Question 1. Mention hormones secreted by anterior pituitary. Describe action of growth hormone. How is hormone synthesis regulated?
Answer:
Hormones secreted by anterior pituitary:
- Growth hormone
- Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH) in females
- Interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH) in males.
- Prolactin.
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
Growth hormone:
Actions:
1. On metabolism:
- On protein metabolism.
- GH increases the amino acids transport into the cells from the E.C.F.
- Increases RNA translation in the cells due to which ribosomes are activated and more proteins are synthesize.
- It stimulates transcription of DNA to RNA.
- Inhibits the catabolism of proteins.
- Releases insulin which has anabolic effect on proteins.
- On fat metabolism.
- Increases mobilization of fats from adipose tissues.
- Increases circulating free fatty acids levels
- Increases hepatic oxidation of fatty acids to ketone bodies.
- On carbohydrate metabolism.
- Increases hepatic glucose output.
- Reduces the peripheral utilization of glucose for energy production.
- Decreases glucose uptake by the tissues.
- Increases the concentration of glycogen in the cells.
- It has diabetogenic effect as it causes continuous stimulation of the B cells in the islets of langerhans
- in pancreas to secrete more insulin.
- On mineral metabolism.
- Increases Ca2+, absorption from GIT.
- Decreases Na+, K+, Ca2+ and phosphorous excretion from kidneys.
2. Effect of Bone, cartilage and viscera:
- GH increases the number of cells.
- Increases conversion of chondrocytes into osteogenic cells.
- Increases calcium absorption for mineralization of bone.
- Before epiphyseal closure.
- Stimulates proliferation of chrondrocytes.
- Stimulates DNA and RNA synthesis.
- Increases the length of the bones.
- After epiphyseal fusion.
- GH no longer increases the length of the bones.
- However, bone thickening occurs.
- Before epiphyseal closure.
3. Action of milk production:
- Increases milk production in lactating mothers.
4. Other actions:
- Stimulates erythropoiesis.
- Stimulates the growth of lymphoid tissue.
- Stimulates the growth of genetalia.
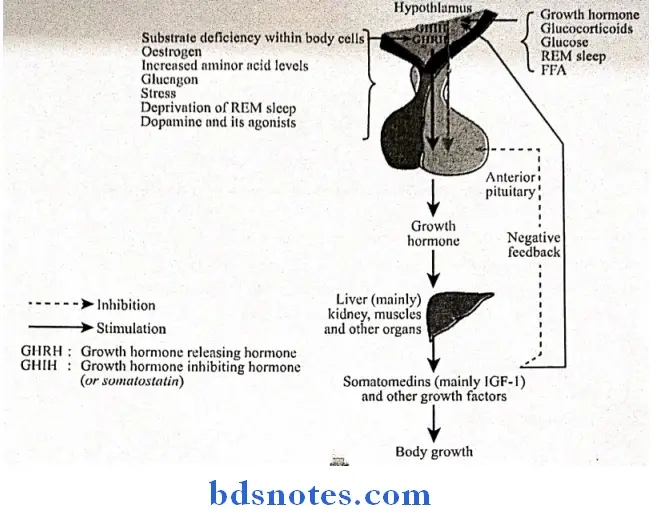
Regulation:
- Growth hormone is synthesized in the anterior lobe of pituitary gland.
- Growth hormone secretion is under negative feedback control by two hypothalamic hormones – GH releasing hormone (GHRH) and GH inhibiting hormone (GHIH) and GH releasing polypeptide (GHRP)
- Hypothalamus releases GHRH and GHRP.
↓
This releases GH from anterior pituitary
↓
GH acts on liver to secrete somatomedin C
↓
Somatomedin-C Increases release of GHIH from hypothalamus and
Inhibits the release of GHRP from hypothalamus.
↓
GHIH inhibits release of GH from pituitary
GHRP acts on pituitary directly and inhibits secretion of GH.
- GH and GHRH inhibits its own secretion by feedback stimulating the release of GHIH from hypothalamus.
Question 2. Name the hormones of posterior pituitary gland. Explain their action and regulation of secretion. (or) Oxytocin.
Answer:
Hormones of posterior pituitary:
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
- Oxytocin.
1. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH):
- Antidiuretic hormone Actions:
- ADH increases the water reabsorption from distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct.
- Increases urea absorption from collecting ducts.
- Promotes Na+ reabsorption from the thick ascending limb of loop of Henle.
- Causes constriction of the arteries in all parts of the body.
- Causes contraction of smooth muscle and increases peristalsis of GIT and detrusor contraction.
- Antidiuretic hormone Regulation:
- Stimulants of ADH are.
- Decrease in the ECF volume.
- Increase in osmolar concentration in the ECF.
- Stimulants of ADH are.
Increase in osmolarity of blood.
↓
Stimulation of osmoreceptors situated in the hypothalamus near supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.
↓
Impulses are send to posterior pituitary
↓
Causes release of ADH
↓
ADH causes reabsorption of water from renal tubules.
2. Oxytocin:
- Oxytocin Actions:
- Milk ejection oxytocin stimulates contraction of the myoepithelium lining the duct of mammary
- glands causes milk ejection.
- Stimulates contraction of the smooth muscle of uterus.
- It facilitates the process of labour.
- Facilitates the transport of sperm to the uterus by uterine contraction.
- Causes relaxation of blood vessels producing fall in B.P.
- Thus,
- On pregnant uterus.
- Oxytocin facilitates labour.
- On non-pregnant uterus.
- Facilitates transport of sperms.
- On pregnant uterus.
Oxytocin Regulation:
1. Milk ejection reflex:
Stimulation of touch receptors present on the mammary glands.
↓
Impulses via somatic afferent nerve fibers reach paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of hypothalamus.
↓
These impulses releases oxytocin.
↓
Oxytocin causes.
- Contraction of myoepithelial cells.
- Ejection of milk from mammary glands.
2. Action on uterus.
Dilation of cervix.
↓
Stimulation of receptors on the cervix
↓
Impulses via somatic afferent nerve fibers reach paraventicular and supraoptic nuclei of hypothalamus
↓
These impulses releases oxytocin.
↓
Oxytocin causes contraction of uterus and enhances labor

Question 3. Describe synthesis and action of thyroid hormone add a note on hyperthyroidism.
Answer:
Thyroid hormone Synthesis:
- Stages involved in the synthesis of thyroid hormones are
1. Thyroglobulin synthesis:
- Thyroid follicular cells synthesize thyroglobulin and secrete it into the lumen by exocytosis.
- Synthesis of thyroglobulin occurs continuously.
- After synthesis, the thyroglobulin is stored in the follicle.
2. Trapping of iodide:
- Iodide is transported actively from the blood into the follicular cell against the electrochemical gradient.
- Iodide is carried along with sodium into the follicular cell.
3. Oxidation of iodide:
- Oxidation of iodide occurs inside the follicular cells in the presence of iodide peroxidase enzyme.
- Iodide is oxidized to iodine.
4. Iodination of tyrosine:
- It is accelerated by iodinase enzymes.
- It occurs in several stages.
- Tryosine is iodized to monoidotyrosine (MIT)
- Next, when a second iodine is added it forms diiodotyrosine (DIT).
5. Coupling reactions:
Coupling reactions occurs to give rise to different thyroid hormone.
These reactions are as follows.
DIT + DIT→ T4 called thyroxine
DIT+ MIT→T3 called tri-iodo-thyroxine.
Actions of thyroid hormone:
1. On basal metabolic rate (BMR):
- Thyroid hormones increases the metabolic activities of almost all tissues of the body.
- They stimulate heat production during these reactions.
- Thus, they increases BMR by also increasing oxygen consumption by tissues.
2. On metabolism:
- On protein metabolism:
- T4 increases protein synthesis.
- Increases the translation of RNA.
- It increases the synthesis of RNA.
- T4 causes protein catabolism due to increase in BMR.
- On carbohydrate metabolism:
- T4 increases peripheral utilization of glucose Increases absorption of glucose from GIT.
- Decreases the rate of secretion of insulin.
- Increases breakdown of glycogen into glucose accelerates gluconegenesis.
- On fat metabolism:
- Increases synthesis of cholesterol in liver.
- Decreases fat storage.
- Increases free fatty acid level in blood.
- Increases breakdown of cholesterol in liver.
- On vitamin metabolism:
- If thyroxine secretion is increased, there is decrease in vitamin levels.
- T4 is required for hepatic conversion of B-corotene to vitamin A and for the conversion of vitamin A to retinine.
3. On body temperature:
- Thyroid hormone induces thermogenesis.
4. On growth:
- T4 is important for normal body growth and skeletal maturation.
- T4 helps in tissue differentiation and maturation.
- T4 promote growth and development of the brain during fetal life and the first few years of postnatal life.
5. On body weight:
- Increase in thyroxine secretion decreases the body weight due to decrease in fat storage.
6. On blood:
- Thyroxine is one of the maturation factor of erythropoiesis.
7. On cardiovascular system:
- T4
- Increases heart rate
- Increases force of myocardial contraction
- Increases cardiac output, thus increases systolic BP.
- Produces vasodilatation, thus decreases diastolic BP.
- Increases pulse pressure.
8. On respiration:
- Increases the rate and force of respiration.
9. On GIT:
- T4 increases apatite and thereby food intake.
- Increases secretions and movements of GIT.
10. On CNS:
- T4 is stimulating factor for the central nervous system.
- It increases the blood flow to brain.
11. On skeletal muscle:
- Thyroxine induce excess neuronal activity.
- Lack of thyroxine makes the muscles more sluggish.
12. On sleep:
- Hyposecretion of thyroxine causes somnolence.
13. On sexual function:
- Thyroxine is essential for normal sexual function.
- Hyposecretion leads to
- Loss of libido.
- Menorrhagia and polymenorrhea.
- Hypersecretion leads to.
- Impotence
- Oligomenorrhea and amenorrhea.
- Hyposecretion leads to
Hyperthyroidism:
It is the condition resulting from increased circulating levels of free T4 and T3.
Causes:
- Grave’s disease – autoimmune disease
- Thyroid adenoma – localized tumour
- Presence of TSH like substances.
Features:
- Increased sweating
- Increased motility, catabolism
- Decreased body weight.
- Goitre – enlargement of thyroid gland
- Tachycardia and atrial fibrillation
- Cardiac failure.
LAB Investigation:
- Serum TSH level-normal or decreases.
- Low cholesterol level.
- Polycythemia.
- Hyperglycemia.
Question 4. Give an account of synthesis, function and regulation of parathyroid hormone. Add a note on tetany. (or) Enumerate the actions of thyroxin.
Answer:
Synthesis of parathormone:
- Prepro-PTH containing 115 amino acids enters endoplasmic reticulum of cells of parathyroid glands.
- Prepro-PTH is converted into pro-PTH containing 96 amino acids
- Pro-PTH enters golgi apparatus
- Here, it is converted into PTH.
Functions:
1. On bones:
- PTH stimulates osteoclasts and osteoblast to cause resorption of calcium from bones.
- Thus, it increases plasma Ca2+ and decreases plasma PO43-.
2. On kidneys:
- Increases reabsorption of calcium from renal tubules.
- Thus, decrease Ca2+excretion in urine and increases serum Ca2+ level.
- PTH decrease reabsorption of PO43- level
- PTH increases the formation of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol from 25-hydroxycholecalciferol.
3. On GIT:
- Increases calcium absorption from the gut.
4. On lactating mothers:
- Decreases the amount of Ca2+ secreted into the milk.
Regulation:
1. Directly by serum Ca2+ level.
Decrease in serum Ca2+ level.
↓
Stimulate parathyroid gland
↓
Increases PTH production
↓
Mobilization of Ca2+ from bones.
↓
Normalises serum Ca2+.
2. Indirectly by serum PO43-
Increase in serum PO43- level.
↓
Decreases serum
↓
Ca2+ level
↓
Inhibit 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol.
↓
Increases PTH.
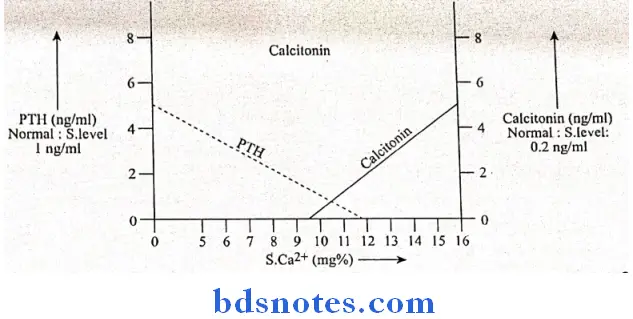
Tetany:
- A low ionic Ca2+ level in the blood results in tetany.
Features:
- Tingling and numbness in the extremities.
- Feeling of stiffness with cramps in extremities
- Laryngeal stridor associated with airway obstruction.
- Chvostek’s sign – facial irritability resulting from ipsilateral contraction of the facial muscles.
- Carpopedal spasm – flexion at the wrist and thumb with hyperextension of remaining fingers.
- Troussaeu’s sign – In the lower limbs toes are plantar – flexed and feet are drawn up on inflation of a BP cuff.
- Hypotension, arrhythmia.
- Decreased permeability of the cell membrane.
- Seizures, mental retardation.
- Hair loss.
- Dry skin with brittle nails.
Question 5. Write an essay on distribution, normal level and hormonal control of plasma calcium and phosphorous.
Answer:
1. Calcium:
Distribution:
- Calcium is present in three forms.
- Ionized or diffusible calcium- 50%.
- It is found freely in the plasma.
- It is essential for vital functions.
- Non-ionized or non-diffusible calcium- 8-10%.
- Present as calcium bicarbonate.
- Calcium bound to albumin – 40-42%.
- Ionized or diffusible calcium- 50%.
Normal level:
- Normal serum calcium is 9-11 mg/dl.
Hormonal control:
- Calcium concentration is regulated by the action of following hormones.
- Vitamin D.
- It increases serum calcium level by.
- Increasing Ca2+ from the small intestine
- Stimulates osteoclasts to mobilize Ca2+ into ECF from bones.
- Increases reabsorption of Ca2+ from renal tubules.
- Parathormone (PTH).
- Increases plasma Ca2+ by promoting bone resorption.
- Increases reabsorption of Ca2+ from renal tubules and decreases its excretion
- Increases calcium absorption from gut.
- Decreases the amount of Ca2+ secreted in the milk.
- Calcitonin:
- Inhibit osteoclasts activity.
- Inhibits intestinal absorption of Ca2+
- Vitamin D.
2. Phosphorous:
- Distribution:
- 80-85% – In skeleton
- 15-20% – In intracellular phosphate pool.
- Value:
- In adults 2.5-4 mg/dl.
- In children – 5-6 mg/dl.
- Hormonal control:
- Phosphate level is regulated by
- Vitamin D:
- Increases PO43- absorption from GIT.
- Has osteolytic activity on bones.
- Increases reabsorption of phosphate ions from renal tubules.
- Parathorome – PTH:
- Decreases PO43- level by its osteoclastic activity.
- Decreases renal reabsorption of PO43- and increases its excretion.
- Increases PO43- absorption from GIT.
Question 6. Name of the hypoglycaemic hormone of the body. Discuss its action, regulation of its secretion and features of deficiency of the hormone. (or) Insulin.
Answer:
Insulin:
- Insulin is the hypoglycaemic hormone.
Actions:
1. On carbohydrate metabolism.
- Increases the glucose entry into the tissues.
- Increases peripheral utilization of glucose.
- Promotes the rapid conversion of glucose into glycogen.
- Inhibits enzyme of glycogen breakdown.
- Decreases glucose output from the liver prevents gluconeogenesis.
- Prevents glycogenolysis.
2. On fat metabolism.
- Promotes the synthesis of free fatty acids and triglycerides.
- Facilitates transport of fatty acids into adipose tissue.
- Promotes storage of fat.
3. On protein metabolism.
- Facilitates transport of amino acids into cells from blood.
- Promotes amino-acid uptake and protein synthesis.
- Decreases protein breakdown.
- Prevents conversion of proteins into glucose.
4. On growth.
- Insulin promotes growth by protein anabolism.
Regulation:
1. Substrate control.
- Control by carbohydrates.
- Increase in blood glucose increases insulin secretion by its direct action on B-cells.
- Control by protein and fat derivatives.
- Mixture of amino acids and fat derivatives stimulates B-cells to increases the insulin secretion.
2. Hormonal control.
- GIT hormones.
- Gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinn and GIP increases insulin secretion.
- Glucagon, growth hormone and corticosteroid stimulate insulin secretion indirectly.
3. Neural control.
- By ANS.
- Stimulation of parasympathetic nerves increases insulin secretion.
- Stimulation of sympathetic nerves inhibits insulin secretion.
- By CNS.
- During feeding, vagal activity increases which increases insulin secretion.
- During starvation, sympathetic activity increases which decreases insulin secretion.
4. cAMP.
- β-adrenergic receptor stimulation increases cAMP that increases insulin secretion.
- α-adrenergic receptor stimulation decreases cAMP that decreases insulin secretion.
Diabetes mellitus:
- It is a condition occurring due to deficiency of insulin hormone.
Features:
- Hyperglycemia – raised blood glucose.
- Glycosuria presence of glucose in urine.
- Polyuria – increased frequency of urine.
- Polydipsia – increased thirst.
- Polyphagia – intake of excess food.
- Dehydration.
- Loss of weight.
- Ketonuria.
- Osmotic diuresis.
- Acidosis due to excretion of ketoacids in urine.
- Acetone breathing – occur in severe ketoacidosis.
- Kussmaul breathing – due to severe acidosis.
- Circulatory shock- occur in severe diabetes.
- Coma- due to reduction in the concentration of bicarbonate ions.
- Increase in blood sugar level develops hyperosmolarity of plasma leading to coma.
Question 7. Give the normal blood glucose level. Name the hormones that affect blood glucose level give four Important functions of insulin.
Answer:
Normal blood glucose level:
- Normal fasting blood glucose is 70-90 mg/dl.
- Postprandial blood glucose is 120-140 mg/dl.
Hormones that affect blood glucose level:
1. Insulin.
- Decreases blood sugar level by.
- Facilitating transport of glucose.
- Facilitates uptake of glucose by cells.
- Increases peripheral utilization of glucose.
- Decreases glucose output from the liver.
- Increases glycogenesis.
- Prevents glycogenolysis.
- Prevents gluconeogenesis.
2. Glucagon.
- It increases the blood sugar level by.
- Stimulating glycogenolysis.
- Promoting gluconeogenesis.
- Utilizing amino acids for glucose formation.
Question 8. What is normal serum calcium level? Name hormones regulating it. Describe the functions of parathormone.
Answer:
Normal serum calcium level:
- 9-11 mg/dl
Hormones regulating normal calcium level:
- Calcium concentration is regulated by the action of following hormones
1. Vitamin D
- Increases calcium level by
- Increasing calcium from the small intestine
- Stimulates osteoclasts to mobilize calcium into ECF from bones
- Increases reabsorption of calcium from renal tubules
2. Parathormone
- Increases plasma calcium by promoting bone resorption
- Increases reabsorption of calcium from renal tubules and decreases its excretion
- Increases calcium absorption from gut
3. Calcitonin
- Inhibits osteoclast activity
- Inhibits calcium absorption from intestine
Functions of parathormone (PTH):
1. On bones
- PTH stimulates osteoclasts and osteoblast to cause resorption of calcium from bones
- Thus, it increases plasma calcium and decreases plasma phosphate
2. On kidneys
- Increases reabsorption of calcium from renal tubules
- Thus decreases calcium excretion in urine and increases serum calcium level
- PTH decreases reabsorption of phosphate
- Increases formation of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol from 25-hydroxycholecalciferol
3. On GIT
- Increases calcium absorption from gut
4. On lactating mothers
- Decreases the amount of calcium secreted into the milk
Question 1. Name the posterior pituitary hormones. Explain action of any one of them.
Answer:
Posterior pituitary hormones:
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
- Oxytocin.
Question 3. Enumerate the hormones of anterior pituitary gland and give the important function of one hormone.
Answer:
Hormones of anterior pituitary:
- Growth hormone.
- Thyroid stimulating hormone.
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone.
- Follicle stimulating hormone.
- Luteinizing hormone in females.
- Interstitial cell stimulating hormones in males.
- Prolactin.
Question 5. Explain the regulation of secretion of thyroid hormone.
Answer:
Regulation of thyroid hormone:
1. Role of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) secreted by anterior pituitary.
- Increases size and secretory activity of the cells.
- Increases I- trapping mechanism.
- Increases proteolysis of thyroglobulin.
- Increases synthesis of thyroglobulin into colloid.
2. Role of hypothalamus.
- Thyrotrophin releasing hormone (TRH) is released into the hypothalamohypophyseal portal vessels and transported to the anterior pituitary.
- Here, its stimulates the secretion of TSH.
3. Role of iodine in the diet.
- When iodine level is moderate, the blood level of thyroid hormone is normal.
- When iodine intake is high, it decreases the formation and release of thyroid hormone.
4. Role of other factors.
- Leptin from adipose tissue and a-melanocyte stimulating hormone from pituitary increase the release of TRH and synthesis of thyroid hormone.
- Low body temperature stimulates synthesis of thyroid hormone.
- Stress, somatostatin, glucocorticoids and dopamine decreases the secretion of thyroid hormone.

Question 6. Myxedema.
Answer:
It is the thyroid disorder characterized by edematous appearance.
Causes:
- Hypothyroidism.
- Lack of thyroid hormone.
Features:
- Goiter.
- Puffiness of face with periorbital swelling.
- Dropping of upper eyelid.
- Loss of hair.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Nonpitting type of edema.
- Dry, thickened, rough and yellow skin.
- Anaemia.
- Fatigue.
- Low BMR.
- Hypersensitive to cold.
- Memory loss
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Increase in body weight.
- Increase in serum cholesterol.
- Constipation.
Question 7. Thyroid hormones.
Answer:
1. Tri-iodo-thyronine-T3:
- It is iodine containing amino acids secreted by the follicular cells.
- It has less affinity for plasma proteins and combines loosely with them.
- Thus, it is released quickly.
- It acts on the target cells immediately.
- It forms only 9-10% of total secretion.
Synthesis:
- It is synthesized by oxidative condensation of mono-iodo-tyrosine (MIT) and Di-iodo tyrosine (DIT).MIT + DIT → Tri-iodo-thyronine (T3)
2. Tetraiodothyronine – T4:
- It is secreted by the follicular cells.
- It has more affinity for plasma proteins and strongly binds to it.
- Thus, it is released slowly and acts slowly.
Synthesis:
- It is synthesized by coupling of 2 molecules of Di-iodo- tyrosine (DIT).DIT + DIT Thyroxine, T4
3. Calcitonin:
- It is calcium-lowering hormone.
- It is secreted by parafollicular cells which lie in between the follicular cells.
- It is polypeptide chain with 32 amino acids.
- It decreases the blood calcium level by acting on bones, kidney and intestine.
- Thus, it counteracts the action of parathormone.
Question 8. What are the manifestations of cretinism?
Answer:
Manifestations of cretinism:
- Mental retardation.
- Dwarfism.
- Protruded abdomen.
- Enlarged, protruded tongue.
- Dripping of saliva.
- Failure of sexual development.
- Baby develops croaking sound while crying.
- The enlarged tongue obstructs swallowing and breathing.
Causes:
- Congenital absence of thyroid gland
- Genetic disorder.
- Lack of iodine in the diet.
Question 9. Explain the role of parathormone in the regulation of blood calcium level.
Answer:
Regulation of blood calcium by PTH:
- FTH maintains blood calcium level with the critical range of 9-11 mg %.
- Bones:
- PTH stimulates osteoblasts and osteoclasts and promote bone resorption.
- Thus increases plasma Ca2+
- Permeability of bone cells to Ca2+ is increased.
- This causes osteoblasts to pump Ca2+ into extracellular fluid (ECF).
- Kidneys:
- PTH increases Ca2+ reabsorption from renal tubules.
- PTH decreases Ca2+ excretion in urine.
- Thus, it raises blood calcium level.
- GIT:
- PTH increases the absorption of calcium ions from the GIT indirectly.
- It increases the formation of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalcifer in the kidneys.
- This increases the absorption of Ca+
- Lactating mammary glands:
- PTH decreases the amount of Ca2+ secreted into the milk.
- Bones:
Question 12. What is the role of adrenal gland in condition of stress?
Answer:
- The exposure to any type of stress, increases the secretion of ACTH.
- This is turn, increases glucocorticoid secretion.
- The increase level of glucocorticoid offers resistance to the body against stress by following ways
- Glucocorticoids increases transport of amino acids from tissues to liver cells.
- This causes synthesis of new proteins to withstand stress.
- It releases more fatty acid to generate more energy during stress.
- It enhances vascular reactivity to catecholamines and fatty acid mobilizing action of catecholamines, which withstand stress.
- It prevents severity of other body changes caused by stress.
- Glucocorticoids increases transport of amino acids from tissues to liver cells.
Question 13. What are the hormones of adrenal cortex? Describe the action of glucocorticoids.
Answer:
Hormones of adrenal cortex:
- Mineralocorticoids
- Glucocorticoids
- Sex hormones.
Actions of glucocorticoids:
1. On carbohydrate metabolism.
- It increases the blood glucose level by.
- Promoting gluconeogenesis.
- Increases liver glucose formation
- Prevents peripheral utilization of glucose by cells.
2. On protein metabolism.
- It causes protein breakdown.
- Inhibits transport of amino acids into the cells.
- Increases transport of amino acids in liver to produce glucose.
3. On fat metabolism.
- Favours mobilization of fatty acids from adipose tissue to liver and increases gluconeogenesis.
- Increases the concentration of fatty acids in blood.
- Increases the utilization of fat for energy.
4. On mineral metabolism.
- Increases retention of Na+ and excretion of K by the kidney.
- Decreases blood Ca2+ by inhibiting its absorption from intestine and increases its excretion through urine.
5. On water metabolism.
- Increases aldosterone secretion to cause excessive retention of water.
6. On muscles.
- Increases the release of amino acids from muscles.
7. On bone.
- Glucocorticoids excess.
- Inhibits new bone formation.
- Causes bone matrix breakdown.
- Decreases serum Ca2+
8. On blood cells.
- Decreases the number of circulating eosinophils
- Increases destruction of eosinophils.
- Decrease no. of basophils, lymphocytes.
- Increases circulating neutrophils, RBCs and platelets.
9. On vascular response.
- It is essential for constrictor action of adrenaline and nonadrenaline.
- Enhances catecholamine synthesis.
- Sensitizes arterioles to the constrictor action of noradrenaline.
10. On CNS.
- It is essential for normal functioning of nervous system.
11. Permissive action.
- It is essential for catecholamines to produce pressor response and bronchodilation.
12. On resistance to stress.
- It enhances the body resistance to stress.
13. Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic action.
- Inhibits inflammatory response to tissue injury.
- Suppresses clinical manifestation of allergy.
14. Immunosuppressive action.
- It suppresses the body immune by decreasing the number of circulating T-lymphocytes.
Question 14. What is aldosterone? Describe the regulation of synthesis of aldosterone.
Answer:
Aldosterone is mineralocorticoid containing 21 – C atom
Regulation of its secretion:
1. Increase in potassium ion in ECF
↓
Potassium ion acts on zonaglomerulosa
↓
Increases secretion of aldosterone
2. Renin angiotensin mechanism
Decrease in sodium ion concentration and ECF volume
↓
Renin angiotensin mechanism
↓
Acts on juxtaglomerular apparatus
↓
Secretes renin
↓
Secretes angiotensin
↓
Conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II by angiotensin converting enzyme
↓
Results in secretion of aldosterone
↓
Increases retention of sodium and water
↓
This inhibits juxta glomerular apparatus to release renin
↓
Angiotensin II is not formed
↓
Aldosterone secretion is thus stopped
3. Adrenocorticotropic hormone has mild stimulating effect on aldosterone secretion.
Question 15. Mention the hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary gland. What is meant by neuroendocrine reflex.
Answer:
Hormones secreted by posterior pituitary gland:
- Anti-diuretic hormone
- Oxytocin
Neuroendocrine reflex:
- It is initiated by the stimulation of sensory neurons that causes a release of a neurohormone from the neurosecretory cells.
- Example: Milk ejection reflex
Milk ejection reflex:
- Stimulation of touch receptors present on the mammary glands
- Impulse via somatic afferent nerve fibres reach paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of hypothalamus
- These impulse releases oxytocin
- Oxytocin causes
- Contraction of myoepithelial cells
- Ejection of milk from mammary glands
Question 1. Hormones produced by the posterior pituitary and one action of any one of them.
Answer.
Hormones of posterior pituitary:
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
- Oxytocin.
Action of ADH:
- Increases water reabsorption from renal tubules.
- Causes water retention.
- Increases peristalsis of GIT.
Question 2. Abnormalities of growth hormone.
Answer:
1. Gigantism:
- It occurs due to overproduction of growth hormone during adolescence.
- It is characterized by excessive growth of long bones.
2. Acromegaly:
- It occurs due to excessive secretion of growth hormone during adulthood.
- It is characterized by enlargement of the peripheral region.
3. Dwarfism:
- It occurs due to deficiency of growth hormone secretion.
- It is characterized by the stunted growth.
Question 3. Acromegaly.
Answer:
- It is a condition occurring due to excessive secretion of growth hormone during adulthood.
Features:
- Prognathism.
- Enlargement of sinuses
- Protrusion of supraorbital ridges, broadening of nose, thickening of lips, thickening of forehead.
- Enlargement of hands and feet.
- Kyphosis.
- Cardiomegaly, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly.
- Osteoarthritis.
- Gynaecomastia.
- Hyperglycaemia, glycosuria.
- Hypertension.
Question 4. Dwarfism.
Answer:
- It is a condition occurring due to deficiency of growth hormone secretion.
Features:
- Stunded growth.
- Sexual immaturity.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Adrenal insufficiency.
Question 5. Gigantism.
Answer:
- It is a condition occurring due to over production of growth hormone.
Features:
- Tall stature
- Gynaecomastia
- Large hands and feet
- Hyperglycaemia, glycosuria Coarse facial features.
Loss of libido.
Question 8. Goiter.
Answer:
It means enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Types:
1. Toxic Goitre.
- Occurs in hyperthyroidism.
- It occurs due to tumour of the gland which increases the number of hormone secreting cells.
2. Nontoxic Goitre.
- It occurs in hypothyroidism.
- It occurs due to enlargement of the gland.
- It has 2 subtypes.
- Endemic colloid goitre.
- It is due to the deficiency of iodine.
- Idiopathic nontoxic goitre.
- It occurs due to unknown causes.
- Endemic colloid goitre.
Question 9. Hypothyroidism.
Answer:
- It is the condition resulting from reduced circulating levels of free T4 and T3.
- It occurs due to autoimmune disease, which causes destruction of the gland.
- Mostly, it begins as glandular inflammation called thyroiditis.
- Eventually it results in fibrosis of the gland.
- It leads to
1. Myxedema in adults.
- It is characterized by edematous appearance.
2. Cretinism in children,
- It may occur due to iodine deficiency.
Question 10. Functions of calcium.
Answer:
Calcium is essential for.
- Formation and growth of bones and teeth.
- Neuronal activity.
- Blood coagulation.
- Neurotransmitter release
- Muscular activity for excitation – contraction coupling.
- Secretory activity of the glands.
- Secretion of hormones.
- For the action of intracellular enzymes.
Question 11. Parathormone.
Answer:
- It is a protein hormone secreted by chief cells of parathyroid gland.
Function:
- It maintains the blood calcium level within normal range by acting on bone, kidney and GIT.
Regulation:
- The secretion of parathormone is regulated by blood calcium level.
- A fall in calcium level stimulates secretion and rise in calcium level inhibits secretion.
Question 14. Insulin.
Answer:
Insulin is secreted by B cells in the islets of langerhans of pancres.
Functions:
- It is the only hormone that reduces blood glucose level.
- Causes protein synthesis.
- Stimulates fat synthesis
- Promotes growth.
Question 15. Glycosuria.
Answer:
- It is the presence of glucose in the urine.
- Normally glucose does not appear in urine.
- But, when glucose level rises above 180 mg/dl in blood, glucose appears in urine.
- It is the renal threshold level for glucose.
Question 16. Hormones regulating blood glucose.
Answer:
- Hormone that decreases blood glucose. Insulin is the only hormone.
- Hormones that increases blood glucose.
- Epinephrine and nor-epinephrine.
- Glucagon
- Adrenal cortical hormones
- Growth hormone.
- ACTH.
- Thyroid hormones.
Question 17. Thyrotoxicosis.
Answer:
Synonym:
- Grave’s disease
Fetures:
- It is an autoimmune disease which causes hyperthyroidism.
- Normally thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) combines with surface receptors of thyroid cells and causes the synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones.
- But, in Grave’s diseases the thyroid stimulating autoantibodies produced by B-lymphocytes activate the TSH receptors and increase the secretion of thyroid hormone.
Question 18. Glucogon.
Answer:
- It is secreted from a-cells in the islets of Langerhans of pancreas.
Functions:
- Increases blood glucose level.
- Stimulates glycogenolysis.
- Promotes gluconeogenesis.
- Inhibits secretion of gastric juice.
- Increases secretion of bile from liver.
Question 19. Aldosterone.
Answer:
It occurs in plasma in a very small concentration, 60% being bound to protein mainly to albumin.
Actions:
- It increases the reabsorption of sodium from renal tubules.
- Aldosterone by stimulating Na+ reabsorption it causes water
retention. - This increases ECF volume which leads to increases in blood pressure.
- Aldosterone increases potassium excretion.
- Enhances sodium absorption from intestine.
- Sodium is reabsorbed from sweat glands through the action of aldosterone.
Question 20. Hormones produced by adrenal cortex.
Answer:
1. Mineralocorticoids.
- Secreted by zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex.
- Aldosterone,
- Increases sodium reabsorption from renal tubules.
- Increases potassium excretion.
- Deoxycorticosterone.
- Aldosterone,
2. Glucocorticoids.
- They act mainly on glucose metabolism and increases blood glucose level,
- They are
- cortisol
- cortisone
- corticosterone.
3. Sex hormones.
- They are secreted mainly in zona reticularis
- They are.
- Androgen mainly
- Oestrogen and progesterone in small amounts.
Question 21. Functions of glucocorticoids.
Answer:
- Increases blood glucose level
- Causes protein breakdown
- Provide resistance to stress
- Has anti-inflammatory and antiallergic action.
- Has immunosuppressive action.
- Enhances catecholamine synthesis
- Increases Na* reabsorption and K+ excretion.
- Increased retention of water
- Required for proper functioning of nervous system.
Question 22. Addison’s disease.
Answer:
- It is the failure of adrenal cortex to secrete all the corticosteroids.
Types:
- Primary addison’s diseases
- Secondary addison’s diseases
- Tertiary addisons’s disease
Features:
- Hypotension.
- Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea
- Decreased resistance to stress
- Mental confusion
- Muscular weakness
- Dehydration
- Decreased cardiac output
- Hypolglycaemia
- Suspectibility to infection.
- Hypersensitive to taste and smell.
Question 23. LH in males and females.
Answer:
In males:
- It stimulates the interstitial cells of Leydig cells in testes.
- Thus, it is known as interstitial cell stimulating hormone.
- It is essential for the secretion of testosterone from Leydig cells.
In famels:
- It causes maturation of vesicular follicle into graffian follicle.
- Responsible for ovulation.
- Required for formation of corpus luteum.
- Activates secretory functions of corpus luteum.
Question 24. Milk ejection reflex
Answer:
Milk Ejection Reflex:
Stimulation of touch receptors present on the mammary gland
↓
Impulses via somatic afferent nerve fibred reach paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of hypothalamus
↓
These impulses releases oxytocin
↓
Oxytocin causes
1. Contraction of myoepithelial cells
2. Ejection of milk from mammary glands
Question 25. Name hormones that help to maintain calcium homeostasis.
Answer:
Hormones Regulating Plasma Calcium Are:
- Vitamin D
- Parathormone
- Calcitonin
Question 26. Mention four functions of cortical hormones.
Answer:
Functions of cortical hormones
- Increases the blood glucose levels
- Favours mobilisation of faaty acids
- Increases retention of sodium ions and excretion of potassium ion
- Increases aldosterone secretion
- Increases release of amino acids from muscles.
Question 27. Name any four hormones that act on bone.
Answer:
Hormones acting on bone:
- Growth hormone-stimulates bone formation
- Parathyroid hormone-stimulates formation and resorption
- Calcitonin – permits formation, inhibits skeletal resorption, promotes mineral deposition.
Question 28. Name three hyperglycaemic hormones.
Answer:
Hyperglycaemic hormones:
- Glucagon
- Growth hormone
- Glucocorticoids
- Epinephrine
- Thyroid
Question 29. List the hormones synthesized by the anterior pituitary.
Answer:
Hormones secreted by anterior pituitary:
- Growth hormone
- Thyroid stimulating hormone
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- Follicle stimulating hormone
- Luteinizing hormone in females
- Interstitial cell stimulating hormone in males
- Prolactin
Question 30. Osteoporosis
Answer:
- Osteoporosis is a bone resorption disease characterized by decreased density of normally mineralized bone which results in the thinning of bone tissue and decreased mechanical strength.
- It leads increased fragility of bones and increased risk of bone fracture.
Causes:
- In females following menopause due to deficiency of estrogen
- Tobacco smoking
- Malnutrition
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Excess consumption of alcohol
- Use of proton pump inhibitors
Question 31. Dwarfism versus cretinism
Answer:

Question 32. Antidiuretic hormone.
Answer:
- It is hormone secreted by posterior pituitary
Actions:
- Increases the water reabsorption from distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct
- Increases urea absorption from collecting duct
- Promotes sodium reabsorption from the thick ascending limb of loop of Henle
- Causes constriction of the arteries in all parts of the body
- Causes contraction of smooth muscle and increases peristalsis of GIT and detrusor contraction
Regulation:
- Stimulants of ADH are
- Decrease in the ECF volume
- Increase in osmolar concentration in the ECF
Increase in osmolarity of blood
↓
Stimulation of osmoreceptors situated in the hypothalamus near supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei
↓
Impulses are send to posterior pituitary
↓
Causes release of ADH
↓
ADH causes reabsorption of water from renal tubules.

Leave a Reply