Question 1. Describe the relations, blood supply, nerve supply & applied anatomy of parotid gland (or) Parotid duct (or) Give secretomotor nerve supply of parotid gland
Answer:
Parotid Gland Relations:
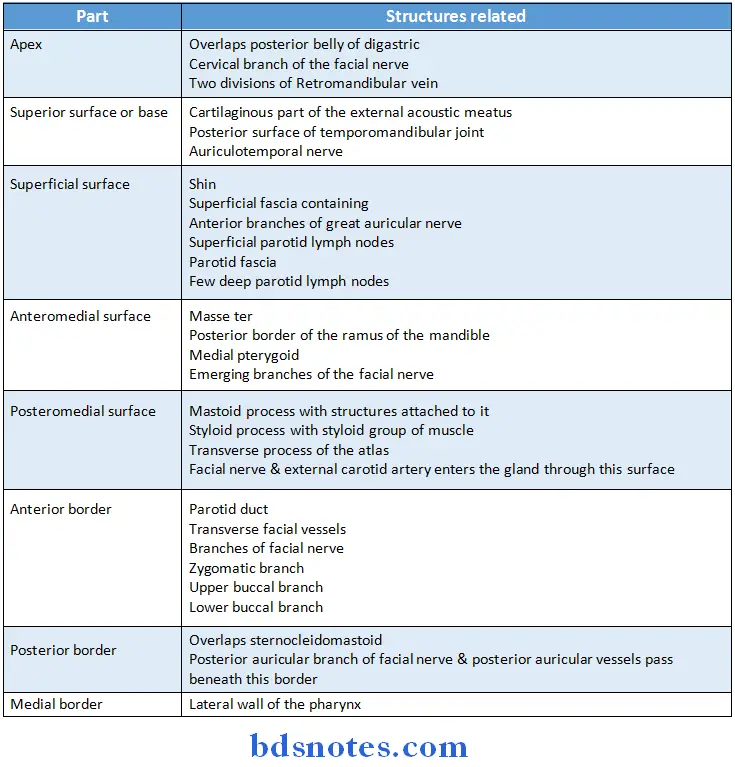
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
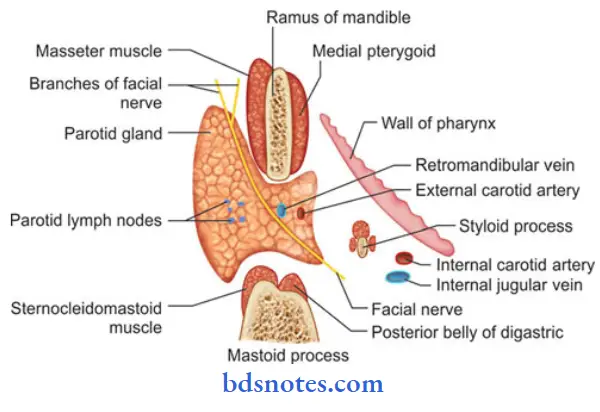
Parotid Gland Blood Supply:
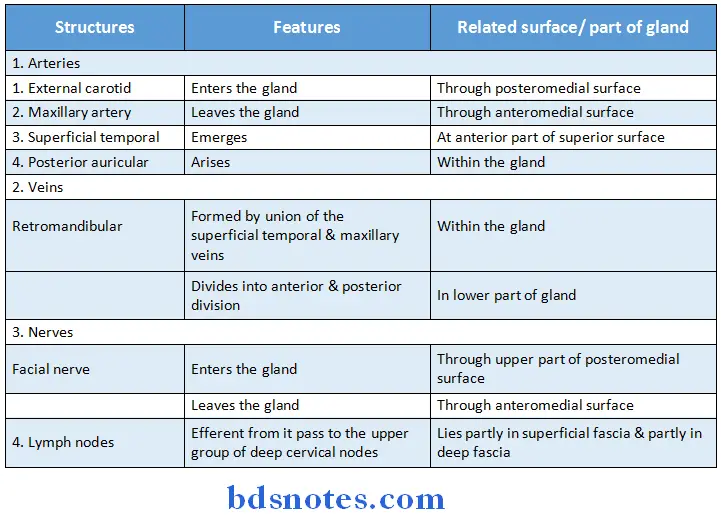
- Parotid gland is supplied by external carotid artery & its branches
- The veins drains into
-
- External jugular vein
- Internal jugular vein
Parotid Gland Nerve Supply:
1. Parasympathetic nerves:
- They are Secretomotor
- They pass through following pathway
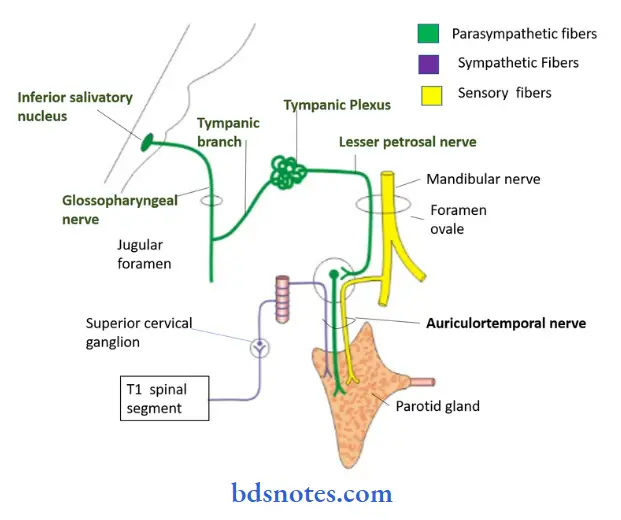
2. Sympathetic nerves:
- They are vasomotor
- They are derived from plexus around middle meningeal artery
3. Sensory nerves:
- Gland receives sensory supply from Auriculotemporal nerve
- While parotid fascia is supplied by sensory fibres of great
auricular nerve
Parotid Gland Applied Anatomy:
- Parotid swelling are very painful due to unyielding nature of the parotid fascia
- Parotid gland can be infected by the mumps virus
- It causes bilateral parotid swelling
- Its complications are Orchitis & pancreatitis
- Spread of infection from the oral cavity can result in parotid abscess
- It is best drained by Hilton’s method
- During parotidectomy, the gland is removed in two parts- superficial & deep
- It is to preserve facial nerve
- Frey’s syndrome is the complication of parotidectomy
- Mixed parotid tumour is slow growing, painless & lobulated
- Its malignant transformation causes pain, rapid growth, fixation & involves facial nerve
Question 2. Describe the external features, relations nerve supply & development of parotid gland (or) Name the arteries seen in the substance of parotid gland (or) Anatomy of parotid gland
Answer:
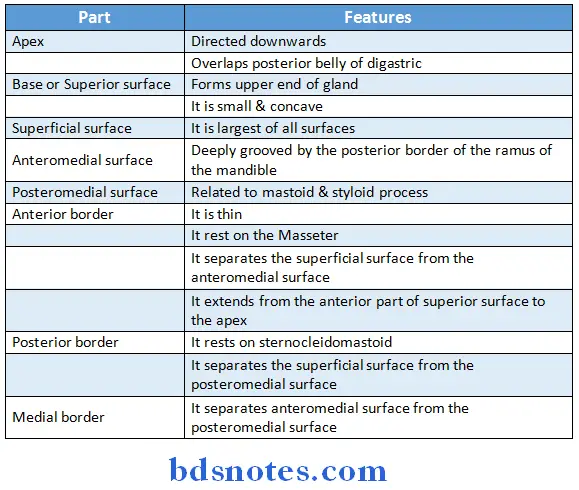
Parotid Gland External Features:
- Parotid gland is three sided pyramid in shape
- It has
- Apex
- Four surfaces
- Superior
- Anteromedial
- Superficial
- Posteromedial
- Three borders
- Anterior
- Medial
- Posterior
Parotid Gland Development:
- It is ectodermal in origin
- It develops from the buccal epithelium just lateral to the angle of mouth
- Its outgrowth branches forms duct system & acini
- The mesoderm forms intervening connective tissue septa
Question 3. Describe parotid gland under following heading. Morphology, Histology.
Answer:
Parotid Gland Morphology:
1. Size
- It is largest of all salivary gland
2. Shape
- It is three sided pyramid with apex directed downwards
- It has four surfaces & three borders to separate them
3. Weight
- It weighs 15 grams
Parotid Gland Histology:
- In the parotid gland the spherical secretory end peices are all serous
- The pyramidal shaped acinar cells have a spherical, basally situated nucleus
- It surrounds a small, central lumen
- It may contain fat cell spaces
Parotid Gland Ducts:
1. Intercalated ducts
- They are numerous & long
- They are lined with cuboidal epithelium
- Nuclei of myoepithelial cells may appear
2. Striated ducts
- They are numerous
- They are round or elongated tubules
- It consists of simple columnar epithelium
- Nuclei are round & centrally placed
- Lumina are relatively larger in size
Question 4. Beginning, course, termination & relations of parotid duct
Answer:
Parotid Duct:
- It is thick walled & about 5 cm long
Parotid Duct Beginning:
- It emerges from the middle of the anterior border of the gland
Parotid Duct Course:
- It runs forwards & slightly downwards on the masseter
- At its anterior border, it turns medially & pierces
- Buccal pad of fat
- Buccopharyngeal fascia
- Buccinator
- Next it runs forwards for a short distance between the buccinator & the oral mucosa
- Finally turns medially
Parotid Duct Termination:
- It opens into the vestibule opposite the crown of the maxillary second molar tooth
Question 5. Describe structures passing through parotid gland
Answer:
Structures passing through parotid gland:
Question 6. Parotid duct opening.
Answer:
Parotid duct:
- It is thick walled & about 5 cm long
Parotid duct Beginning:
- It emerges from the middle of the anterior border of the gland
Parotid duct Course:
- It runs forwards & slightly downwards on the masseter
- At its anterior border, it turns medially & pierces
1. Buccal pad of fat
2. Buccopharyngeal fascia
3. Buccinator
- Next it runs forwards for a short distance between the buccinator & the oral mucosa
- Finally turns medially
Parotid duct Termination:
- It opens into the vestibule opposite the crown of the maxillary second molar tooth
Question 7. Nerve supply to parotid gland
Answer:
Nerve supply to parotid gland :
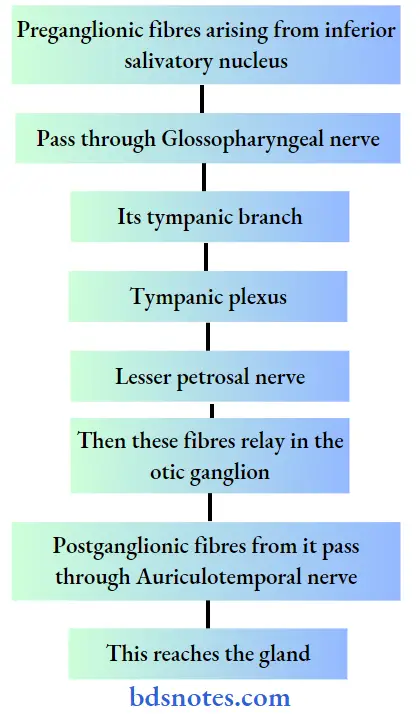
1. Parasympathetic nerves:
- They are Secretomotor
- They pass through following pathway
2. Sympathetic nerves:
- They are vasomotor
- They are derived from plexus around middle meningeal artery
3. Sensory nerves:
- Gland receives sensory supply from Auriculotemporal nerve
- While parotid fascia is supplied by sensory fibres of great auricular nerve
Question 8. Structures pierced by the parotid duct
Answer:
At the anterior border of masseter, the parotid duct turns medially & pierces
- Buccal pad of fat
- Buccopharyngeal fascia
- Buccinator
Question 9. Parotid lymph nodes
Answer:
Parotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found near the parotid gland in the immune system.
They are of two types:
1. Superficial parotid lymph nodes
- The superficial parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes anterior to the ear.
- Their afferent vessels drain the root of the nose, the eyelids, the frontotemporal region, the external acoustic meatus and the tympanic cavity, possibly also the posterior parts of the palate and the floor of the nasal cavity.
- The efferents of these glands pass to the superior deep cervical glands.
2. Deep parotid lymph nodes
- The deep parotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found below the parotid gland.
- The afferents of the subparotid glands drain the nasal part of the pharynx and the posterior parts of the nasal cavities.
- Their efferents pass to the superior deep cervical glands.

Leave a Reply