Periodontal Flap
Question 1. Define and classify periodontal flaps.
Or
Write short note on types of periodontal flap.
Answer. Periodontal flap is a section of gingiva and/or mucosa surgically elevated from underlying tissues to provide visibility and access to bone and root surface.
Classification/Types of Flap
According to thickness of flap/bone exposure after flap reflection:
- Full thickness/mucoperiosteal flap: All the soft tissues including periosteum are elevated.
- Partial thickness/mucosal flap/split thickness flap: reflection of only the epithelium and a layer of underlying connective tissue.
According to the placement of flap after surgery:
- Non-displaced flap: Flap is returned and suture back to its original position.
- Displaced flap: Flap is repositioned coronal, apical or lateral to its original position. e.g. lateral displaced flap, coronally displaced flap, apically displaced flap.
Read And Learn More: Periodontics Question And Answers
According to design of flap/management of the papilla:
- Conventional flap: Splitting the papilla into facial half and lingual/palatal half, e.g. modified Widman flap, undisplaced flap, apically displaced flap.
- Papilla preservation flap: Entire papilla is incorporated into one of the flaps.
Question 2. Classify periodontal flap used in pocket therapy. Describe modified Widman flap in detail (Draw diagram).
Or
Discuss in detail modified Widman who procedure.
Or
Define flap. Classify periodontal flaps. Discuss in detail modified Widman flap.
Or
Classify periodontal flaps write in detail modified Widman flap surgery.
Or
Define periodontal flap and give its classification. Describe modified Widman flap in detail.
Or
Classify flap and describe modified Widman flap.
Or
Define and classify periodontal flaps. Describe the technique of modified widman flap and a note about healing.
Or
Define and classify periodontal flaps. Write in detail about modified Widman flap.
Or
Define and classify periodontal flaps. Describe the technique of modified Widman flap and a healing process.
Or
Define and classify periodontal flaps. Describe modified Widman flap in detail.
Answer. Periodontal flap is a section of gingiva and/or mucosa surgically elevated from underlying tissues to provide visibility and access to bone and root surface.
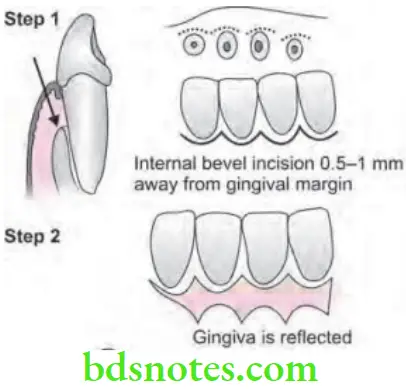
Modified Widman Flap
It is presented in 1974 by Ramfjord and Nissle.
- Step 1: It is an initial, internal bevel incision 0.5 to 1 mm away from gingival margin, directed to alveolar crest. Vertical releasing incisions are not required.
- Step 2: Gingiva is reflected with periosteal elevator.
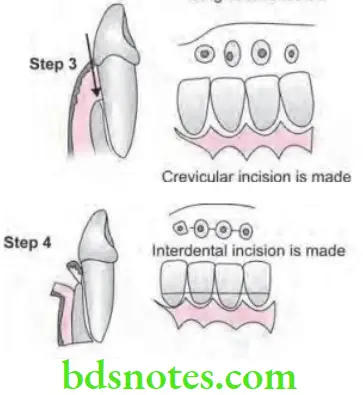
- Step 3: A crevicular incision is made from bottom of the pocket to the bone, circumscribing the triangular wedge of tissue containing pocket lining.
- Step 4: After flap is reflected, third incision is made in interdental space with Orban’s knife and gingival collar is removed.
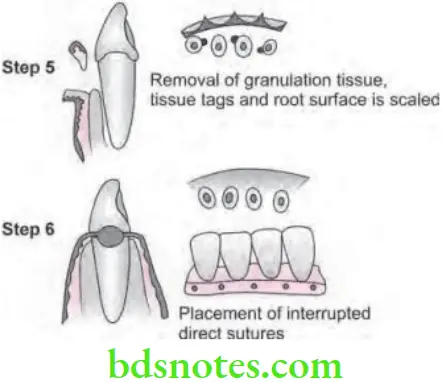
- Step 5: Tissue tags and granulation tissue are removed with a curette. The root surfaces are checked and scaled.
- Step 6: Bone architecture is not corrected, good approximation of flaps is necessary. Every effort is made to adapt the facial and lingual interproximal tissue adjacent to each other in such a way that no interproximal bone remain exposed at the time of suturing.
- Step 7: Interrupted direct sutures are placed in each inter dental space and covered with tetracycline ointment and with a periodontal surgical pack
Healing After Flap Surgery
- Immediately after suturing (0 to 24 hours), connection between the flap and the tooth or bone surface is established by the blood clot, which consists of a fibrin reticulum with many polymorphonuclear leukocytes, erythrocytes, debris from injured cells and capillaries at the edge of the wound. There are also bacteria and an exudate or transudate as a result of tissue injury.
- One to three days after flap surgery: Space between the flap and the tooth or the bone is thinner and epithelial cells migrate over the border of the flap, when the flap is closely adapted to the alveolar process there is only a minimal inflammatory response.
- One week after flap surgery: Epithelial attachment to the root has been established by means of hemidesmosomes and a basal lamina. The blood clot is replaced by granulation tissue derived from gingival connective tissue, bone marrow and the periodontal ligament.
- Two weeks after surgery: Collagen fibers begin to appear parallel to the tooth surface. Union of the flap and the tooth is still weak (due to immature collagen fibers) but clinically it appears almost normal.
- One month after surgery: A fully epithelialized gingival crevice with a well defined epithelial attachment is present. Supracrestal fibers begin to adapt a functional arrangement.
Question 3. Classify periodontal flap. Describe step-by-step procedure for flap surgery.
Answer.
Following are the flap techniques:
- Modified Widman flap.
- Undisplaced flap.
- Palatal flap.
- Apically displaced flap.
- Distomolar surgery.
Undisplaced Flap
In this procedure, the entire soft tissue pocket wall is removed with initial incision.
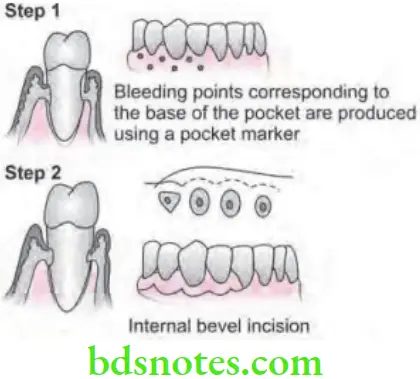
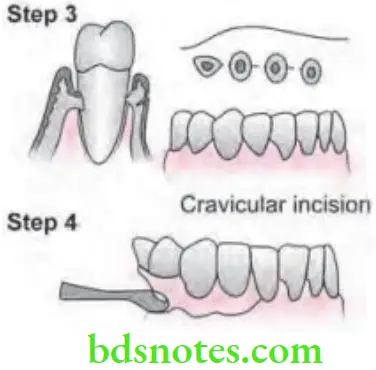
- Step 1: Pockets are measured with periodontal probe and bleeding point is produced on the outer surface of gingiva to mark the base of the pocket. In this procedure, final placement of flap is determined by first incision.
- Step 2: Initially, internal bevel incision is made following the scalloping bleeding points made on the gingiva, incision is usually carried to a point apical to alveolar crest depending on thickness of tissue. The thicker the tissue, more apical will be the end point of the incision.
- Step 3: The second or crevicular incision is made from the bottom of pocket to bone to detach connective tissue from bone.
- Step 4: Flap is then reflected with periosteal elevator.
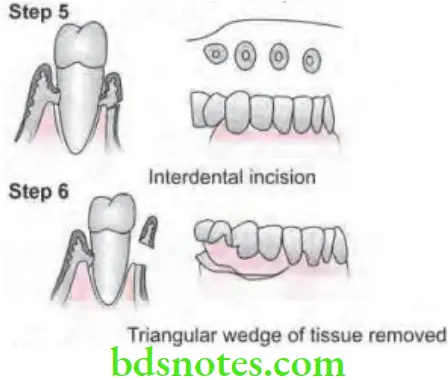
- Step 5: Interdental incision is made with a interdental knife.
- Step 6: Triangular wedge of tissue is created by three incisions removed with a curette.
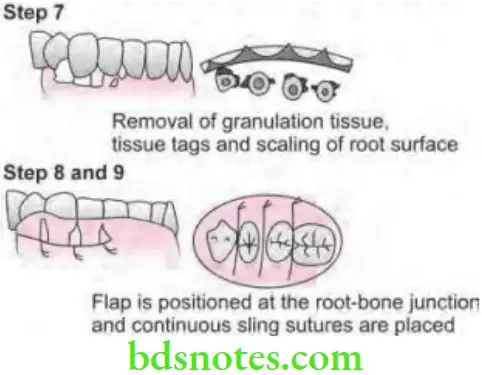
- Step 7: Area is debrided, removing tissue tags and granulation tissue with sharp curette. The roots are scaled.
- Step 8: Flap is then placed back to end at root bone junction.
- Step 9: Flaps are sutured together with continuous sling suture or interrupted sutures.
Question 4. Enumerate the methods of pocket elimination. Describe the rationale and procedure of modified Widman flap surgery.
Answer. The methods of pocket elimination are as follows:
- New attachment techniques:
- Excision new attachment procedure.
- Ultrasonic curettage
- Removal of pocket wall:
- Retraction or shrinkage by scaling and root planning.
- Surgical removal by gingivectomy technique or undisplaced flap.
- Apical displacement with an apically displaced flap.
- Removal of tooth side of pocket, which involves either extraction of tooth or hemisection.
Rationale
- To expose root surfaces for instrumentation.
- For removal of pocket lining.
Question 5. What are indications for mucogingival surgery? Describe apically displaced flap surgery.
Answer. Mucogingival surgery refers to periodontal surgical procedures designed to correct defect in morphology, position and/or amount of gingiva surrounding the teeth.
Mucogingival Surgery Indications
- Augmentation of edentulous ridge.
- Prevention of ridge collapse associated with tooth extraction.
- Crown lengthening.
- Loss of interdental papilla which presents as esthetic/phonetic defect.
Apically Displaced Flap Surgery
Used for both pocket irradiation and widening of zone of attached gingiva:
- Step 1: Internal bevel incision is made 1 mm from the crest of the gingiva and directed towards the crest of the bone.
- Step 2: Crevicular incision is made followed by initial elevation of flap and than interdental incision is performed, the wedge of the tissue containing the pocket wall is removed.
- Step 3: Vertical releasing incisions are made extending beyond the mucogingival junction. If objective is full thickness flap, then it is elevated by blunt dissection with periosteal elevator. If split thickness flap is required, then it is elevated by sharp dissection using bard parker knife to split it.
- Step 4: Remove all the granulation tissue, root planing is done and flap is displaced apically at the tooth bone junction.
- Step 5: If a full thickness flap was performed, then a sling suture around the tooth prevents the flap from sliding to a position more apical than that desired, and the periodontal dressing can avoid its movement in a coronal direction. A partial thickness flap is sutured to the periosteum using a direct loop suture or a combination of loop and anchor sutures. Place a dry foil over the flap before covering it with dressing to prevent the introduction of pack under the flap.
Question 6. Write short note on incisions in periodontal flap surgery.
Or
Write short answer on incisions in periodontal flap surgery.
Answer. Following are the incisions in the periodontal flap surgery:
- Horizontal incisions
- Internal bevel incision
- Cervical or sulcular incision
- Interdental incision
- Vertical incision
- Thinning incision
- Cut back incision
- Periosteal incision
Horizontal Incisions
- Horizontal incisions are directed along the margin of the gingiva in a mesial or a distal direction.
- Two types of horizontal incisions have been recommended: the internal bevel incision, which starts at a distance from gingival margin and is aimed at the bone crest and the crevicular incision, which starts at the bottom of the pocket and is directed to the bone margin.
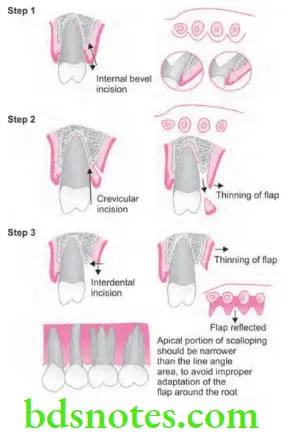
Internal Bevel Incision
- The internal bevel incision is basic to most of the periodontal flap procedures.
- It is also known as first incision as it is the initial incision in reflection of periodontal flap.
- It is also known as reverse bevel incision as its bevel is in the reverse direction as compared to external bevel incision.
- It is the incision from which the flap is reflected to expose the underlying bone and root.
- Objectives of internal bevel incision
- It removes the pocket lining.
- It conserves the relatively uninvolved outer surface of the gingiva, which, if apically positioned, becomes attached gingiva.
- It produces a sharp, thin flap margin for adaptation to the bone-tooth junction.
- The #11 or #15 surgical scalpel is used most often to make internal bevel incision.
- Internal bevel incision starts from a designated area on the gingiva and is directed to an area at or near the crest of the bone.
- The starting point on gingiva is determined by whether the flap is apically displaced or not displaced.
Crevicular Incision
- It is also known as the second incision and is made from the base of the pocket to the crest of the bone.
- This incision is carried around the entire tooth with the help of 12 no. surgical blade.
- Purpose of this incision is to facilitate the removal of inflammatory granulation tissue surrounding the cervical area left after reflecting the primary flap.
Interdental Incision
- It is also known as third incision.
- After crevicular incision a periosteal elevator is used to separate the flap from bone. With this access, the periodontal surgeon can able to make the third or interdental incision, to separate the collar of the gingiva which is left around the tooth.
- Orban knife is usually utilized for this incision.
- Incision is given at facial and lingual radicular area and also interdentally connecting facial and lingual segments to free gingiva completely around the tooth.
Vertical Incisions
- Vertical or oblique releasing incisions can be used on one or both ends of the horizontal incision, depending on the design and purpose of the flap.
- Vertical incisions at both ends are necessary if the flap is to be apically displaced.
- Vertical incisions must extend beyond the mucogingival line, reaching the alveolar mucosa, to allow for the release of the flap to be displaced.
- In general, vertical incisions in the lingual and palatal areas are avoided.
- Incisions should be made at the line angles of a tooth either to include the papilla in the flap or to avoid it completely.
- The vertical incision should also be designed so as to avoid short flaps (mesiodistal) with long, apically directed horizontal incisions because these could jeopardize the blood supply to the flap.
Thinning Incision
- It extends from gingiva towards the base of flap in palatal flap and distal wedge procedures.
- It is given with the help of 11 No. or 15 No. surgical blade.
Cut Back Incision
- It is made at apical aspect of releasing incision and is directed towards the base of flap in laterally positioned flap.
- It is given with the help of 11 No. or 15 No. surgical blade.
Periosteal Releasing Incision
- It is made at the base of flap serving the underlying periosteum.
- It is given with the help of 15 No. or 15C No. surgical blade.
Question 7. Describe the objectives, indications, contraindications and procedure of modified Widman’s flap operation.
Answer.
Widman’s Flap Operation Objective
- To facilitate root instrumentation.
- To remove pocket lining.
Widman’s Flap Operation Indications
- Irregular bony contours
- Deep craters
- Pockets on teeth in which a complete removal of root irritants is not clinically possible
- Grade 2 or 3 furcation involvement
- Root resection/hemisection
- Intrabony pockets on distal areas of last molars
- Persistent inflammation in areas with moderate to deep pockets.
Widman’s Flap Operation Contraindications
- Uncontrolled medical conditions such as:
- Unstable angina
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Myocardial infarction/stroke within 6 months.
- Poor plaque control
- High caries rate
- Unrealistic patient expectations or desires.
Question 8. Write short note on full thickness flap.
Answer. It consists of the complete mucoperiosteum, i.e. surface epithelium, connective tissue and periosteum which are raised by a periosteal elevator. It is also called as mucoperiosteal flap.
- Dissection in full thickness flap is blunt.
- Full thickness flap heals by primary intention.
- Procedure is significantly easy.
- In full thickness flap there is no periosteal retention.
- Blood supply to flap is significant.
- Wide zone of keratinized gingiva is absent with full thickness flap.
- Possibility of elimination or reduction of periodontal pocket is present.
- Bleeding, postoperative swelling and postoperative pain and discomfort is less in full thickness flap.
- Possibility of flap penetration is less with full thickness flap.
- Augmentation of band of attached gingiva is possible by full thickness flap.
Full Thickness Flap Indication
It is used to expose the bone surface in osseous surgery.
Full Thickness Contraindications
- Area where treatment for osseous defect with mucogingival problem is not required.
- Thin periodontal tissue with probable osseous dehiscence and osseous fenestration.
- Area where alveolar bone is thin.
Question 9. Write short note on internal and external bevel incisions.
Answer.
Internal Bevel Incision
- The internal bevel incision is basic to most of the periodontal flap procedures.
- It is also known as first incision as it is the initial incision in reflection of periodontal flap.
- It is also known as reverse bevel incision as its bevel is in the reverse direction as compared to external bevel incision.
- It is the incision from which the flap is reflected to expose the underlying bone and root.
Objectives of Internal Bevel Incision
- It removes the pocket lining.
- It conserves the relatively uninvolved outer surface of the gingiva, which, if apically positioned, becomes attached gingiva.
- It produces a sharp, thin flap margin for adaptation to the bone-tooth junction.
- The #11 or #15 surgical scalpel is used most often to make internal bevel incision.
- Internal bevel incision starts from a designated area on the gingiva and is directed to an area at or near the crest of the bone.
- The starting point on gingiva is determined by whether the flap is apically displaced or not displaced.
External Bevel Incision
- External bevel incision is the choice of incision in surgical gingivectomy technique.
- External bevel incision is given at an angle of 45° apical to the base of pocket with the help of Kirkland knife or blade no. 11 or 15 with Bard-Parkar handle no. 3 or angulated Blake’s handle.
- The angle in this incision is beveled to 45° to tooth surface and should recreate the normal festooned pattern of gingiva. If in external bevel incision beveling is failed to 45° angle this leaves a broad fibrous plateau which takes more time than required to develop a physiologic contour.
- Blade in this incision should pass fully through the tissue to the tooth in coronal direction.
- External bevel incision should be as close as possible to the bone without exposing it so as to remove the soft tissue coronal to the bone.
Question 10. Write indications and contraindications of periodontal flap surgery.
Answer.
Indications for Periodontal Flap Surgery
- In gaining the access for root debridement.
- For reducing or eliminating the pocket depth, so that patient can maintain root surfaces free of plaque.
- For reshaping soft and hard tissues to attain harmonious topography.
- For regenerating the alveolar bone, periodontal ligament and cementum.
Contraindications for Periodontal Flap Surgery
- In patients having poor plaque control.
- In patients with high caries rate.
- In unrealistic patient expectation and desire.
- In uncontrolled medical conditions such as:
- Unstable angina
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Myocardial infarction/Stroke within the six months.
Question 11. Write short answer on internal bevel gingivectomy.
Answer. Undisplaced flap differs from modified Widman flap in that the soft tissue pocket wall is removed with the initial incision; thus it is considered as an “internal bevel gingivectomy”.
- The undisplaced flap and the gingivectomy are two different techniques which surgically removes the pocket wall.
- To perform this technique without creating mucogingival problem, periodontist should determine that an amount of attached gingiva should be left after removing the pocket wall.

Leave a Reply