Production Of X-Ray
Question 1. describe in detail components of X-ray tube and functions of each component.
or
Draw labeled diagram of X-ray tube. (Main X-ray generating system).
or
Write short answer on components of an X-ray tube.
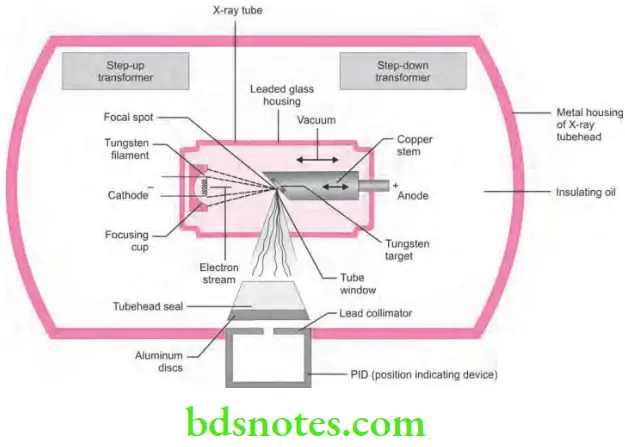
Answer. X ray tube is the heart of the X-ray generating system. This consists of a glass vacuum tube from which all of the air has been removed. The X-ray tube used in dentistry measures approximately several inches long by one inch in diameter.
Read And Learn More: Oral Radiology Question And Answers
The Parts of the X-ray tube
- A leaded glass housing
- A negative cathode
- A positive anode.
- A leaded glass housing: It is a leaded glass vacuum tube that prevents X-rays from escaping in all directions (radiation leakage). One central area of the leaded glass tube has a “window” that permits the X-ray beam to exit the tube and directs the X-ray beam towards the aluminum disk, lead collimator and position indicating device. This is also used for earthing.
- A negative cathode: It is principally composed of two parts:
- Filament.
- Focusing cup
X-ray Tube Filament
- The filament is the source of electrons in the tube, it is made up of a coil of tungsten wire, approximately 0.2 cm in diameter, 1–2 mm wide, 0.1–0.2 mm thick and 7 to 15 mm in length. lt is mounted on two strong stiff wires, that support it and carry the electric current.
- These two mounted wires lead through the glass envelope to serve as a connection to the low and high voltage electrical source.
- The filament is heated to incandescence through a range of temperatures by varying voltage (10 V), across the filament from a step-down transformer in a low voltage circuit.
- The hot filament emits electrons that are separated from the outer orbits of tungsten atoms at a rate proportional to its temperature by a process called “Thermionic emission”.
- The electrons lost by the filament form a cloud or space charge around the filament.
- Amilliampere control provides forfineadjustment of voltage across the filament and in turn the flow of heating current through it.
- The milliampere control, thereby controls the quantity of electrons the filament emits, which in turn controls tube current. Vaporization of the filament occurs over a period of time.
- When the particles vaporize (turn into gaseous form) they solidify on the glass of the X-ray tube, which is called ’sunburning’ or ’sun-tanning of the tube. This reduces the output of the X-ray tube, destruction of the vacuum and integrity of the tube, resulting in ’arcing’ and ultimate tube failure. Thorium is added to the filament material to make the tube last longer.
X-ray Tube Focusing Cup
- The focusing cup is a negatively charged concave reflector cup of molybdenum or nickel and houses the filament.
- The focusing cup electrostatically focuses the electrons emitted by the incandescent filament into a narrow beam, directed at a small rectangular area in the anode—the focal spot.
- The electrons are caused to move in this direction because of a strong electric field interposed between the cathode and the anode, by a high negative charge placed on the cathode which repels the electrons in the electron cloud towards the anode which has a high positive charge. This is achieved by applying a high voltage circuit between the anode and the cathode.
- To facilitate the movement of the electron cloud, the X—ray tube is evacuated as completely as possible to prelude collision of moving electrons with gas molecules, which could significantly reduce their speed. It also prevents oxidation or burn out of the filament.
- A positive anode or the positive electrode: lt consists of a wafer thin tungsten plate (target) embedded in a solid copper stem. The purpose of the target is to convert the kinetic energy of the electrons generated from the filament into X—ray photons. The position of the anode is indicated externally as a depression, usually a red dot on the tube head by the manufacturer.
Question 2. Describe the parts of an X-ray tube and add a note on X-ray production.
or
Described parts of an X-ray tube along with a note on production of X-rays
Answer. For parts of an X-ray tube refer to Ans 1 of same chapter.
Production of X-rays
- X-rays are produced in X-ray tube. When the X-ray machine is turned on, the electric current enter the control panel; via the plugged in cord and then to the tube head via extension wires in extension arms.
- The current is directed to the filament circuit through the step-down transformer, it reduces the 110 to 220 voltage to 3 to 5 volts.
- The filament circuit uses the 3 to 5 volts to heat the tungsten filament. The hot filament emits electron, this emission of electron from the cathode is known as thermionic emission. It forms the electron cloud around the cathode.
- When the exposure button is pushed the high voltage current is activated and the electron cloud is accelerated in X-ray tube from cathode to anode.
- Molybdenum cup of cathode directs the electron to the anode target in narrow beam.
- When the electron strikes the tungsten target, their kinetic energy is converted to X-ray energy. Less than 1% of the energy is converted to X-rays, the remaining 99% is lost as heat.
- The heat produced is carried away by copper stem and absorbed by the insulating oil in the tube head.
- The area where electron strike on tungsten (anode) is known as focus spot (Tungsten focus).
- Produced X-rays only exit from the X-ray tube via unleaded glass window portion of tube.
- X-rays travel through the unleaded glass window, the tube head seal, the aluminum discs, which filter the long wave X-rays from the beam.
- The size and shape of the X-ray beam is controlled by the lead collimator. X-ray beam then travels down the lead lines position indicating device and exit the tube head at the opening of position indicating device.
- X-rays produced in the X-ray tube vary in their energy and their wavelength, depending on how electrons interacted with tungsten atoms in anode. So kinetic energy of electrons is converted to X-ray photon either through Bremsstrahlung radiation or through characteristic radiation.
General (Bremsstrahlung Radiation or Breaking Radiation)
- The term refers to the sudden breaking of high speed electrons when they hit the tungsten target in the anode. About 70% of the X-rays are produced in this manner.
- If the electron hits the nucleus of the tungsten atom all its kineticenergyisconvertedinto“HighEnergyX-rayPhoton”.
- But most of the time, instead of hitting the nucleus, most electrons just miss the nucleus of the tungsten atom. When the electron comes close to the nucleus, it is attracted to the nucleus and slows down, consequently an X-ray photon is released. The electron that misses the nucleus continues to penetrate many such tungsten atoms producing many lower energy X-ray photons, before it imparts all its kinetic energy.
- As a result general radiation consists of X-rays of many different energies and wavelengths. It is also known as continuous spectrum.
Characteristic Radiation
- It is produced when a high speed electron dislodges an inner shell electron from tungsten atom and leads to ionization of atom. Once the electron is dislodged remaining orbiting electrons are rearranged to fill the vacancy. This rearrangement causes loss of the energy which results in the X-ray photon, with the energy equal to the difference in two orbital energy states. So X-rays produced are known as characteristic radiation.
- This radiation accounts for very small part of X-rays which are produced in dental X-ray machine and occur at 70 kVp and above.
Question 3. Write short note on cathode in X-ray tube.
Answer. Cathode present in X-ray tube consists of negative electrode, so it is known as negative cathode.
Negative cathode Principally composed of two Parts
- Filament.
- Focusing cup
Question 4. Write short note on Bremsstrahlung radiation.
Answer. It is also known as breaking radiation.
- The term refers to the sudden breaking of high speed electrons when they hit the tungsten target in the anode. About 70 % of the X-rays are produced in this manner.
- If the electron hits the nucleus of the tungsten atom all its kinetic energy is converted into “High Energy X-ray Photon”.
- But most of the time, instead of hitting the nucleus, most electrons just miss the nucleus of the tungsten atom. When the electron comes close to the nucleus, it is attracted to the nucleus and slows down, consequently an X-ray photon is released. The electron that misses the nucleus continues to penetrate many such tungsten atoms producing many lower energy X-ray photons before it imparts all its kinetic energy.
- As a result general radiation consists of X-rays of many different energies and wavelengths. It is also known as continuous spectrum.
Question 5. Write short note on white radiation.
Answer. A form of radiation that results from the rapid deceleration of high-speed electrons striking target, as occurs when the electron beam of a tungsten cathode strikes the tungsten or molybdenum target of the anode in an X-ray tube. Most of the X-rays emitted from a diagnostic or therapeutic X-ray unit represent white radiation.Also called Bremsstrahlung radiation.
- The term refers to the sudden breaking of high speed electrons when they hit the tungsten target in the anode. About 70 % of the X-rays are produced in this manner.
- If the electron hits the nucleus of the tungsten atom all its kinetic energy is converted into “High Energy X-ray Photon”.
- But most of the time, instead of hitting the nucleus, most electrons just miss the nucleus of the tungsten atom. When the electron comes close to the nucleus, it is attracted to the nucleus and slows down, consequently an X-ray photon is released. The electron that misses the nucleus continues to penetrate many such tungsten atoms producing many lower energy X-ray photons before it imparts all its kinetic energy.
- As a result general radiation consists of X-rays of many different energies and wavelengths. It is also known as continuous spectrum.
Question 6. Write short note on line focus principle.
Answer. The focal spot is the area on the target onto which the focusing cup directs the electrons from the filament.
- As the focal spot becomes smaller, heat generated per unit target area becomes greater. Thus in order to derive benefit from a small focal spot and yet to effectively distribute the bombarding electrons over a greater surface of a large target, the target is placed at an angle to the electron beam.
- In practice, the target is inclined at an angle of 200 to the central ray of electrons. This causes the effective focal spot to be 1 mm × 1 mm, in contrast to 1 mm × 3 mm of the actual focal spot size. This results in a smaller source of X-rays and sharper image with a larger actual focal spot for effective heat dissipation. This is known as “Line focus principle”.
Question 7. describe the working of X-ray machine and write in detail about production of X-ray.
Answer. Working of X-ray machine and production of X-rays
- When the X-ray machine is turned on, the electric current enter the control panel; via the plugged in cord and then to the tube head via extension wires in extension arms.
- The current is directed to the filament circuit through the step down transformer, it reduces the 110 to 220 voltage to 3 to 5 volts.
- The filament circuit uses the 3 to 5 volts to heat the tungsten filament. The hot filament emits electron, this emission of electron from the cathode is known as thermionic emission. It forms the electron cloud around the cathode.
- When the exposure button is pushed the high voltage current is activated and the electron cloud is accelerated in X-ray tube from cathode to anode.
- Molybdenum cup of cathode directs the electron to the anode target in narrow beam.
- When the electron strikes the tungsten target, their kinetic energy is converted to X-ray energy. Less than 1 % of the energy is converted to X-rays, the remaining 99 % is lost as heat.
- The heat produced is carried away by copper stem and absorbed by the insulating oil in the tube head.
- The area where electron strike on tungsten (anode) is known as focus spot (Tungsten focus).
- Produced X-rays only exit from the X-ray tube via unleaded glass window portion of tube.
- X-rays travel through the unleaded glass window, the tube head seal, the aluminum discs, which filter the long wave X-rays from the beam.
- The size and shape of the X-ray beam is controlled by the lead collimator. X-ray beam then travels down the lead lines position indicating device and exit the tube head at the opening of position indicating device.
Question 8. Define radiation. Explain with the help of diagram the construction of X-ray tube and production of X-rays.
or
Discuss in detail about production of X-ray. draw a well-labeled circuit diagram of X-ray tube.
or
Draw a labeled diagram for X-ray tube and discuss production of X-rays.
Answer. Radiation is defined as the emission and propagation of energy through space or a substances in form of waves or particles.
Construction of X-ray tube
- X-ray tube: It is the main X-ray generating system. It consists of three parts i.e. lead glass housing, negative cathode and positive anode.
- Lead glass housing is a glass vacuum tube which prevents X-rays in escaping all the directions.
- Negative cathode consists of filament and focusing cup. Filament is basically a coiled wire of tungsten and produces electron on heating. Focusing cup is a holder formed by molybdenum and it houses the filament. Focusing cup focus electrons in a narrow beam and direct beam across the tube towards tungsten target of anode. Cathode supply the electrons which are necessary in generation of X-rays.
- Positive anode converts electrons into X-ray photons. Anodes are of two types, i.e. stationary and rotating anode.
- Circuits: In X-ray machine, two types of circuits are used, i.e. filament circuit or high voltage circuit.
- Filament circuit is of low voltage, i.e. 3 to 5 volts. It regulates flow of electric current to filament of X-ray tube.
- High voltage circuit uses 65,000 to 1,00,000 volts which provide high voltage required to accelerate electrons for generation of X-rays in X-ray tube
- Transformers: It either increases or decrease voltage in an electrical circuit. Transformers are of three types i.e.
- Step-down transformer: It decreases the voltage from incoming 110 to 220 line voltage to 3 to 4 volt as required for the filament circuit.
- Step-up transformer: It increases the voltage from incoming 110 to 220 line voltage to 65,000 to 1,00,000 volts as required by high voltage circuit.
- Auto transformer: It serves as a voltage compensator, which correct minor fluctuation in current.
- Timer: It completes the circuit with high voltage transformer and controls the time for which high voltage is applied to the tube.
- Tube rating: It is the maximum safe interval the tube is energized at given range of voltage (kVp) and the tube current (mA) values.
- Duty cycle: It refers to how frequently successive exposures can be made.

For production of X-ray refer to Ans 2 of same chapter.
Question 9. Write short note on angle of truncation.
Answer.
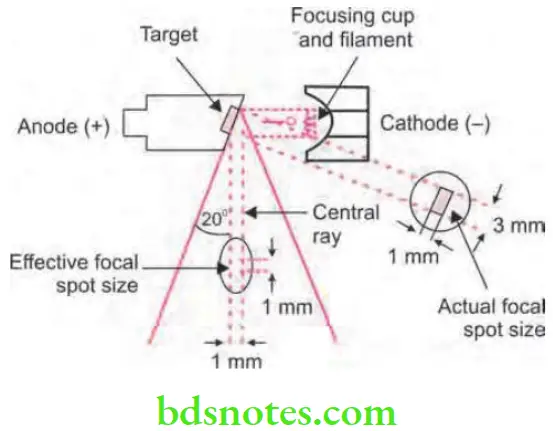
In the practice, inclination of target is at 20° to central ray of electrons. This leads to effective focal spot to be 1 mm × 1 mm in contrast to 1 mm × 3 mm of actual focal spot size. This results in formation of small source of X-rays and sharp image with large actual focal spot for the effective heat dissipation. The 20° angle is known as angle of truncation.
Question 10. Draw a neat labeled diagram and explain construction and working of dental X-ray machine.
Answer.
Construction of dental X-ray Machine
Dental X-ray machine is made up of three parts or components:
- Control panel
- Extension arm
- Tube head
Construction of dental X-ray Machine Control panel
It contains
- A on and off switch and an indicator light.
- An exposure button and indicator light.
- Control devices (time, kilovoltage, milliamperage, selectors).
The control panel is plugged into an electrical outlet.
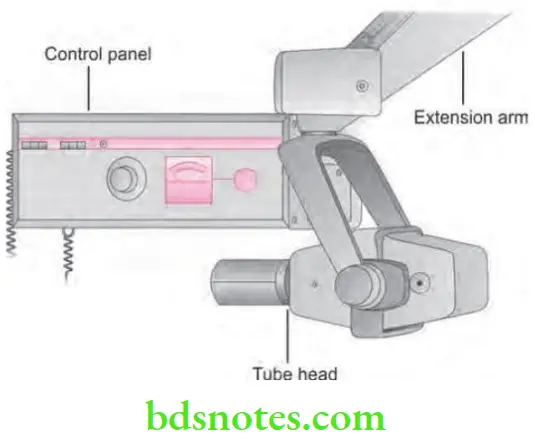
Construction of dental X-ray Machine Extension Arm
- It extends from control panel to tube head.
- It houses the electrical wires.
- The extension arm also allows the movement and positioning of tube head.
Construction of dental X-ray Machine Tube head
- It is an important part of X-ray machine.
- It contains heavy metal housing, that contains X-ray tube that produce X-rays.
- Following are the components of tube head:
- Metal housing: This is a metal body of tube head that surrounds the X-ray tube and transformer.
- Insulating oil: That surrounds the X-ray tube and transformer inside the tube head, it prevents over heating during X-ray production.
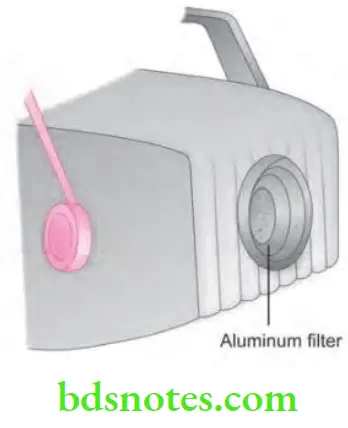
- Tube head seal: Aluminum or leaded glass of the tube head, it act as filter to the X-ray beam and seal the oil in tube head. Permit the exit of X-rays.
- Aluminum disk: Sheets of 0.5 mm thick aluminum is placed in the path of X-ray beam. They act as filter of X-ray beam. In dental X-ray tube head, there are two types of filtration:
- Inherent filtration: When the primary beam passes through the glass window of the X-ray tube, the insulating oil and the tube head seal. It is approximately equivalent to 0.5 to 1 mm of aluminum.
- Added filtration: Placement of aluminum disks in the path of the X-ray beam between the collimator and the tube head seal in dental X-ray tube head.
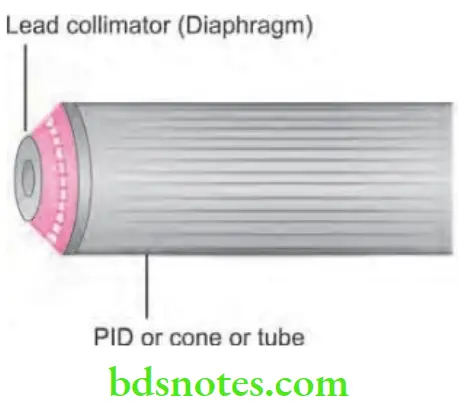
- Lead collimator: It is a lead plate with controlled hole. It is used to restrict the size and shape of the X-ray beam. It is placed directly over the opening of the metal housing where X-ray exit. They are of two types, i.e. fixed (dentistry) and adjustable. Lead collimator reduces the patient’s exposure.
- Position indicating device (PID): It is also called “Open ended lead cylinder” or “Cone”. It extends from opening of metal housing of tube head. It appears as an extension of tube head and it aims and shape X-ray beam. They are of following type, i.e. conical, Rectangular and round. Both rectangular and round PID are available in two lengths, i.e. Short (5 inches) Long (16 inches). Long PID is preferred because less divergence of X-ray beam occurs. Rectangular type is most effective in reducing patient’s exposure.
- X-ray tube: It is the main X-ray generating system. It consists of three parts, i.e. lead glass housing, negative cathode and positive anode.
- Lead glass housing is a glass vacuum tube which prevents X-rays in escaping all the directions.
- Negative cathode consists of filament and focusing cup. Filament is basically a coiled wire of tungsten and produces electron on heating. Focusing cup is a holder formed by molybdenum and it houses the filament. Focusing cup focus electrons in a narrow beam and direct beam across the tube towards tungsten target of anode. Cathode supply the electrons which are necessary in generation of X-rays.
- Positive anode converts electrons into X-ray photons.
- Circuits: In X-ray machine two types of circuits are used, i.e. filament circuit or high voltage circuit.
- Filament circuit is of low voltage, i.e. 3 to 5 volts. It regulates flow of electric current to filament of X-ray tube.
- High voltage circuit uses 65,000 to 1,00,000 volts which provide high voltage required to accelerate electrons for generation of X-rays in X-ray tube
- Transformers: It either increases or decrease voltage in an electrical circuit.
- Timer: It completes the circuit with high voltage transformer and controls the time for which high voltage is applied to the tube.
- Tube rating: It is the maximum safe interval the tube is energized at given range of voltage (kVp) and the tube current (mA) values.
- Duty cycle: It refers to how frequently successive exposures can be made.
Working of dental X-ray Machine
- When the X-ray machine is turned on, the electric current enter the control panel; via the plugged in cord and then to the tube head via extension wires in extension arms.
- The current is directed to the filament circuit through the step down transformer, it reduces the 110 to 220 voltage to 3 to 5 volts.
- The filament circuit uses the 3 to 5 volts to heat the tungsten filament. The hot filament emits electron, this emission of electron from the cathode is known as thermionic emission. It forms the electron cloud around the cathode.
- When the exposure button is pushed the high voltage current is activated and the electron cloud is accelerated in X-ray tube from cathode to anode.
- Molybdenum cup of cathode directs the electron to the anode target in narrow beam.
- When the electron strikes the tungsten target, their kinetic energy is converted to X-ray energy. Less than 1 % of the energy is converted to X-rays, the remaining 99 % is lost as heat.
- The heat produced is carried away by copper stem and absorbed by the insulating oil in the tube head.
- The area where electron strike on tungsten (anode) is known as focus spot (Tungsten focus).
- Produced X-rays only exit from the X-ray tube via unleaded glass window portion of tube.
- X-rays travel through the unleaded glass window, the tube head seal, the aluminum discs, which filter the long wave X-rays from the beam.
- The size and shape of the X-ray beam is controlled by the lead collimator. X-ray beam then travels down the lead lines position indicating device and exit the tube head at the opening of position indicating device.
Question 11. Write short note on collimation and filtration.
Or
Write short note on filtration and collimation.
Or
Write short note on filtration.
Answer.
Filtration
An X-ray beam has photons of different energies but only the photon with sufficient energy are able to penetrate the anatomic structures and useful in diagnostic radiography. Those photons with low penetrating power (long wavelength) contribute only to patient exposure and not to information on film. Thus for patient safety these photons with low power should be removed. This procedure of increasing the quality of radiation by removal of low power photon is known as “Filtration”.
It is done by placing an aluminum filter in path of beam.
Type of Filtration
- Inherent filtration.
- Added filtration
- Total filtration
Inherent Filtration
Filtration provided by materials of X-ray tube head, e.g. glass, insulating oil and the tube head seal. It is equivalent to 0.5 to 1.5 mm of aluminum.
Added Filtration
As the name suggests additional, an additional aluminum disk is placed between the tube head seal and collimator in the path of primary beam. It is 0.5 mm thick.
Total Filtration
- Total filtration is the sum of Inherent filtration and Added filtration.
- At or below 70 kVp requires minimum total filtration of l.5 mm of aluminum thickness.
- Above 70 kVp require a minimum total filtration of 2.5 mm of aluminum thickness.
- Contrast and quality of films get increase with the use of filter.
Collimation
Collimation is the process of restriction of the size of X-ray beam and thus the volume of irradiated tissue of patient from which the scattered photons originate.
- It allow only useful beam to emerge (useful beam is defined as that part of the primary radiation which is allowed to emerge through collimating device).
- When an X-ray beam falls on tissue 90% of it is absorbed by tissue and 10% result in scattered beam and travels in all direction.
- The scattered radiation does not contribute to information but only adds to film fog and degrades the image.
- The collimation decreases the risk of radiation, minimizes scattered radiation and decreases the fog with sharper image and better contrast.
- In intraoral machines, there are fixed collimators and in extraoral machines, they are adjustable.
Uses of collimation
- It reduces the volume of irradiated tissues and decreases the radiation exposure to patient.
- It reduces the size of X-ray beam and amount of scattered photons.
- It reduces the film fog and enhances the quality of image.
Types of collimators
Following are the type of collimators:
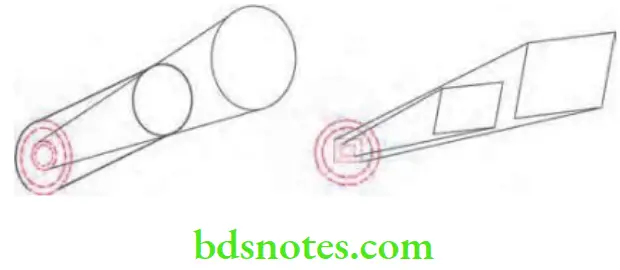
Diaphragm Collimator
- It consists of a thick plate of radiopaque material with opening in it.
- Collimator should lie over the port in X-ray head by which X-ray beam emerges.
- Aperture should be of different size and shape depending on requirement.
Tubular Collimator
- It is a tube which is manufactured by radiopaque material.
- Combination of diaphragm type and tubular type is used.
- The combination helps in reducing the penumbra at periphery of image.
- Longer the tube small is penumbra.
Rectangular Collimator
- They limit the size and they are larger than size of an X-ray film.
- It can be incorporated in a film-holding device.
Slit Collimator
- It is used in OPG machines.
- In CT machines, collimators are of two types i.e.
- Source collimator: It lies in front of X-ray tube and reduces the beam of radiation to form maximum required fan beam and determines the emitted dose.
- Detector collimator: It is positioned directly in front of detector and isused toshield detector againstscattered radiation and prevent the artifacts.
Question 12. Write short note on collimator.
Answer. Radiation beam emitted by X-ray tube is shaped using special diaphragm known as collimator. Collimation is the method by which one can control size and shape of the X-ray beam.
- Collimator decreases the risk of radiation, minimizes scattered radiation and decreases the fog with sharp image and better contrast.
- Collimators used in intra-oral machines are fixed while in extra-oral machines collimators used are adjustable.
Types of Collimators
Following are the type of collimators:
Diaphragm collimator
- It consists of a thick plate of radiopaque material with opening in it.
- Collimator should lie over the port in X-ray head by which X-ray beam emerges.
- Aperture should be of different size and shape depending on requirement.
Tubular collimator
- It is a tube which is manufactured by radiopaque material.
- Combination of diaphragm type and tubular type is used.
- The combination helps in reducing the penumbra at periphery of image.
- Longer the tube small is penumbra.
Rectangular collimator
- They limit the size and they are larger than size of an X-ray film.
- It can be incorporated in a film-holding device.
Slit collimator
It is used in OPG machines.
In CT machines, collimators are of two types i.e:
- Source collimator: It lies in front of X-ray tube and reduces the beam of radiation to form maximum required fan beam and determines the emitted dose.
- Detector collimator: It is positioned directly in front of detector and is used to shield detector against scattered radiation and prevents the artifacts.
Question 13. describe X-ray tube in detail and factor controlling production of X-ray beam.
Answer. For X-ray tube in detail refer to Ans 1 of same chapter.
Factors controlling Production of X-ray Beam
Following are the factors which control production of X-ray beam:
- Tube current
- Tube voltage
- Exposure time
- Filtration
- Collimation
- Inverse square law
- Quality of X-ray beam
- Quantity of X-ray beam
- Half value layer
X-ray Tube current
- Tube current (mA) determines the number of X-ray photons generated.
- Increase in the mA increases the generation of more electrons at cathode which strike the target to produce more X-ray photons.
- So the quantity of radiation produced by the X-ray tube is directly proportional to the tube current and the time, tube is operated.
- Linear relationship exist between mA and tube output.
X-ray Tube Voltage
- Tube voltage is the measurement of electrical force which causes electrons to move from negative cathode to positive anode.
- Energy of electrons is controlled by the tube voltage. As there is an increase in (kVp), energy of each electron striking the target increases which leads to increase in number of X-ray photons generated.
- Increase in kVp increases number of photons generated; increase mean energy of photons and increases maximum energy of photons.
Exposure Time
- When the exposure time is doubled and kVp as well as mA should be kept constant the number of X-ray photons generated become doubled.
- As changes in exposure time is made this influences the quantity of X-rays produced.
Filtration
- In filtration X-ray photons of less penetrating power are removed by placing a filter in path of primary beam, this allows only X-ray photons of sufficient energy to pass through.
- Usage of filters increases the contrast and quality of film while the density gets affected, so when there is an increase in filtration, increase in the exposure time is needed.
Collimation
- Collimator shape or restrict the size of an X-ray beam which strikes the tissue of a patient.
- Collimation leads to decrease in the size of X-ray beam and the amount of scattered photons.
- Volume of irradiated tissues is decreased by the collimation so there is decrease in exposure of radiation to the patient.
- Collimation reduces the film fog and enhances the quality of image.
Inverse square Law
- The law states that the intensity of an X-ray beam at a given point is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of radiation.
- Decrease in intensity of X-ray is because of divergent nature of X-rays.
Quality of X-ray Beam
- Quality of X-ray beam is its mean energy or penetrating ability.
- Quality of an X-ray beam is governed by its kVp. As there is increase in kVp, X-ray photons of high energy and better penetrating power are produced.
Quantity of X-ray Beam
- It refers to the number of X-ray photons produced.
- Quantity depends on the product of mA and exposure time in seconds.
- As there is increase in mA, more number of electrons are released in cathode and they strike the target to produce more number of X-ray photons.
Half Value Layer
- It refers to the thickness of specified material which is required to reduce the intensity of an X-ray beam by one half.
- Half value layer designates the penetrating power of X-ray beam.

Leave a Reply