Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. A key feature that differentiates Stage 3 gingivitis from stage 2 lesion is an increase in the number of:
- Lymphocytes
- Plasma Cells
- Mast cells
- Polymorphs
Answer. 2. Plasma Cells
Question 2. It is likely that cell-mediated immune reactions (delayed hypersensitivity) occur in periodontitis because subjects with periodontitis have:
- High levels of histamine in involved gingival tissue
- IgG antibodies reactive with plaque bacterial agents
- T-lymphocytes sensitized to bacterial plaque antigens
- High levels of collagenase in gingival fluids
Answer. 3. T-lymphocytes sensitized to bacterial plaque antigens
Question 3. Anchoring fibrils are composed of:
- Type 5 and Type 7 collagen
- Type 1 and Type 3 collagen
- Type 4 collagen
- Type 4 and Type 3 collagen
Answer. 1. Type 5 and Type 7 collagen
Question 4. Glucose levels in GCF are:
- Equal to glucose level in serum
- Zero
- 3-4 times greater than serum levels
- More than 10 times the serum levels
Answer. 3. 3-4 times greater than serum levels
Read And Learn More: Periodontics Question And Answers
Question 5. First organism to appear in oral cavity:
- Streptococcus sanguinis
- Streptococcus salivarius
- Streptococcus mutans
- Lactobacilli
Answer. 2. Streptococcus salivarius
Question 6. Interleukin 2 is secreted by:
- B-lymphocytes
- T-lymphocytes
- Neutrophils
- Macrophages
Answer. 2. T-lymphocytes
Question 7. Gingival sulcular epithelium:
- Show deep rete pegs
- Shows no rete pegs
- Is parakeratinized
- Is orthokeratinized
Answer. 2. Shows no rete pegs
Question 8. Which of the following four bacterial species, which is least likely to bound in plaque?
- Actinomyces viscosus
- Streptococcus mutans
- Streptococcus salivarius
- Streptococcus sanguinis
Answer. 2. Streptococcus mutans
Question 9. Majority of oral microorganisms are:
- Strict anaerobes
- Gram-positive bacilli
- Spirochetes
- Facultative anaerobes
Answer. 4. Facultative anaerobes
Question 10. All of the following are protective agent in periodontal disease except:
- S. sanguinis
- C. Ochracea
- V. Parvula
- B. Oralis
Answer. 3. V. Parvula
Question 11. Normal depth of gingival sulcus in adult does not exceed:
- 0.5 – 1 mm
- 2 – 3 mm
- 1 – 2 mm
- 1 – 3 mm
Answer. 2. 2 – 3 mm
Question 12. An isolated area in which root is denuded of bone and marginal bone is intact and is covered only by periosteum and gingiva is called:
- Fenestration
- Dehiscence
- Infracrestal pocket
- Hemiseptum defect
Answer. 1. Fenestration
Question 13. The periodontium does not include:
- Cementum
- Dentine
- Periodontal ligament
- Bone lining the socket
Answer. 2. Dentine
Question 14. Gingiva is attached to enamel by:
- Hemidesmosomes
- Desmosomes
- Tight junction
- Gap Junction
Answer. 4. Gap Junction
Question 15. Width of attached gingiva is thinnest at:
- 1st premolar
- Central incisor
- Lateral incisor
- 1st molar
Answer. 2. Central incisor
Question 16. For caries and periodontal disease common causative factor is:
- Plaque
- Subgingival calculus
- Pellicle
- Materia Alba
Answer. 1. Plaque
Question 17. Gingiva is not stippled in:
- Infants
- Young people
- Old people
- Teenagers
Answer. 1. Infants
Question 18. In periodontal disease calculus is considered as:
- Contributing factor
- Primary factor
- Etiologic factor
- Governing factor
Answer. 1. Contributing factor
Question 19. Supragingival plaque causes:
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
- Pericoronitis
- Aphthous ulcers
Answer. 2. Periodontitis
Question 20. Which of the following structures is keratinized?
- Attached gingiva
- Sulcular epithelium
- Col
- Junctional epithelium
Answer. 1. Attached gingiva
Question 21. PGE2-mediated bone resorption in periodontal disease is inhibited by:
- Calcitonin
- Estrogens
- NSAIDs
- Vitamin D and Calcium
Answer. 3. NSAIDs
Question 22. Decalcified freeze dried bone allograft is considered as:
- Osteogenic
- Osteoinductive
- Osteoconductive
- Osteoplastic
Answer. 2. Osteoinductive
Question 23. The cause of bone destruction in juvenile periodontits is:
- Phagocytosis is reduced
- Reduced neutrophilic chemotaxis
- Decrease host resistance
- Highly virulent microorganism
Answer. 2. Reduced neutrophilic chemotaxis
Question 24. Gingival sulcular epithelium:
- Shows deep rete pegs
- Shows no rete pegs
- Is parakeratinized
- Is orthokeratinized
Answer. 2. Shows no rete pegs
Question 25. The predominant immunoglobulin is:
- IgA
- IgD
- IgE
- IgG
Answer. 1. IgA
Question 26. GTR is related to:
- Gingivoplasty
- Frenectomy
- Mucogingival surgery
- Gingivectomy
Answer. 3. Mucogingival surgery
Question 27. Bioactive glass is:
- Isograft
- Xenograft
- Allograft
- Alloplast
Answer. 4. Alloplast
Question 28. The probing pressure applied by CPITN probe:
- 10 g
- 25 g
- 35 g
- None of the above
Answer. 2. 25 g
Question 29. If interdental bone is apical to interradicular bone, it is:
- Positive architecture
- Plateau
- Negative architecture
- None of the above
Answer. 3. Negative architecture
Question 30. Main aim of root planning is to remove:
- Plaque
- Calculus
- Necrotic cementum
- All of the above
Answer. 3. Necrotic cementum
Question 31. Most common extraoral cause of halitosis:
- Indigestion
- Chronic sinusitis
- Alcohol intake
- Diabetes mellitus
Answer. 2. Chronic sinusitis
Question 32. Common etiology of periodontitis is:
- Occlusal trauma
- Systemic factor
- Local irritating factor
- Hormonal defects
Answer. 3. Local irritating factor
Question 33. A white soft, sticky deposit on tooth surface is:
- Materia alba
- Linea alba
- Plaque
- Calculus
Answer. 3. Plaque
Question 34. Stippling is seen on:
- Marginal gingiva
- Attached gingiva
- Interdental gingiva
- All of the above
Answer. 2. Attached gingiva
Question 35. Pellicle formation on enamel starts with:
- Absorption of glycoprotein from saliva
- Focal areas of mineralization
- Bacterial colonization
- Absorption of endotoxin
Answer. 1. Absorption of glycoprotein from saliva
Question 36. Periodontitis is caused by:
- Malnutrition
- Supragingival plaque
- Biofilm
- Faulty tooth brushing
Answer. 3. Biofilm
Question 37. Melanin pigmentation is:
- Physiological
- Pathological
- Hormonal
- Nutritional
Answer. 1. Physiological
Question 38. Pathological deepening of gingival sulcus is:
- Gingival pocket
- Infrabony pocket
- Periodontal pocket
- Pseudo pocket
Answer. 3. Periodontal pocket
Question 39. Sharpey’s fibers are inserted into:
- Cementum
- Bone
- Dentine
- All of the above
Answer. 1. Cementum
Question 40. Mucogingival junction is present between:
- Attached gingiva and alveolar mucosa
- Attached gingiva and marginal gingiva
- Attached gingiva and interdental gingiva
- Interdental gingiva and marginal gingiva
Answer. 1. Attached gingiva and alveolar mucosa
Question 41. Furcation is measured by:
- Naber’s probe
- Florida probe
- Miller’s probe
- CPITN probe
Answer. 1. Naber’s probe
Question 42. Kirkland and orban knife are used for:
- Curettage
- Gingivectomy
- Root planning
- Scaling
Answer. 2. Gingivectomy
Question 43. Common sign of occlusal trauma is (TFO)
- Tooth mobility
- Fracture of cusps
- Resorption of alveolar bone
- Widening of periodontal ligament
Answer. 1. Tooth mobility
Question 44. Which of the following is first formed after tooth brushing:
- Materia alba
- Plaque
- Pellicle
- Calculus
Answer. 3. Pellicle
Question 45. More objective sign of gingivitis is:
- Increase in gingival size
- Increase in crevicular fluid
- Increase in gingival redness
- Bleeding on probing
Answer. 4. Bleeding on probing
Question 46. Indication of gingivectomy is:
- Edema of gingiva
- Infrabony pocket
- Adequate attached gingiva
- Pocket depth below mucogingival junction
Answer. 4. Pocket depth below mucogingival junction
Question 47. Chemicals used in root preparation are:
- Citric acid
- Fibronectin
- Tetracycline
- All the above
Answer. 4. All the above
Question 48. Tannic acid acts as:
- Astringent
- Keratolytic
- Demulcent
- Antiseptic
Answer. 1. Astringent
Question 49. Frenectomy is a:
- Gingival surgery
- Periodontal plastic surgery
- Osseous surgery
- All the above
Answer. 2. Periodontal plastic surgery
Question 50. Stippling is seen on:
- Marginal gingiva
- Attached gingiva
- Interdental gingiva
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Attached gingiva
Question 51. Parts of periodontium:
- Calculus
- Dental plaque
- Bone grafts
- Cementum
Answer. 4. Cementum
Question 52. Parts of gingival epithelium:
- Connective tissue
- Gingival fibers
- Oral epithelium
- Periodontal ligament
Answer. 3. Oral epithelium
Question 53. Function of saliva:
- Antimicrobial
- Digestion
- Mineralization of plaque
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 54. Stages of plaque (Pick the incorrect):
- Plaque maturation
- Initial adhesion and attachment
- Growth factors
- Formation of pellicle
Answer. 3. Growth factors
Question 55. Plaque hypothesis:
- Specific plaque hypothesis
- Non-specific plaque hypothesis
- Experimental
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 56. Gingival fibers:
- Oblique fibers
- Apical fibers
- Horizontal fibers
- Circular fibers
Answer. 4. Circular fibers
Question 57. Gingival epithelium cells (Pick the incorrect):
- Keratinocytes
- Merckel cells
- Melanocytes
- Fibroblasts
Answer. 4. Fibroblasts
Question 58. Stages of gingivitis:
- Initial stages
- Early stages
- Established stage
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 59. Father of periodontics:
- Glickman
- Newman
- Frichard
- Grossman
Answer. 1. Glickman
Question 60. Drugs inducing gingival enlargement:
- Ibuprofen
- Paracetamol
- Phenytoin
- Diazepam
Answer. 3. Phenytoin
Question 61. Attached gingiva is always:
- Stippled
- Non-keratinized
- Resistant to masticatory forces
- All the above
Answer. 3. Resistant to masticatory forces
Question 62. Signs of TFO are all of the following except:
- Mobility of teeth
- Formation of pocket
- Widening of periodontal ligament
- Migration of teeth
Answer. 2. Formation of pocket
Question 63. Frenectomy is a:
- Gingival surgery
- Mucogingival surgery
- Osseous surgery
- All of the above
Answer. 2. Mucogingival surgery
Question 64. A score of 0.7-1.9 of Russell’s index indicates:
- Simple gingivitis
- Simple periodontitis
- Established stage of periodontitis
- Terminal stage of periodontitis
Answer. 1. Simple gingivitis
Question 65. Clinical signs of gingivitis appear in which stage:
- Initial or stage 1
- Early or stage 2
- Established or stage 3
- Terminal stage of periodontitis
Answer. 2. Early or stage 2
Question 66. During pocket elimination by reflecting flap, the incision which removes pocket lining:
- Internal bevel or first incision
- Second or crevicular incision
- Third incision
- All of the above
Answer. 1. Internal bevel or first incision
Question 67. Main aim to restoration of carious lesion in phase 1 therapy:
- To restore function of tooth
- To reduce microbial source
- To restore form of tooth
- All the above
Answer. 2. To reduce microbial source
Question 68. The pattern of vibration of magnetostrictive type of ultrasonic scaler is:
- Elliptical
- Linear
- Back and forth
- None
Answer. 1. Elliptical
Question 69. Which of the following ingredients of a toothpaste acts as a detergent?
- An essential oil
- Glycerine
- Sodium lauryl sulphate
- Sodium metaphosphate
Answer. 3. Sodium lauryl sulphate
Question 70. Crater in inter-dental bone is best eliminated by:
- Gingivectomy
- Osseous recountouring
- Osseous regeneration
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Osseous recountouring
Question 71. Close apposition of the gingival epithelium to the tooth surface without complete obliteration of the pocket is called as:
- New attachment
- Reattachment
- Epithelial adaptation
- Repair
Answer. 3. Epithelial adaptation
Question 72. Collagen fibers that emerge from the supra-alveolar part of the cementum and pass outward beyond the alveolar crest in an apical direction into the mucoperiosteum are called as:
- Circular fibers
- Dentoperiosteal fibers
- Dentogingival fibers
- Interpapillary fibers
Answer. 2. Dentoperiosteal fibers
Question 73. Human oral spirochetes are:
- Gram-positive and aerobic
- Gram-positive and strict anaerobic
- Gram-negative and aerobic
- Gram-negative and strict anaerobic
Answer. 4. Gram-negative and strict anaerobic
Question 74. The essential distance between most apical extension of the crown margin and the alveolar bone crest should be atleast:
- 1 mm
- 2 mm
- 3 mm
- 4 mm
Answer. 2. 2 mm
Question 75. Living cells in saliva are referred to as orogranulocytes comprise of:
- Lymphocytes
- Polymorphonuclear leukocytes
- Macrophages
- All of the above
Answer. 2. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes
Question 76. Carbohydrate present in the greatest amount in the matrix of supragingival plaque is:
- Dextran
- Levan
- Galactose
- Methyl pentose
Answer. 1. Dextran
Question 77. Periodontopathic microorganisms counteract activity of defense cells by inhibiting mechanism of:
- PMN chemotaxis
- Phagocytosis
- Bactericidal activity
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 78. Subclinical gingivitis represents gingival inflammation in the following stage:
- Initial lesion
- Early lesion
- Established lesion
- Advanced lesion
Answer. 1. Initial lesion
Question 79. The preponderant inflammatory cell type present in stage 3 gingivitis is:
- Plasma cell
- Monocyte
- Neutrophil
- Lymphocyte
Answer. 1. Plasma cell
Question 80. Gingival inflammation affecting the gingival margin, attached gingiva and interdental papillae is known as:
- Marginal gingivitis
- Papillary gingivitis
- Generalized gingivitis
- Diffused gingivitis
Answer. 4. Diffused gingivitis
Question 81. Cementum is thickest at:
- Apical third
- Coronal third
- Furcation area
- Middle third of root
Answer. 1. Apical third
Question 82. Gingival cleft are caused by:
- Trauma from occlusion
- Faulty brushing technique
- Normal frenal pull
- Improper brushing technique
Answer. 2. Faulty brushing technique
Question 83. Pocket depth of 5 mm is noted. There is gingival recession of 3 mm, total attachment loss is:
- 5 mm
- 2 mm
- 3 mm
- 8 mm
Answer. 4. 8 mm
Question 84. Gingivoplasty is:
- Recontouring the gingiva in absence of pockets
- Eliminate periodontal pocket and reshaping as a part of technique
- Eliminate periodontal pocket
- Correction of osseous defect
Answer. 1. Recontouring the gingiva in absence of pockets
Question 85. Predominant immunoglobulin is saliva:
- IgA
- IgD
- IgE
- IgG
Answer. 1. IgA
Question 86. The best indication for osseous grafts for bone regeneration procedure is:
- One walled infrabony pockets
- One walled suprabony pockets
- Two walled infrabony pockets
- Three walled infrabony pockets
Answer. 4. Three walled infrabony pockets
Question 87. The first sequential step in osseous resection technique:
- Vertical grooving
- Radicular blending
- Flattening interproximal bone
- Gradualising marginal bone
Answer. 1. Vertical grooving
Question 88. Computerized periodontal probe is known as:
- Florida probe
- Periotemp probe
- Automated probe
- DNA probe
Answer. 1. Florida probe
Question 89. Periotest is used for detecting:
- Enzyme in GCF
- Tooth mobility
- Antibodies
- Inflammatory mediators
Answer. 2. Tooth mobility
Question 90. Life saver shaped enlargement of marginal gingiva are called:
- Stillman’s cleft
- McCall’s festoons
- Window peak
- Craters
Answer. 2. McCall’s festoons
Question 91. A key feature that differentiates stage 3 gingivitis from stage 2 gingivitis is an increase in the number of:
- Lymphocytes
- Plasma cells
- Mast cells
- Polymorphs
Answer. 2. Plasma cells
Question 92. Latest group of fibers in periodontal ligament:
- Oblique fiber
- Inter-radicular group
- Trans-septal group
- Horizontal group
Answer. 1. Oblique fiber
Question 93. Alveolar bone proper is also known as:
- Trabecular bone
- Bundle bone
- Cribriform bone
- Cortical bone
Answer. 2. Bundle bone
Question 94. The only microorganism that increases significantly during pregnancy is:
- P. gingivalis
- Spirochetes
- P. intermedia
- F. nucleatum
Answer. 3. P. intermedia
Question 95. Connective tissue of gingiva is also known as:
- Lamina densa
- Lamina propria
- Lamina lucida
- Lamina dura
Answer. 2. Lamina propria
Question 96. Three wall interbony defect is:
- Three walls missing
- Three walls present
- Hemi-septal defect
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Three walls present
Question 97. Hemisection is:
- Removal of one or more roots from a multirooted tooth leaving the majority of crown intact.
- Spliting of a two rooted teeth in two parts
- Removal of one or more roots from a multirooted tooth with a crown
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Spliting of a two rooted teeth in two parts
Question 98. Splinting of several teeth together as for a fixed prosthesis is done to:
- Distribute occlusal load
- Facilitate plaque removal
- For better aesthetics
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Distribute occlusal load
Question 99. Furcation lesion is clinically detected by:
- Curette
- Hoe
- Naber’s probe
- Periosteal elevator
Answer. 3. Naber’s probe
Question 100. Which of the following materials has osteoinductive property:
- Autogenous graft
- Hydroxyapatite
- Plastic materials
- Cartilage
Answer. 2. Hydroxyapatite
Question 101. The principle fibers of PDL are composed of mainly of collagen type:
- Type 1
- Type 4
- Type 3
- Type 8
Answer. 1. Type 1
Question 102. The term given to bone adjacent to the PDL that contains a great number of Sharpey’s fibers:
- Bundle bone
- Periosteum
- Interdental septum
- Osteoid
Answer. 1. Bundle bone
Question 103. Crystals making the bulk of the inorganic portion of calculus are:
- Hydroxyapatite and Brushite
- Hydroxyapatite and Mg Whitlockite
- Brushite
- Hydroxyapatite and octacalcium phosphate
Answer. 4. Hydroxyapatite and octacalcium phosphate
Question 104. Bone cysts in the oral cavity in hyperparathyroidism is called as:
- Brown tumors
- Blue tumors
- Dentigerous cysts
- Osteosarcoma
Answer. 1. Brown tumors
Question 105. Low levels of which of the following vitamins affect the metabolism of collagen within the periodontium:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin C
Answer. 4. Vitamin C
Question 106. Optimum levels of which of the following vitamin would maintain the epithelium’s barrier function to bacterial products:
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin B6
- Folic acid
Answer. 1. Vitamin C
Question 107. Terminal portions of the principle fibers that are inserted into cementum and bone:
- Sharpey’s fibers
- Cementicles
- Osteocytes
- Oxytalin fibers
Answer. 1. Sharpey’s fibers
Question 108. Periodontitis is considered as the 6th complication of:
- CVS disease
- Diabetes
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Answer. 2. Diabetes
Question 109. Process by which cells ingest particles of a size visible to light microscopy:
- Chemotaxis
- Opsonization
- Phagocytosis
- Necrosis
Answer. 3. Phagocytosis
Question 110. An immunoglobulin that binds a known antigen is:
- Cytokine
- Antibody
- Complement
- Receptor
Answer. 2. Antibody
Question 111. Drugs known to cause gingival enlargement includes all of the following except:
- Nifedipine
- Diltiazem
- Sodium valproate
- Carbamazepine
Answer. 2. Diltiazem
Question 112. Extraction of teeth with class III and IV furcation defects with advanced attachment loss may be indicated due to all the following criteria except:
- Inadequate plaque control
- Poor socioeconomic factors
- Good long-term prognosis
- Poor patient corporation
Answer. 3. Good long-term prognosis
Question 113. Signs of TFO are all the following except:
- Mobility of teeth
- Formation of pocket
- Periodontal ligament widening
- Tooth migration
Answer. 4. Tooth migration
Question 114. Brushing technique recommended in case of gingival recession is:
- Bass method
- Modified Bass method
- Modified Stillman’s method
- All of the above
Answer. 3. Modified Stillman’s method
Question 115. The objective of root planing is to remove:
- Plaque
- Necrotic cementum
- Calculus
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 116. The procedure that may be indicated to correct abnormal diastema between maxillary central incisor is:
- Frenectomy
- Frenotomy
- Both a and b
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Frenectomy
Question 117. All the following statements of periodontal surgical techniques are true except:
- Increases accessibility to root surface
- Reduce/eliminate pocket depth
- Replace soft and hard tissue to attain a harmonious topography
- Replacement of lost tooth structure
Answer. 4. Replacement of lost tooth structure
Question 118. Probe used in case of furcation involvement is:
- William’s periodontal probe
- UNC probe
- Naber’s probe
- All of the above
Answer. 3. Naber’s probe
Question 119. Kirkland knife is used in:
- Periodontal flap surgery
- Gingivectomy
- Scaling
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Gingivectomy
Question 120. Widening of attached gingiva accomplishes all of the following objectives, except:
- Enhances plaque removal from gingival margin
- Improves esthetics
- Reduces/eliminates marginal tissue recession
- Reduces inflammation around restored tooth
Answer. 3. Reduces/eliminates marginal tissue recession
Question 121. The transition from gingivitis to periodontitis:
- Always occur within 2 months
- Is accompanied by severe pain
- Occurs as a result of extension of inflammation into periodontal tissues
- None of the above
Answer. 4. None of the above
Question 122. ANUG (NUG) does not usually lead to periodontal pocket formation because:
- There is no destruction of periodontal structures
- It is an acute condition
- Lack of periodontal microorganisms
- Necrotic changes involve junctional epithelium
Answer. 4. Necrotic changes involve junctional epithelium
Question 123. Marginal gingiva is unaffected by trauma from occlusion because:
- It is keratinized
- Its blood supply is sufficient to maintain it
- It is firmly attached to underlying alveolar bone
- All of the above
Answer. 2. Its blood supply is sufficient to maintain it
Question 124. Aggressive periodontitis is characterized by:
- Rapid rate of progression
- Slow rate of progression
- Plaque and calculus
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Rapid rate of progression
Question 125. The mucogingival line can be demarcated by:
- Using Naber’s probe
- Drying the gingiva
- With Schiller’s solution
- Fremitus test
Answer. 3. With Schiller’s solution
Question 126. In modified Widman’s flap:
- Crevicular incision is made from the base of pocket to the bone
- Internal bevel incision is made from base of the pocket to the bone
- Indicated only in anterior teeth
- Indicated only in teeth with gingival recession
Answer. 1. Crevicular incision is made from the base of pocket to the bone
Question 127. Dental calculus contains:
- Vital microorganisms
- Nonvital microorganisms
- Both of the above
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Nonvital microorganism
Question 128. The diagnosis and evaluation of periodontal pocket is best done by:
- Radiographs
- Using disclosing agents
- Periodontal probing
- Periodontal surgery
Answer. 3. Periodontal probing
Question 129. The cells responsible for bone resorption are:
- Fibroblasts
- Cementoblasts
- Osteoblasts
- Osteoclasts
Answer. 4. Osteoclasts
Question 130. Which of the following cell type contain a vasoactive amine that is released in the inflammatory process and is active in causing vascular permeability?
- B-lymphocyte
- T-lymphocyte
- Mast cells
- Plasma cells
Answer. 3. Mast cells
Question 131. Group of fibers considered as belonging to gingival due to their non-osseous attachment are:
- Alveolar crest fibers
- Horizontal fibers
- Apical fibers
- Transseptal fibers
Answer. 4. Transseptal fibers
Question 132. One of the following is related to the theories pertaining to the mechanism of tooth support:
- Hydrodynamic theory
- Viscoelastic system theory
- Ecologic plaque hypothesis
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Viscoelastic system theory
Question 133. Average width of PDL space documented is:
- 0.002 mm
- 0.02 mm
- 0.2 mm
- 2 mm
Answer. 3. 0.2 mm
Question 134. In the AAP 1999 International Workshop for Classification of Periodontal Disease, gingival disease of viral origin are classified under:
- Dental plaque induced gingival lesions
- Non-plaque induced gingival lesions
- Periodontitis as manifestation of systemic disease
- Aggressive periodontitis
Answer. 2. Non-plaque induced gingival lesions
Question 135. Mechanism of coating a pathogen with recognizable ligand to enable the phagocyte to and ingest pathogens is known as:
- Phagocytosis
- Chemotaxis
- Ag-presentation
- Opsonization
Answer. 4. Opsonization
Question 136. Stippling is absent in:
- Adults
- Teenagers
- Children between the age of 5 to 12 years
- Infants
Answer. 4. Infants
Question 137. Focal infection theory was developed in 1900 by:
- PD Miller
- William Hunter
- WD Miller
- Socransky
Answer. 2. William Hunter
Question 138. Pocket resulting due to gingival enlargement is:
- Gingival pocket
- Pseudo pocket
- Relative pocket
- All of the above
Answer. 2. Pseudo pocket
Question 139. Most common complication associated with tortuous pocket is:
- ANUP
- ANUG
- Periodontal pockets
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 140. Most tolerating probing force is:
- 0.25 N
- 0.50 N
- 0.75 N
- 0.95 N
Answer. 3. 0.75 N
Question 141. The root most often retained following resection of mandibular molar is:
- Mesial root
- Distal root
- All of the above
- None of the above
Answer. 3. All of the above
Question 142. Critical zones in pocket surgery include all of the following except:
- The soft tissue wall
- The tooth surface wall
- The bone
- The attached gingiva
Answer. 2. The tooth surface wall
Question 143. Most ideal result of periodontal therapy is achieved by:
- New attachment
- Epithelial adaptation
- None of the above
- All of the above
Answer. 1. New attachment
Question 144. Bioactive glass is:
- Isograft
- Xenograft
- Allograft
- Alloplast
Answer. 4. Alloplast
Question 145. Exposure of the teeth by apical migration of gingiva is known as:
- Supraeruption
- Passive eruption
- Active eruption
- Transcription
Answer. 2. Passive eruption
Question 146. Cementum overlaps the enamel in % of cases:
- 5 to 10%
- 60 to 65%
- 90 to 100%
- 2 to 5%
Answer. 2. 60 to 65%
Question 147. The proportion of persons in the population who have the disease of interest at a given point of time is:
- Incidence
- Risk
- Prevalence
- Gingivitis
Answer. 3. Prevalence
Question 148. All of the following are included in phase I therapy except:
- Calculus removal and root planning
- Antimicrobial therapy
- Minor orthodontic movement
- Endodontic therapy
Answer. 4. Endodontic therapy
Question 149. Distance between the gingival margin and base of pocket is referred as:
- Biologic width
- Probing depth
- Biological depth
- Clinical attachment
Answer. 2. probing depth
Question 150. Periodontitis is considered to be localized, if:
- > 30% of sites are involved
- < 30% of sites are involved
- > 50% of sites are involved
- < 50% of sites are involved
Answer. 2. < 30% of sites are involved
Question 151. Periodontal abscess is also known as:
- Periapical abscess
- Gingival abscess
- Lateral abscess
- Pericoronal abscess
Answer. 3. Lateral abscess
Question 152. Which one of the following process is also referred as “healing by scar”?
- Regeneration
- Repair
- New attachment
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Repair
Question 153. Which one of the following is a putative periodontal pathogen?
- Actinomyces naeslundii
- Actinomyces viscosus
- Streptococcus sanguinis
- Porphyromonas gingivalis
Answer. 4. Porphyromonas gingivali
Question 154. Which stage of gingivitis is called as subclinical gingivitis?
- Initial lesion
- Early lesion
- Established lesion
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Initial lesion
Question 155. Gracey curette is the instrument of choice for:
- Removal of subgingival calculus
- Removal of soft tissue lining pocket
- Root planing and removal of altered cementum
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 156. According to current followed classification of periodontitis (AAP – 1999), which one of the following is not a type of periodontitis?
- Aggressive periodontitis
- Chronic periodontitis
- Refractory periodontitis
- Periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic disease
Answer. 3. Refractory periodontitis
Question 157. Concentration of which one of the following drug is 2–10 times more in gingival cervice as compared to serum?
- Metronidazole
- Doxycycline
- Amoxicillin
- Ciprofloxacin
Answer. 2. Doxycycline
Question 158. Life preserver shaped enlargement of marginal gingiva is called as:
- McCall’s Festoon
- Gingival crater
- Widows peak
- Stillman’s cleft
Answer. 2. Gingival crater
Question 159. A 6-year-old boy presents with vesiculating painful ulcers with diffuse erythematous gingiva. Patient is also febrile with 102°F of temperature since 3 days and also has lymphadenopathy. The most likely diagnosis is:
- Herpes zoster
- Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
- Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
- Recurrent aphthous stomatitis
Answer. 3. Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
Question 160. Clinical attachment level is measured from:
- Gingival margin to base of pocket
- CEJ to the base of pocket
- CEJ to the gingival margin
- CEJ to the mucogingival junction
Answer. 2. CEJ to the base of pocket
Question 161. Mulberry shaped lesion is found in:
- Idiopathic gingival enlargement
- Enlargement associated with systemic disease
- Drug-induced gingival enlargement
- None of the above
Answer. 3. Drug-induced gingival enlargement
Question 162. Largest group of periodontal fibers:
- Horizontal group
- Transseptal group
- Oblique group
- Apical group
Answer. 3. Oblique group
Question 163. Thickness of periodontal ligament at alveolar crest at age of 11 to 16 years:
- 0.16 mm
- 0.20 mm
- 0.17 mm
- 0.23 mm
Answer. 4. 0.23 mm
Question 164. Cementum resorption may be caused by:
- Local factor
- Systemic factor
- Idiopathic factor
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 165. Bundle bone contains:
- Periodontal ligaments
- Sharpey’s fibers
- Cementum
- All of the above
Answer. 2. Sharpey’s fibers
Question 166. Punched out ulcers are found in:
- HIV lesions
- NUG
- Herpetic gingivostomatitis
- None of the above
Answer. 4. None of the above
Question 167. 0.5 mm probing depth of periodontal pockets, line of treatment is:
- Gingival curettage
- Gingivectomy
- Flap surgery
- All above
Answer. 3. Flap surgery
Question 168. Stippling is present with:
- Marginal gingiva
- Attached gingiva
- Mucogingival junction
- Alveolar mucosa
Answer. 2. Attached gingiva
Question 169. Citric acid used for root conditioning has pH:
- 3
- 2
- 1
- 4
Answer. 3. 1
Question 170. Pellagra is due to deficiency of:
- Thiamine
- Riboflavin
- Niacin
- Folic acid
Answer. 3. Niacin
Question 171. Principal cell of gingival epithelium is:
- Keratinocyte
- Giant cells
- Fibroblast
- All of the above
Answer. 1. Keratinocyte
Question 172. Orban’s knife is used for:
- Gingivectomy
- Curettage
- Root planning
- None
Answer. 1. Gingivectomy
Question 173. Lamina propria is another name of:
- Gingival connective tissue
- Alveolar bone
- Cementum
- All of the above
Answer. 2. Alveolar bone
Question 174. Cul–de–sac appearance is seen in:
- Grade 1 furcation
- Grade 2 furcation
- Grade 3 furcation
- Grade 4 furcation
Answer. 2. Grade 2 furcation
Question 175. Insertion angle of a curette is:
- 45 to 90°
- 45°
- 0°
- > 90°
Answer. 1. 45 to 90°
Question 176. Sulcular epithelium is:
- Orthokeratinized
- Parakeratinized
- Non-keratinized
- None
Answer. 3. Non-keratinized
Question 177. CBCT is an advancement in:
- Culture
- X-ray technique
- Immunofluorescence
- None
Answer. 2. X-ray technique
Question 178. Periodontium consists of:
- Gingiva
- Cementum
- Alveolar bone
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 179. Drug causes gingival enlargement:
- Penicillin
- Macrolides
- Nitroimidazole
- Cyclosporin
Answer. 4. Cyclosporin
Question 180. Kirkland knife is used in:
- Gingivectomy
- Flap surgery
- Laser surgery
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Gingivectomy
Question 181. The color of gingiva is due to:
- Capillaries
- Thickness of epithelium
- Thickness of keratinization
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 182. Cul-de-sac appearance is seen in:
- Grade 1 furcation involvement
- Grade 2 furcation involvement
- Grade 3 furcation involvement
- Grade 4 furcation involvement
Answer. 2. Grade 2 furcation involvement
Question 183. Insertion angle of a curette is:
- 0°
- 45°
- 90°
- >90°
Answer. 2. 45°
Question 184. Kirkland knife is used for:
- Curettage
- Gingivectomy
- Root planning
- Scaling
Answer. 2. Gingivectomy
Question 185. The following graft has best prognosis:
- Autograft
- Xenograft
- Both a and b
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Autograft
Question 186. Principle cells of gingival epithelium is:
- Keratinocyte
- Giant cells
- Fibroblasts
- All of the above
Answer. 1. Keratinocyte
Question 187. Drug of choice in dental infection:
- Penicillin
- Macrolide
- Nitroimidazole
- None
Answer. 1. Penicillin
Question 188. Periodontium consists of:
- Gingiva
- Cementum
- Alveolar bone
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 189. Periodontitis is the 6th complication of:
- COPD
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Diabetes mellitus
- All of the above
Answer. 3. Diabetes mellitus
Question 190. CBCT is an advancement in:
- X-ray technique
- Culture
- Microbiological methods
- Immunofluorescence method
Answer. 1. X-ray technique
Question 191. Gingival col is:
- Orthokeratinized
- Parakeratinized
- Both (a) and (b)
- Non-keratinized
Answer. 4. Non-keratinized
Question 192. Stippling is absent in:
- Infants
- Children
- Adolescents
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Infants
Question 193. The predominant immunoglobulin in saliva is:
- IgA
- IgG
- IgE
- IgD
Answer. 1. IgA
Question 194. McCall Festoons are seen in which teeth:
- Central incisors
- Canines and premolars
- Lateral incisors
- Molars
Answer. 2. Canines and premolars
Question 195. Which of the following is a common osseous lesion in periodontitis:
- Crater
- Fenestration
- Buttressing bone
- Ledge
Answer. 1. Crater
Question 196. Periochip contains:
- Metronidazole
- Tetracycline
- Chlorhexidine
- Doxycycline
Answer. 3. Chlorhexidine
Question 197. Demineralized freezed dried bone allograft is considered as:
- Osteoinductive
- Osteoconductive
- Osteogenic
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Osteoinductive
Question 198. Generalized gingival recession occurs in:
- TFO
- Faulty tooth brushing technique
- ANUG
- Pericoronitis
Answer. 2. Faulty tooth brushing technique
Question 199. Which of the following is mucogingival surgery:
- Gingivoplasty
- Widman’s flap
- Gingivectomy
- Free gingival graft
Answer. 4. Free gingival graft
Question 200. Method to increase attached gingiva is:
- Widman’s flap
- Undisplaced flap
- Apical flap
- Modified Widman flap
Answer. 3. Apical flap
Question 201. The sulcular epithelium is:
- Parakeratinized
- Non-keratinized
- Orthokeratinized
- None
Answer. 2. Non-keratinized
Question 202. Vertical loss of alveolar bone is seen in:
- Adult periodontitis
- Juvenile periodontitis
- Scleroderma
- Hyperparathyroidism
Answer. 2. Juvenile periodontitis
Question 203. Metronidazole is used for:
- Gingivitis
- HIV
- Periodontitis
- ANUG
Answer. 4. ANUG
Question 204. Dental floss is used to clean:
- Occlusal surfaces
- Mesial and distal surfaces
- Buccal and lingual surfaces
- Interdental region
Answer. 4. Interdental regopm
Question 205. Gingivectomy technique may be performed for:
- Elimination of bony pocket
- Elimination of gingival enlargement
- Elimination of suprabony periodontal abscess
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 206. The width of attached gingiva on the facial aspect is generally greater in:
- Maxillary molar area
- Mandibular molar area
- Mandibular incisor area
- Maxillary incisor area
Answer. 3. Mandibular incisor area
Question 207. Periochip is a commercially available local drug delivery system, containing:
- Doxycycline
- Chlorhexidine
- Minocycline
- Metronidazole
Answer. 2. Chlorhexidine
Question 208. Treatment of severe periodontitis in anterior region:
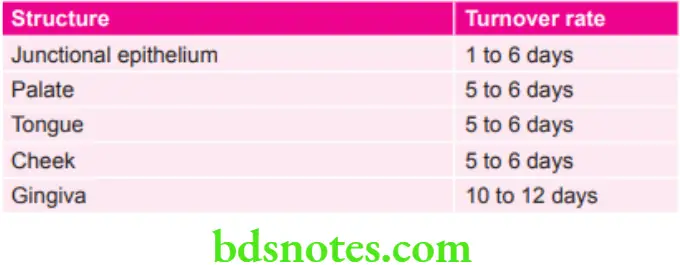
- Curettage
- Modified Widman flap
- Coronally displaced flap
- None
Answer. 4. None
Question 209. Predominant cells found in Stage III gingivitis are:
- PMNS
- Lymphocytes
- PMNs and lymphocytes
- Plasma cells
Answer. 4. Plasma cells
Question 210. Basic incision in periodontal surgery is:
- Internal bevel incision
- First incision
- Reverse bevel incision
- Crevicular incision
Answer. 1. Internal bevel incision
Question 211. Periodontal angular osseous defects are classified on the basis of:
- Number of bony walls remaining
- Number of bony walls lost
- Location of epithelial attachment
- None
Answer. 1. Number of bony walls remaining
Question 212. Major factors which determine stability of periodontal instruments are:
- Instrument grasp and sharpness
- Instrument grasp and finger rest
- Instrument grasp and dry field
- Instrument grasp and adaptation
Answer. 2. Instrument grasp and finger rest
Question 213. Mucogingival junction:
- Recedes with age
- Recedes with periodontitis
- Remains stationary throughout age
- Ascends with age
Answer. 3. Remains stationary throughout age
Question 214. Thickness of junctional epithelium at base of sulcus:
- 1 to 5 cell thick
- 5 to 10 cell thick
- 10 to 29 cell thick
- 30 to 50 cell thick
Answer. 3. 10 to 29 cell thick
Question 215. Dentogingival unit comprises of:
- Gingival fibers only
- Junctional epithelium and connective tissue attachment
- Junctional epithelium and periodontal ligament
- None
Answer. 4. None
Question 216. Following are the members of red complex, except:
- P. gingivalis
- T. denticola
- P. intermedia
- B. Forsythus
Answer. 3. P. intermedia
Question 217. Most abundant principal fiber of periodontal ligament is:
- Alveolar crest group
- Horizontal group fiber
- Oblique group fiber
- None
Answer. 3. Oblique group fiber
Question 218. Periodontal flap indicated to increase the width of attached gingiva:
- Undisplaced flap
- Apically displaced flap
- Kirkland flap
- Modified Widman flap
Answer. 2. Apically displaced flap
Question 219. Example of automated periodontal probe is:
- Nabers probe
- Williams probe
- CPITN probe
- Florida probe
Answer. 4. Florida probe
Question 220. Angle of insertion of instrument beneath the gingival margin is:
- Between 0 to 40 degree
- Between 40 to 90 degree
- More than 90 degree
- None
Answer. 1. Between 0 to 40 degree
Question 221. Which one of the following procedure increases width of keratinized gingiva:
- Modified Widman flap
- Undisplaced flap
- Apically displaced flap
- Coronally displaced flap
Answer. 3. Apically displaced flap
Question 222. In which one of the following condition there is no change in gingival fluid:
- Chronic gingivitis
- Pregnancy
- Periodontal abscess
- Trauma from occlusion
Answer. 4. Trauma from occlusion
Question 223. Loss of attachment is measured from:
- Crest of gingiva to base of pocket
- CEJ to base of pocket
- CEJ to crest of gingival margin
- None of the above
Answer. 2. CEJ to base of pocket
Question 224. In which one of the following it is most difficult to predict the prognosis:
- Acute periodontal abscess
- Chronic periodontitis
- Aggressive periodontitis
- Inflammatory gingival enlargement
Answer. 3. Aggressive periodontitis
Question 225. Which stage of gingivitis is also called as subclinical gingivitis:
- Initial lesion
- Early lesion
- Advanced lesion
- Established
Answer. 1. Initial lesion
Question 226. Radius of action of bacterial plaque or inducing bone loss is:
- 0.1 to 0.5 mm
- >2.5 mm
- 2.5 to 3.5 mm
- 1.5 to 2.5 mm
Answer. 4. 1.5 to 2.5 mm
Question 227. Which one of the following is known to have tactile perception:
- Merkel cells
- Langerhans cells
- Melanocytes
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Merkel cells
Question 228. Which one of the following smoking does not lead to:
- Increased gingival bleeding
- Increased periodontal destruction
- Increased attachment loss
- Increased subgingival temperature
Answer. 4. Increased subgingival temperature
Question 229. Which one of the following is a type of pedicle gingival autograft:
- Laterally displaced
- Coronally displaced
- Semilunar coronally displaced
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 230. Which one of the following is most predictable technique of pocket reduction:
- Reconstructive osseous surgery
- Periodontal flaps
- Curettage
- Resective osseous surgery
Answer. 4. Resective osseous surgery
Question 231. Radicular blending is a…………………….procedure
- Osteotomy procedure
- Ostectomy procedure
- Osteoplasty procedure
- Both a and b
Answer. 3. Osteoplasty procedure
Question 232. Linear gingival erythema is a characteristic feature of:
- ANUG
- Acute herpetic gingivostomatitis
- HIV gingivitis
- Chronic gingivitis
Answer. 3. HIV gingivitis
Question 233. The distance between junctional epithelium and alveolar bone:
- Increases with age
- Remains constant
- Decreases with age
- None
Answer. 2. Remains constant
Question 234. Pattern of bone destruction in periodontal defect is affected by:
- Tooth mobility
- Depth of pocket
- Presence of pus
- Pathway of inflammation
Answer. 2. Depth of pocket
Question 235. Which organism is increased in pregnant females:
- P. melanogenica
- E. corrodens
- P. gingivalis
- P. intermedia
Answer. 4. Intermedia
Question 236. Predominant gingival group affected by early lesion in gingiva:
- Circular and horizontal
- Circular and oblique
- Circular and dentogingival
- None
Answer. 3. Circular and dentogingival
Question 237. Glucose level in GCF is:
- 3 to 4 times greater than serum level
- Zero
- Equal to serum level
- None
Answer. 1. 3 to 4 times greater than serum level
Question 238. Commonest plunger cusp is:
- Buccal cusp of second mandibular molar
- Distolingual cusp of second maxillary molar
- Lingual cusp of mandibular premolar
- All of the above
Answer. 2. Distolingual cusp of second maxillary molar
Question 239. Trauma from occlusion affects following except:
- Epithelial attachment
- Cementum
- Periodontal ligament
- Enamel
Answer. 1. Epithelial attachment
Question 240. Bioactive glass is a:
- Isograft
- Alloplast
- Allograft
- Xenograft
Answer. 2. Alloplast
Question 241. Gracey curettes use to scale distal surface of posterior teeth are:
- Gracey curette ½, 13/14 & 11/12
- Gracey curette 11/12, 13/14 & 5/6
- Gracey curette 7/8 & 9/10
- Gracey curette 13/14 & 17/18
Answer. 4. Gracey curette 13/14 & 17/18
Question 242. 6th complication of diabetes mellitus is:
- Retinopathy
- Neuropathy
- Nephropathy
- Periodontitis
Answer. 4. Periodontitis
Question 243. All of the following are periodontal phases of treatment plan except:
- Surgical phase
- Maintenance phase
- Non-surgical phase
- Refractory phase
Answer. 4. Refractory phase
Question 244. Which of the following is a BANA (Benzoyl-argininenaphthylamide) based chair side diagnostic kit:
- Periocheck
- Perioscan
- Periogard
- Periotemp
Answer. 2. Perioscan
Question 245. The turnover rate of junctional epithelium has been estimated to be:
- Approximately 3 days
- Approximately 6 days
- Approximately 10 days
- Approximately 14 days
Answer. 2. Approximately 6 days
Question 246. Elastase is capable of degrading:
- Elastin
- Collagen
- Fibronectin
- Any of the above
Answer. 1. Elastin
Question 247. In advanced lesion of gingival inflammation we can see:
- Loss of periodontal connective tissue attachment
- Plasma cells contributing > 50% of all cell types
- Alveolar bone loss
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All the above
Question 248. C-reactive protein (CRP) synthesis is controlled by:
- IL-1
- IL-6
- IL-10
- IL-13
Answer. 2. IL-6
Question 249. Actinomycetemcomitans bacteriocins are active against:
- S. sanguis
- S. uberis
- A. viscosus
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 250. The ecological plaque hypothesis has been proposed by:
- Walter Loesche
- PD Marsh
- Theilade
- Socransky
Answer. 2. PD Marsh
Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. Close opposition of the gingival epithelium to the tooth surface without complete obliteration of the pocket is called as ……………
Answer. Epithelial adaptation
Question 2. The junctional epithelium replaces itself approximately every …………… Days.
Answer. 7
Question 3. The most effective and stable grasp for all periodontal instruments is ……………
Answer. Modified pen grasp
Question 4. Subclinical gingivitis represents gingival inflammation in the …………… stage
Answer. Initial
Question 5. An endotoxin which is targeted against epithelial cells is ……………
Answer. Lipooligosaccharide
Question 6. The carbohydrate present in greatest amount in the matrix of supragingival plaque is ……………
Answer. Dextran
Question 7. Punched out crater-like depressions at the crest of interdental papillae are characteristic of ……………
Answer. Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG)
Question 8. Most effective mechanical interdental cleansing aid used in Type I embrasure is ……………
Answer. Dental floss
Question 9. The only scaler which is used with push stroke is……………
Answer. Chisel Scaler
Question 10. Hemorrhage which usually occurs few days after surgery is referred to as ……………
Answer. Reactionary hemorrhage
Question 11. Cementum is defined as ……………
Answer. Cementum is a calcified avascular mesenchymal tissue that forms the outer covering of anatomic root.
Question 12. Drugs causing gingival enlargement are ……………
Answer. Anti-convulsants, immunosuppressant, calcium-channel blockers
Question 13. Dental plaque is defined as ……………
Answer. “Dental plaque is defined as a soft deposit that forms the biofilm adherent to tooth surface or other hard surfaces in oral cavity including removable and fixed restorations”.
Question 14. Oral manifestations of diabetes mellitus are ……………
Answer. Following are the oral manifestations of diabetes mellitus:
- Burning mouth syndrome
- Candidiasis
- Gingivitis
- Dental caries
- Glossodynia
- Lichen planus
- Periodontitis
- Salivary dysfunction
- Taste dysfunction
- Xerostomia.
Question 15. Gingival index was given by ……………
Answer. Loe H and Silness J (1963)
Question 16. Classify periodontic-endodontic lesions ……………
Answer. Classification by Rotstein and Simon (2004)
- Endodontic
- Periodontal
- Combined diseases:
Classification based on theoretical pathways
- Primary endodontic lesions
- Primary periodontal diseases
- Combined diseases.
- Primary endodontic disease with secondary periodontal involvement
- Primary periodontal disease with secondary endodontic involvement
- True combined lesions.
Question 17. Periodontic plastic surgery is defined as ……………
Answer. Periodontal plastic surgery is defined as “the surgical procedures performed to correct or eliminate anatomic, developmental or traumatic deformities of gingival or alveolar mucosa”.
Question 18. Theories of dentinal hypersensitivity are ……………
Answer. Neural theory, odontoblastic transduction theory, hydrodynamic theory, modulation theory.
Question 19. Causes of gingival recession are ……………
Answer. Following are the causes of gingival recession:
- Tooth malposition or position of tooth in arch.
- Presence of dehiscence and fenestration
- Gingival ablation from soft tissues.
- Faulty toothbrushing habit.
- Primary trauma from occlusion
- Orthodontic movement in labial direction
- Improper restorations
Question 20. Osseointegration term is defined as ……………
Answer. Osseointegration is defined as “direct structural and functional connection between ordered, living bone and the surface of a load carrying implant”.
Osseointegration is defined as “a contact established between normal and remodeled bone and an implant surface without the interposition of the non bone and connective tissue”.
Important Numerical Values
Areas of Narrow and Broad Periodontal Ligament

Various Keratin Proteins and their Important Characteristics

Various Areas Along with Presence of Histological Bone

Various Microbes in Children and Adult Plaque

Enumeration of Bacterias which Invade Host Tissue Cells Directly
- A. actinomycetemcomitans
- P. gingivalis
- F. nucleatum
- T. denticola
Enumeration of Various Primary Colonizers inDental Plaque
- Streptococcus gordonii
- Streptococcus intermedius
- Streptococcus mitis
- Streptococcus oralis
- Streptococcus sanguinis
- Actinomyces gerencserial
- Actinomyces israelii
- Actinomyces naeslundii
- Actinomyces oris
- Actinomyces odontolyticus
- Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype a
- Capnocytophaga gingivalis
- Capnocytophaga ochracea
- Capnocytophaga sputigena
- Eikenella corrodens
- Veillonella parvula
Enumeration of Various Secondary Colonizers in Dental Plaque
- Campylobacter gracilis
- Campylobacter rectus
- Campylobacter showae
- Eubacterium nodatum
- Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype b
- Fusobacterium nucleatum ssp nucleatum
- Fusobacterium nucleatum ssp vincentii
- Fusobacterium nucleatum ssp polymorphum
- Fusobacterium periodonticum
- Parvimonas micraPrevotella intermedia
- Prevotella loescheii
- Prevotella nigrescens
- Streptococcus constellatus
- Tannerella forsythia
- Porphyromonas gingivalis
- Treponema denticola
Various Types of MMPs (Matrix Metalloproteinases) and Their Names

Various Methods of Collecting and Measuring GCF
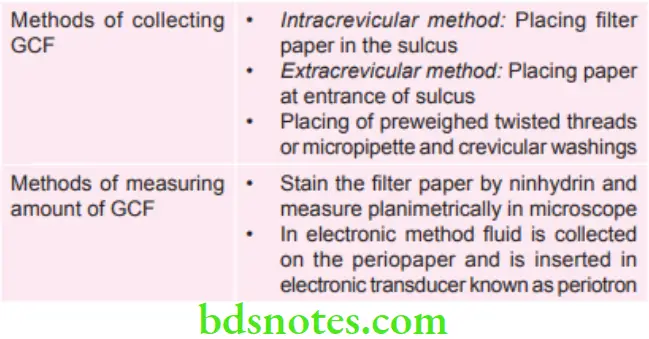
Enzymes of GCF
- Lysosomal enzyme is beta-glucuronidase
- Cytoplasmic enzyme is lactic acid dehydrogenase
- Collagenases secreted by PMN and fibroblasts
- Lysosomal enzyme is phospholipase
Sigmund Socransky Criteria
In this criterion, periodontal microorganisms are judged to be the potential pathogens. Following is the criteria:
- Be associated with the disease with increase in number of organisms at diseases sites.
- Be eliminated or decreased with treatment.
- Should demonstrate host response
- Should demonstrate virulence factors
- Be capable of causing disease in experimental animals
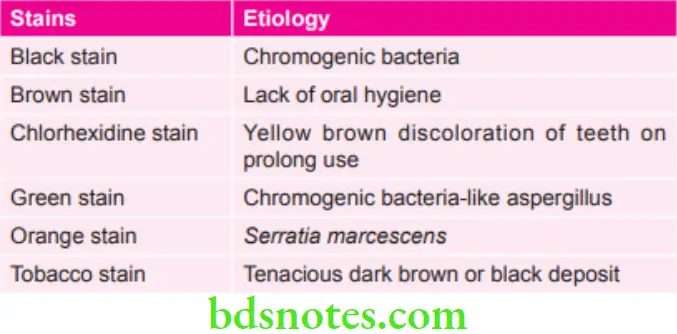
Various Stains and their Etiology
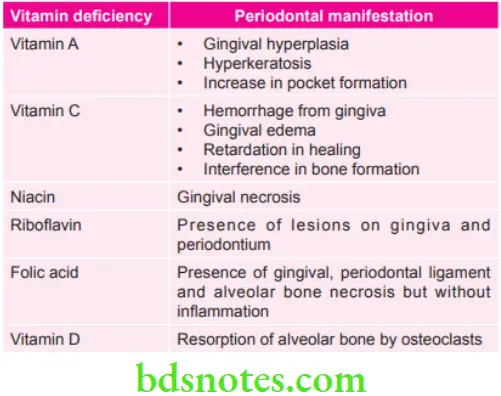
Various Vitamin Deficiencies and their Periodontal Manifestations
Various Metals Leading to Gingival Pigmentation

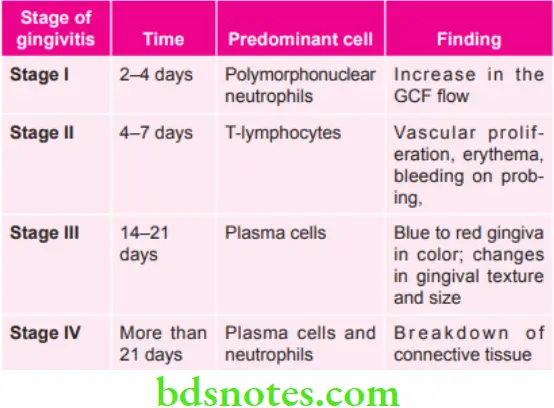
Stages of Gingivitis and their Features
Enumeration of Inflammatory Hyperplasia
- Epulis fissuratum
- Epulis granulomatosum
- Fibroma
- Hormonal tumor
- Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
- Parulis
- Peripheral giant cell granuloma
- Peripheral ossifying fibroma
- Pulp polyp
- Pyogenic granuloma
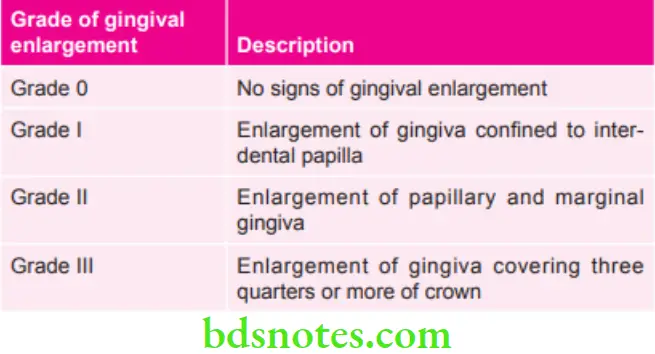
Various Grades of Gingival Enlargement
Staging of ANUG by Horning and Cohen
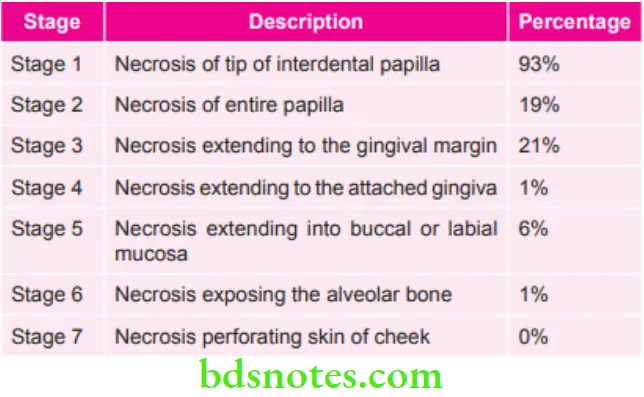
Staging of Oral Necrotizing Diseases by Horning and Cohen

Various Types of Pockets

Enumeration of Diseases in which Defective Neutrophil Function is Present
- Agranulocytosis
- Chèdiak-higashi syndrome
- Diabetes mellitus
- Juvenile periodontitis
- Neutropenia
- Papillon-Lèfevre syndrome
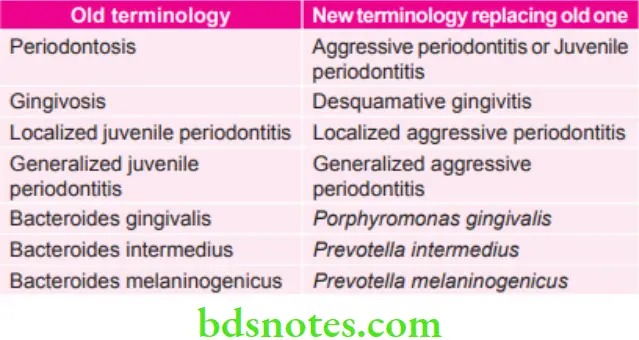
New Names of Old Terminology
Enumeration of Systemic Diseases in Which Prepubertal Periodontitis is Seen
- Blood dyscrasias, i.e. leukemia
- Chèdiak-Higashi syndrome
- Down’s syndrome
- Hypophosphatasia
- Neutropenia
- Papillon-Léfevre syndrome
Grading of Mobility of Tooth by Miller

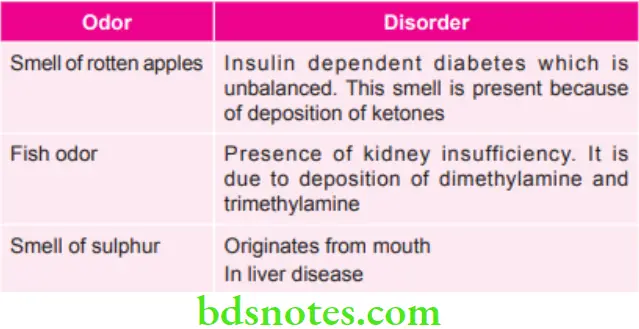
Specific Characteristic of an Odor Which Give Clue for Disease
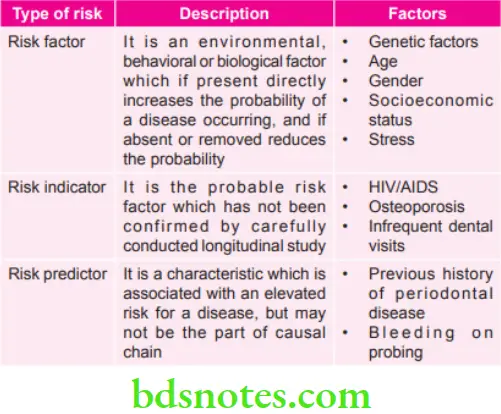
Various Risks in Periodontal Diseases
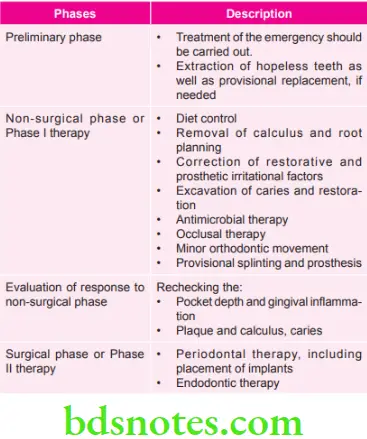
Summary of Various Phases of Periodontal Therapy
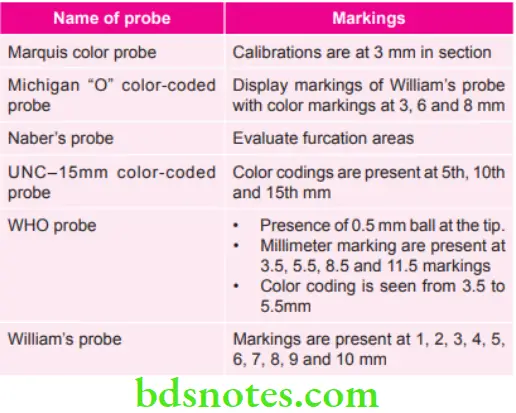
Markings Present of Various Probes
Various Finger Rests

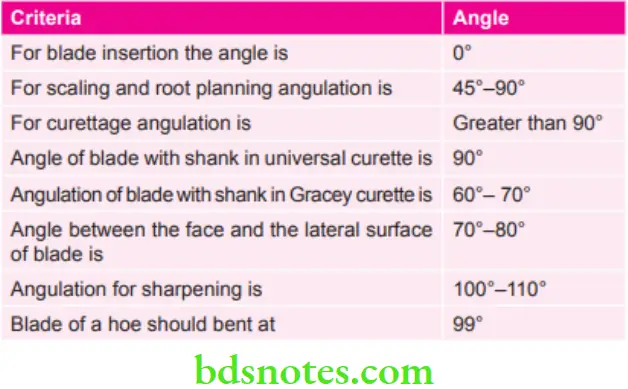
Various Angles used in Instrumentation of Periodontal Instruments
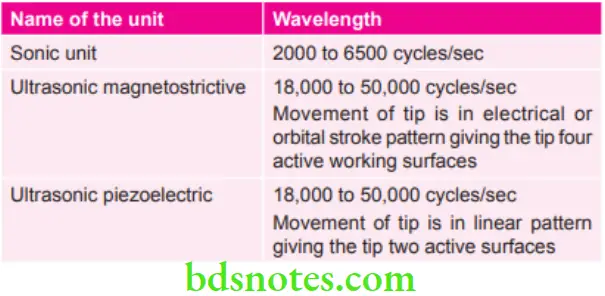
Wavelengths of Sonic and Ultrasonic Instruments
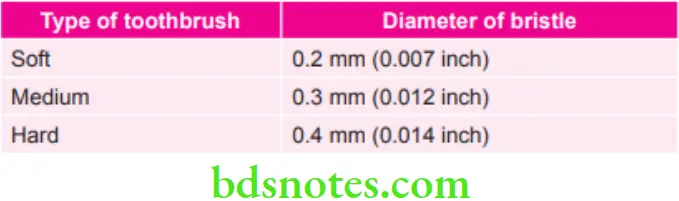
Various Types of Toothbrush with Diameter of their Bristles
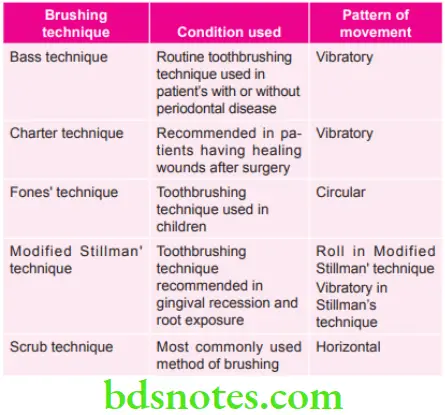
Various Brushing Techniques used in Various Conditions and their Pattern of Movement
Various Embrasures and their Cleaning Aids

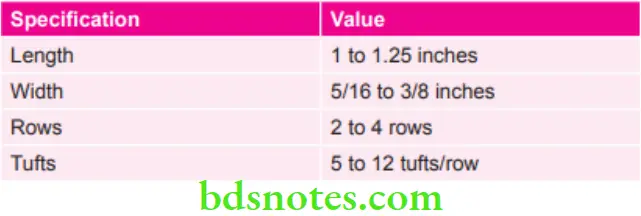
According to ADA Specifications of Toothbrush
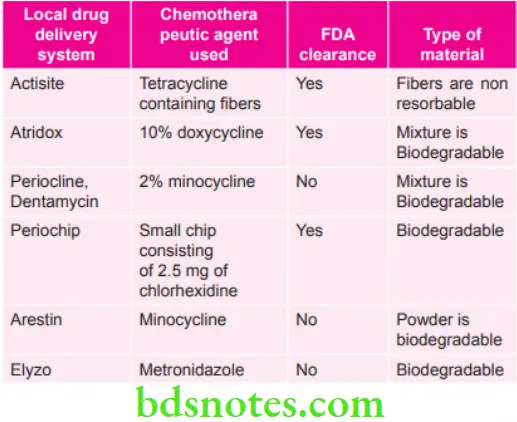
Various Local Drug Delivery Systems
Concept of Full Mouth Disinfection
- Full mouth debridement i.e scaling and root planning completed within 24 hour period
- Brush the tongue with 1% chlorhexidine gel for 1 min.
- Rinse mouth with 0.2% chlorhexidine solution for 2 min.
- Irrigate periodontal pockets with 1% chlorhexidine solution
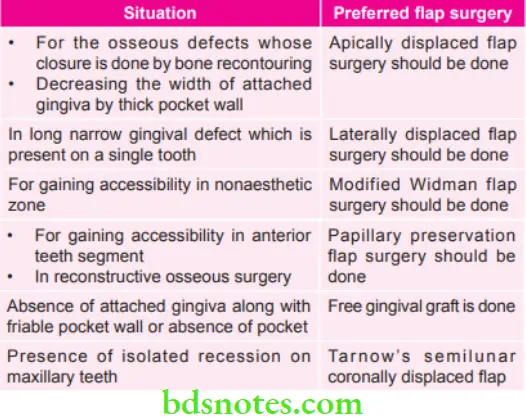
Various Situations and Preferred Flap Surgeries in Them
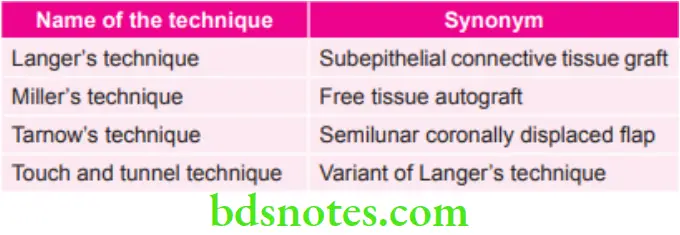
Various Techniques and their Synonyms
Classification of Gingival Recession given by Miller

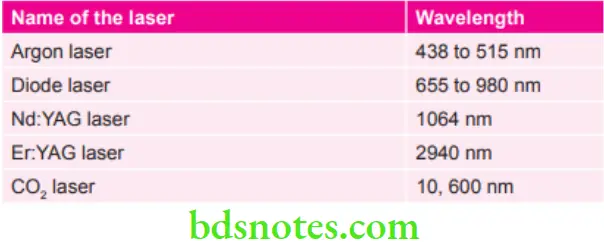
Classification of Various LASERs

Wavelengths of Various Lasers
Various Elements of Implants

Various Numerical Values Regarding Placement ofImplant in Posterior Area

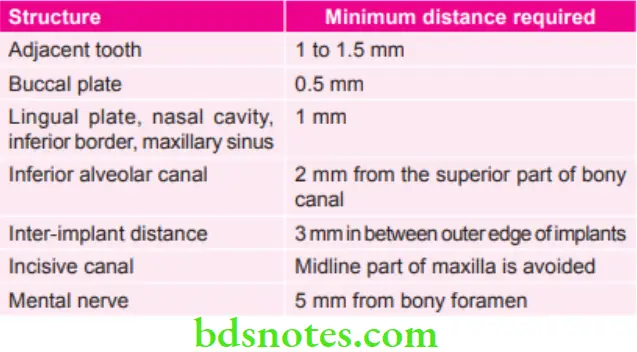
Minimum Distance Required Between Implants and Indicated Structures
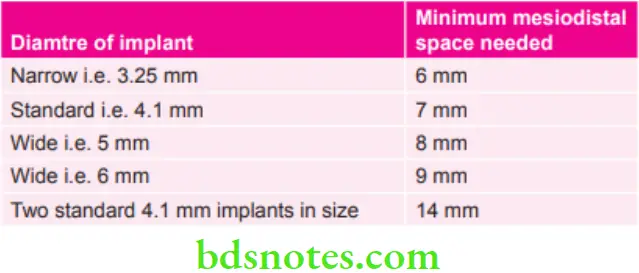
Minimum Mesiodistal Space Needed for Placing the Implants
Various Turnover Rates
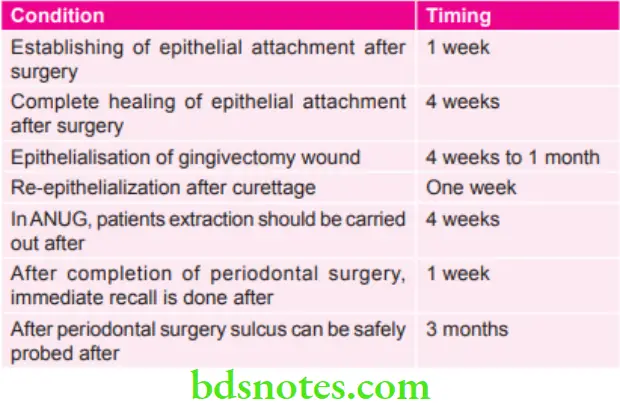
Various Conditions and their Timings
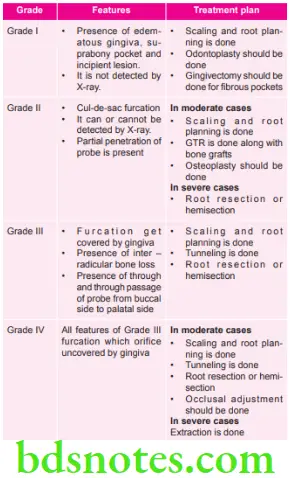
Various Types of Furcations, their Featuresand Treatment
Various American Gracey Curettes

Various Langer Curettes

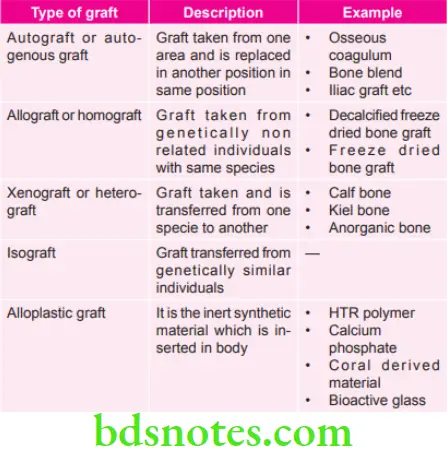
Various Types of Grafts
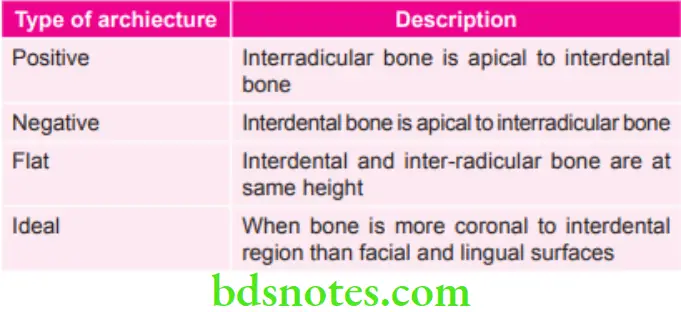
Various types of Architectures
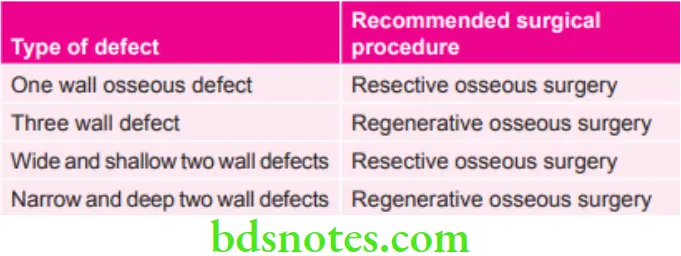
Various types of Defects and Recommended Surgical Procedures in Them
Organoleptic Rating by the Judge for Testing Breadth Malodor

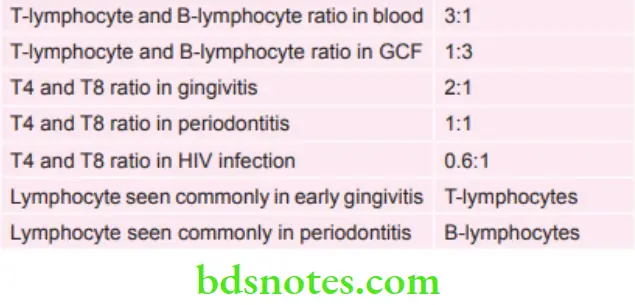
Some Information about the Lymphocytes
Chemotherapeutic Agents in Local Drug Delivery System
- Actisite – Tetracycline containing fibers
- Atridox – 10% doxycycline
- Periocline – 2% minocycline
- Periochip – a small chip consists of 2.5mg of chlorhexidine
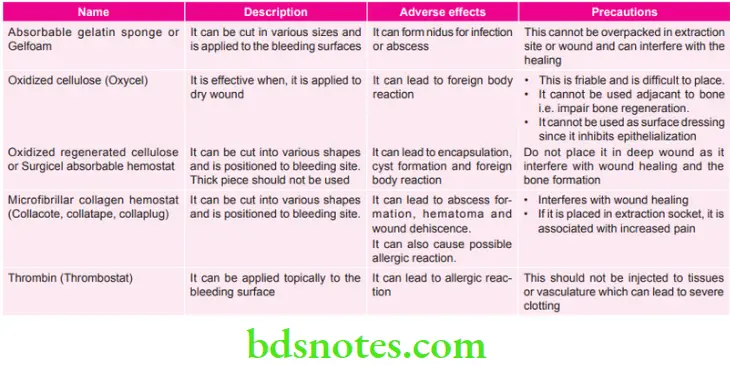
Various Absorbable Hemostatic Agents
Various Electrodes and their Uses


Leave a Reply