The Permanent Mandibular Premolars
Question 1. Describe in detail the morphology of the permanent mandibular 1″ premolar.
Answer:
Buccal aspect:
- The Crown appears symmetrical and roughly trapezoidal.
- The buccal surface is convex and smooth with no developmental grooves present.
- The slight curvature of the cervical line is seen.
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
- The mesial and distal outlines along with the slopes are slightly concave.
- Developmental depression is seen between the 3 lobes.
- The buccal ridge is a continuous ridge extending from the cervical margin to the cusp tip.
Lingual aspect:
- The crown and root tapers lingually with the lingual cusp being smaller.
- The cervical portion is narrow and convex.
- The contact areas and marginal ridges are more pronounced.
- The lingual cusp is short and less developed.
- The mesial and distal occlusal fossae are seen on each side of the triangular ridge.
- The mesiolingual developmental groove is seen separating the mesiobuccal and lingual lobes.
- The root shows a smooth and convex narrow ridge, developmental depression with developmental groove mesially, and ends into a pointed apex.
Mesial aspect:
- The crown outline is roughly rhomboidal.
- The buccal cusp tip is nearly centered over a root.
- The buccal outline of the crown is prominently curved.
- The lingual outline of the crown is less convex.
- The distance from the cervical line lingually to the tip of the lingual cusp is about 2/3rd of the distance from the cervical line buccally to the tip of the buccal cusp.
- The mesiobuccal lobe is prominent.
- The lingual border of the mesial marginal ridge merges with the developmental depression mesiolingually and harbors the mesiolingual developmental groove.
- The cervical line is regular and curves occlusal.
- The root outline is tapered and ends in a pointed apex.
- The lingual outline is straight while the buccal outline is more curved.
- The mesial surface of the root is smooth and flat shallow grooves are present.
Distal aspect:
- The distal marginal ridge is higher above the cervix.
- There is no developmental groove on the distal marginal ridge.
- The surface is smoothly convex.
- The distal contact area is broader
- The cervical line has less curvature.
- The root surface is more convex.
- A shallow development depression is present.
Occlusal aspect:
- It is roughly diamond-shaped.
- The buccal ridge and the mesiobuccal and distobuccal line angles are prominent.
- The marginal ridges are well-developed.
- The lingual cusp is small
- The surface shows a heavy buccal triangular ridge and a small lingual triangular ridge.
Fossae:
- Mesial and distal fossae correspond in location to the mesial and distal triangular fossae.
- The mesial fossa is more linear.
- The distal fossa is more circular and is circumscribed by the distobuccal cusp ridge, the distal marginal ridge, the buccal triangular ridge, and the distolingual cusp ridge.
Developmental groove:
- The mesial developmental groove extends buccolingually.
- Over the mesiolingual surface, it becomes mesiolingual developmental groove.
- Distal developmental groove. It is crescent-shaped.
- It contains a distal developmental pit with accessory supplemental grooves.
Measurements:
- Cervico-occlusal crown length – 8.5 mm
- Root length – 14 mm
- Mesiodistal crown diameter -7 mm
- Mesiodistal crown diameter at cervix – 5 mm
- Bucco-lingual crown diameter -7.5 mm
- Bucco-lingual crown diameter at cervix -6.5 mm
- Curvature of cervical line – mesial – 1 mm
- The curvature of the cervical line, – distal – 0 mm
Question 2. Describe in detail the morphology of the permanent mandibular 2nd premolar.
Answer:
Buccal aspect:
- It shows a shorter buccal cusp.
- Mesiobuccal and distobuccal cusp ridges show less angulation.
- The contact areas are broad.
- The root is broader with a blunt apex.
Lingual aspect:
- The lingual lobes are well-developed. Loss of the occlusal surface is seen.
- Longer and larger mesiobuccal cusp and distolingual cusps are seen.
- A groove is present between them
- The surface is smooth and spheroidal.
- The root is wide lingually.
- Less mesial and distal sides are seen.
- The root surface is smoothly convex.
Mesial aspect:
- The crown and root are wider buccolingually.
- The buccal cusp is shorter.
- The lingual lobe is greater.
- The marginal ridge is at right angles to the long axis.
Distal aspect:
- The more occlusal surface is seen.
- The distal marginal ridge is at a lower level.
- The crown is tipped distally.
Occlusal aspects:
- The three-cusp type appears square lingual to the buccal cusp ridges when highly developed.
- The three cusps that are distinct are the largest buccal cusp, next mesiolingual cusp and the distolingual cusp is the smallest.
- The two cusps type appears round lingual to the buccal cusp ridges.
- Each cusp has well-formed triangular ridges.
Central pit:
Location:
- Midway between the buccal cusp ridge and the lingual margin of the occlusal surface.
- Slightly distal to the central point between mesial and distal marginal ridges.
Fossa:
- Mesial triangular fossa – distal to mesial marginal ridge.
- Distal triangular fossa-mesial to the distal marginal ridge.
Developmental groove:
- The mesial developmental groove travels in a mesiobuccal direction and ends in a mesial triangular fossa.
- The distal developmental groove travels in a distobuccal direction and ends in a distal triangular fossa.
- Lingual developmental groove extends lingually between the two lingual cusps and ends on the lingual surface of the crown.
- Supplemental grooves and depression are often seen radiating from the developmental grooves.
Two cusps type:
- It travels in a mesiodistal direction.
- It is most often crescent-shaped.
- It terminates in mesial and distal fossae.
- Central developmental groove:
- It travels in a mesiodistal direction.
- It is most often crescent-shaped.
- It terminates in mesial and distal fossae.
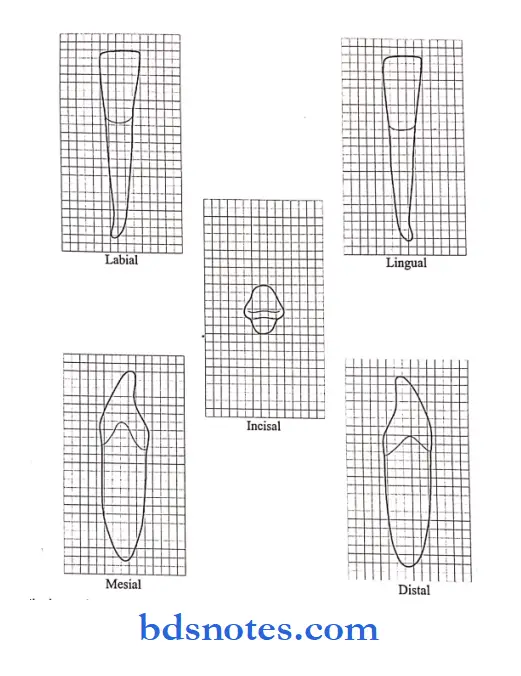
- Mandibular left second premolar, buccal aspect. (Grid 1 SQuestion mm)
- Mandibular left second premolar, lingual aspect. (Grid 1 SQuestion mm)
- Mandibular left second premolar, mesial aspect. (Grid 1 SQuestion mm)

Measurements:
- Cervico-occlusal crown length – 8 mm
- Root length – 14.5 mm
- Mesiodistal crown diameter -7 mm
- Mesiodidstal crown diameter at cervix – 5mm
- Buccolingual crown diameter – 8 mm
- Bucco-lingual crown diameter at cervix -7mm
- The curvature of cervical line – mesial
- The curvature of the cervical line – distal – 0 mm
- Mandibular left second premolar, distal aspect.
Question 3. Differentiate between permanent mandibular 1st premolar and 2nd premolar.
Answer:

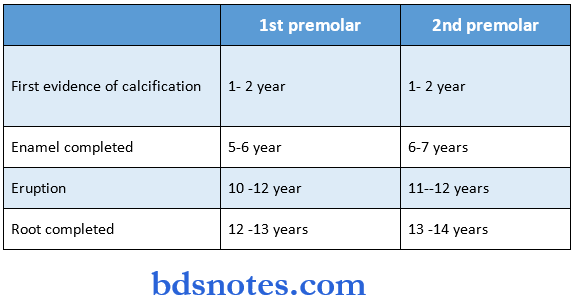
Question 4. Chronology of mandibular 1st and 2nd premolar.
Answer:

Leave a Reply