 2nd pharyngeal arch
- Supplied by the facial nerve
- Represent (morphologically) panniculus carnosus
Question 6. Give the origin, insertion, nerve supply and actions of the buccinator muscle.
Answer.
Buccinator Muscle Origin
- Upper fibres, from the alveolar process of the maxilla, opposite upper molar teeth.
- Lower fibres, from the alveolar process of the mandible, opposite lower molar teeth.
- Middle fibres, from pterygomandibular raphe.
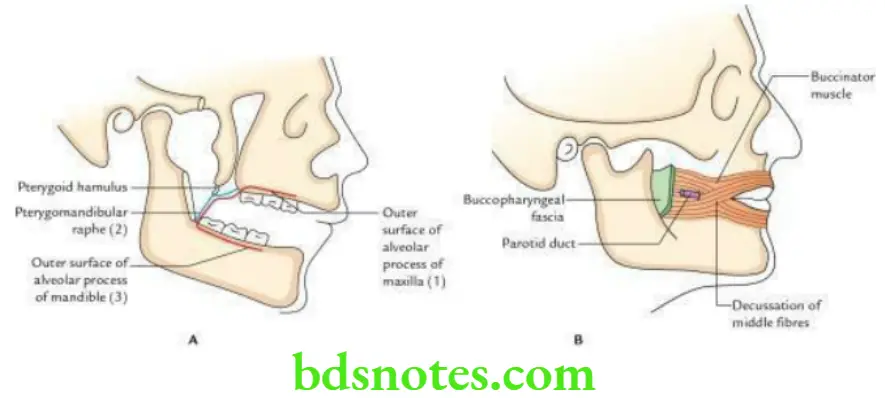
Buccinator Muscle Insertion
- Upper fibres pass straight to be inserted into the upper lip.
- Lower fibres pass straight to be inserted into the lower lip.
- Middle fibres decussate before passing to the respective lips.
Buccinator Muscle Nerve supply By facial nerve.
Buccinator Muscle Actions
- Flatten’s cheek against gum and teeth.
- Prevents accumulation of food into the vestibule of the mouth.
- Helps in blowing the cheek (hence is also called the whistling muscle).
Question 7. Define the temple (superficial temporal region) and enumerate the layers of soft tissue present in this region.
Answer.
The temple is an area on the side of the skull between the superior temporal line and the zygomatic arch.
Superficial Temporal Region Soft-tissue layers:
There are six layers of soft tissue in this region. From superficial to deep, these are:
- Skin
- Superficial fascia
- Thin extension of epicranial aponeurosis
- Temporal fascia
- Temporalis muscle
- Pericranium
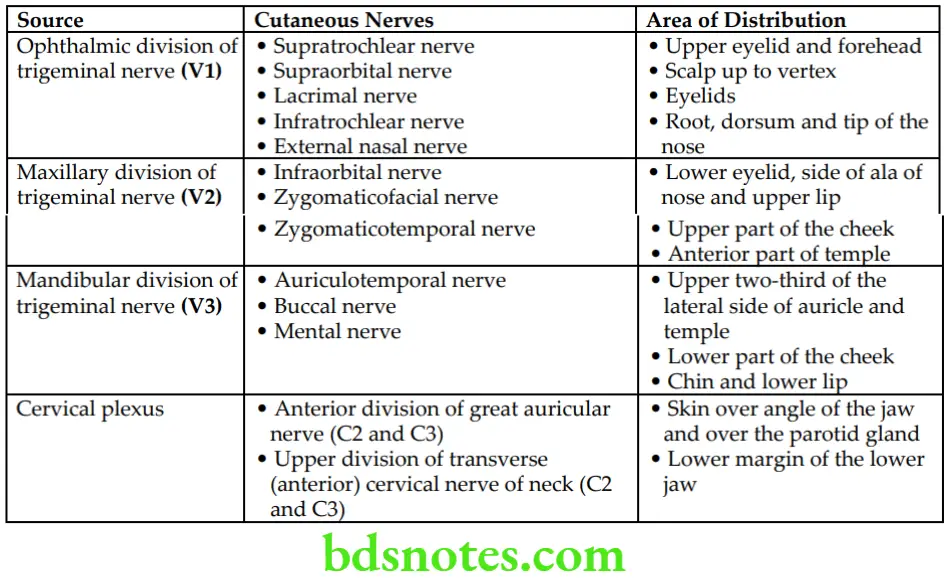
Question 8. Describe the sensory innervation of the face in brief.
Answer.
The sensory innervation to the skin of the whole face is derived from the branches of the trigeminal nerve except the skin over the angle of the lower jaw, which is innervated by the great auricular nerve, a branch of the cervical plexus.
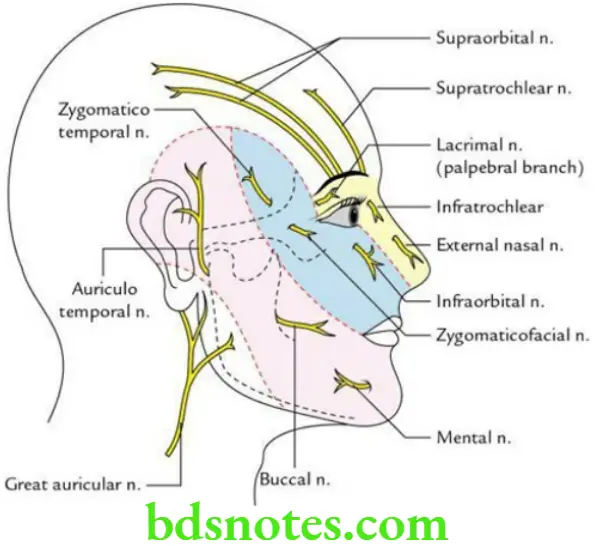
Sensory Innervation of the Head and Face
Question 9. Write a short note on the dangerous area of the face.
Answer.
Dangerous area of the face: This includes:
- Upper lip
- The lower part of the nose including the nasal septum
- Adjoining parts of the cheek
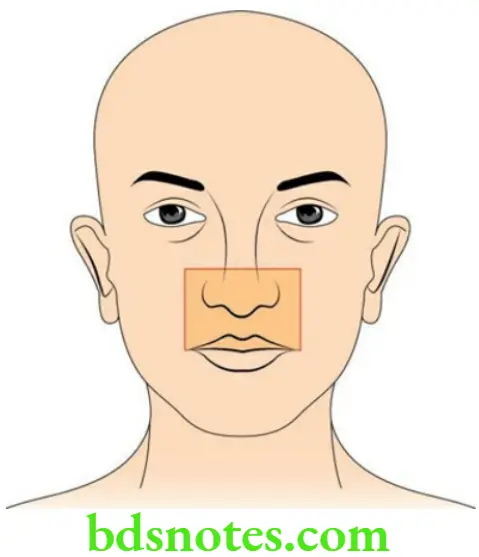
This area is dangerous because infective emboli from this area can reach the cavernous sinus and cause cavernous sinus thrombosis. As a result, cranial nerves present within the cavernous sinus are compressed leading to paralysis of the muscles of the eyeball.
Route of spread: The venous blood from the dangerous area of the face is drained into the cavernous sinus as follows:
Deep facial vein → pterygoid venous plexus → emissary vein → cavernous sinus
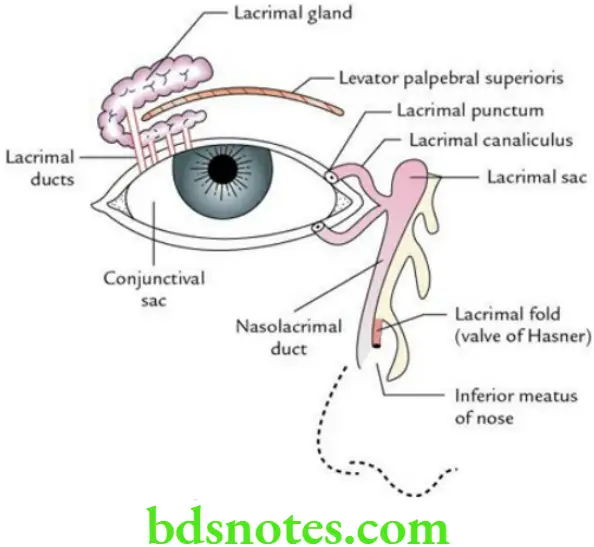
Question 10. Write a short note on the lacrimal apparatus.
Answer.
The group of structures concerned with the formation and drainage of lacrimal fluid (tear fluid) constitutes the lacrimal apparatus.
Lacrimal Apparatus Components Lacrimal apparatus consists of the following components:
- The lacrimal gland and its ducts
- Conjunctival sac
- Lacrimal puncta and lacrimal canaliculi
- Lacrimal sac
- Nasolacrimal duct
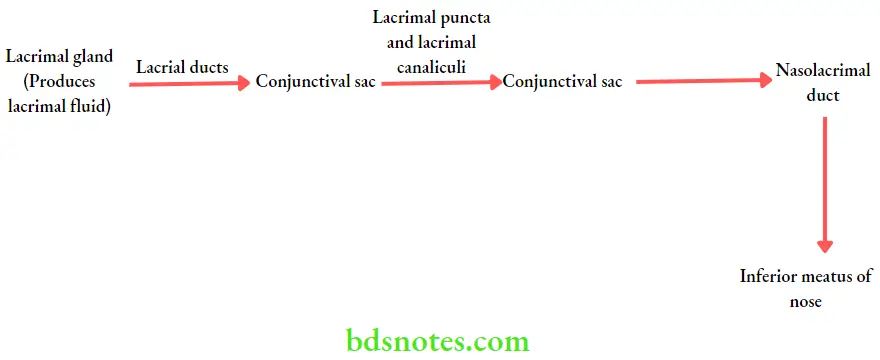
Lacrimal Apparatus Route of drainage
Lacrimal Apparatus Applied anatomy
Dacryocystitis It is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac and presents with pain, oedema and redness at the medial angle of the eye.
Epiphora: The obstruction of the lacrimal fluid pathway (i.e. at the level of puncta, canaliculi or nasolacrimal duct) causes overflow of tears on the cheek. It is called epiphora.
Question 11. Describe the development of the face in brief.
Answer.
The face develops from five mesenchymal processes, which appear around the stomodeum (primitive mouth).
- Frontonasal process – unpaired
- Maxillary processes – paired
- Mandibular processes – paired
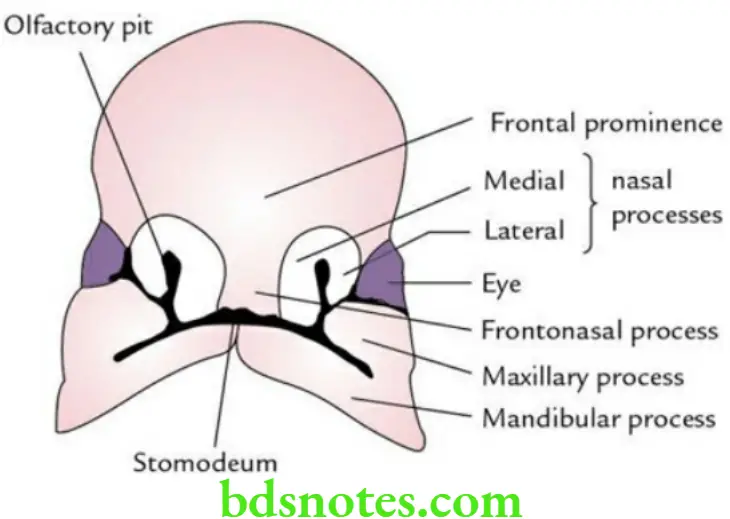
Frontonasal process:
- It lies above the stomodeum and is formed by the proliferation of mesenchyme deep into the ectoderm in front of the forebrain.
- On either side of the frontonasal process, the ectoderm thickens to form olfactory placodes. As each olfactory placode depresses from the surface, the olfactory pit is formed. A horseshoe-shaped elevation is formed around each olfactory pit. The medial limb of horseshoe-shaped elevation is called the medial nasal process, while its lateral limb is called the lateral nasal process.
Maxillary processes: These develop from the mesenchyme of the first arch. They are dorsolateral to lateral nasal processes and are separated from them on each side by the optic vesicle and a lineal furrow of ectoderm termed nasolacrimal groove. Ectodermal cells in the floor of this groove proliferate to form the solid ectodermal cord. The canalization of this cord gives rise to the nasolacrimal duct.
Mandibular processes: These are derived from the mesenchyme of the 1st pharyngeal arch.
The various parts of the face derived from the above-mentioned processes are given in the box below.

Face Applied anatomy
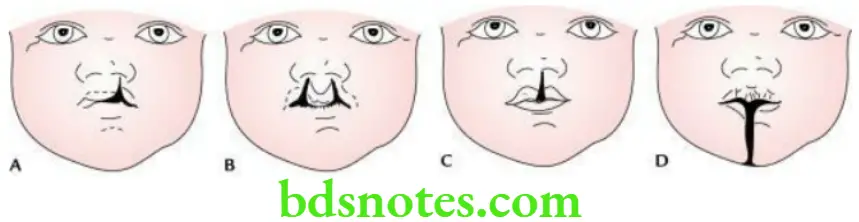
- Cleft upper lip
- Median cleft (or hare lip) occurs if the frontonasal process fails to form philtrum.
- Lateral cleft develops if the frontonasal process fails to fuse with the maxillary process. It can be unilateral or bilateral.
- A cleft lower lip occurs if two mandibular processes fail to fuse with each other. It is very rare.
- Oblique facial cleft occurs if the maxillary process fails to fuse with the lateral nasal process. The oblique cleft extends from the median angle of the eye to the upper lip.

Leave a Reply