Pterygopalatine fossa
The pterygopalatine fossa is a pyramidal-shaped space that lies in the depth of the pterygomaxillary fissure.
Question 1. Define pterygopalatine fossa and enumerate its boundaries and contents.
Answer.
Pterygopalatine Fossa Boundaries
Anterior: Posterolateral surface of maxilla.
Posterior: Pterygoid process and greater wing of the sphenoid.
Medial: Perpendicular plate of palatine.
Lateral: Fossa presents a pterygomaxillary fissure.
Floor: Angle between the anterior and posterior walls of the fossa.
Roof: Body of sphenoid.
Pterygopalatine Fossa Contents
- Maxillary nerve
- Pterygopalatine ganglion
- Maxillary artery (3rd part)
Question 2. Describe the maxillary nerve under the following headings:
- Origin,
- Course and
- Branches.
Answer.
Maxillary Nerve Origin and Course The maxillary nerve arises from the trigeminal ganglion in the middle cranial fossa. It passes forward and traverses the foramen rotundum to reach the upper part of the pterygopalatine fossa. From fossa, it enters the orbit by passing through the inferior orbital fissure.
As it enters the orbit, it is called the infraorbital nerve. In the orbit it first runs in the infraorbital groove, and then passes through the infraorbital canal, to finally appear on the face by emerging through the infraorbital foramen.
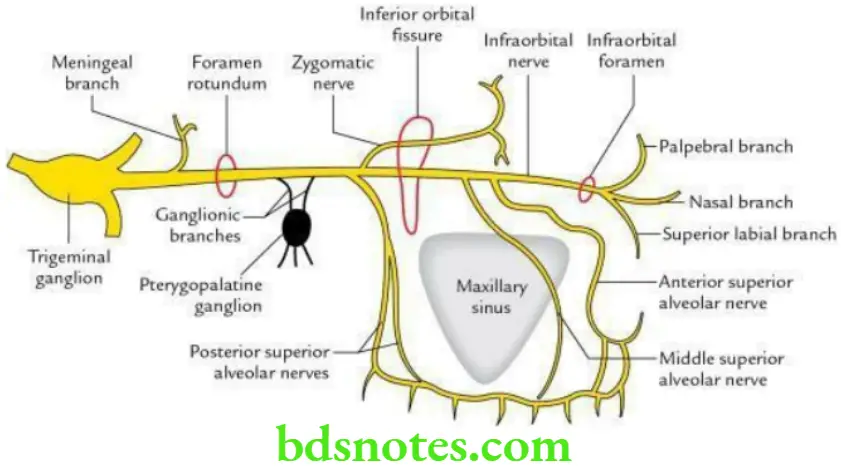
Thus, the maxillary nerve traverses through four successive regions during its course:
- Middle cranial fossa,
- Pterygopalatine fossa,
- Orbit and
- Face.
Note: The infraorbital nerve is considered as the continuation of the maxillary nerve.
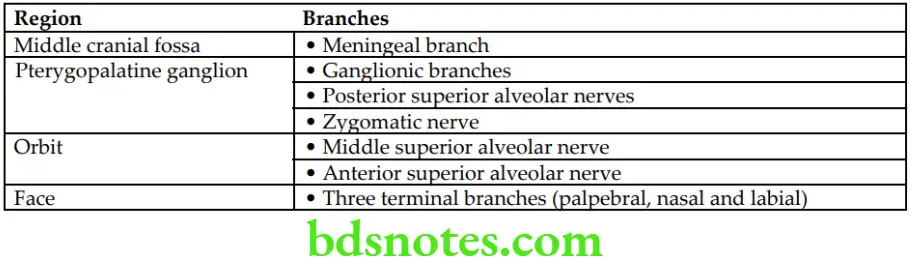
Maxillary Nerve Branches
Branches of Maxillary Nerve
Question 3. Describe the pterygopalatine ganglion (sphenopalatine ganglion) in brief under the following headings:
- Location,
- Roots,
- Branches,
- Distribution and
- Applied anatomy.
Answer.
Pterygopalatine Ganglion Location The pterygopalatine ganglion is the largest peripheral parasympathetic ganglion. It is located in the pterygopalatine fossa.
Pterygopalatine Ganglion Roots It has following three roots:
Parasympathetic root: From greater petrosal nerve.
- Sympathetic root: From sympathetic plexus around internal carotid artery through deep petrosal nerve.
- Sensory root: From maxillary nerve.
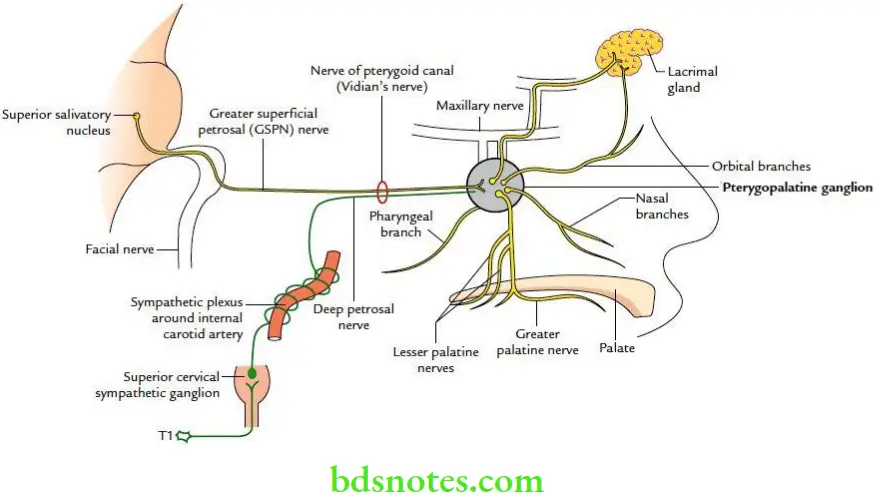
Pterygopalatine Ganglion Branches
- Orbital branches
- Palatine branches
- Nasal branches
Pterygopalatine Ganglion Distribution
- Parasympathetic (secretomotor) fibres: Supply the lacrimal, nasal and palatine glands.
- Sympathetic (vasomotor) fibres: Supply the mucous membrane of the nose, paranasal air sinuses and nasopharynx.
- Sensory fibres: Provide sensory innervation to the periosteum of orbit and mucous membrane of nose, palate and pharynx.
Pterygopalatine Ganglion Applied anatomy
- Allergic conditions such as hay fever or cold cause irritation of the pterygopalatine ganglion, which leads to running of the nose and eyes. For this reason, the pterygopalatine ganglion is also termed the ganglion of hay fever.
- The alcohol injection is occasionally used to relieve/treat intractable cases of allergic rhinitis.

Leave a Reply