Model Analysis
Question 1. Write short note on Nance analysis.
Answer.
- Carey’s analysis helps in determining the extent of the discrepancy.
- Many malocclusions occur as a result of discrepancy between arch length and tooth material.
- It is performed on lower cast.
- If space required is less than space available, spacing occur.
- If space required is more than space available, crowding occur.
So it is important to determine the total amount of crowding in patients with malaligned teeth.
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Question And Answers
Determination of Arch Length
- Arch length anterior to the first permanent molar is measured using a sof brass wire.
- Wire is placed contacting the mesial surface of the fist molar (permanent) of one side and passed over the buccal cusps of the premolars and along the anterior and is continued on the opposite side in the same way up to mesial surface of the opposite fist permanent molar.
- If anteriors are proclined the wire is passed along the cingulum of anterior teeth.
- If anteriors are retroclined the wire in anterior segment passes labial to the teeth.
- If the anterior teeth are well aligned the wire passes over the incisal edge of anteriors.
Determination of Tooth Material
The mesiodistal width of the teeth anterior to the fist molars (from 2nd premolar to 2nd premolar) is measured separately and summed up.
Determination of Discrepancy
Discrepancy = arch length-tooth material.
Carey’s Analysis Inference

Question 2. Write short note on Ashley Howe’s analysis.
Answer.
Ashley Howe’s Analysis
Ashley Howe considered tooth crowding to be due to deficiency in arch width rather than arch length.
Determination of total tooth material (TTM): Mesiodistal width of all teeth anterior to 2nd molars and values are summed up (12 teeth).
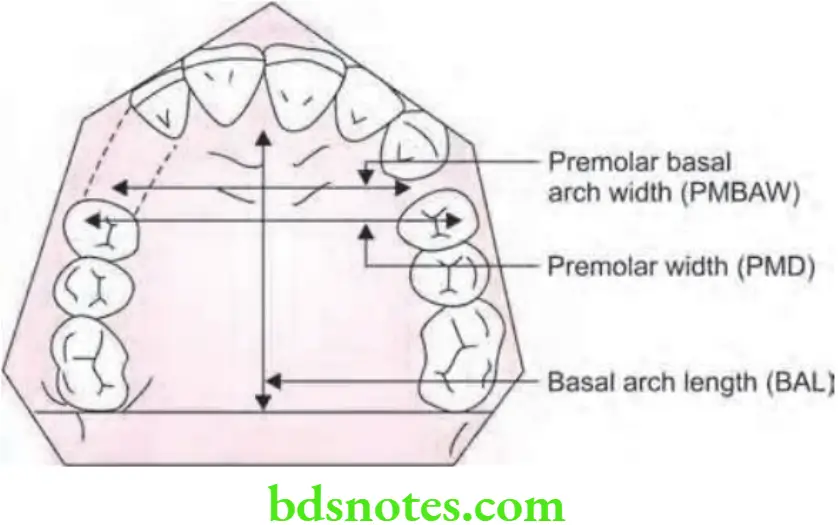
Determination of premolar diameter (PMD): The premolar diameter is the arch width from the tip of buccal cusp of one 1st premolar to the buccal tip of opposite 1st premolar.
Determination of premolar basal arch width (PMBAW): Measurement of width from one canine fossa to other side, it gives us the width of dental arch at the apical base.
Percentage of canine fossa width to tooth material: It is obtained by following formula
\(\text { PMBAW } \%=\frac{\text { PMBAW } \times 100}{T T M}\)
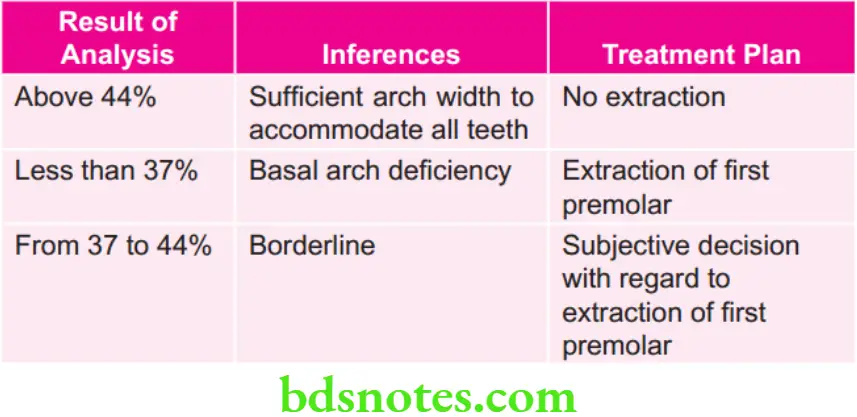
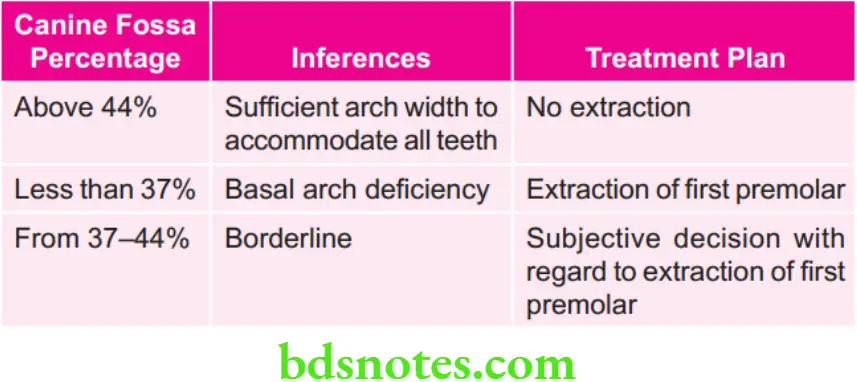
Arches are considered suffient for accommodation of all teeth if value is more than 44%.
Inference of Ashley Howe’s Analysis
Question 3. Write short note on Pont’s index.
Answer.
Pont’s Index
Pont’s in 1909 presented a system in which by the measurement of the four maxillary anterior, the width of the arch in the premolar and molar region established automatically.
Pont’s Analysis Helps in:
- Determining whether the dental arch is narrow or is normal.
- Determining the need for lateral arch expansion.
- Determining how much expansion is possible at the premolar and molar region.
Determination of Sum of Incisors (SI)
SI = Mesiodistal width of all four maxillary anterior (incisors).
Determination of Measured Premolar Value (MPV)
Width of dental arch in premolar region from distal pit of fist premolar of one side to distal pit of 1st premolar of opposite side.
Determination of Measured Molar Value (MMV)
Width of dental arch in molar region from mesial pit of 1st molar on one side to other side.
Determination of Calculated Premolar Value (CPV)
\(\mathrm{CPV}=\frac{\mathrm{SI} \times 100}{80}\)
Determination of Calculated Molar Value (CPV):
\(\frac{S I \times 100}{64}\)
Inference
- If measured value is less than calculated value, it indicates the need of extraction.
- Thus, it is possible to determine how much expansion is needed in the molar and the premolar region.
Question 4. Write short note on Bolton’s analysis.
Answer.
Bolton’s Analysis
Bolton’s analysis evaluates teeth for both maxillary and mandibular arches, for size discrepancies.
- According to Bolton a ratio exist between mesiodistal width of maxillary and mandibular teeth.
- In cases of tooth size discrepancy, teeth in one arch may occupy more space than teeth in opposite arch leading to occlusal misfitng. So such cases should be identified before treatment.
Procedure
- Sum of mandibular 12 teeth: Mesiodistal width of first permanent mandibular molars of one side to first permanent mandibular molar of other side is measured and summed up.
- Sum of maxillary 12 teeth: Mesiodistal width of first permanent maxillary molars of one side to fist permanent maxillary molar of other side is measured and summed up.
- Sum of mandibular 6 teeth, i.e. anteriors: Mesiodistal width of permanent mandibular canine of one side to permanent mandibular canine of other side is measured and summed up.
- Sum of maxillary 6 teeth, i.e. anteriors: Mesiodistal width of permanent maxillary canine of one side to permanent maxillary canine of other side is measured and summed up.
Estimation of Overall Ratio
It is calculated by following formula:
Overall Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Sum of mandibular } 12}{\text { Sum of maxillary } 12} \times 100\)
- Ideal overall ratio is 91.3%. This indicates good overbite and overjet relationship.
- If ratio is more than 91.3%. This indicates mandibular tooth material excess.
- If ratio is less than 91.3%. This indicates maxillary tooth material excess.
- Quantification of overall tooth material excess is done by following formulas.
For Maxillary Tooth Material Excess
= \(\text { Sum of maxillary } 12-\frac{\text { Sum of mandibular } 12 \times 100}{91.3}\)
For Mandibular Tooth Material Excess
= \(\text { Sum of mandibular } 12-\frac{\text { Sum of maxillary } 12 \times 91.3}{100}\)
Determination of Anterior Ratio
Anterior ratio is calculated by following formula:
Anterior Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Sum of mandibular } 6}{\text { Sum of maxillary } 6} \times 100\)
- Ideal anterior ratio is 77.2%.
- If ratio is more than 77.2%. This indicates mandibular anterior tooth material excess.
- If ratio is less than 77.2%. This indicates maxillary anterior tooth material excess.
- Quantification of overall anterior tooth material excess is done by following formulas.
For maxillary anterior excess
= \(\text { Sum of maxillary } 6-\frac{\text { Sum of maxillary } 6 \times 100}{77.2}\)
For mandibular tooth anterior excess
= \(\text { Sum of mandibular } 6-\frac{\text { Sum of maxillary } 6 \times 77.2}{100}\)
Question 5. Write short note on models used in orthodontics.
Answer. Models used in orthodontics are as follows:
Orthodontics Classification
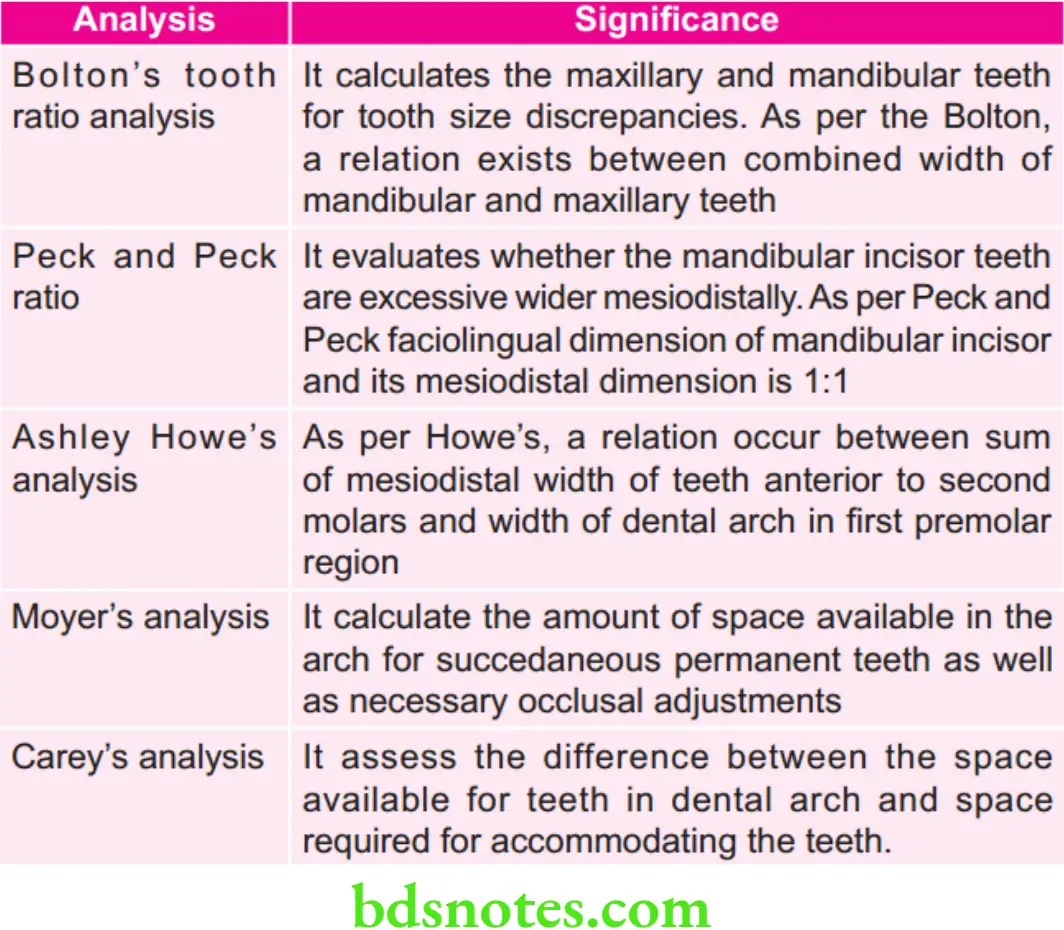
Model analysis to study size relationship of group of teeth
- Bolton tooth ratio model analysis.
- Peck and Peck ratio.
- Sanin-Savara model analysis.
Model analysis for studying relation of tooth size-to-size of supporting structures
- Pont’s model analysis.
- Ashley Howe’s model analysis.
- Korkhau’s model analysis.
- Linderhearth’s analysis.
- Diagnostic set-up.
Model analysis in mixed dentition
- Tanaka Johnston model analysis.
- Moyer’s mixed dentition model analysis.
- Staley and Kerber model analysis.
- Radiographic method.
Model analysis for studying relation of tooth size and available space in permanent dentition
- Arch perimeter model analysis.
- Carey’s model analysis.
- Total space model analysis.
Question 6. Write short note on Kesling’s diagnostic setup.
Answer. The diagnostic set-up was fist proposed by HD Kesling in 1956.
It helps the clinician to estimate arch length discrepancy.
Kesling’s Diagnostic Procedure
- Both the maxillary and mandibular studying casts of patient are prepared.
- Trimming of the base of both the study casts is done parallel to occlusal plane.
- In mandibular cast horizontal cuts are made 3 mm apical to gingival margin with the help of fret saw blade.
- Vertical cuts are also made to separate the individual teeth.
- Trimming of mesial and distal ends of root is done for facilitating the seating at new position.
- In the formed slit during cuttng the teeth wax blocks are placed.
- On study casts mandibular incisor teeth are arranged at an angle of 65° to Frankfort horizontal plane.
- Canines as well as premolars should be placed in correct contact relationships.
- If the remaining space is inadequate for receiving fist molars, extraction should be indicated. First premolars should be eliminated from the set up and are placed to second premolars in contact with canines.
- Cutting of maxillary teeth is carried out and they are repositioned in wax set-up by articulating them with mandibular set-up.
Kesling’s Diagnostic Indication
- It is useful in visualizing and testing the effect of complex tooth movement and extractions on the occlusion.
- Patient can be motivated by simulating the various corrective procedures on the cast.
- Tooth size arch length discrepancy can be visualized by means of a set-up.
- It acts as a guide for extractions in the treatment plan.
Question 7. Write short note on mixed dentition analysis.
Or
Discuss mixed dentition analysis.
Or
Write long answer on mixed dentition analysis.
Answer. Mixed dentition analysis measures the amount of space available in an arch for the eruption of permanent canines and premolars.
- During mixed dentition stage the permanent teeth are not fully erupted so for the estimation of unerupted permanent teeth mixed dentition analysis is carried out.
- Aim of mixed dentition analysis is to compare space available for unerupted permanent canines and premolars with space needed, the diffrence of both provide the orthodontist the amount of spacing and crowding which is expected.
- Following are the mixed dentition analysis, i.e.
- Moyer’s mixed dentition analysis
- Tanaka-Johnston analysis
- Staley and Kerber analysis
- Radiographic method.
- Moyer’s mixed analysis calculates the amount of space available in the arch for succedaneous permanent teeth as well as necessary occlusal adjustments.
- Tanaka-Johnston analysis evaluates the width of unerupted canines and premolars which is based on sum of width of mandibular incisors.
- As the name determines the radiographic method, radiographs are used. In this radiograph evaluates the size of unerupted tooth by using following formula:
\(\frac{\mathrm{Y} 1=\mathrm{X}_1 \times \mathrm{Y} 2}{\mathrm{X} 2}\)
Here,
Y1 is width of unerupted tooth whose measurement is to be determined.
Y2 is width of unerupted tooth on radiograph.
X1 is width of erupted tooth which is measured on cast.
X2 is width of erupted tooth which is measured on radiograph.
Question 8. Write short note on Peck and Peck analysis.
Answer. It is also known as Peck and Peck ratio.
- According to the analysis ratio between the mesiodistal and faciolingual dimension of lower incisor should be 1:1.
- Peck and Peck analysis is done only for lower central incisors and lateral incisors.
- In the analysis the measurements are carried out intraorally.
- While making out the ratio if mesiodistal dimension is more proximal stripping is done.
- The analysis is given for the stability of rotational correction of mandibular incisors.
- Peck and Peck analysis is done by following formula:
\(\frac{\text { Mesiodistal width }}{\text { Faciolingual diameter }} \times 100\)
- After obtaining the value from the above formula it is matched with the ranges which are:
-
- Normal Peck and Peck ratio for central incisors is 88 to 92%
- Normal Peck and Peck ratio for lateral incisors is 90 to 95%.
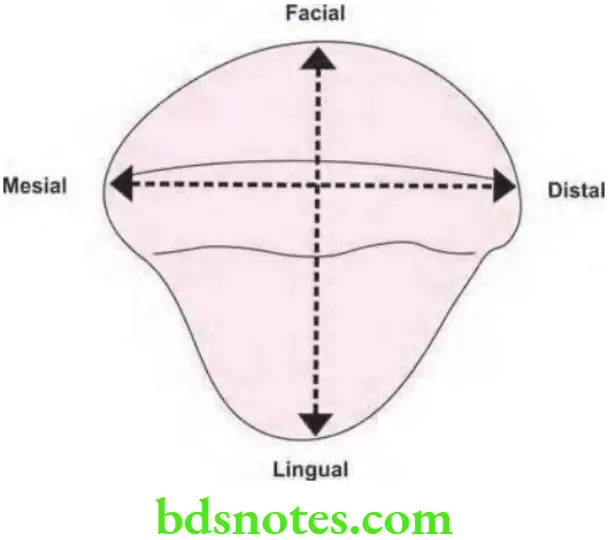
Question 9. Describe canine fossa percentage.
Answer. Canine fossa percentage is one of the criteria used in Ashley Howe’s analysis.
- Premolar basal arch width is assessed by use of canine fossa.
- In obtaining premolar basal arch width (PMBAW) the measurement of width is taken from canine fossa of one side to another side.
- This provides the orthodontist the width of dental arch at the apical base or the junction between basal bone and alveolar process.
- Percentage of canine fossa width (PMBAW%) to total tooth material (TTM) is obtained by dividing fist premolar basal arch width divided by tooth material and multiplied by 100.
\(\mathrm{PMBAW} \%=\frac{\mathrm{PMBAW} \times 100}{\mathrm{TTM}}\)
Question 10. Write short note on Linderharth index.
Answer. Linderharth had given formula for predetermining width of ideal arch which is based on the mesiodistal width of crowns of maxillary incisors.
- Liderharth index is a maxillary expansion index. It suggests that how much maxillary expansion is needed to eliminate crowding.
- As per Linderharth ratio of combined incisor to transverse arch width from center of occlusal surface of teeth in fist premolar area is ideally 0.85 and in fist molar area it is 0.65.
Linderharth Index Method
- Mesiodistal width of maxillary incisors is measured and added.
- In premolar area width of arch is measured from deepest point in transverse fissure of fist premolar in same arch to fist premolar in opposite arch.
- In molar area width of arch is measured from point of intersection of transverse fissure with buccal fissure of fist permanent molar on same side to fist permanent molar of opposite side.
- In premolar region expected arch width is SI × 100/85
- If the value which is measured is less than the calculated value it suggests the need for expansion.
- In molar region expected arch width is SI × 100/65.
- If the value which is measured is less than the calculated value it suggests the need for expansion.

Leave a Reply