Pharmacology Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. All Can Be Used In Acute Bronchial Asthma Except:
- Salbutamol
- Ipratropium
- Cromolyn sodium
- Corticosteroids
Answer: 3. Cromolyn sodium
Question 2. Antiemetic With Minimum Risk Of Extrapyramidal Symptoms:
- Metoclopramide
- Domperidone
- Chlorpromazine
- Prochlorperazine
Answer: 3. Chlorpromazine
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question And Answers
Question 3. Xerostomia Can Be Produced By:
- Anticholinergic drugs
- Antipsychotic drugs
- Antihistaminics
- All the above
Answer: 4. All the above
Question 4. Gingival Hyperplasia Is Adverse Effct Of:
- Metronidazole
- Phenytoin
- Chlorhexidine
- Alloftheabove
Answer: 2. Phenytoin
Question 5. Vitamin K Is an Antidote To:
- Heparin
- Warfarin
- Streptokinase
- Lepinidin
Answer: 2. Warfarin
Question 6. Drug Contraindicated To A Patient Of Peptic Ulcer Is:
- Aspirin
- Paracetamol
- Misoprostol
- Sucralfate
Answer: 1. Aspirin
Question 7. Shortest Acting Muscle Relaxant Is:
- Succinylcholine
- Pancuronium
- Doxacurim
- Tubocurarine
Answer: 1. Succinylcholine
Question 8. Antihistamine With Maximum Risk Of Sedationis:
- Fexofenadine
- Levocetirizine
- Diphenhydramine
- Loratidine
Answer: 3. Diphenhydramine
Question 9. Diffusion Hypoxia Is an Adverse Effct Of:
- Nitrous oxide
- Halothane
- Isoflurane
- All the above
Answer: 1. Nitrous oxide
Question 10. Agents Used To Harden And Dry The Pulp And Tissues Of the Root Canal Are:
- Astringents
- Mummifying agents
- Denitrifies
- Styptics
Answer: 2. Mummifying agents
Question 11. All Of The Following Are Calcium Channel Blockers Except:
- Diltiazem
- Atenolol
- Verapamil
- Amlodipine
Answer: 2. Atenolol
Question 12. Digoxin In Habits The Enzyme:
- Acetylase
- Na+ ATPase
- Na+K + ATPase
- Phosphodiosterol
Answer: 3. Na+K + ATPase
Question 13. All The Following Have a Role In Calcium Metabolism Except:
- Paratharmone
- Thyroxin
- Calcitonin
- Vitamin D
Answer: 2. Thyroxin
Question 14. Inhibitor Of Growth Hormone Secretion Is Called:
- Somatotropin
- Somatomedoan
- Somatrom
- Somatostatin
Answer: 4. Somatostatin
Question 15. All Of The Following Are Primarily Bacteriostatic Except:
- Chloramphenicol
- Tetracycline
- Erythromycin
- Ciprofloxacin
Answer: 3. Erythromycin
16. Identify A Third Generation Cephalosporin From The Following:
- Cofactor
- Cefadroxil
- Cephalexin
- Cefotaxime
Answer: 4. Cefotaxime
Question 17. First Aminoglycoside Discovered Was:
- Gentamycin
- Kanamycin
- Streptomycin
- Tobramycin
Answer: 3. Streptomycin
Question 18. Drugs Interfering With Platelet Function Are:
- Aspirin and NSAIDs
- Clopidogrel
- Dipyridamole
- Sulphasalazine
Answer: 1. Aspirin and NSAIDs
Question 19. The Following Antiviral Drug Used Against Herpes Infection:
- Famciclovir
- Acyclovir
- Ritonavir
- Idoxuridine
Answer: 2. Acyclovir
Question 20. Pick A Biguanide Oral Hypoglycemic Drug From The Following:
- Glipizide
- Tolbutamide
- Metformin
- Acarbose
Answer: 3. Metformin
Question 21. A drug With HalfLife 12 Hours Is Administered 12 Hourly. The Time Required To Achieve Steady State Kinetics:
- 12 hrs
- 24 hrs
- 48 hrs
- 96 hrs
Answer: 1. 12 hrs
Question 22. The Fraction Of Unchanged Drug Reaching The Systemic Circulation After Its Administration is:
- Absorption
- Bioavailability
- Distribution
- Biotransformation
Answer: 2. Bioavailability
Question 23. A Short Dental Surgery Is To Be Performed Under Ga The Patient Needs The Immediate Return To Previous Mental Status. The Best Intravenous Anesthetic Is:
- Propofol
- Ketamine
- Thiopentonesodium
- Desflurane
Answer: 4. Desflurane
Question 24. All Of The Following Can Be Used In Peptic Ulcer Except:
- Aspirin
- Prostaglandin
- Cimetidine
- Metronidazole
Answer: 1. Aspirin
Question 25. ΒBlockers Can Be Used In All Except:
- Hypertension
- Angina
- Arrhythmia
- Bradycardia
Answer: 4. Bradycardia
Question 26. Which One Of The Following Is Not Produced By Prostaglandins:
- Pain
- Fever
- Inflammation
- Peptic ulcer
Answer: 4. Peptic ulcer
Question 27. Very High Dose Of Paracetamol Can Produce:
- Peptic ulcer
- Bronchial asthma
- Hepatic damage
- All of above
Answer: 3. Hepatic damage
Question 28. Chlorpromazine Can Produce:
- Extrapyramidal symptoms
- Drynessofmouth
- Postural hypotension
- All of above
Answer: 4. All of above
Question 29. Effect Of An OnDepolarizing Neuromuscular Blocker Used During Surgery Can Be Reversed By:
- Neostigmine
- Succinylcholine
- Atropine
- Mifacurium
Answer: 1. Neostigmine
Question 30. The Drug Preferred For the Management Of Status Epilepticus Is:
- Phenobarbitone
- Diazepam
- Valproic acid
- Lamotrigine
Answer: 1. Phenobarbitone
Question 31. The Side effects Which Primarily Limit the Acceptability Of Oral Iron Therapy Is:
- Epigastric pain and bowel upset
- Black stools
- Staining of teeth
- Metallic taste
Answer: 1. Epigastric pain and bowel upset
Question 32. The Following Can Be Used To Antagonize The Action Of Heparin In the Case Of Over Dose:
- Heparin sulfate
- Dextran sulfate
- Protamine sulfate
- Ancrod
Answer: 3. Protamine sulfate
Question 33. The Most Important Toxicity Of Amphotericin B Is:
- Nephrotoxicity
- Neurotoxicity
- Hepatotoxicity
- Bone marrow depression
Answer: 1. Nephrotoxicity
Question 34. Select The Macrolide Having Clinically Useful Antileprotic Activity:
- Azithromycin
- Clarithromycin
- Erythromycin
- Roxithromycin
Answer: 2. Clarithromycin
Question 35. The Following Drug Can Cause Rickets In Children By Interfering With Vitamin Direction:
- Tetracycline
- Digoxin
- Phenytoin
- Ciprofloxacin
Answer: 3. Phenytoin
Question 36. The Insulin Preparation Of Choice In Diabetic Ketoacidosis Is:
- Regular insulin
- Lente insulin
- isophane insulin
- A mixture of plain and isophane insulin
Answer: 1. Regular insulin
Question 37. The Following Factors Enhance Renin Release From The Kidney Except:
- Fall in blood pressure
- Reduction in blood volume
- Enhanced sympathetic activity
- Volume overload
Answer: 2. Reduction in blood volume
Question 38. Which Of The Following Drugs Is A Potassium Channel Opener:
- Nicorandil
- Hydralazine
- Glibenclamide
- Amiloride
Answer: 1. Nicorandil
Question 39. Loss Of Taste sensation Can Be A Side Effect Of The Following Antihypertensive Drug:
- Clonidine
- Captopril
- Verapamil
- Prazosin
Answer: 2. Captopril
Question 40. All Of The Following Are Primarily Bacteriostatic Except:
- Chloramphenicol
- Tetracycline
- Erythromycin
- Ciprofloxacin
Answer: 3. Erythromycin
Question 41. Preanesthetic Medication Used To Reduce Excessive Secretion Is:
- Atropine
- Diazepam
- Pilocarpine
- Fentanyl
Answer: 1. Atropine
Question 42. Adrenaline Is Combined With Lignocaine:
- To reduce the toxicity of lignocaine
- To prolong the duration of action
- To provide a bloodless field for surgery
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 43. Prostaglandin Synthesis Is Inhibited By:
- Misoprostol
- Omeprazole
- Aspirin
- Cyproheptadine
Answer: 3. Aspirin
Question 44. Drug Contraindicated To A Patient Of Bronchial Asthma Are:
- β-agonist
- β-blockers
- Leukotrine antagonist
- Anticholinergic drug
Answer: 2. β-blockers
Question 45. Specific Antidote Used In Organophosphorus Poisoning Is:
- Atropine
- Naloxone
- Neostigmine
- N-acetylcysteine
Answer: 1. Atropine
Question 46. Atropine Is Contraindicated To A Patient Of:
- Bradycardia
- Corneal ulcer
- Glaucoma
- Peptic ulcer
Answer: 3. Glaucoma
Question 47. Dissociative Anesthesia Is Produced By:
- Thiopental sodium
- Propofol
- Ketamine
- Etomidate
Answer: 3. Ketamine
Question 48. Benzodiazepines Are Used As:
- Antianxiety drugs
- Anticonvulsants
- Anesthetic adjuvants
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 49. Xerostomia Can Be Managed By:
- Atropine
- Pilocarpine
- Promethazine
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 50. A Drug That Has Affity For A Receptor But No Intrinsic Activity is:
- Agonist
- Partial agonist
- Antagonist
- Inverse agonist
Answer: 3. Antagonist
Question 51. The drug Of Choice In Acute Attack Of Angina Pectoris Is:
- Amyl nitrate
- Nifedipine
- Digoxin
- Glyceryl Trinitrate
Answer: 4. Glyceryl Trinitrate
Question 52. Active Metabolite Of Enalapril Is:
- Enalaprilat
- Ramipril
- ProEnalapril
- Captopril
Answer: 1. Enalaprilat
Question 53. All The Following Are Potassium Channel Activators Except:
- Captopril
- Nicorandil
- Cromakalim
- Pinacidil
Answer: 1. Captopril
Question 54. Term Chemotherapeutic Agent Is First Introduced By:
- Domagk
- Fleming
- Paul Ehrlich
- Florey
Answer: 3. Paul Ehrlich
Question 55. All Of The Following Are Narrow Spectrum Drugs Except:
- Penicillin G
- Streptomycin
- Erythromycin
- Chloramphenicol
Answer: 4. Chloramphenicol
Question 56. The Following Sulfonamide Is Short Acting:
- Sulfadiazine
- Sulfamethoxazole
- Sulfadoxine
- Sulfamethopyrazine
Answer: 1. Sulfadiazine
Question 57. The following Are Secreted By Anterior Pituitary Except:
- ACTH
- FSH
- ADH
- LH
Answer: 3. ADH
Question 58. Dimercaprol Is Not Used In Poisoning Due To:
- Arsenic
- Mercury
- Gold
- Iron
Answer: 4. Iron
Question 59. All Of The Following Are Polyene Antibiotics Except:
- Amphotericin B
- Nystatin
- Clotrimazole
- Natamycin
Answer: 3. Clotrimazole
Question 60. Normal Ca Level In Serum:
- 9–11mg%
- 14–l8mg%
- 3–5mg%
- 28–38mg%
Answer: 1. 9–11mg%
Question 61. Route Of Administration Of Streptomycin In Treatment Of Tuberculosis Is:
- Intradermal injection
- Subcutaneous injection
- Intramuscular injection
- Intravenous injection
Answer: 3. Intramuscular injection
Question 62. Microsomal Enzyme Inducer Is:
- Chloramphenicol
- Cimetidine
- Erythromycin
- Rifampicin
Answer: 4. Rifampicin
Question 63. Alkalinization Of Urine Favors the Excretion Of:
- Morphine
- Phenobarbitone
- Atropine
- Methyl alcohol
Answer: 4. Methyl alcohol
Question 64. Broad Spectrum AntiEpileptic Drug Is:
- Phenytoin
- Ethosuximide
- Sodium valproate
- Primidone
Answer: 3. Sodium valproate
Question 65. Propranolol Is Contraindicated In:
- Hyperthyroidism
- Myocardial infarction
- Bronchial asthma
- Hypertension
Answer: 3. Bronchial asthma
Question 66. Scurvy Is Treated By:
- Thiamine
- Riboflavin
- Niacin
- Ascorbic acid
Answer: 4. Ascorbic acid
Question 67. Montelukast Is:
- An antihistaminic
- A leukotrineantagonist
- A bronchodilator
- An antitussive
Answer: 2. A leukotrineantagonist
Question 68. Lactulose Is Used As:
- Antidiarrheal agent
- Laxative agent
- Antiemetic agent
- A peptic ulcer healing agent
Answer: 2. Laxative agent
Question 69. Fluoxetine Is:
- An antidepressant drug
- An antipsychotic drug
- An antimanic drug
- An antiepileptic drug
Answer: 1. An antidepressant drug
Question 70. Glycopyrrolate Is Used In:
- Bronchial asthma
- Biliary colic
- Overactive bladder
- Preanesthetic medication
Answer: 4. Preanesthetic medication
Question 71. Absorption Of Oral Iron Preparations Can Be Facilitated By CoAdministration Of:
- Antacids
- Tetracycline
- Phosphates
- Ascorbic acid
Answer: 4. Ascorbic acid
Question 72. Select The Fibrinolytic Drug That Is Antigenic:
- Streptokinase
- Urokinase
- Alteplase
- Both(a)and(b)
Answer: 1. Streptokinase
Question 73. Which Antileprotic Drug Suppresses Lepra Reaction And Reversal Reaction As Well:
- Dapsone
- Rifampicin
- Clofazimine
- Minocycline
Answer: 3. Clofazimine
Question 74. Adverse Effects Of Ketoconazole Include The Following Except:
- Gynecomastia
- Oligozoospermia
- Kidney damage
- Menstrualirregularities
Answer: 3. Kidney damage
Question 75. The Vitamin That Is Regarded To Be A Hormone Is:
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin A
Answer: 1. Vitamin D
Question 76. Insulin Resistance Can Be Minimized By The Use Of:
- Corticosteroids
- Tolbutamide
- Protamine
- Human insulin
Answer: 4. Human insulin
Question 77. Persistent Dry Cough May Occur As A Side Effct Of The Following Anti Hypertensive Drug:
- Enalapril
- Atenolol
- Diltiazem
- Methyldopa
Answer: 1. Enalapril
Question 78. Furosemide Is To Be Preferred Over Hydrochlorothiazide When Hypertension Is Accompanied By:
- Asthma
- Hyperuricemia
- Diabetes
- Congestive heart failure
Answer: 4. Congestive heart failure
Question 79. Identify A Third Generation Cephalosporin From The Following:
- Cofactor
- Cefadroxil
- Cephalexin
- Cefotaxime
Answer: 4. Cefotaxime
Question 80. The Most Frequent Side Effct Of Oral Ampicillin Is:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loose motions
- Constipation
- Urticaria
Answer: 1. Nausea and vomiting
Question 81. Which Is Cytochrome P450 Inhibitor:
- Rifampicin
- Ketoconazole
- Phenytoin
- Isoniazid
Answer: 2. Ketoconazole
Question 82. Therapeutic Index Is A Measure Of:
- Safety
- Potency
- Efficy
- Selectivity
Answer: 1. Safety
Question 83. Which Of The Following Drugs Is The Long-Acting Beta 2 Antagonist:
- Salbutamol
- Pirbuterol
- Salmeterol
- Orciprenaline
Answer: 3. Salmeterol
Question 84. Flumazenil Is:
- Opiateant agonist
- Opiate agonist
- Antianginal drug
- Diazepam antagonist
Answer: 4. Diazepam antagonist
Question 85. A Patient On Aspirin Will Have an Increase In:
- Bleeding time
- Clotting time
- Prothrombin time
- Activated partial thromboplastin time
Answer: 1. Bleeding time
Question 86. NSAIDs Lacking AntiInflmmatory Action Is:
- Ibuprofen
- Diclofenac sodium
- Celecoxib
- Paracetamol
Answer: 4. Paracetamol
Question 87. Vitamin Which Act As A Hormone Is:
- A
- C
- D
- E
Answer: 1. D
Question 88. Agents Used To Harden And Dry The Pulp And Tissues Of the Root Canal Are:
- Astringents
- Mummifying agents
- Dentifrices
- Styptics
Answer: 2. Mummifying agents
Question 89. Ram Has A 4ml Lignocaine Vial Of 2% Solution.How Much Lignocaine Is Present In 1 Ml:
- 2 mg
- 8 mg
- 20 mg
- 200 mg
Answer: 2. 8 mg
Question 90. All Of The Following Are Cardio Selective Beta Blocker Except:
- Esmolol
- Atenolol
- Propranolol
- Metoprolol
Answer: 3. Propranolol
Question 91. The Physical Property Of Charcoal, Kaolin Is Responsible For Which Of The Following Actions:
- Osmotic activity
- Adsorptive activity
- Radioactivity
- Radio-opacity
Answer: 2. Adsorptive activity
Question 92. Calciton In Is Responsible For Maintaining Plasma Calcium Concentration By:
- Inhibiting bone resorption by osteoclasts
- Inhibiting calcium absorption in GIT
- Increasing PCT absorption of calcium
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 93. Calcium Channel Blocker With Maximum Peripheral Effect:
- Verapamil
- Nifedipine
- Diltiazem
- Dilazine
Answer: 2. Nifedipine
Question 94. What Isused To Treat White Patches In The Mouth Under The Denture:
- Nystatin
- Triazolem
- Clindamycin
- Tetracycline
Answer: 1. Nystatin
Question 95. LongTerm Steroid Treatment Results In:
- Resorption of bone matrix
- Decreased vitamin D activation
- Decrease calcium loss in urine
- Increase calcium absorption from the gut
Answer: 1. Resorption of bone matrix
Question 96. Absorption Of Oral Iron Preparation Can Be Facilitated By CoAdministration Of:
- Antacids
- Tetracycline
- Phosphates
- Ascorbic acid
Answer: 4. Ascorbic acid
Question 97. In A Patient Of Megaloblastic Anemia, Preferred Line Of The Rapyis:
- Vitamin B12 alone
- Folicacidalone
- Vitamin B12 + folicacid
- Iron supplements
Answer: 3. Vitamin B
Question 98. AntiMicrobial Drug Combinations Are Aimed At Achieving The Following Except:
- Faster and more complete elimination of injecting organism
- Treat injection when the nature and sensitivity of infecting organism are not definite
- Prevent resistance
- Prevent superinfection
Answer: 4. Prevent superinfection
Question 99. The Most Important Reasons For Highly Restricted Use Of PenicillinG Infection In Present-Day Therapeutics Its:
- Narrow spectrum of activity
- Potential to cause hypersensitivity reactions
- The short duration of action
- Neurotoxicity
Answer: 2. Potential to cause hypersensitivity reactions
Question 100. Short Acting Nifedipine Formulations Are Not Recommended Now For The Treatment Of Hypertension Because:
- It tends to increase heart rate and cardiac work
- It involves pronounced reflex sympathetic discharges
- It can impair hemodynamics in patients with diastolic dysfunction
- All of the above
Answer: 2. It involves pronounced reflex sympathetic discharges
Question 101. Antiemetic With Minimum Risk Of Extrapyramidal Symptom Is:
- Metoclopramide
- Domperidone
- Chlorpromazine
- Prochlorperazine
Answer: 2. Domperidone
Question 102. Which Of The Following Is A Prodrug?
- Enalapril
- Clonidine
- Salmeterol
- Acetazolamide
Answer: 1. Enalapril
Question 103. Pinpoint Pupil Suggests Poisoning Of:
- DDT
- Opiates
- Belladonna
- Barbiturates
Answer: 2. Opiates
Question 104. Ondansetron Is A Potent:
- Anxiolytic
- Analgesic
- Antidepressant
- Antiemetic
Answer: 4. Antiemetic
Question 105. Astringents Are Substances That:
- Irritate sensory nerve endings
- Precipitate proteins
- Penetrate target cell nucleus
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Precipitate proteins
Question 106. Ethosuximide Is Used In:
- Tonic-clonic seizures
- Myoclonic seizures
- Simple partial seizures
- Absence seizures
Answer: 4. Absence seizures
Question 107. Treatment Of DrugInduced Parkinsonism Is:
- Levodopa
- Bromocriptine
- Anticholinergic
- Selective
Answer: 3. Anticholinergic
Question 108. All Of The Following Are Narrow Spectrum Drugs Except:
- Penicillin G
- Streptomycin
- Erythromycin
- Chloramphenicol
Answer: 4. Chloramphenicol
Question 109. Corticosteroid Therapy Can Aggrevate The Following Disorders Except:
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Peptic ulcer
Answer: 1. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Question 110. Superinfections Are More Common With:
- Use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics
- Short course antibiotics
- Use of antibiotics that are completely absorbed from the small intestines
- Use antibiotic combinations covering both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
Answer: 3. Use of antibiotics that are completely absorbed from the small intestines
Question 111. Which Of The Following Drug Interferes With DNA Synthesis?
- Rifampicin
- Idoxuridine
- Norfloxacin
- Chloramphenicol
Answer: 2. Idoxuridine
Question 112. The Drug Of Choice For Treating Insulin Overdose Is:
- 20% IV glucose
- Adrenaline
- Glucagon
- Betamethasone
Answer: 1. 20% IV glucose
Question 113. Which Of The Following Drug Acts Directly On Blood Vessels:
- Hydralazine
- X-methyldopa
- Captopril
- Propranolol
Answer: 1. Hydralazine
Question 114. The Combination Of Amoxycillin And Clavulanic Acid Is Used Because:
- It broadens the spectrum of amoxicillin
- It decreases the side effects of amoxicillin
- It decreases the toxicity of clavulanic acid
- It increases the oral bioavailability of amoxicillin
Answer: 1. It broadens the spectrum of amoxicillin
Question 115. The Drug Of Choice In Cardiogenic Shock Is:
- Dopamine
- Propranolol
- Dobutamine
- Adrenaline
Answer: 1. Dopamine
Question 116. Stress Increases All Hormone Levels Except:
- ACTH
- Noradrenaline
- Insulin
- Glucagon
Answer: 4. Glucagon
Question 117. Patients Taking Warfarin Should Not Be Given:
- Paracetamol
- Aspirin
- Codeine
- Epinephrine
Answer: 2. Aspirin
Question 118. Example Of Second Generation Antihistamine:
- Cyclizine
- Diphenhydramine
- Astemizole
- Cyproheptadine
Answer: 3. Astemizole
Question 119. Oral Hypoglycemic Agent Most Likely To Be Prescribed For Patients With Refractory Obesity:
- Chlorpropamide
- Glyburide
- Metformin
- Tolbutamide
Answer: 3. Metformin
Question 120. H2 Blocker Most Likely To Inhibit P450 Drug Metabolizing System:
- Ranitidine
- Cimetidine
- Famotidine
- Nizatidine
Answer: 2. Cimetidine
Question 121. Toxicity Associated With Thiazide Diuretics:
- Hyperkalemic states
- Hypouricemia
- Hypolipidemia
- Hyponatremia
Answer: 4. Hyponatremia
Question 122. Drug Of First Choice For Absence Seizures:
- Primidone
- Ethosuximide
- Phenytoin
- Diazepam
Answer: 2. Ethosuximide
Question 123. Antipsychotic Drug With Leas Textrapyramidal Toxicity:
- Fluphenazine
- Haloperidol
- Clozapine
- Chlorpromazine
Answer: 3. Clozapine
Question 124. Not Classified As A Type Lantiarrhythmic:
- Lidocaine
- Quinidine
- Adenosine
- Encainide
Answer: 3. Adenosine
Question 125. Drugs Activating This Receptor Are Used In Treating Asthma:
- Beta1adrenergic
- Muscarinic
- Beta 2 adrenergic
- Nicotinic
Answer: 3. Beta 2 adrenergic
Question 126. In Organophosphate Poisoning, This Agent May Be Capable Of ReActivating Inhibited Acetylcholinesterase:
- Atropine
- Pilocarpine
- Mecamylamine
- 2-PAM
Answer: 4. 2-PAM
Question 127. Fluoroquinolone, Which Is More Active Against Gram+Ve Organisms Is:
- Norfloxacin
- Moxifloxacin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Ofloxacin
Answer: 2. Moxifloxacin
Question 128. Captopril Is Not A Preferred Ace Inhibitor In The Treatment Of Hypertension Because of It:
- Produces tolerance
- Can cause arrhythmias
- Produces cough
- Is not well absorbed orally
Answer: 3. Produces cough
Question 129. Fortified Procaine Penicillin has the advantage of:
- Quick on-set and long action
- Quick on a set and short action
- Less anaphylactic shock
- Being available as an infusion
Answer: 1. Quick on-set and long action
Question 130. Low-dose aspirin is used as prophylaxis management of angina due to its:
- Anticoagulation
- Analgesic action
- Antiplatelet action
- Fibrinolytic action
Answer: 3. Antiplatelet action
Question 131. Furosemide Produces Diuresis By Acting On The:
- Loop of Henle
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Collecting duct
- Blood vessels in the glomerulus
Answer: 1. Loop of Henle
Question 132. Prophylaxis with antimicrobials is best when used:
- From 7 days prior to surgery
- Perioperatively
- 7 days before to 7 days after surgery
- In low doses
Answer: 2. Perioperatively
Question 133. Insulin Induced Lipodystrophy Can Be Reduced By:
- Givinglowdoses
- Changing sites of injections
- Using Ivy daily
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Changing sites of injections
Question 134. The Antimicrobial Safe In Pregnancy Is:
- Ciprofloxacin
- Gentamycin
- Erythromycin
- Doxycycline
Answer: 3. Erythromycin
Question 135. Deficiency Of Vitamin D Will Cause:
- Decreased calcium absorption from the gut
- Increased PTH release
- Increased resorption of bones
- All of the above
- None of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 136. The Drug Of Choice For Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis Is:
- Macrolide
- Tetracycline
- Fluoroquinolone
- Cephalosporin
Answer: 1. Macrolide
Question 137. Flumazenil Is:
- Opiateant agonist
- Opiate agonist
- Antianginal drug
- Diazepamant agonist
Answer: 4. Diazepamant agonist
Question 138. All Of The Following Are Cardioselective Beta Blocker Except:
- Esmolol
- Atenolol
- Propranolol
- Celiprolol
Answer: 3. Propranolol
Question 139. Not Classified As An H2 Receptor Blocker:
- Famotidine
- Terfenadine
- Nizatidine
- Cimetidine
Answer: 2. Terfenadine
Question 140. Example Of Second Generation Antihistamine:
- Cyclizine
- Diphenhydramine
- Astemizole
- Cyproheptadine
Answer: 4. Cyproheptadine
Question 141. Long-Acting Glucocorticoids:
- Cortisone
- Fluprednisolone
- Triamcinolone
- Betamethasone
Answer: 4. Betamethasone
Question 142. Drug Of First Choice For Absence Seizures:
- Primidone
- Ethosuximide
- Phenytoin
- Diazepam
Answer: 2. Ethosuximide
Question 143. Anti-Parkinson Drug That Probably Acts By Direct Dopamine Receptor Stimulation:
- Benztropine
- Selegiline
- Bromocriptine
- Amantadine
Answer: 3. Bromocriptine
Question 144. An Example Of A Typical Antipsychotic Agent:
- Thioridazine
- Thiothixene
- Risperidone
- Chlorpromazine
Answer: 1. Thioridazine
Question 145. Narcotic Agonists—Most Serious Adverse Effects:
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Respiratory depression
- Convulsions
- Endogenous depression
Answer: 2. Respiratory depression
Question 146. Ototoxicity And Nephrotoxicity Associated With This Antibiotic:
- Cefotaxime
- Amikacin
- Aztreonam
- Ceftriaxone
Answer: 2. Amikacin
Question 147. The Drug Which Is Used To Treat Both Tuberculosis And Leprosyis:
- Isoniazid
- Clofazimine
- Rifampicin
- Dapsone
Answer: 3. Rifampicin
Question 148. For Prophylaxis Of Angina, All These Drugs Can Be Used Except:
- Isosorbide dinitrate
- Propranolol
- Aspirin
- Sodium nitroprusside
Answer: 2. Propranolol
Question 149. Grey Baby Syndrome Can Occur With:
- Tetracycline
- Chloramphenicol
- Anticancer drugs
- Streptomycin
Answer: 2. Chloramphenicol
Question 150. Calcium Is Needed By The Body For All These Actions Except:
- Impulse generation in heart and nerves
- Coagulation of blood
- Hydration of the skin
- Formation of bones and teeth
Answer: 3. Hydration of the skin
Question 151. While A Patient Is On Chronic Corticosteroid Treatment, We Should Monitor:
- Blood glucose levels
- Blood pressure
- Weight
- None of the above
- All of the above
Answer: 5. All of the above
Question 152. Ciprofloxacin Is Active Against:
- Gram+ve organisms only
- Gram–veo organisms only
- Both gram+ve and gram–ve organisms
- Atypical organisms only
Answer: 3. Both gram+ve and gram–ve organisms
Question 153. Parenteral Iron Is Usually Indicated In:
- Megaloblastic anemia
- Severe iron deficiency with chronic bleeding
- Prophylaxis in pregnant women
- Growing children
Answer: 2. Severe iron deficiency with chronic bleeding
Question 154. Radioactive Iodine(I131) Can Produce:
- Vomiting due to radiation
- Permanent hypothyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism
- Joint pains
Answer: 2. Permanent hypothyroidism
Question 155. Doxycycline Is Preferred To Other Tetracyclines Because:
- It is long-acting
- It is safe during pregnancy
- It does not affect teeth and bones in small children
- All of the above
Answer: 1. It is long-acting
Question 156. Oropharyngeal Candidiasis Can Be Treated By:
- Nystatin
- Clotrimazole
- Fluconazole
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 157. All Of The Following Are Cardio Selective Beta Blockers Except:
- Atenolol
- Esmolol
- Bisoprolol
- Celiprolol
Answer: 3. Bisoprolol
Question 158. Drug Of Choice For Status Epilepticus:
- Ethosuximide
- Diazepam
- Primidone
- Valproate
Answer: 2. Diazepam
Question 159. Drug Of Choice For Atropine Poisoning:
- Neostigmine
- Pilocarpine
- Physostigmine
- Adrenaline
Answer: 3. Physostigmine
Question 160. Antipsychotic Drug With Least Extrapyramidal Toxicity:
- Clozapine
- Haloperidol
- Chlorpromazine
- Fluphenazine
Answer: 1. Clozapine
Question 161. Flumazenil Is:
- Opiateant agonist
- Opiate agonist
- Diazepam antagonist
- Antianginal drug
Answer: 3. Diazepam antagonist
Question 162. All Of The Following Can Be Used In Peptic Ulcer Except:
- Aspirin
- Metronidazole
- Cimetidine
- Prostaglandin
Answer: 1. Aspirin
Question 163. Very High Dose Of Paracetamol Can Produce:
- Bronchial asthma
- Hepatic damage
- Peptic ulcer
- Kidney damage
Answer: 2. Hepatic damage
Question 164. Gingival Hyperplasia Is Adverse Effct Of:
- Metronidazole
- Phenytoin
- Chlorhexidine
- Aspirin
Answer: 2. Phenytoin
Question 165. Xerostomia Can Be Produced By:
- Anticholinergic drugs
- Antipsychotic drugs
- Antihistaminics
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 166. Vitamin K Is an Antidote To:
- Heparin
- Warfarin
- Lepirudin
- Streptokinase
Answer: 2. Warfarin
Question 167. Captopril Is Not A Preferred Ace Inhibitor In The Treatment Of Hypertension Because of It:
- Produces tolerance
- Can cause arrhythmias
- Produces cough
- Is not well absorbed orally
Answer: 3. Produces cough
Question 168. Low Dose Aspirin Is Used As Prophylaxis In the Management Of Angina Due To Its:
- Anticoagulant action
- Analgesic action
- Antiplatelet action
- Fibrinolytic action
Answer: 3. Antiplatelet action
Question 169. The Drug Of Choice For Treating Insulin Over Dosage Is:
- 20% IV glucose
- Adrenaline
- Glucagon
- Betamethasone
Answer: 3. Glucagon
Question 170. Deficiency Of Vitamin D Will Cause:
- Decreased calcium absorption from the gut
- Increased resorption of bones
- Increased PTH release
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 171. The Combination Of Amoxicillin And Clavulanic Acid Is Used Because:
- It broadens the spectrum of amoxicillin
- It decreases the side effects of amoxicillin
- It decreases the toxicity of clavulanic acid
- It increases the oral bioavailability of amoxicillin
Answer: 1. It broadens the spectrum of amoxicillin
Question 172. Stress Increases All Hormone Levels Except:
- ACTH
- Noradrenaline
- Insulin
- Glucagon
Answer: 3. Insulin
Question 173. Select The Macrolide Having Clinically Useful Antileprotic Activity:
- Azithromycin
- Clarithromycin
- Erythromycin
- Roxithromycin
Answer: 2. Clarithromycin
Question 174. All Of The Following Are Narrow Spectrum Drugs Except:
- Penicillin G
- Streptomycin
- Erythromycin
- Chloramphenicol
Answer: 4. Chloramphenicol
Question 175. The Side Effect Which Primarily Limits the Acceptability Of Oral Iron Therapy Is:
- Epigastric pain and bowel upset
- Black stools
- Staining of teeth
- Metallic taste
Answer: 1. Epigastric pain and bowel upset
Question 176. The Following Can Be Used To Antagonize The Action Of Heparin In Case Of Overdose:
- Heparin sulfate
- Dextransulphate
- Protamine sulfate
- Ancrod
Answer: 3. Protamine sulfate
Question 177. Drug Contraindicated In Patient Of Peptic Ulcer Are:
- Aspirin
- Paracetamol
- Misoprostol
- Sucralfate
Answer: 1. Aspirin
Question 178. Shortest Acting Muscle Relaxant Is:
- Pancuronium
- Doxacurium
- Tubocuraxine
- Succinylcholine
Answer: 4. Succinylcholine
Question 179. Antihistamine With Maximum Risk Of Sedation Is:
- Fexofenadine
- Cetrizine
- Diphenhydramine
- Loratidine
Answer: 3. Diphenhydramine
Question 180. Drug Of Choice For Status Epilepticus:
- Ethosuximide
- Primidone
- Valproate
- Diazepam
Answer: 4. Diazepam
Question 181. Vitamin K Is an Antidote To:
- Heparin
- Warfarin
- Streptokinase
- Lipindin
Answer: 2. Warfarin
Question 182. ΒBlockers Can Be Used In All Except:
- Hypertension
- Angina
- Arrhythmia
- Bradycardia
Answer: 2. Angina
Question 183. All Can Be Used In Acute Bronchial Asthma Except:
- Salbutamol
- Ipratropium
- Cromolyn sodium
- Corticosteroids
Answer: 3. Cromolyn sodium
Question 184. H2 Blocker Most Likely To Inhibit P450 Drug Metabolizing System:
- Ranitidine
- Cimetidine
- Famotidine
- Nizatidine
Answer: 2. Cimetidine
Question 185. Long-Acting Glucocorticoids:
- Cortisone
- Prednisolone
- Triamcinolone
- Betamethasone
Answer: 4. Betamethasone
Question 186. Water Soluble Vitamin is:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin K
Answer: 2. Vitamin B
Question 187. Low Dose Aspirin Is Used As Prophylaxis In the Management Of Angina Due To Its:
- Anti-coagulant action
- Anti-platelet action
- Analgesic action
- Fibrinolytic action
Answer: 2. Anti-platelet action
Question 188. Insulin Induced Lipodystrophy Can Be Reduced By:
- Giving low dosages
- Changing sites of injections
- Using IV daily
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Changing sites of injections
Question 189. Corticosteroid Therapy May Aggravate The Following Disorders Except:
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Peptic ulcer
Answer: 1. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Question 190. Which Of The Following Drug Interferes With Dna Synthesis?
- Rifampicin
- Idoxuridine
- Norfloxacin
- Chloramphenicol
Answer: 2. Idoxuridine
Question 191. Which Of The Following Drugs Act Directly On The Blood Vessels?
- Hydralazine
- Methyldopa
- Captopril
- Propanolol
Answer: 1. Hydralazine
Question 192. The Drug Of Choice In Cardiogenic Shock Is:
- Dopamine
- Propranolol
- Dobutamine
- Adrenaline
Answer: 1. Dopamine
Question 193. Patients Taking Warfarin Should Not Be Given:
- Paracetamol
- Aspirin
- Codeine
- Epinephrine
Answer: 2. Aspirin
Question 194. Loss Of Taste Sensation Can Be A Side Effect Of The Following Antihypertensive:
- Clonidine
- Captopril
- Verapamil
- Prasocin
Answer: 2. Captopril
Question 195. Digoxin Inhibits The Enzyme:
- Acelylase
- Na+ ATPase
- Na+K + ATPase
- Phosphodiesterase
Answer: 3. Na+K + ATPase
Question 196. All Of The Following Have a Role In Calcium Metabolism Except:
- Parathormone
- Thyroxin
- Calcitonin
- Vitamin D
Answer: 2. Thyroxin
Question 197. Half-Life Of A Drug May Be Helpful To Determine:
- Dosage schedule of a drug
- Level of absorption
- Distribution into different body systems
- Time to get the steady state
Answer: 4. Time to get the steady state
Question 198. A 3YearOld Child Has Been Admitted To Emergency With Suspicious Of Atropine Overdose As There Are:
- Abdominal
- Increase gastric secretion
- Increased cardiac rate
- Pupillary constriction
Answer: 3. Increased cardiac rate
Question 199. Epinephrine Does Not Causes Increased Concentration Of:
- Glucose in the blood
- Lactate in the blood
- Free fatty acids in the blood
- Triglycerides in fat cells
Answer: 4. Triglycerides in fat cells
Question 200. A Young Man Of 24 Years Age Is Suffering From Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Which Drug Is Preferred For His Problem:
- Zolpidem
- Buspirone
- Midazolam
- Triazolam
Answer: 2. Buspirone
Question 201. Which One Of The Following Antiseizure Drugs Can Cause Coarsening Of Facial Features, Hirsuitism, Gingival Features, or Gingival Hyperplasia?
- Valproic acid
- Carbamazepine
- Ethosuximide
- Phenytoin
Answer: 4. Phenytoin
Question 202. Only Aspirin Can:
- Reduce fever
- Irreversibly inhibit its target enzyme
- Prevents episodes of gouty arthritis
- Reduce the risk of colon cancer
Answer: 2. Irreversibly inhibit its target enzyme
Question 203. Which Of The Following Drug Isused In The Treatment Of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
- Naproxen
- Allopurinol
- Colchicine
- Sulfinpyrazone
Answer: 1. Naproxen
Question 204. Morphine Should Be Used In Caution In All Of The Following Except:
- Biliary tract surgery
- Pulmonary edema
- Last stage of labor
- Hypothyroidism
Answer: 2. Pulmonary edema
Question 205. A 35YearOld Patient Complaining Of Severe Pain Along The Right Side Of Jaw And Face, The Best Choice Of This Neuralgic Pain Is:
- Methadone
- Ibuprofen
- Carbamazepine
- Lorazepam
Answer: 3. Carbamazepine
Question 206. Which Of The Following Local Anesthetic Is Used Exclusively For Its Good Surface Anesthetic Activity And Low Toxic Potential?
- Cocaine
- Benzocaine
- Bupivacaine
- Procaine
Answer: 2. Benzocaine
Question 207. Which Of The Following Inhalational Anesthetic Agents Is Having the Fastest Onset Of Action?
- Nitric oxide
- Isoflurane
- Nitrous oxide
- Enflurane
Answer: 3. Nitrous oxide
Question 208. Cephalosporins Show Their AntiMicrobial Action By:
- Binding to cytoplasmic receptor proteins
- Inhibition of β lactamases
- Inhibition of transpeptidation reactions
- Interference with the synthesis of ergosterol
Answer: 3. Inhibition of transpeptidation reactions
Question 209. The Most Appropriate Drug Regimen For Empiric Treatment Of Gram Negative Bacilli In Bloodis:
- Ampicillin+Sulbactam
- Aztreonam
- Cefazolin
- Imipenem+Cilastatin
Answer: 2. Aztreonam
Question 210. Doxycycline Is:
- Bactericidal
- Not excreted in feces
- Having a short elimination half-life
- Not as effective as tetracycline against H.pylori
Answer: 4. Not as effective as tetracycline against H.pylori
Question 211. Which Of The Following Is Useful For Genital Herpes Infection?
- Acyclovir
- Amantadine
- Ritonavir
- Trifluridine
Answer: 1. Acyclovir
Question 212. A Young Girl Of 20 Years Of Age, Has Taken A Suicidal Overdose Of Digoxin. The Drug Of Choice For Her Treatments:
- Lidocaine
- Phenytoin
- Digoxinantibodies
- Potassium chloride
Answer: 3. Digoxinantibodies
Question 213. A 30 Years Old Male Suffering From Cerebral Edema, Will Be Treated With:
- Furosemide
- Amiloride
- Ethacrynic acid
- Mannitol
Answer: 4. Mannitol
Question 214. Which Of The Following Is A Mast Cell Stabilizer?
- Ipratropium
- Prednisone
- Terbutaline
- Cromolyn sodium
Answer: 4. Cromolyn sodium
Question 215. Which Of The Following Statement Is Least Related To Chlorhexidine 0.2%?
- Usefulinreducingplaqueformation
- Stainingofteeth
- Increasedformationofcalculi
- Noteffctiveingingivitis
Answer: 4. Noteffctiveingingivitis
Question 216. Which Of The Following Attributes Is Rarely Seen With Azadhirachta Indica (Neem)?
- Can be used in toothpaste
- Shows antimicrobial activity
- Has mild abrasive effects
- Cannot inhibit plaque formation
Answer: 4. Cannot inhibit plaque formation
Question 217. Which Of The Following Is A Selective COX2 Inhibitor:
- Indomethacin
- Aspirin
- Etoricoxib
- Paracetamol
Answer: 3. Etoricoxib
Question 218. Which Antibiotic Is Suitable For Anaerobic Infections:
- Ampicillin
- Metronidazole
- Streptomycin
- Vancomycin
Answer: 2. Metronidazole
Question 219. ΒBlockers Are Used In All Conditions Except:
- Hypertension
- Asthma
- Angina
- Heart failure
Answer: 2. Asthma
Question 220. Which Drug Is Not Used For Helicobacter Pyroli Infection?
- Clarithromycin
- Amoxycillin
- Metronidazole
- Gentamycin
Answer: 4. Gentamycin
Question 221. Drug Of Choice For Treatment Of Myasthenia Gravis:
- Neostigmine
- Physostigmine
- Rivastigmine
- Donepezil
Answer: 2. Physostigmine
Question 222. The Most Common Adverse Effct Of Salbutamol Is:
- Hyperglycemia
- Tremors
- Raynaud’seffct
- Hypertension
Answer: 2. Tremors
Question 223. Antidiabetic Drug Not Producing Hypoglycemia Is:
- Metformin
- Insulin
- Glyburide
- Glimepiride
Answer: 1. Metformin
Question 224. Antithyroid Drug Such As Propylthiouracil Inhibits:
- 5 α reductase
- Xanthine oxidase
- Thyroidper oxidase
- Cyclooxygenase
Answer: 3. Thyroidper oxidase
Question 225. One Of The Following Is K+Sparing Diuretic:
- Furosemide
- Spironolactone
- Acetazolamide
- Mannitol
Answer: 2. Spironolactone
Question 226. The Drug Of Choice For the Treatment Of Organophosphorus Poisoning Is:
- Propranolol
- Prazosin
- Finasteride
- Atropine
Answer: 4. Atropine
Question 227. Drug Of Choice For Treatment Of Gonorrhea Is:
- Ampicillin
- Cloxacillin
- Ceftriaxone
- Ofloxacin
Answer: 3. Ceftriaxone
Question 228. Antiemetic Drug Having D2 Receptor Blocking Action Is:
- Domperidone
- Ondansetron
- Cisapride
- Proguanil
Answer: 1. Domperidone
Question 229. Ovulation Inducing Agent Is:
- Estrogen
- Raloxifene
- Clomiphene
- Tamoxifen
Answer: 3. Clomiphene
Question 230. Which Drug Is Preferred For Treatment Of Exertional Angina?
- Diltiazem
- Nifedipine
- Amlodipine
- Nimodipine
Answer: 1. Diltiazem
Question 231. Drugs Used To Treat Peptic Ulcer Is All Except:
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Ranitidine
- Omeprazole
- Sucralfate
Answer: 1. Sodium bicarbonate
Question 232. Common Local Anesthetic Used In Dental Practice:
- Procaine
- Lignocaine
- Bupivacaine
- Cocaine
Answer: 2. Lignocaine
Question 233. Cell Wall Active Drugs Are All Except:
- Penicillin
- Cephalosporin
- Erythromycin
- Vancomycin
Answer: 3. Erythromycin
Question 234. Before Dental Procedure To Avoid Bacterial Endocarditis In Patients Having Valve Prosthesis, Which Drug Is Preferred:
- Penicillin G
- Streptomycin
- Metronidazole
- Tetracycline
Answer: 2. Streptomycin
Question 235. Commonly Used Antiplaque Mouthwash Antiseptic Is:
- Chloroxylenol
- Chlorhexidine
- KMnO4
- Boric acid
Answer: 2. Chlorhexidine
Question 236. For Radical Cure Of P.Vivex Malaria, Which Drug Is Used:
- Chloroquine
- Mefloquine
- Primaquine
- Halofantrine
Answer: 1. Chloroquine
Question 237. The Active Form Of Vitamin D3 Is:
- 1α (OH) D3
- Calcitriol
- 25 (OH) vitamin D3
- Calcipotriene
Answer: 2. Calcitriol
Question 238. Which Of The Following Is Not A Mechanism Of Action Of ΒLactam?
- Inhibits transpeptidase enzyme
- Inhibits PBPs which inhibit autolysis
- Inhibits beta lactamase
- Inhibits cell wall synthesis
Answer: 2. Inhibits PBPs which inhibit autolysis
Question 239. Gum Hyperplasia Is An Adr With One Of The Following:
- Phenytoin
- Isotretinoin
- CCBs
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 240. Which Of The Following Is The Safest Analgesic For Use In Pregnant Women?
- Aspirin
- Indomethacin
- Paracetamol
- Tramadol
Answer: 3. Paracetamol
Question 241. Partial Agonist Stabilizes The Following Conformation Form As A Result Of Drug Receptor Interaction:
- DR
- DR
- DR and DR both
- AR
Answer: 1. DR
Question 242. Among Adrs Which Ones Have More Morbidity And Mortality?
- Chronic cumulative Type C
- Carcinogenicity and mutagenicity Type D
- Bizarre or idiosyncratic ones Type B
- Withdrawal reactions
Answer: 3. Bizarre or idiosyncratic ones Type B
Question 243. Which Of The Following Is Second Generation Prokinetic?
- Metoclopramide
- Cisapride
- Domperidone
- Itopride
Answer: 3. Domperidone
Question 244. A Spirin Should Be Stopped………………, Prior to Elective Dental Surgery:
- 1 to 2 days
- 3 to 4 days
- 5 to 6 days
- 7 to 8 days
Answer: 4. 7 to 8 days
Question 245. The Order Of Nerve Function Blockade Obtained With Local Anesthetics Is As Follows:
- Sym>pain>motor
- Pain>sym>motor
- Motor>sym>pain
- Sym>motor>pain
Answer: 1. Sym>pain>motor
Question 246. Which Of The Following Is A NSAID With a Long Duration Of Action?
- Aspirin
- Paracetamol
- Diclofenac
- Ibuprofen
Answer: 3. Diclofenac
Question 247. In First Order Kinetics, A Constant………………….., Is Excreted Per Unit Time:
- Amount
- Fraction
- Concentration
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Fraction
Question 248. Which One Of The Following Is The Drug Of Choice For the Treatment Of Oral Candidias?
- Pilocarpine
- Nystatin
- amphotericin B
- Tranexamic acid
Answer: 2. Nystatin
Question 249. Which Therapeutic Modality Is Most Important For Treatment Of Acute Diarrhea?
- Oral rehydration solution
- Norfloxacin
- Metronidazole
- Norflxacin and metronidazole
Answer: 1. Oral rehydration solution
Question 250. Drug of choice for treatment of dry cough:
- Codeine
- Noscapine
- Dextromethorphan
- Ambroxol
Answer: 1. Codeine
Question 251. All Of The Following Drugs May Lead To Hyperprolactinemia Except:
- Metoclopramide
- Haloperidol
- Domperidone
- Furosemide
Answer: 2. Haloperidol
Question 252. Drugs Which Should Be Given With In 6 Hours Of Myocardial Infarction Are All Of The Above Except:
- Aspirin
- Streptokinase
- Statins
- Diltiazem
Answer: 3. Statins
Question 253. Which Of The Following Is Not A Skeletal Muscle Relaxant?
- Succinylcholine
- Benzodiazepine
- Glycopyrrolate
- Botulinum toxin
Answer: 3. Glycopyrrolate
Question 254. Which One of the Following Is Not Preferred For Long-Term Prophylaxis Against Bronchial Asthma?
- Prednisone
- Beclomethasone
- Triamcinolone
- Budesonide
Answer: 1. Prednisone
Question 255. The Drug Of Choice For the Treatment Of Anaphylactic Shock Is:
- Oral dexamethasone
- Noradrenaline
- Dopamine
- Adrenaline
Answer: 4. Adrenaline
Question 256. Which Of The Following Is a Safe Sthypnotic Agent?
- Phenobarbitone
- Zolpidem
- Diazepam
- Lorazepam
Answer: 2. Zolpidem
Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. The antidote of iron………………………
Answer: Desferrioxamine
Question 2. Adverse effects of theophylline……………………..
Answer: Nausea and Vomiting, Convulsions, tremors, high blood sugar
Question 3. Dietary Fiber ……………………
Answer: Bran, Psyllium, Ispaghula, Methycellulary
Question 4. Antithyroid drugs ……………………….
Answer: Carbimazole, Methimazole, Propylthiouracil
Question 5. Calcitonin ………………………………………………….
Answer: Produced by parafollicular cells of the thyroid and reduces blood calcium level.
Question 6. Drugs for obese Type II diabetes mellitus ……….
Answer: Oral Hypoglycemics
Question 7. Selective COX2 inhibitors ………………….
Answer: Celecoxib, Rafecoxib, Valdecoxib, Etoricoxib
Question 8. Peripheral Skeletal Muscle Relaxants ……………
Answer: Succinylcholine
Question 9. Antiplatelet drugs………………………………………
Answer: Aspirin, Clopidogrel
Question 10. Vinblastin………………………………………………….
Answer: It is an antimicrotubule drug that treats certain kinds of cancer such as Hodgkin’s lymphoma, breast cancer, and testicular carcinoma
Question 11. Drug of choice in typhoid fever……………….
Answer: Ciprofloxacin
Question 12. The antagonist of heparin……………………….
Answer: Protamine sulfate
Question 13. A drug used by sublingual route……………………..
Answer: Nitroglycerine
Question 14. Drug for insomnia……………………….
Answer: Zolpidem
Question 15. An antiinflmmatory agent ………………………..
Answer: It refers to the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation, For Example. Analgesic
Question 16. Morphine Antagonist………………………
Answer: Naloxone and Naltrexone
Question 17. Any purgative used for constipation………………
Answer: Caster Oil
Question 18. Any oral hypoglycemic agent……………………..
Answer: Phenformin
Question 19. Night Blindness……………………………
Answer: Deficiency of Vitamin A
Question 20. Antacid ………………
Answer: An agent that neutralizes acidity.
Question 21. Proton Pump Inhibitor …………………….
Answer: Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole
Question 22. Drug for leprosy …………………………….
Answer: Dapsone, Clofazimine, Rifampin, Ethionamide
Question 23. Prokinetic drug……………………………….
Answer: Metoclopramide, Domperidone, Cisapride
Question 24. Central Sympatholytics …………………………….
Answer: Clonidine, Methyldopa
Question 25. Drugs for vertigo ………………………………..
Answer: Labyrinthine suppressants, vasodilators, diuretics, corticosteroids
Question 26. Drug for choice in acute gingivitis ………………….
Answer: Metronidazole and Penicillin
Question 27. Drugs for acute abdominal pain …………………..
Answer: Butylscopolamine, Acetaminophen, NSAIDs
Question 28. Drug for headache ……………………………
Answer: Ketorolac, Aspirin, Indomethacin, and Naproxen
Question 29. The antagonist of streptokinase ………………….
Answer: Epsilon amino-caproic acid (EACA)
Question 30. Analgesic and antipyretic devoid of antiinflmmatory activity (name of drug) …………………………………
Answer: Paracetamol
Question 31. Newer antihistaminics ……………………….
Answer: Fexofenadine, Loratidine, Desloratadine, Cetrizine, Levocetirizine, Azelastein, Mizolastine, Ebastine, Rupatadine
Question 32. Two indications of atropine injection ………………….
Answer:
- Preanesthetic medication
- Antispasmodic
Question 33. Two reasons for combining adrenaline with lignocaine……………………………
Answer:
- It prolongs the duration of action of local anesthetics by decreasing their rate of removal from the site into the systemic circulation.
- It increases the intensity of nerve block.
Question 34. Two indications of enalapril………………….
Answer:
- In hypertension
- In postmyocardial infarction
Question 35. Two differences between aspirin and paracetamol…….
Answer:
- Paracetamol does not affect acid-base balance while aspirin affects acid-base balance.
- Paracetamol is safer in asthmatics while aspirin precipitate asthma in sensitive individuals.
Question 36. Two longtermsideeffctsofcorticosteroids…………….
Answer:
- Delayed healing of the wound.
- Increase susceptibility to infection
Question 37. Two indications of saline cathartics………………..
Answer:
- To relieve acute constipation
- To ease defecation in patients with painful hemorrhoids or other rectal disorders and to avoid excessive straining and concurrent increase in abdominal pressure in patients with hernias
Question 38. Most appropriate drug for diabetic ketoacidosis …………………….
Answer: Insulin
Question 39. Most appropriate drug for anaphylactic shock …………….
Answer: Adrenaline hydrochloride
Question 40. Most appropriate drug for angina pectoris ……………………
Answer: Glyceryl Trinitrate
Question 41. Drugs for severe pain of acute myocardial infarction……………..
Answer: Morphine, pethidine
Question 42. Drugs for benign prostrate hypertrophy…………………..
Answer: Terazosin, Doxazosin, Tamsulosin, Finasteride
Question 43. Intravenous general anesthetics…………………….
Answer: Thipentone sodium, Propofol, Methohexitone sodium, propofol, and etomidate
Question 44. Drugs used as mydriatics…………………….
Answer: Cyclopentolate, tropicamide
Question 45. Persistent depolarizers…………………….
Answer: Succinylcholine
Question 46. Vitamin E …………………….
Answer: It is used as an antioxidant and anti-sterility factor.
Question 47. BAL …………………….
Answer: Full form is British Anti-L website. It is a chelating agent.
Question 48. Leukoterine Antagonist
Answer: Zileuton, zafilukast, montelukast, pranlukast and iralu-kast
Question 49. Contraindications of morphine.
Answer: Morphine is contraindicated in hypotension, hepatic damage, prostate hypertrophy, head injury, and hypothyroidism.
Question 50. Drugs for severe pain of acute myocardial infarction.
Answer: IV morphine and cyclizine
Question 51. Drugs for benign prostrate hypertrophy.
Answer: α1 adrenergic blockers, i.e. prazosin, 5-α reductase in-inhibitor, i.e. Finasteride.
Question 52. Drugs are used as mydriatics.
Answer: Homatropine, cyclopentolate, tropicamide.
Question 53. Drugs used for acute abdominal pain.
Answer: Butylscopolamine, Acetaminophen, NSAIDs
Question 54. Drugs used as miotics.
Answer: Pilocarpine and anticholinergic drugs
Question 55. Drugs for cardiogenic shock.
Answer: Dopamine and dobutamine
Question 56. Drugs used as surface anesthetics.
Answer: Soluble: Cocaine, Lignocaine, tetracaine, benoxinate Insoluble: Benzocaine and butyl aminobenzoate
Question 57. Drugs for insomnia.
Answer: Hypnotics or Benzodiazepines
Question 58. Newer antihistaminics.
Answer: Fexofenadine, Loratidine, Desloratadine, Cetrizine, Levocetirizine, Azelastein, Mizolastine, Ebastine, Rupatadine
Question 59. Drugs for anaphylactic shock.
Answer: Adrenaline, Hydrocortisone, Pheniramine, and Intravenous fluids
Question 60. Which drug is given to a patient suffering from an acute attack of angina? Write the preferred route of administration…………………..
Answer: Nitroglycerine sublingually.
Question 61. Write the names of centrally acting cough suppressant drugs………………
Answer:
Opioids: Codeine, pholcodine, morphine, and ethylmorphine
Nonopioids: Noscapine and dextromethorphan
Antihistaminics: Chlorpheniramine, diphenhydramine and promethazine.
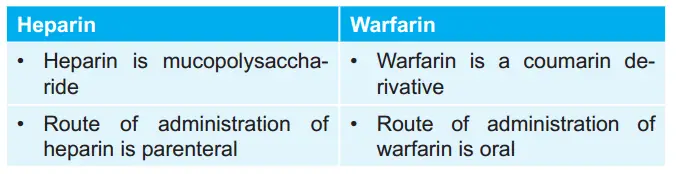
Question 62. Write two important differences between heparin and warfarin.
Answer:
Question 63. Write two important therapeutic uses of adrenaline.
Answer: In anaphylactic shock and in mydriatics.
Question 64. Define adverse drug reactions.
Answer: The term adverse drug reaction has been defined as any noxious effect which is suspected to be due to a drug occurring at doses normally used requiring treatment or a decrease in dose or indicating caution in future use of the same drug.
Question 65. Define the term and give examples: mummifying agents.
Answer: Mummifying agents are used for drying and hardening of tissues of the root canals and pulp to protect it from infection and to maintain aseptic condition, For Example. iodoform, tannic acid, liquid formaldehyde, paraformaldehyde, and cresol.
Question 66. Enlist centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant drug.
Answer:
- Mephenesin group: Mephenesin, carisoprodol, and chlorzoxazone.
- Benzodiazepines: Diazepam and others
- GABA derivatives: Beclofen
- Central Alpha 2 agonist: Tizanidine.
Question 67. Describe the role of fluoride in dental care.
Answer: Hydroxyapatite crystals lead to the hardness of tooth enamel. But the hydroxyapatite crystals are readily dissolved by the action of acids over a period of time.
Fluoride radical is highly reactive, so it exchanges with hydroxyl radical and leads to the formation of fluorapatite.
Fluorapatite is more compact, and harder, and is a less acid-labile substance than hydroxyapatite. This leads to teeth becoming more caries-resistant.
Question 68. Enlist the drugs used in the treatment of vomiting.
Answer:
- Anticholinergics: Hyoscine and dicyclomine
- H1 antihistamines: Promethazine, diphenhydramine, dimenhydrinate, doxylamine cyclizine, meclozine, and cinnarizine
- Neuroleptics: Chlorpromazine, prochlorperazine, haloperidol, etc.
- Prokinetic drugs: Metoclopramide, domperidone, cisapride, mosapride, and tegaserod
- 5HT3 antagonists: Ondansetron, Granisetron
- Adjuvant antiemetics: Cannabinoids, benzodiazepines, dexamethasone.
Question 69. Enlist local anesthetic drugs.
Answer:
- Injectable:
- Low potency and duration: Procaine
- Intermediate potency and duration: Lignocaine and prilocaine
- High potency and long duration: Tetracaine, bupivacaine, ropivacaine, and dibucaine
- Surface anesthetic:
- Soluble: Cocaine, lignocaine, tetracaine, benoxinate
- Insoluble: Benzocaine and butylaminobenzoate.
Question 70. Enumerate styptics.
Answer: Following are the styptics:
- Astringents
- Adrenaline
- Thrombin
- Fibrin glue
- Gelatin
- Collagen
- Calcium alginate
- Oxidized cellulose
- Tranexamic acid
- Hemocoagulase
- Rusell’s viper snake venom.
Question 71. Enumerate anticaries drugs.
Answer: Fluorides
Non-fluoride agents: Xylitol chewing gum, 1:1 mixture of chlorhexidine/thymol varnish, calcium, and phosphate in toothpaste.
Question 72. Enumerate bronchodilators.
Answer:
- Sympathomimetics: Salbutamol, terbutaline, bambuterol, salmeterol, formoterol
- Methylxanthines: Theophylline, aminophylline, and doxophylline
- Anticholinergics: Ipratropium bromide, tiotropium bromide
Question 73. Enumerate diuretics.
Answer:
- Thiazides: Hydrochlorothiazide, chlorthalidone, and indapamide
- High ceiling: Furosemide, bumetanide, and torasemide
- Potassium-sparing: Spironolactone, triamterene, and amiloride.
Question 74. Enumerate 4th-generation cephalosporins.
Answer: Cefepime and cefpirome.
Question 75. Enumerate antifungal agents.
Answer:
1. Antibiotics
- Polyenes: Amphotericin B, Nystatin, Natamycin, Hamycin
- Heterocyclic benzofuran: Griseofulvin
2. Antimetabolite: Flucytosine
3. Azoles
- Imidazoles
- (Topical): Clotrimazole, meconazole, oxiconazole
- (Systemic): Ketoconazole
- Triazoles (Systemic): Fluconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole
4. Allylamine: Terbinafi
5. Other topical agents: Benzoic acid, sodium thiosulphate, butenafine, undecylenic acid, quiniodochlor, and ciclopirox olamine.
Question 76. Enumerate NSAIDs.
Answer: Following are the NSAIDs:
- Non-selective COX inhibitors:
- Salicylates: Aspirin
- Propionic acid derivatives: Ibuprofen, ketoprofen, naproxin
- Anthranilic acid derivative: Mefenamic acid
- Arylacetic acid derivative: Diclofenac, aceclofenac
- Oxicam derivatives: Piroxicam, tenoxicam
- Pyrrolo-pyrrole derivative: Ketorolac
- Indole derivative: Indomethacin
- Pyrazolone derivative: Phenyl butazone, oxyphenbutazone
- Preferential COX-2 inhibitors: Nimesulide, meloxicam, nabumetone
- Selective COX-2 inhibitors: Celecoxib, parecoxib, etoricoxib
- Analgesic. Antipyretic with poor anti-inflammatory action:
- Paraaminophenol derivative: Paracetamol (Acetaminophen)
- Pyrazolone derivatives: Metamizole, propiphenazone
- Benzoxazocine derivative: Nefopam
Question 77. Enumerate Antimalarial drugs.
Answer: Following are the antimalarial drugs:
- 4-aminoquinolines: Chloroquine, amodiaquine, piperaquine
- Quinoline-methanol: Mefloquine
- Cinchona alkaloid: Quinine, quinidine
- Biguanides: Proguanil, chlorproguanil
- Diaminopyrimidines: Pyrimethamine
- 8–aminoquinoline: Primaquine, bulaquine
- Sulphonamides and sulphone: Sulfadoxine, sul-famethopyrazine, dapsone
- Tetracyclines: Tetracycline, doxycycline
- Sesquiterpene lactones: Artesunate, artemether, arteether
- Amino alcohols: Halofantrine, lumefantrine
- Mannich base: Pyronaridine
- Naphthoquinone: Atovaquone.
Question 78. Enumerate Antidepressants.
Answer:
1. Reversible inhibitors of MAO-A: Moclobemide and clorgyline
2. Tricyclic antidepressants:
- NA + 5HT reuptake inhibitors: Imipramine, amitriptyline, Trimipramine, Doxepin, Dothiepin, and Clomipramine
- B-Predominantly NA reuptake inhibitors: Desipramine, Nortriptyline, Amoxapine, and Reboxetine
3. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: Fluoxetine, Fluvoxamine, Paroxetine, Sertraline, Citalopram, Escitalopram.
4. Atypical anti-depressants: Trazodone, Mianserin, Mirtazapine, Venlafaxine, Duloxetine, Tianeptine, Amineptine, Bupropion
Question 79. Drugs used as mitotic.
Answer: Pilocarpine, anticholinergics.
Question 80. Drugs for cardiogenic shock.
Answer: Epinephrine, Norepinephrine, dopamine, dobutamine
Question 81. Drugs used as surface anesthetics.
Answer: Soluble: Cocaine, Lidocaine, Tetracaine Insoluble: Benzocaine, Butylaminobenzoate, Oxethazine
Question 82. Drugs for insomnia.
Answer: Diazepam, Lorazepam
Question 83. Drugs for anaphylactic shock.
Answer: Adrenaline, Hydrocortisone, Pheniramine, and Intravenous fluids
Question 84. Drugs for myasthenia gravis.
Answer:
- Anti-cholinesterases: Neostigmine, pyridostigmine, and ambenonium
- Corticosteroids: Prednisolone
- Immunosuppressive drugs: Cyclosporin, azathioprine
Question 85. Drugs for congestive cardiac failure.
Answer: There are two distinct goals of drug therapy in congestive heart failure:
1. Relief of congestive/low output symptoms and restoration of cardiac performance. Drugs used are:
- Inotropic Drugs: Digoxin, dobutamine and amrinone, milrinone
- Diuretics: Furosemide, Thiazide
- Vasodilators: ACE inhibitors, Angiotensin antagonists, hydralazine, nitrate, nitroprusside
- β blockers: Metoprolol, Bisoprolol, Carvedilol.
2. Arrest/reversal of disease progression and prolongation of survival:
- ACE inhibitors/Angiotensin antagonist
- β blockers
- Aldosterone antagonist: Spirinolactone.
Question 86. Drugs used as tocolytics.
Answer: Tocolytics are also known as uterine relaxants. Drugs used are:
- Adrenergic agonists: Ritodrine
- Calcium channel blockers: Nifedipine
- Oxytocin antagonist, i.e. Atosiban
- Magnesium sulfate
- Miscellaneous drugs: Ethyl alcohol, nitrates, progesterone, general anesthetics, and indomethacin
Question 87. Answer the Cotrimoxazole.
Answer: Fixed dose combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole is known as cotrimoxazole.
Question 88. Answer the Metoclopramide.
Answer: Metoclopramide is a prokinetic drug that is a substituted benzamide
Question 89. Answer the Propranolol.
Answer: Propranolol is a non-selective β adrenergic-blocking drug. The drug does not lead to intrinsic sympathomimetic activity.
Question 90. Answer the Antacids.
Answer: Antacids are the basic substances that neutralize gastric acid and raise the pH of gastric contents. The following are the drugs:
- Systemic antacids: Sodium bicarbonate, sodium citrate
- Nonsystemic antacids: Aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate, magaldrate, calcium carbonate.
Question 91. Answer the Antiemetic drugs.
Answer: Antiemetics are the drugs that suppress vomiting. The following are the drugs:
- Anticholinergics: Hyoscine and dicyclomine
- H1 Antihistaminics: Promethazine, diphenhydramine, dimenhydrinate, doxylamine cyclizine, meclozine, and cinnarizine
- Neuroleptics: Chlorpromazine, prochlorperazine, haloperidol, etc.
- Prokinetic drugs: Metoclopramide, domperidone, cisapride, mosapride, and tegaserod
- 5HT3 Antagonists: Ondansetron, Granisetron
- NK1 receptor antagonists: Aprepitant, Fosaprepitant
- Adjuvant antiemetics: Benzodiazepines, dexamethasone, Dronabinol, Nabilone.
Question 92. Enumerate Antiemetics for cancer therapy.
Answer: Following are the antiemetics for cancer therapy:
- Domperidone
- Metoclopramide
- Granisetron
- Ondansetron
- Aprepitant
- Levomepromazine
- Prochlorperazine
- Cyclizine
- Haloperidol
- Nabilone
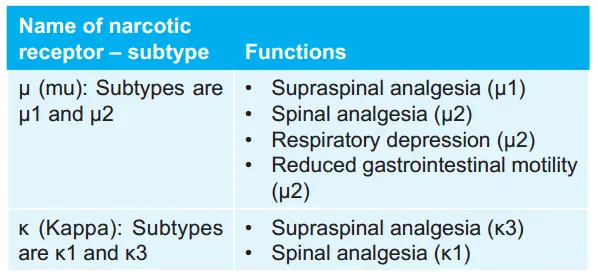
Question 93. Enumerate narcotic receptor—subtypes and functions.
Answer:
Name Two Most Suitable Drugs For Following
Question 1. Pseudomembranous colitis
Answer: Metronidazole and vancomycin
Question 2. Paucibacillary leprosy
Answer: Dapsone and rifampicin
Question 3. Acute gastroenteritis
Answer: Metoclopramide and ondansetron
Question 4. Plasmodium vivax malaria
Answer: Primaquine, chloroquine
Question 5. Typhoid fever
Answer: Ciprofloxacin and cefixime
Question 6. Nonsystemic antacids
Answer: Magnesium hydroxide and aluminum hydroxide
Question 7. Motion sickness
Answer: Cinnarizine and meclizine
Question 8. Nonsedating antihistaminics
Answer: Fexofenadine and loratadine
Question 9. Bronchodilators
Answer: Salbutamol and ipratropium
Question 10. Absence seizures
Answer: Sodium valproate and ethosuximide
Question 11. Tuberculosis
Answer: Isoniazid and rifampin
Question 12. Anti-5 HT drugs
Answer: Ondansetron and dolasetron
Question 13. Open-angle glaucoma
Answer:Acetazolamide and timolol
Question 14. Antipseudomonal drugs
Answer: Carbenicillin, ticarcillin
Question 15. Atypical antipsychotic drugs
Answer: Chlorpromazine and triflpromazine
Question 16. Cerebroactive drugs
Answer: Tacrine and Rivastigmine
Question 17. Antimaniac drugs
Answer: Lithium carbonate and carbamazepine
Question 18. Gouty arthritis
Answer:Indomethacin and naproxen
Question 19. Thyrotoxicosis
Answer: Radioactive iodine and propylthiouracil
Question 20. Status epilepticus
Answer: Phenytoin and diazepam
Question 21. Isolated systolic hypertension in elderly
Answer: Diuretics and ACE inhibitors
Question 22. Prophylaxis of angina pectoris
Answer: Aspirin and atorvastatin
Question 23. Congestive cardiac failure
Answer: Digitalis and β blockers
Question 24. Prophylaxis of gouty arthritis
Answer: Allopurinol and febuxostat
Question 25. Peptic ulcer
Answer: Omeprazole and ranitidine
Question 26. Schizophrenia
Answer:Clozapine and olanzapine
Question 27. Noninsulin dependent diabetes mellitus
Answer: Sulphonylureas and meglitinides
Question 28. Generalized tonic-clonic seizures
Answer: Sodium valproate and phenytoin
Question 29. Hyperthyroidism
Answer: Carbimazole and propylthiouracil
Question 30. Insomnia
Answer:Lorazepam and diazepam
Question 31. Organophosphorous poisoning
Answer: Atropine and pralidoxime
Question 32. Acute congestive glaucoma
Answer: Acetazolamide and hypertonic mannitol
Question 33. Long-acting tetracyclines
Answer: Oxytetracycline and demeclocycline
Question 34. Leprosy
Answer: Rifampin and Dapsone
Question 35. Long-acting glucocorticoids
Answer: Dexamethasone and betamethasone
Question 36. Cardioselective βblockers
Answer: Metoprolol and atenolol
Question 37. Drugs are given by sublingual route
Answer: Glycertrinitrate, Isosorbide dinitrate
Question 38. Disadvantages of the intravenous route of drug administration
Answer:
- Vital organs like the heart, brain, and liver are exposed to high concentrations of drugs.
- Thrombophlebitis of injected vein
Question 39. Teratogenic drugs
Answer: Thalidomide and Phenytoin
Question 40. Drugs whose bioavailability is reduced by food
Answer: Isoniazid and rifampicin
Question 41. Drugs used in the management of hypovolemic shock
Answer: Ringer lactate and dopamine
Question 42. General anesthetic drugs
Answer: Nitrous oxide and ether
Question 43. Local hemostatics
Answer: Thrombin and fibrin
Question 44. Obtundents
Answer: Clove oil and stannous chloride
Question 45. Dentifrices
Answer: Potassium nitrate and carbamide peroxide
Question 46. Drugs effective in megaloblastic anemia
Answer: Hydroxocobalamin and folic acid
Question 47. Anticoagulants
Answer: Heparin and warfarin
Question 48. Diuretics
Answer: Furosemide and spironolactone
Question 49. Mummifying agents
Answer: Formaldehyde and iodoform + phenol
Question 50. Chelating agents
Answer: EDTA and dimercaprol
Question 51. Bronchodilators
Answer: Salbutamol and terbutaline
Question 52. Hypertensive Emergency
Answer: Sodium nitroprusside + esmolol combination and labetalol
Question 53. Anaerobic infections
Answer: Metronidazole and clindamycin
Question 54. Short-acting glucocorticoids
Answer: Hydrocortisone
Question 55. Nonsystemic antacids
Answer: Aluminium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide
Question 56. Typhoid fever
Answer: Ciprofloxacin and cotrimoxazole
Question 57. Adverse effects of aspirin (any two)
Answer: Hypersensitivity and Reye’s syndrome
Question 58. Antifungal agents (two names)
Answer: Nystatin and fluconazole
Question 59. Drugs for an acute attack of migraine
Answer: Ergotamine
Question 60. Drugs for fever
Answer: Paracetamol, Aspirin
Question 61. Drugs for toothache
Answer:Ibuprofen, Ketorol
Question 62. Drugs for oral thrush
Answer:Cotrimazole, Nystatin, Fluconazole
Question 63. ACE inhibitors
Answer:Captopril, Enalapril
Question 64. H1 antihistaminic drugs
Answer: Cyclizine, Fexofenadine
Question 65. Antiemetic drugs
Answer: Metoclopramide and domperidone
Question 66. Antitussive
Answer: Codeine, Pholcodeine
Question 67. Drug for typhoid fever
Answer: Ciprofloxacin and chloramphenicol
Question 68. Organophosphorus poisoning
Answer: Atropine and Pralidoxime
Question 69. Allergic Rhinitis
Answer: Intranasal Corticosteroid and Antihistaminics
Question 70. Infective endocarditis
Answer: Amoxycillin and Cephalexin
Question 71. Bacterial meningitis
Answer: Ceftriaxone and Betamethasone
Question 72. Partial seizures
Answer: Carbamazepine and Phenytoin
Viva-Voce Questions For Practical Examination
Question 1. Which is the route used for localized lesions and is given in high concentration?
Answer: Local route
Question 2. Name the oldest and most common route of drug administration.
Answer: Oral route
Question 3. Name the drugs which are given through the sublingual route.
Answer: Clonidine, Nifedipine, Nitroglycerine, Isoprenaline, Methyltestosterone
Question 4. What is the main advantage of the sublingual route?
Answer: The liver gets bypassed
Question 5. Name the drugs given by transdermal patches.
Answer: Nitroglycerine, hyoscine, clonidine.
Question 6. By which route controlled administration of drugs is best possible?
Answer: Inhalation
Question 7. Name the route of drug administration which is commonly used in emergencies.
Answer: Parenteral
Question 8. Name the route of drug administration avoided in shocked patients.
Answer: Subcutaneous
Question 9. Name the route in which the drug is given should be less in quantity.
Answer: Intravenous
Question 10. Name the type of drugs which diffuse through the membrane.
Answer: Lipid soluble
Question 11. Name the process of transport across the cell in particulate form by the formation of vesicles.
Answer: Pinocytosis
Question 12. Name the process which involves the movement of a drug from its site of administration in circulation.
Answer: Absorption
Question 13. Where does the accumulation of digoxin occur?
Answer: Muscle proteins
Question 14. Name the antimalarial drug which gets deposited in the liver and retina.
Answer: Chloroquine
Question 15. Name the antibiotic which gets deposited in bones and teeth.
Answer: Tetracycline
Question 16. Name the primary site for drug metabolism.
Answer: Liver
Question 17. Which is the active drug of paracetamol?
Answer: Phenacetin
Question 18. Name the active drug of morphine.
Answer: Codeine
Question 19. Name the inactive drugs which get converted to become active drugs.
Answer: Prodrug
Question 20. Where do microsomal enzymes are located?
Answer: Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Question 21. From where do most of the drugs are excreted?
Answer: Urine
Question 22. In which types of kinetic reaction the rate of elimination is directly proportional to drug concentration?
Answer: First-order kinetics
Question 23. In which types of kinetic reaction the rate of elimination remains constant irrespective of drug concentration?
Answer: Zero-order kinetics
Question 24. Which are the hit-and-run drugs?
Answer: MAO inhibitors, Omeprazole, Reserpine
Question 25. Name the agent which activates a receptor to produce its effect.
Answer: Agonist
Question 26. Name the agent which prevents the action of the agonist of the receptor and does not produce its own effect.
Answer: Antagonist
Question 27. Name the phenomenon when the optimal therapeutic effect is exerted only over the narrow range of plasma drug concentration, one below and above this range, and beneficial effects are suboptimal.
Answer: Therapeutic window
Question 28. Name the drugs which show the therapeutic window phenomenon.
Answer: Clonidine and glipizide
Question 29. Name the phenomenon by which the action of one drug is facilitated by another.
Answer: Synergism
Question 30. Name the effects of two drugs that are produced in the same direction.
Answer: Additive
Question 31. Name the phenomenon when one drug inhibits the action of another.
Answer: Antagonistic
Question 32. Which drugs should not combine with the other drugs?
Answer: Corticosteroids
Question 33. What does Young’s formula use for calculating the drug dosage?
Answer: Corticosteroids
Question 34. If a diabetic is on insulin therapy develops severe hypoglycemia which drug he had taken.
Answer: Propranolol
Question 35. What is the main side effect of furosemide and aminoglycoside?
Answer: Ototoxicity
Question 36. If corticosteroid therapy is suddenly cessation, what can happen?
Answer: Acute adrenal insufficiency
Question 37. Name the drugs which can cause fetal abnormality when given to pregnant mothers.
Answer: Teratogenicity
Question 38. Name the chemical synthesized locally in cholinergic nerve endings.
Answer: Acetylcholine
Question 39. Which drug blocks muscarinic effects?
Answer: Atropine
Question 40. Which is the most common drug used in open-angle glaucoma?
Answer: Pilocarpine
Question 41. Name the anticholinesterase drug which crosses the blood-brain barrier.
Answer: Physostigmine
Question 42. Name the drug used in the treatment of myasthenia gravis.
Answer: Physostigmine
Question 43. Name the drugs which are primarily used in the treatment of cobra bite.
Answer: Atropine and neostigmine
Question 44. Name an antidote for belladonna poisoning.
Answer: Physostigmine
Question 45. Name the drug used to treat anticholinesterase poisoning.
Answer: Atropine
Question 46. Name the drug which is used to test the errors of refraction.
Answer: Homatropine
Question 47. Name the drug used in motion sickness.
Answer: Homatropine
Question 48. Where does the synthesis of adrenaline occur in the human body?
Answer: Adrenal medulla
Question 49. Name the drug which has potent action on both α and β receptors.
Answer: Adrenaline
Question 50. Name the drugs which lead to activation of both α and β1 but not β2 receptors
Answer: Noradrenaline
Question 51. Name the drug which has both β1 and β2 action with little or no α action.
Answer: Isoprenaline
Question 52. Name the drug which is commonly used in both anaphylaxis and laryngeal edema.
Answer: Adrenaline
Question 53. For the treatment of this disease, ergotamine is commonly used.
Answer: Migraine
Question 54. Name the drug which both blocks α and β receptors.
Answer: Labetalol
Question 55. Name an antimalarial drug that leads to neuromuscular blockade.
Answer: Quinine
Question 56. Which anesthetic agent causes vasodilatation?
Answer: Cocaine
Question 57. Name the first synthetic local anesthetic agent.
Answer: Procaine
Question 58. Which is the most potent, most toxic, and long-acting local anesthetic agent?
Answer: Dibucaine
Question 59. Name the drugs which are also known as local hormones.
Answer: Autacoids
Question 60. Name the drug for controlling vertigo and vomiting.
Answer: Prochlorperazine
Question 61. Name a 5HT antagonist which is an antiemetic.
Answer: Ondansetron
Question 62. Name an ACE inhibitor that is also a prodrug.
Answer: Enalapril
Question 63. Name the drugs which enhance the bronchial secretions decrease viscosity and lead to sputum removal via cough.
Answer: Expectorants
Question 64. Name the drug which stabilizes mast cells.
Answer: Sodium cromoglycate
Question 65. By which route all insulin preparations are given?
Answer: Subcutaneous route
Question 66. Which are the oral hypoglycemic which decrease blood glucose levels in both normal patients and noninsulin-dependent diabetic patients?
Answer: Sulfonylureas
Question 67. Name the oral hypoglycemic which needs some amount of insulin for their action.
Answer: Biguanides
Question 68. Name an oral hypoglycemic drug that leads to weight gain.
Answer: Gliclazide
Question 69. Name the drug which is a glucocorticoid antagonist.
Answer: Mifepristone
Question 70. Which drug shows diffusion hypoxia?
Answer: Nitrous oxide
Question 71. Name the anesthetic agent which leads to dissociative anesthesia.
Answer: Ketamine
Question 72. Why methanol produces toxic effects?
Answer: Due to the formation of formic acid which leads to retinal damage
Question 73. Which antiepileptic drug leads to gum hyperplasia?
Answer: Phenytoin
Question 74. Name the least toxic antiepileptic drug.
Answer: Phenobarbitone
Question 75. Name the drug of choice which is commonly used in trigeminal neuralgia.
Answer: Carbemazepine
Question 76. Name the drug of choice for petit mal epilepsy.
Answer: Sodium valproate
Question 77. Which is the drug of choice in grand mal epilepsy?
Answer: Phenytoin
Question 78. Which is the drug of choice in status epilepticus?
Answer: Diazepam
Question 79. Name the drug used in Parkinsonism.
Answer: Levodopa
Question 80. Name the drug which is excreted in both bile and urine after a month of discontinuation.
Answer: Chlorpromazine
Question 81. Name an antidote for morphine.
Answer: Naloxone
Question 82. Which is the hallmark feature of salicylate poisoning?
Answer: Hyperventilation
Question 83. Name the drug which is indicated for closure of patent ductus arteriosus.
Answer: Indomethacin
Question 84. Name the safest nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
Answer: Indomethacin
Question 85. Which NSAID does not lead to the retention of sodium ions and water retention?
Answer: Ibuprofen
Question 86. Name the antidote for paracetamol poisoning.
Answer: N–acetylcysteine
Question 87. Name an immunomodulator drug.
Answer: Levamisole
Question 88. Name the most commonly used glycoside drug.
Answer: Digoxin
Question 89. Which is the most common side effect caused by nitrates?
Answer: Headache
Question 90. Name the calcium channel blocker having the highest bioavailability.
Answer: Amlodipine
Question 91. Name the most common side effects of ACE inhibitors.
Answer: Dry persistent cough
Question 92. In pregnancy which is the most common antihypertensive drug used?
Answer: Hydralazine
Question 93. Which is the site of action of thiazide drugs?
Answer: Distal convoluted tubule
Question 94. Which is the site of action of potassium-sparing diuretics?
Answer: Collecting tubule
Question 95. Name the most common adverse effect of diuretics.
Answer: Hypokalemia
Question 96. Name the antidote used in iron poisoning.
Answer: Desferrioxamine
Question 97. Deficiency of which ion leads to interference in the synthesis of haem?
Answer: Copper ion
Question 98. During pregnancy, an anticoagulant is used.
Answer: Heparin
Question 99. Name the antagonist used for heparin.
Answer: Protamine sulfate
Question 100. Name the antidote for warfarin.
Answer: Vitamin K
Question 101. Name the antidote used for fibrinolytic agents.
Answer: Epsilon aminocaproic
Question 102. Name the drug used in hypercholesterolemia.
Answer: Lovastatin
Question 103. Name the most commonly used plasma expander.
Answer: Dextran
Question 104. In all antacids what does magnesium salt lead to and what does aluminum salt lead to?
Answer: Magnesium salt act as a laxative while aluminum salts cause constipation
Question 105. Which are the most commonly used drugs for peptic ulcers?
Answer: H2 blocker
Question 106. Name the drug which is used in motion sickness.
Answer: Hyoscine
Question 107. Name the laxative which carries fat-soluble vitamins in stools.
Answer: Liquid paraffin
Question 108. What do you mean by Epsom salt, Glanbers salt, and Rochelle salt?
Answer: Epsom salt is magnesium sulfate, Glanbers salt is sodium sulfate, Rochelle salt is sodium potassium tartrate.
Question 109. Which is the most commonly used antimotility drug?
Answer: Loperamide
Question 110. Which drug leads to the gray baby syndrome?
Answer: Chloramphenicol
Question 111. Name the sulphonamide drug which is useful in meningitis.
Answer: Sulfadiazine
Question 112. Name the first antibiotic which is used clinically.
Answer: Penicillin
Question 113. Penicillin which leads to hypokalemia?
Answer: Penicillin V
Question 114. Name the antibiotic which shows chelating properties.
Answer: Tetracycline
Question 115. Name the commonly used drugs in typhoid fever.
Answer: Chloramphenicol
Question 116. For acute infection, it is the most commonly used aminoglycoside.
Answer: Gentamycin
Question 117. Name the antitubercular drug which inhibits DNA-dependent RNA synthesis.
Answer: Rifampicin
Question 118. Name the antibiotic which is commonly used in pneumonia.
Answer: Erythromycin.
Question 119. Name the antibiotics which inhibit bacterial DNA gyrase.
Answer: Fluoroquinolones
Question 120. Name the drug commonly used in leprosy.
Answer: Dapsone
Question 121. Name the antileprotic drug which shows anti–inflammatory properties.
Answer: Clofazimine
Question 122. Which drug leads to a sulfone reaction.
Answer: Dapsone
Question 123. Name the antiviral drug which is used in herpes infection.
Answer: Acyclovir
Question 124. Name the most common drug used in the treatment of AIDS.
Answer: Zidovudine
Question 125. Name the drug of choice which is used in the treatment of all types of malaria except for resistant P. falciparum malaria.
Answer: Chloroquine
Question 126. Which drug leads to black water fever?
Answer: Quinine
Question 127. Name the drug of choice used in anaerobic infections in dentistry.
Answer: Metronidazole
Question 128. Which drug is known as BAL?
Answer: Dimercaprol
Question 129. Name the drug used in copper poisoning.
Answer: Penicillamine
Question 130. Name the vitamins which enhance the tendency of kidney stone formation.
Answer: Vitamin A and C.
Additional Information
Various Antimicrobial Drugs And Their Mechanism Of Action
Important Chelating Agents
- British anti-Lewisite (BAL): For heavy metal poisoning (mercury poisoning)
- Dimercapto succinic acid (DMSA): For lead poisoning
- EDTA: For heavy metal poisoning
- Penicillamine: For copper poisoning
Various Drugs And Their Effects On the Color Of Urine
Various Antitubercular Drugs
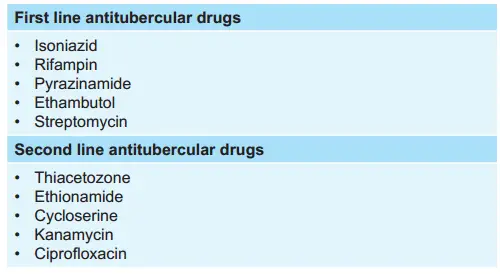
Various Choline Receptors, Their Sites, Selective Agonist And Selective Antagonist
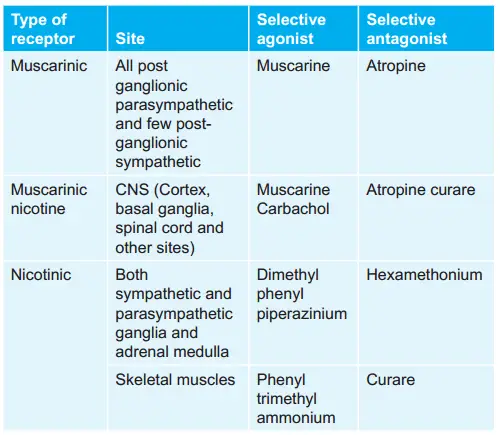
Types Of Hormones Depending On Action Of Receptors
Depending on the action of receptors, hormones are of two types, i.e.
1. Hormones act on receptors that are transcription factors. These are intracellular
- Cytoplasmic transcription factors
- Steroid hormones
- Glucocorticoids
- Androgen
- Estrogen
- Progestin
- Calcitriol
- Nuclear transcription factors
- Thyroid hormones
2. Hormone acting on receptors acting by other mechanisms (Non-transcription factors). They lie in cell membranes
- G protein-coupled receptors
- Adrenaline/Epinephrine
- Glucagon
- TSH, FH, LH
- Calcitonin
- Vasopressin
- Oxytocin
- Enzymatic receptors
- Insulin
- Growth hormone
- Prolactin
Various Drugs In Seizures
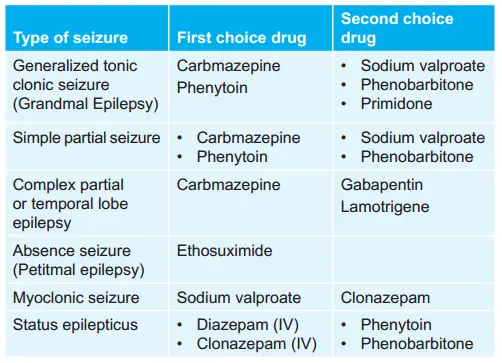
Various Adverse Reactions Of Antipsychotic Drugs
- On central nervous system: Drowsiness, lethargy, and confusion
- On cardiovascular system: Postural hypotension and palpitation
- Anticholinergic: Dry mouth, blurring of vision, and constipation
- On endocrine system: Amenorrhea, infertility, galactorrhea, gynecomastia
- Extrapyramidal effects: Rigidity, tremors, parkinsonism, acute muscular dystonia, restlessness.
Classification Of Biotransformation Reactions
1. Nonsynthetic or Phase I reactions or functionalization reactions
- Oxidation: Barbiturates, phenothiazines, imipramine, ibuprofen, paracetamol, steroids, phenytoin, benzodiazepines, theophylline
- Reduction: Chloralhydrate, chloramphenicol, halothane, warfarin
- Hydrolysis: Procaine, lidocaine, procainamide, aspirin, pethidine, oxytocin, carbamazepine
- Cyclization: Proguanil
- Decyclization: Barbiturates and phenytoin
2. Synthetic or conjugation or Phase II reaction
- Conjugation:
- Glucuronide conjugation: Chloramphenicol, aspirin, paracetamol, lorazepam, morphine, metronidazole, steroid hormones, bilirubin, thyroxin
- Sulfate conjugation: Chloramphenicol, methyl dopa, adrenal and sex steroids
- Glycine conjugation: Salicylates
- Glutathione conjugation: Paracetamol
- Acetylation: Sulfonamides, isoniazid, dapsone, hydralazine, clonazepam
- Methylation: Adrenaline, histamine, nicotinic acid, methyldopa, captopril
- Ribonucleotide synthesis: Purine and pyrimidine anti-metabolites.
Various t1/2
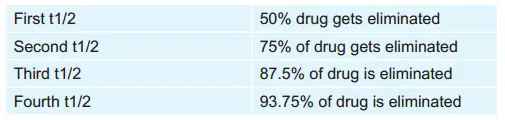
Types Of Antagonism
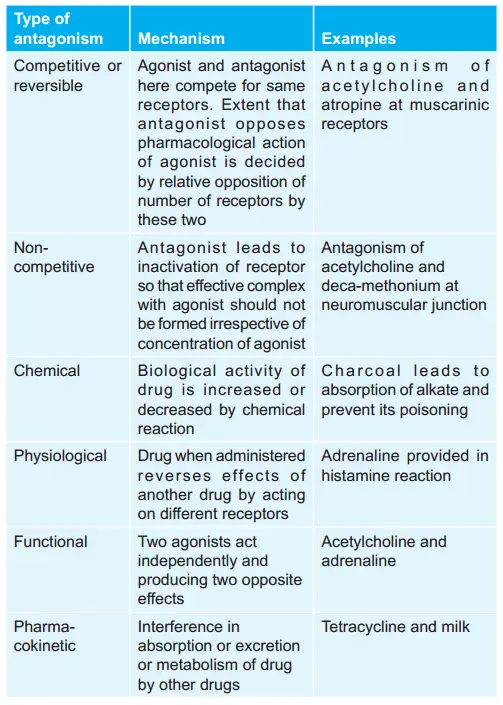
Various Prodrugs And Their Active Form
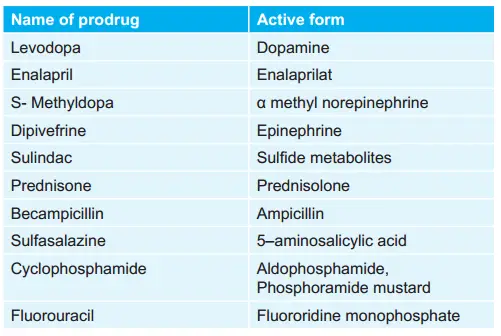
Extent Of First Pass Metabolism
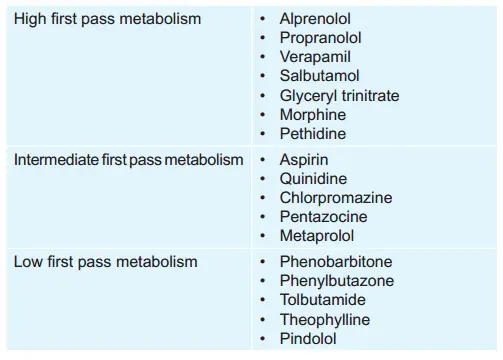
American Society Of Anesthesiologists Physical Status Classification
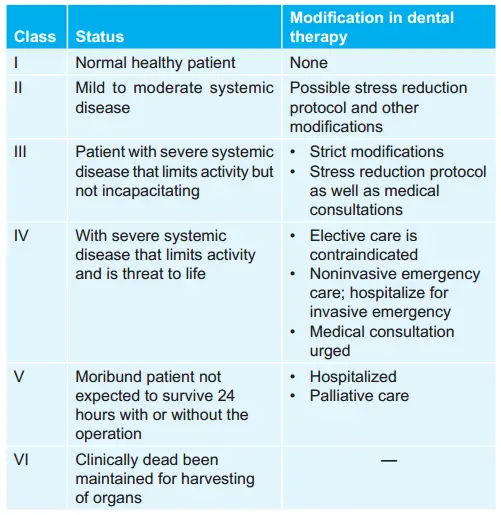
Enumeration Of Drugs Leading To Bronchospasm
- ACE inhibitors
- Aspirin and other NSAIDs
- Beta-adrenergic blockers
- Cholinergic drugs
- Bulk-forming laxatives
- Quinine
- Morphine
Drugs Undergoing Dose Reduction In Renal Failure
- In mild renal failure: Aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, amphotericin B, ethambutol, vancomycin, flucytosine
- In moderate to severe renal failure: Metronidazole, cotrimoxazole, carbenicillin, fluoroquinolones
Drugs Contraindicated In Renal Failure
- Cephalothin
- Cephaloridine
- Nalidixic acid
- Nitrofurantoin
- Talampicillin
- Tetracyclines
Positive Ionotrope Drugs
- Catecholamines: Dopamine, dobutamine, adrenaline, noradrenaline, isoprenaline, Angiotensin II
- Cardiac sensitizers: Levosimendan
- Digoxin
- Digitalis
- Eicosanides: Prostaglandins
- Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: Amrinone, theophylline, and enoximone
- Glucagon
- Insulin
Drugs Which Inhibit Theophylline Metabolism And Its Plasma Levels
- Erythromycin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Cimetidine
- Oral contraceptives
- Allopurinol
Various Cephalosporins
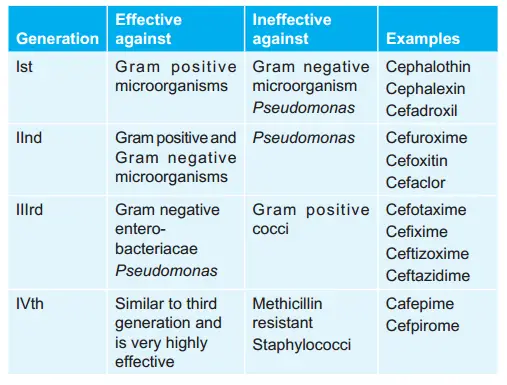
Actions Of Various Histaminergic Receptors
- H1: It leads to smooth muscle contraction.
- H2: It leads to acid secretion from gastric glands; vasodilatation; relaxation of the uterus.
- H3: Inhibits histamine release and sedation; Inhibits H1-mediated bronchoconstriction.
Drugs Leading To Dryness Of Mouth
- Antimuscarinic
- Atropine and related analogs
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Phenothiazines
- Antihistaminics
- Antiemetics
- Ganglionic blockers
Sympathomimetic Drugs
- Ephedrine
- Isoprenaline and related bronchodilators
- Amphetamines
Drugs Contraindicated In Liver Disease
- Erythromycin
- Tetracycline
- Talampicillin
- Perflxacin
- Nalidixic acid
- Pyrazinamide
Drugs Whose Dose Should Be Decreased In Liver Disease
- Chloramphenicol
- Metronidazole
- Clindamycin
- Isoniazid
- Rifampicin
Various Drugs With Their Actions And Examples
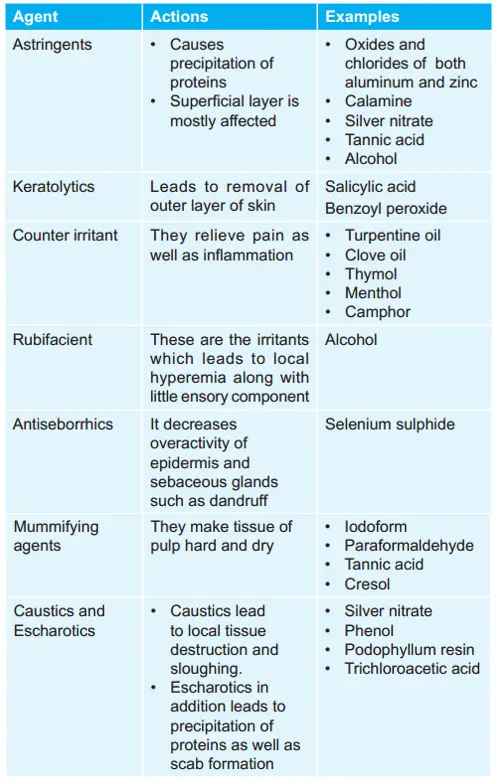
Treatment Of Drug Poisoning Along With Its Treatment

Various Chelating Agents
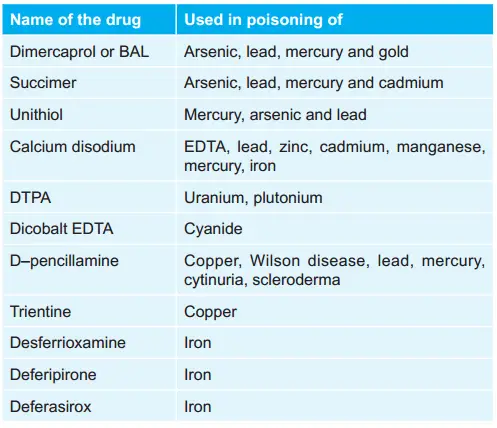
Name Of The Disease And Their Drug Of Choice
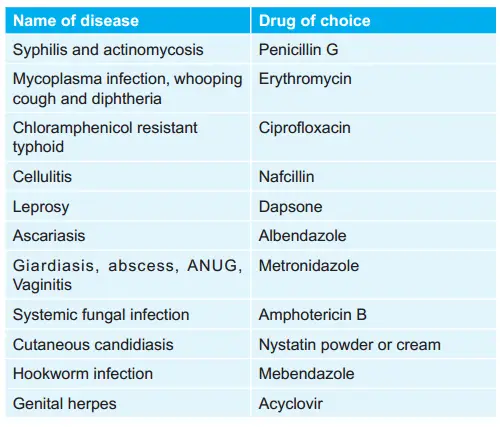
Stages Of Anesthesia
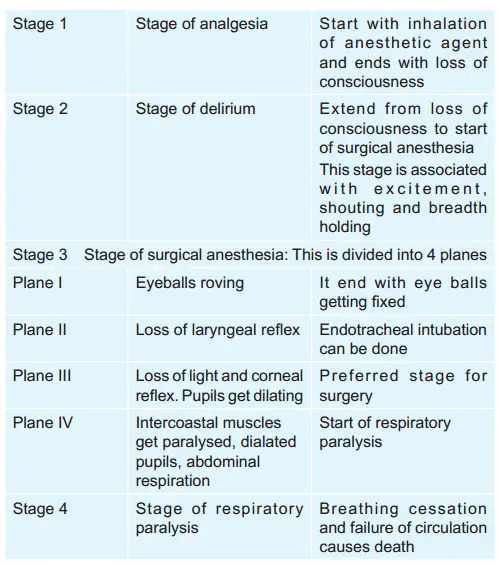
Various Antibiotics And Their Drug Interactions
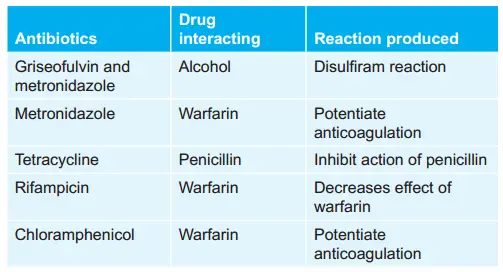

Leave a Reply