Preventive Orthodontics
Question 1. Write short note on various procedures undertaken in preventive and interceptive orthodontics.
Answer. It is defined as “the action taken to preserve the integrity of what appears to be normal occlusion at a specific time”.
Procedures Undertaken in Preventive Orthodontics
Procedures to be undertaken are divided into two types:
- Preventive procedures without appliances
- Parental education
- Predental procedures
- Oral hygiene
- Caries control
- Care of deciduous dentition
- Management of ankylosed teeth
- Maintenance of occlusal equilibrium
- Removal of supernumerary teeth
- Restoration of decayed teeth
- Habit correction
- Disking
- Management of tongue tie
- Locked permanent fist molar.
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Question And Answers
- Preventive procedures with appliances
- Space maintenance
- Mouth protectors.
Preventive Procedures without Appliances
Parent Education
- Preventive orthodontic should begin before the birth of child.
- The expecting mother should be educated on mattrs such as nutrition.
- After birth mother should be educated on proper nursing and care of the child.
- When botted mother advised to use physiologic nipple not conventional nipple.
- The parents should educated for maintenance of good oral hygiene (to prevent nursing botte syndrome).
Predental Procedures
- Preventive procedures should be started before teeth eruption.
- Malocclusion occur because of improper selection of feeding nipple for baby and also because of improper positioning of botte.
- Physiologic nipple should be used.
Oral Hygiene
Oral hygiene measures should be taught to the parents and children.
- Infants (0 to 1 year): Brushing should be advocated with eruption of fist deciduous tooth. Moist gauze or moist cloth is used for massaging the gums and cleaning the teeth.
- Toddlers (1 to 3 years): Toothbrushing should be done with low floridated toothpaste. Parent should brush for the child.
- (3–6 years): Brushing of children is carried out under the supervision of parents. Fluoridated toothpaste should be introduced.
- School age (6–12 years): Brushing technique used should be proper and regular brushing is done.
Caries Control
Provisional caries should be detected properly and proper restoration should be undertaken immediately to prevent mesial movement of adjacent teeth and thus prevent loss of arch length.
Care of Deciduous Dentition
- Resorption pattern of primary teeth should be checked properly which causes establishment of nice occlusion.
- Abnormality in resorption leads to space deficiency.
- Deciduous canines and second deciduous molars are subjected to aberrant absorption
- After shedding of primary teeth, permanent tooth erupt in 3 to 6 months.
Management of Ankylosed Teeth
- Ankylosed deciduous teeth deflect permanent teeth to abnormal location.
- They should be diagnosed and remove surgically at proper time.
Maintenance of Occlusal Equilibrium
This is to be done as preventive, interceptive and corrective orthodontic procedure.
- Functional shifts causing pseudo class III as well as crossbite should be checked and eliminated.
- Overextended restorations should be reduced since they lead to occlusal prematurities.
Removal of Supernumerary Teeth
- Supernumerary and supplemental teeth can interfere with the eruption of nearly normal teeth.
- Supernumerary teeth should be identifid and extracted before they cause displacement of other teeth.
Restoration of Decayed Teeth
- Interproximal filings should be done to prevent loss in space.
- Overextended restoration changes occlusal relationship.
Habit Correction
- Early correction should be done which eliminate unfavorable sequelae of habits which leads to malocclusion.
- Habits such as tongue thrusting, mouth breathing, etc. should be recognized and treated.
Disking
- It is to be done in oversized fist or second deciduous molars.
- It facilitate eruption of permanent teeth.
Management of Tongue Tie
- It occurs because of thickening of genioglossus muscle which join midline of tongue where it elevated in vertical fold.
- It disappears after 4 years of age
- In case if it remains after 4 years frenectomy is done.
- Tongue tie causes difficulty in feeding.
Locked Permanent First Molar
- Tooth can be slightly or deeply locked.
- Deeply locked tooth require extraction of second deciduous molar and space maintenance for second molars.
- Slightly locked permanent fist molar erupts without any treatment.
Preventives Procedure with Appliances
Space Maintenance
Space maintenance is concerned with the maintenance of space lost by early loss of primary tooth by passive appliance or gaining of space lost.
Mouth Protectors
- It provides protection against injuries to teeth in the contact sports.
- They are of two types, i.e. prefabricated and custom made.
Procedures Undertaken in Interceptive Orthodontics
It is defined as “that phase of science and art of orthodontics employed to recognize and eliminate potential irregularities and malpositions in developing dentofacial complex.” Graber The procedures undertaken in interceptive orthodontics are:
- Removal of superanumerary tooth.
- Removal of ankylosed tooth.
- Equilibration of occlusal disharmonies.
- Correction of developing crossbite.
- Control of abnormal habits by Serial extraction, Muscle exercises, Space regainer, Interception of skeletal malrelation.
- Disking.
- Through early straightening of permanent incisors.
- Removal of sof tissues or bony barrier to enable eruption of teeth.
Serial Extraction
Eruption of permanent incisors in early mixed dentition may result in crowding in patients with severe tooth size-arch length discrepancy of 8-10 mm or more. Such patients would ultimately require extraction of four premolars to provide space for proper alignment of remaining permanent teeth. Rationale of serial extraction procedure is to intercept malocclusion at early mixed dentition period by extracting certain primary and permanent teeth and guiding the eruption of remaining permanent teeth in best possible occlusion.
Correction of Developing Crossbite
Anterior crossbite should be intercepted and treated at an early stage, if lef untreated it can cause severe skeletal malocclusion. Dentoalveolar anterior crossbites are best treated by tongue blade therapy. Skeletal anterior crossbites are best treated by myofunctional appliances. Functional anterior crossbite is treated by eliminating occlusal prematurities.
Control of Abnormal Habits
Oral habits such as thumb sucking, tongue thrusting, etc. should be intercepted by the dentist at age of 3.5 years to 4.5 years. Oral habits are intercepted by removal orthodontic appliance such as oral screen or by fied orthodontic appliance such as fied crib.
Proximal Stripping
Proximal stripping of first and second deciduous molars is required to facilitate eruption of adjacent succedaneous permanent teeth into normal occlusion.
Correction of Occlusal Interferences
Occlusal interferences can deflct mandible anteriorly, laterally or posteriorly. So as soon as occlusal prematurities are ruled out by dentist, they should be intercepted by reduction of crown height by pear-shaped stone in center angled handpiece.
Space Regaining
This can be done by using following appliances, i.e.
- By using cantilever spring: Space lost due to mesial driftng of permanent molar as well as distal driftng of deciduous first molar when deciduous molar get lost prematurely, this is regained by use of two figer springs.
- By using jack screw: Space is regained by use of removable orthodontic appliance which has jack screw in a way which increases the arch length which is obtained by distalization of molar.
- Gerber space regainer: It is an orthodontic molar band which is used for the tooth which has to be distalized. It consists of U-shaped hollow tubing.
Removal of Soft Tissue and Bony Barrier to Enable Eruption of Teeth
- It involves excision of soft tissue as well as removal of bone covering the crown of unerupted tooth for making the space so that tooth can erupt easily.
Question 2. Write short note on space maintainers.
Answer. “Space maintainer is a device used to maintain the space created by the loss of a deciduous tooth.”
Classification of Space Maintainers
According of Hitchcock
- Removable or fied or semified.
- With band or without band.
- Functional or nonfunctional.
- Active or passive.
- Certain combination of the above.
According to Raymond C.Thurow
- Removable.
- Complete arch.
- Lingual arch
- Extraoral anchorage.
- Individual tooth.
According to Hinrichsen
- Fixed Space Maintainers.
Class 1:
-
- Nonfunctional types:
- Bar type
- Loop type.
- Functional type:
- Pontic type
- Lingual arch type.
- Nonfunctional types:
Class 2: Cantilever type (distal shoe, band and loop).
- Removable Space Maintainers: Acrylic partial dentures.
Ideal Requirements of Space Maintainer
- It should maintain the entire mesiodistal space created by lost tooth.
- It must restore the function and prevent over eruption of opposing teeth.
- It should be strong enough to withstand the functional forces.
- It should not exert excessive stress on adjoining teeth.
- It must permit maintenance of oral hygiene.
- It should be simple to construct.
- It must not restrict normal growth and development and natural adjustments which take place during the transition form deciduous to permanent dentition.
- The space maintainer should be come in the way of other functions.
Contraindications of Space Maintainer
- Mesiodistal width of underlying permanent tooth is less than space.
- When permanent tooth is near the crest of alveolar edge.
- When underlying permanent tooth is missing.
- Patient and parents are not interested.
- Oral hygiene maintenance is poor.
- Patient is mentally retarded.
Removable Space Maintainers
They are space maintainers which can be removed and reinserted into the oral cavity by the patient.
Advantages
- Easy to clean and maintenance of oral hygiene.
- It allow time for circulation of blood to sof tissue.
- They serve other important functions like mastication, esthetics and phonetics.
- They stimulate eruption of permanent teeth.
- They either maintain or restore the vertical dimensions.
- Dental check up for detection of dental caries can be undertaken easily.
- Room can be given to permanent teeth to erupt without changing the appliance.
- Band construction is always not needed.
- They prevent developing of tongue thrusting habit inside the extraction space.
Disadvantages
- Lost or broken by patient.
- Uncooperative patient not wear appliance.
- Lateral jaw growth may be restricted, if clasps are added.
- They can lead to irritation of underlying soft tissues.
Indication
- When esthetic is important.
- When abutment teeth cannot support a fixed appliance.
- In cleft palate patient who need obturation of palatal defect.
Contraindication
- When radiograph reveals that the unerupted permanent tooth is not going to erupt in less than 5 months of time, removable space maintainer can be given.
- If permanent teeth are not completely erupted, it can be difficult to adapt the bands. So it is advisable to use the removable space maintainer.
- In cases where multiple loss of deciduous tooth is required which may need functional replacement in form of either the partial or complete denture.
Commonly used Removable Space Maintainers
- Acrylic partial dentures.
- Acrylic full/complete denture.
- Removable distal shoe space maintainer.
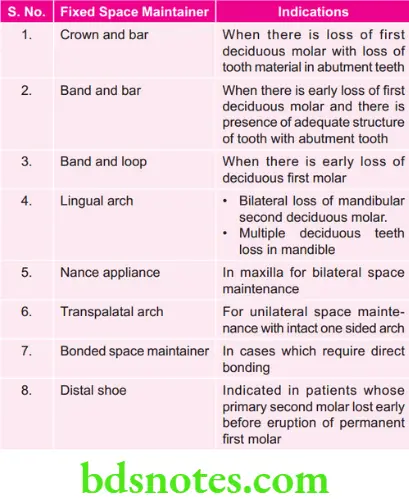
Fixed Space Maintainers
Following are the fixed space maintainers, i.e.
- Functional fixed space maintainers
- Crown and bar
- Band and bar
- Non-functional fixed space maintainers
- Band and loop
- Lingual arch
- Nance appliance
- Transpalatal arch
- Bonded space maintainer
- Cantilever type: Distal shoe
Crown and Bar
- It is a functional space maintainer
- It is indicated in cases where there is loss of fist primary molar with significant loss of tooth material in abutment teeth.
- In its design proper sized stainless steel crown form is chosen for abutment teeth. Contour the stainless steel crown and fit them properly. Join abutment crowns by 0.036 inch stainless steel bar which is soldered to the crowns.
Nance Space Holding Appliance
- It is a non-functional passive type of fied space maintainer which is used in maxillary arch.
- Indicated for bilateral space maintenance.
- In its design it is a maxillary lingual arch which does not contact the anterior teeth. It also approximates anterior palate. Palatal portion incorporates an acrylic buttn which contacts the palate. Area of wire where acrylic is embedded is bent into various configurations for retention of acrylic.
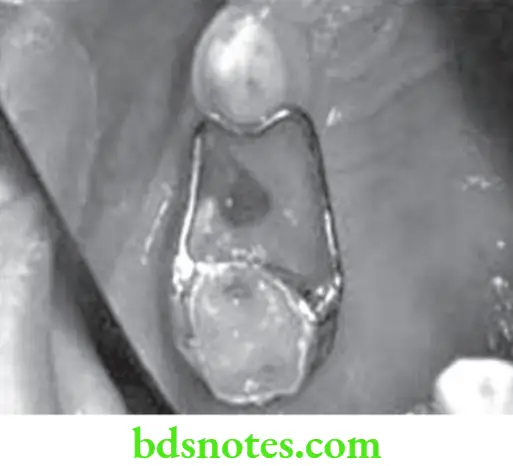
Distal Shoe Space Maintainer
- Distal shoe appliance is also known as intra-alveolar appliance.
- The distal surface of primary 2nd molar guides the unerupted 1st permanent molar.
- When the 2nd primary molar is removed prior to the eruption of the fist permanent molar, the intra-alveolar appliance provides greater control of the path of eruption of the unerupted tooth and prevents undesirable mesial migration.
- The appliance used now is Roche’s distal shoe.
Question 3. Write briefly on preventive orthodontics.
Answer. Preventive orthodontics is defied as “the action taken to preserve the integrity of what appears to be normal occlusion at a specific time”. Graber Preventive orthodontics is defined as “prevention of potential interference with occlusal development”.
Rationale of Preventive Orthodontics
Requirements
- Establishment of good rapport between patient and dental surgeon: Educate the patient about the periodical check up for identifying the problems at early stage and advantages of its prevention by use of appropriate measures.
- Need for the diagnostic records
- In 2 year old child: Clinical examination is done with intraoral radiographs and panoramic radiographs.
- In 5 year old child: Longitudinal records are needed.
- If there is any sign of the developing malocclusion, periapical radiograph should be done once in a year.
- Study casts: In between 6 to 12 years, study casts make an invaluable records. In some of the required cases, study casts should prepare every year to compare and evaluate potential problems.
Identification of Future Orthodontic Problems
- This is the main critical step in preventive orthodontics.
- The future problems are detected by two ways i.e. clinical indicators and radiographic indicators:
Clinical Indicators
- A careful visual examination will reveal the potential problems.
- There should be differentiation of potential problems from self correcting malocclusion.
Radiographic Indicators
Resorption and eruption patterns of primary and permanent dentition are most important radiographic indicators.
Benefits of Preventive Orthodontics
- There are psychological benefits because of prevention of malocclusion.
- Preventive measures eliminate the etiologic factors and there is possible to restore the normal growth and possibility of achieving the bettr results.
- Early treatment of deleterious habits eliminates the problem of malocclusion.
- It makes the treatment economical.
Question 4. Write short note on fixed space maintainer.
Answer. Space maintainers which are to be fixed on the teeth are known as fixed space maintainer.
Types of Fixed Space Maintainers
- Functional space maintainers.
- Crown and bar
- Band and bar.
- Non-functional space maintainers.
- Band and loop
- Lingual arch
- Nance appliance
- Transpalatal arch
- Bonded space maintainer.
- Cantilever type space maintainer.
- Distal shoe space maintainer.
Advantages of Fixed Space Maintainer
- Crowns and bands are to be used and they require very less tooth preparation or no tooth preparation.
- Passive eruption of abutment teeth is not interfered by them.
- Growth of the jaw is not hampered by them.
- Permanent teeth erupt freely in oral cavity.
- Easily used in uncooperative patient.
- If pontics are placed with fixed space maintainers patient may easy undergo mastication with them.
Disadvantages of Fixed Space Maintainer
- Proper skill is needed for their placement.
- They can cause decalcifiation of part of tooth which lies under the band.
- Supraeruption of opposite teeth may occur if pontics are not used.
- If pontic is used and patient fails to report this can cause interference with vertical eruption of abutment tooth.
Question 5. Write short note on distal shoe space maintainer.
Answer. It is also known as Roche’s appliance or Willet’s appliance or Intra-alveolar appliance or Cantilever fixed type space maintainer.
Types
- Fixed
- Functional
- Non-functional
- Removable.
Fixed Distal Shoe Space Maintainer
Design
Roche design a crown and band appliance along with distal intragingival extension which guide fist permanent molar to erupt.
- First primary molar is banded. Place the band over steel crown on abutment tooth.
- Make the impression with bands in the place. Subsequently remove the bands from the teeth and place as well as stabilize the impression before pouring the model.
- Prepare the dental stone model.
- As extraction of deciduous second molar is not done, cut the tooth from the model. Prepare the hole in the model to simulate distal root of second deciduous molar.
- Measure the mesiodistal width of second deciduous molar.
- As if second deciduous molar is absent, take a radiograph to measure mesiodistal space.
- A simple basic method is to measure contralateral side second deciduous molar.
- V shaped gingival extension is about 1 to 1.5 mm below mesial marginal ridge of permanent fist molar.
Indication
In patient where there is early loss of primary second molar before eruption of permanent fist molar.
Contraindications
- In patients where several teeth are missing, abutment to support the appliance may be absent.
- In patient with poor oral hygiene.
- In cases where there is lack of patient or parent cooperation.
- In medically compromised cases such as rheumatic fever, congenital heart defects, juvenile diabetes and blood dyscrasias.
Removable Distal Shoe Space Maintainer
Starkey has given this appliance.
Fabrication
- In its fabrication the tooth which has to be extracted should be cut of and a depression should be made in model to allow processing of acrylic extension.
- Acrylic extends in alveolus and guide the erupting fist molar in position and maintain space for second premolar.
- Cut the extension once the permanent molar erupts in occlusion.
Indication
In unilateral or bilateral early loss of primary second molar before eruption of permanent fist molar.
Question 6. Write short note on space maintenance.
Answer. Space maintenance is defined as “the measures or procedures that are brought into use due to premature loss of deciduous tooth/teeth, to prevent loss of arch development.”
Planning for Space Maintenance
For planning the space maintenance following are the considerations for the factors which inflence development of malocclusion:
- Abnormal oral musculature: Alteration in position of tongue and strong mentalis muscle causes damage to occlusion after loss of deciduous mandibular molar. This leads to collapse of mandibular arch and distal drif of anterior teeth.
- Pernicious oral habits: Habits such as sucking habits, tongue thrusting alter buccinators mechanism which causes collapse of arch aftr premature loss of deciduous teeth.
- Existing malocclusion: Due to early loss of deciduous tooth there is increase in severity of diffrent types of malocclusion such as arch length discrepancy, Class 2 division 1 malocclusion.
- Stage of occlusal development: There is more space loss if the lost tooth is adjacent to the actively erupting tooth.
Factors Considered for Planning of Space Maintenance
Time Elapsed Since Loss of Tooth
- Maximum loss of space occurs within 2 weeks to 6 months of the premature loss of deciduous tooth.
- It is recommended to fabricate the space maintainer before the extraction and to be inserted at the time of extraction.
Dental Age of the Patient
- Dental age is more important than the chronological age of the patient.
- Normally eruption of tooth occurs when ¾ of root development takes place. So space maintainers should be planned depending on formation of root of permanent successor.
- In cases with inadequate root completion space maintainers are indicated.
Amount of Bone Covering the Unerupted Tooth
- The developing premolars usually require 3-5 months to move through 1 mm of covering alveolar bone as observed on a bitewing radiograph.
- If thickness of bone over erupting tooth is more there is delay in tooth eruption while if bone covering the tooth get destroyed, there is speedily eruption of permanent tooth.
- Patients having thick overlying bone need space maintainers even if roots are fully developed.
Sequence of Teeth Eruption
- The status of the developing and erupting teeth adjacent to the space created by the premature loss of the deciduous tooth affect space closure.
- Two clinical conditions are of importance:
- The fist one being premature loss of deciduous second molar. If the level of eruption of the second permanent molar is at a level higher than that of the second premolar, then there is a likelihood of permanent fist molar to tip mesially and impact the eruption of the second premolar.
- The second scenario is that of premature loss of deciduous fist molar and an erupting permanent lateral incisor, which tends to distally ditch the deciduous canine thus effecting the eruption of permanent fist premolar. This also results in lingual inclination of the anteriors especially in the mandible thus resulting in the collapse of the anterior segment.
Congenitally Missing Teeth
It can be deal in two ways, fist one is maintain the space i.e. plan for replacement at later stage and second is allow the space to close.
Delay Eruption of Permanent Tooth
In patients where there is delay in permanent tooth eruption with retained primary tooth, primary tooth should be extracted and space maintainer is provided. This leads to permanent tooth to erupt in normal position.
Time of Tooth Loss and Stage of Occlusion
- This factor should be well considered.
- For instance, if there is loss of deciduous second molar before eruption of permanent fist molar, this requires special space maintainer, i.e. distal shoe space maintainer.

Leave a Reply