Pharynx And Palate
Question 1. Describe the pharynx under the following headings:
- Pharynx Parts,
- Pharynx Structure,
- Pharynx Muscles and
- Pharynx Nerve supply.
Answer.
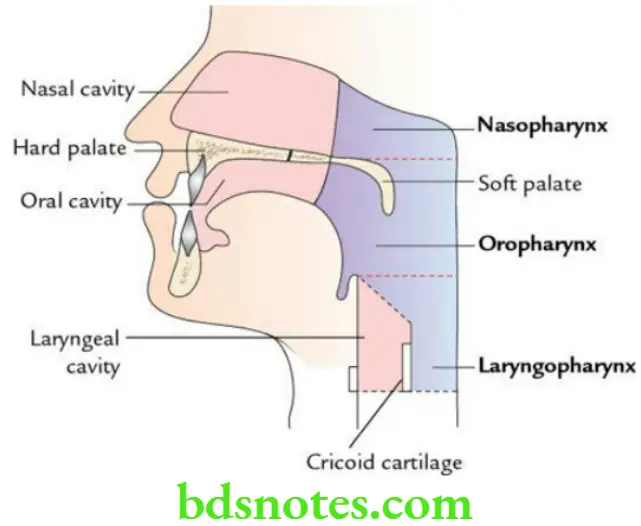
The pharynx is funnel-shaped muscular tube situated behind the nose, mouth and larynx.
Parts of pharynx The pharynx is subdivided into three parts:
- The nasopharynx, lying behind the nose.
- Oropharynx, lying behind the mouth.
- Laryngopharynx, lying behind the larynx.
Pharynx Anatomy
Pharynx Functions
- The nasopharynx provides passage to air only.
- The oropharynx provides passage to both air and food.
- The laryngopharynx provides passage to air only.
Structure of pharynx The pharyngeal wall consists of four layers. From within to outwards these are as follows:
- Mucosa
- Pharyngobasilar fascia
- Muscular coat
- Buccopharyngeal fascia
Pharynx Anatomy
Muscles of pharynx
Three pairs of constrictors (forming outer circular layer of muscle coat):
- Superior constrictor
- Middle constrictor
- Inferior constrictor
Three pairs of longitudinal muscles (forming an inner longitudinal layer of muscular coat):
- Stylopharyngeus
- Palatopharyngeus
- Salpingopharyngeus
Pharynx Nerve supply
Motor: All the muscles of the pharynx are supplied by the cranial root of the accessory nerve (CN 11) via the pharyngeal plexus, except the stylopharyngeus which is supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN 9).
Sensory:
- Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Internal laryngeal nerve
Question 2. Discuss the origin and insertion of the constrictors of the pharynx.
Answer.
Constrictors of the Pharynx Origin
Superior Constrictor: It arises from the pterygoid hamulus, pterygomandibular raphe, posterior end of mylohyoid line and the side of the tongue.
Middle Constrictor: It arises from the lower part of the stylohyoid ligament, lesser and greater cornua of the hyoid bone.
Inferior Constrictor: It consists of two parts – thyropharyngeus and cricopharyngeus.
- Thyropharyngeus: From the oblique line of thyroid cartilage.
- Cricopharyngeus: From the side of cricoid cartilage.
Pharynx Anatomy
Pharynx Insertion All the constrictors of the pharynx are inserted into a median raphe, on the posterior wall of the pharynx. The upper end of this raphe is attached to the pharyngeal tubercle on the basilar part of the occipital bone.
Question 3. Write a short note on the nasopharynx.
Answer.
Nasopharynx is the upper portion of pharynx lying behind the nasal cavities with which it communicates. Internally it is lined by mucous membrane.
Nasopharynx Boundaries
The roof and lateral wall are formed by the body of the sphenoid which forms a continuous sloping surface, and the basilar part of the occipital bone.
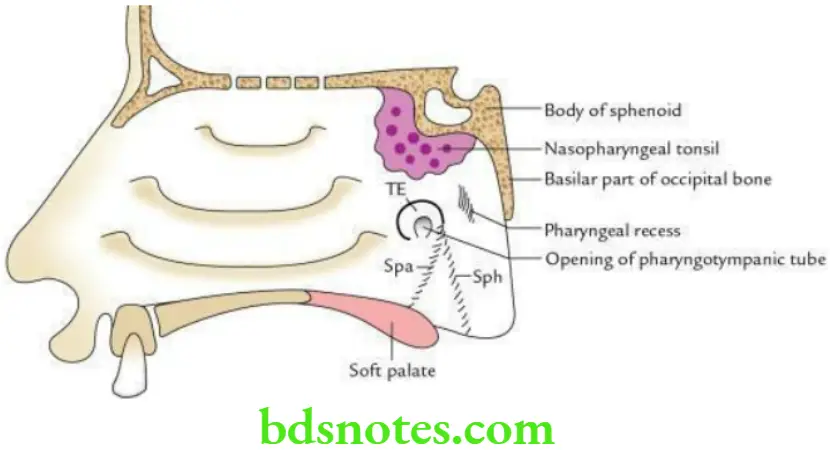
The floor is formed by the sloping upper surface of the soft palate.
Floor Features
- The presence of the nasopharyngeal tonsil at the junction of the roof and posterior wall, deep to the mucous membrane, is more prominent in children. When enlarged it is called as adenoid.
- Pharyngeal opening of pharyngotympanic tube which maintains the equilibrium of air pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane.
- The tubal tonsil is an aggregation of lymphoid tissue along the upper and posterior margin of the tubal opening deep into mucous membrane producing elevation called tubal elevation.
- Salpingopharyngeal and salpingopalatine folds. Out of these two folds, one extends downwards towards the wall of pharynx enclosing salpingopharyngeus muscle and is called the salpingopharyngeal fold, while the other extends downwards and forward to the soft palate enclosing the levator palati muscle and is called salpingopalatine fold.
- The pharyngeal recess is a depression behind the tubal elevation.
Read And Learn More: Selective Anatomy Notes And Question And Answers
Question 4. What is gag reflex?
Answer.
It is a protective reflex characterized by elevation of the palate and contraction of pharyngeal muscles with associated retching and gagging in response to stimulation of mucosa of the oropharynx. The af erent limb of this reflex is formed by the glossopharyngeal nerve, while its ef erent limb is formed by the vagus nerve.
Pharynx Anatomy
Question 5. Write a short note on Killian’s dehiscence and pharyngeal diverticulum.
Answer.
There is a small, triangular region in the lower part of the posterior wall of the pharynx (the junctional region between the thyropharyngeus and cricopharyngeus), which is not covered by muscles. This weak area is termed Killian’s dehiscence. The mucosa and submucosa of the pharyngeal wall may bulge out through this weak area to form the pharyngeal diverticulum/Zenker’s diverticulum.
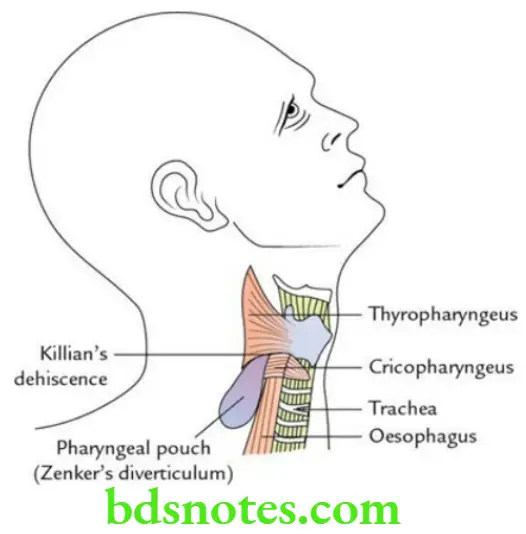
This diverticulum occurs due to neuromuscular incoordination between propulsive thyropharyngeus muscle (supplied by the external laryngeal nerve) and sphincteric cricopharyngeus muscle (supplied by the recurrent laryngeal nerve).
Question 6. Write a short note on Waldeyer’s ring.
Answer.
It is a ring of submucous aggregations of lymphoid tissue, which surrounds the beginning of respiratory and digestive tracts.
Waldeyer’s Ring Formation The Waldeyer’s ring is formed as follows:
- Above and behind, by pharyngeal tonsil
- Below and in front, by lingual tonsil
- On each side, by palatine tonsil
- Superolaterally on each side, by tubal tonsil
Pharynx Anatomy
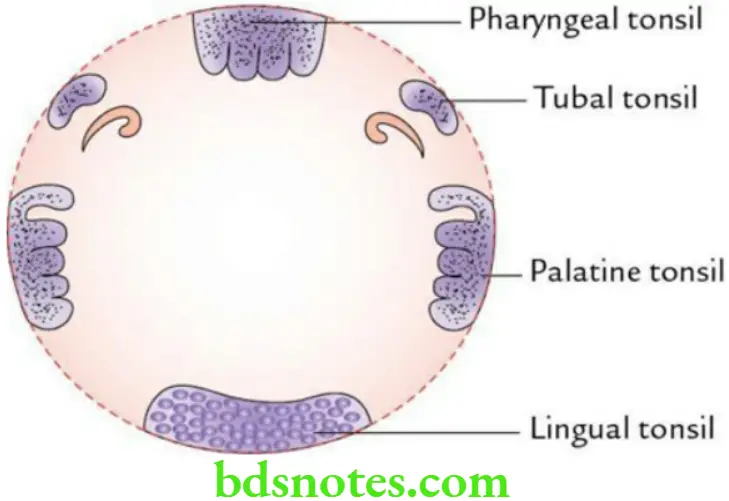
Waldeyer’s Ring Applied Anatomy The Waldeyer’s ring provides the first line of defense to respiratory and digestive tracts by preventing the spread of infection from nasal and oral cavities to these tracts.
Question 7. Describe tonsil under the following headings:
- Tonsil Location,
- Tonsil External features,
- Tonsil Tonsillar bed,
- Tonsil Nerve supply,
- Tonsil Arterial supply,
- Tonsil Venous drainage and
- Tonsil Applied anatomy.
Pharynx Anatomy
Answer.
Tonsil Location The palatine tonsil is an almond-shaped mass of lymphoid tissue (dimension of about 2 cm) located in the tonsillar fossa on each side in the lateral wall of the oropharynx.
The tonsillar fossa is a triangular recess that is bound in front by the palatoglossal fold and behind by the palatopharyngeal fold.
External features of tonsil The tonsils present the following features:
- Two surfaces: medial and lateral
- Two borders: anterior and posterior
- Two ends: upper and lower
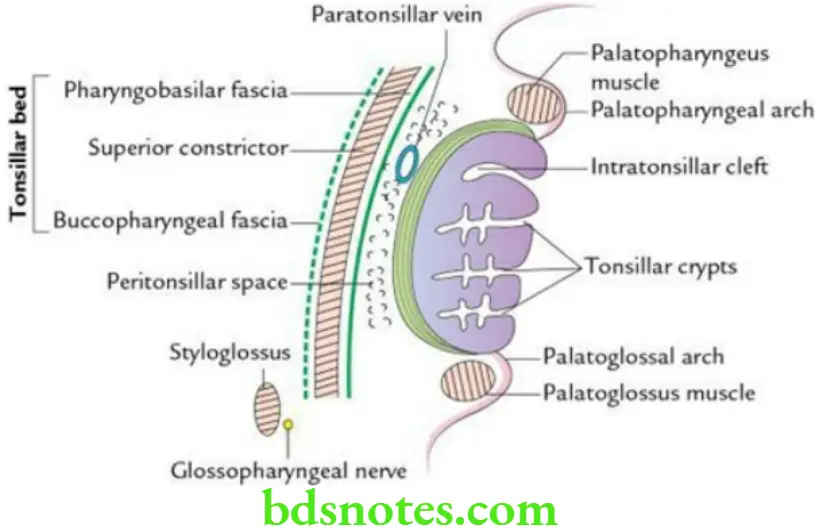
The lateral surface is covered by a sheath of condensed connective tissue called hemicapsule of the tonsil.
Tonsillar bed From deep to superficial, it is formed by:
- Pharyngobasilar fascia
- Superior constrictor muscle supplemented by palatopharyngeus
- Buccopharyngeal fascia
Tonsillar Nerve supply
- Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Lesser palatine nerves
Arterial supply of the tonsil is supplied by the following five sets of arteries:
- Tonsillar branch of the facial artery (principal artery)
- Dorsal lingual branches of the lingual artery
- Ascending pharyngeal artery – a branch of the external carotid artery
- Ascending palatine artery – a branch of the facial artery
- Greater/descending palatine artery – a branch of the maxillary artery
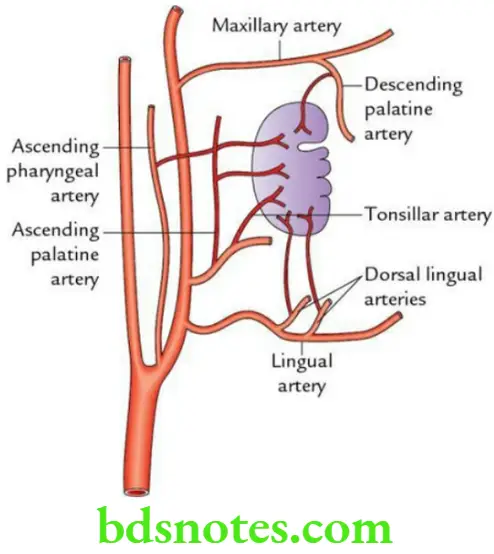
Venous drainage: By peritonsillar vein into pharyngeal venous plexus, which in turn drains into the internal jugular vein.
Hard Soft Palate
Lymphatic drainage: Lymph vessels from the tonsil drain into jugulodigastric lymph nodes. These lymph nodes lie in the angle formed between posterior belly of digastric (inferior border) and internal jugular vein (anterior aspect) deep to the mandible.
Lymphatic drainage Applied anatomy
- Tonsillitis: It is an infection of the tonsil, which is usually of viral origin. This leads to the enlargement of jugulodigastric lymph nodes.
- Quinsy (peritonsillar abscess): It is the name given to collection of pus in the peritonsillar space.
- Referred pain: Pain of the tonsil is referred to middle ear because both are supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve.
- Commonest source of bleeding after tonsillectomy. It is due to damage of the paratonsillar vein.
- After tonsillectomy, all blood clots in the tonsillar fossa are removed to prevent bleeding as removal of these clots allows the retraction of blood vessels due to muscle contraction. The only other organ in the body where such removal of blood clots is done is the uterus.
Pharynx Anatomy
Question 8. Write a short note on the development of tonsil.
Answer.
The tonsil develops from the 2nd pharyngeal pouch in the 4th week of intrauterine life.
- The epithelial lining of the tonsil develops from the endoderm of the 2nd pharyngeal pouch.
- The stroma of tonsil develops from local mesenchyme.
- The lymphocytes of the tonsil are derived from either local mesenchyme or from circulating lymphocytes.
Question 9. Discuss the histological features of a tonsil.
Answer.
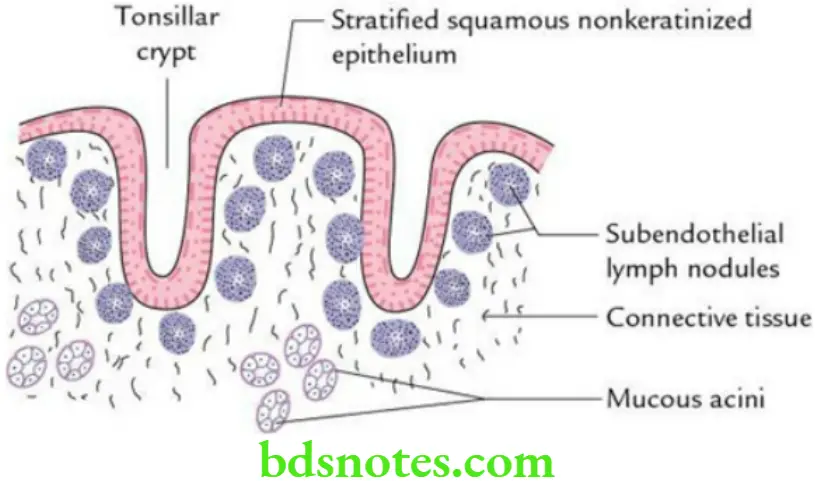
The histological features of the tonsil are as follows:
- The surface is lined by stratified, squamous, nonkeratinized epithelium.
- Surface epithelium dips at places into the substance of tonsil to form tonsillary crypts.
- Presence of subendothelial lymph nodules underneath the stratified squamous epithelium, along the crypts.
- Presence of mucous glands in the deeper part.
- Fibrous capsule on the outer side.
Question 10. Briefly describe the pharyngotympanic tube/auditory tube/eustachian tube.
Answer.
Pharyngotympanic Tube General description
- It is a funnel-shaped osseocartilaginous tube that connects the middle ear cavity (tympanum) with the nasopharynx.
- It is about 4 cm (36 mm) long.
- It is directed downwards, forward, and medially.
- Its bony part forms the lateral one-third of the tube, while its cartilaginous part forms the medial two-third of the tube.
- Its bony part (12 mm long) lies at the base of the skull, lateral to the carotid canal below the tympanic plate of the temporal bone.
- Its cartilaginous part (24 mm long) lies in sulcus tubae – a groove between the greater wing of the sphenoid and the apex of the petrous temporal bone.
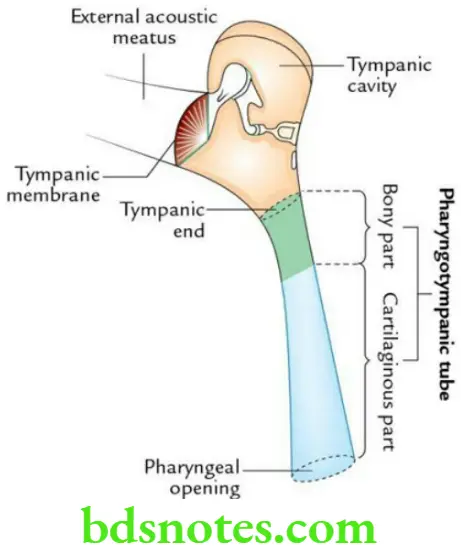
Pharyngotympanic Tube Function Maintains equilibrium of air pressure on either side of the tympanic membrane for its proper vibration by the sound waves.
Pharyngotympanic Tube Applied anatomy This provides passage for infection to travel from the upper respiratory tract (URT) to middle ear causing otitis media. The otitis media is common in children because the auditory tube is much shorter (18 mm) and straight in them.
Question 11. Briefly discuss the hard palate.
Answer.
It is a bony partition between nasal and oral cavities.
Hard Soft Palate
Hard Palate Formation
- Anterior two-third of the hard palate is formed by the palatine processes of the maxillae.
- The posterior one-third of the hard palate is formed by horizontal plates of the palatine bones.
Hard Palate Development
- Small triangular part anteriorly (premaxilla) opposite to incisor teeth develops from frontonasal process.
- Remaining part develops from palatine shelves of maxillary processes.
Question 12. Describe the soft palate in brief.
Answer.
It is a movable, muscular flap suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate. It separates the nasopharynx from the oropharynx.
Muscles of the soft palate Palate has five pairs of muscles:
- Tensor palati
- Levator palate
- Musculus uvulae
- Palatoglossus
- Palatopharyngeus
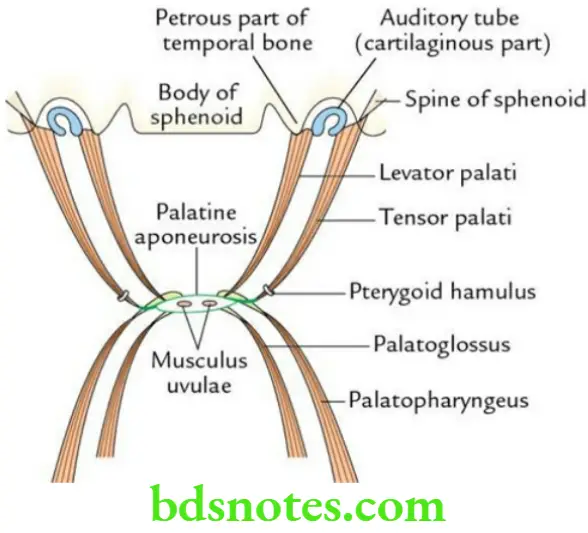
Muscles of the soft palate Nerve supply All the muscles of the palate are supplied by the cranial root of the accessory nerve (CN 11) via pharyngeal plexus, except the tensor palate which is supplied by the mandibular nerve (through nerve to medial pterygoid).
Hard Soft Palate
Muscles of soft palate Applied anatomy The paralysis of the soft palate leads to:
- Nasal regurgitation of food
- Nasal twang of voice
- Flattening of the palatal arch on the side of the lesion
- Deviation of uvula opposite to the side of lesion
Question 13. Describe development and congenital anomalies of palate.
Answer.
Congenital anomalies of palate Development
The primary palate, the small triangular anterior part opposite incisor teeth (i.e. premaxilla), develops from the frontonasal process (strictly speaking from the intermaxillary segment formed by the fusion of medial nasal processes of the frontonasal process).
The secondary palate, the remaining large posterior part, develops from two shelf-like outgrowths, the palatine shelves, on each side from maxillary processes congenital anomalies of palate anomalies
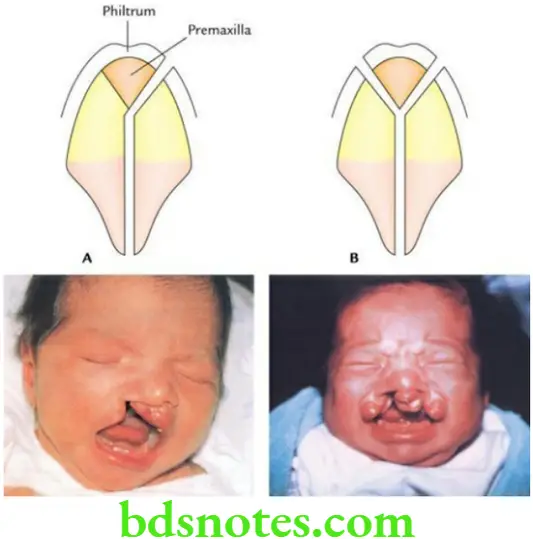
The congenital anomalies of the palate are common due to failure of fusion of its primitive parts, viz. premaxilla and right and left palatine shelves. These are as follows:
- Complete cleft: It may be unilateral or bilateral. It is usually associated with the cleft lip as the philtrum (the median triangular part) of the upper lip also develops from’ the frontonasal process.
- Incomplete cleft lip: It may present as a bifid uvula or cleft of the soft palate (involving only the uvula or the whole of the soft palate.
Question 14. Write a short note on pharyngeal apparatus.
Answer.
The pharyngeal apparatus consists of the following components:
- Five pharyngeal arches
- Four pharyngeal pouches
- Four pharyngeal clefts
- Four pharyngeal membranes
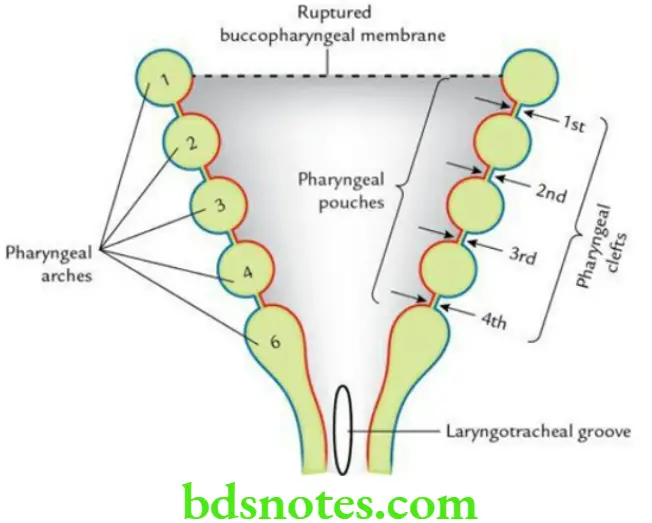
All these components develop in the lateral wall of the primitive pharynx caudal to the primitive mouth/stomodeum.
Question 15. Write a short note on pharyngeal arches.
Answer.
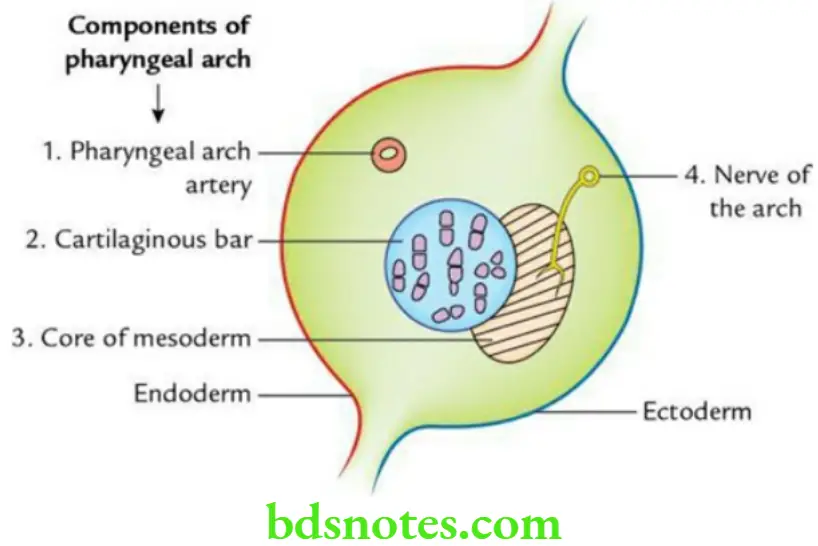
These are horseshoe-shaped cylindrical bars/elevations on either side in the anterolateral portion of wall of primitive pharynx.
Each pharyngeal arch consists of four components:
- A core of mesoderm
- A cartilaginous bar
- A pharyngeal arch artery
- A nerve
Question 16. Enumerate the mesodermal derivatives of 1st and 2nd pharyngeal arches in tabular form.
Answer.
These are as follows:
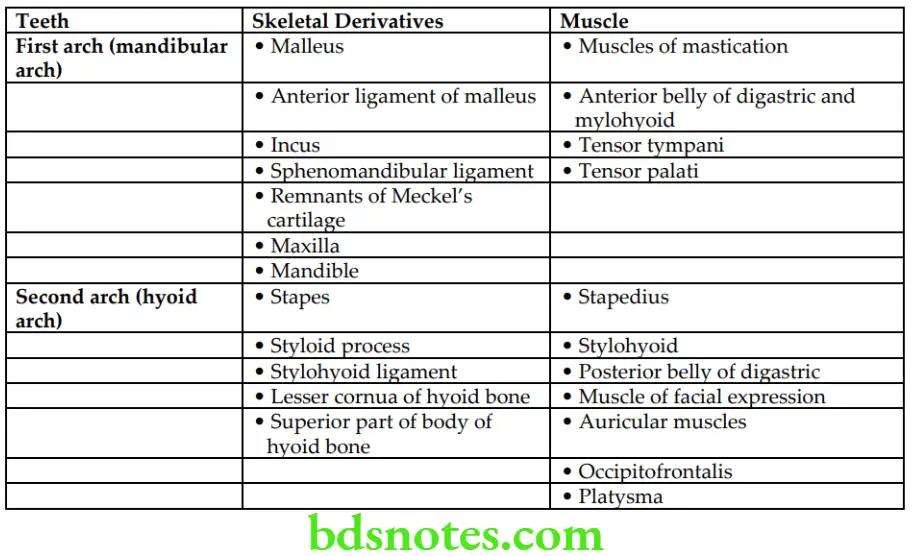
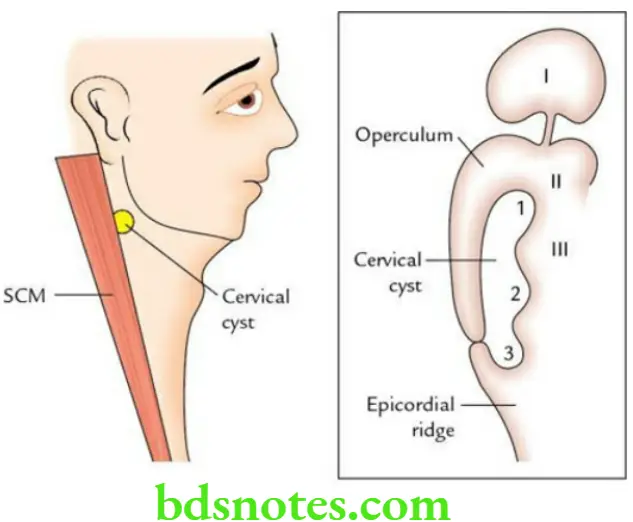
Question 17. Discuss the embryological basis of branchial cyst/cervical cyst.
Answer.
- It is a congenital cyst (lined by ectoderm) that appears on the side of the neck along the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid below and behind the angle of the mandible.
- It appears when 2nd, 3rd and 4th pharyngeal clefts fail to obliterate.
Hard Soft Palate

Leave a Reply