Orthodontics Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. According to Wolf’s law:
- Human teeth drift mesially as interproximal wear occur
- Pressure causes bone resorption
- The optimal level of force for moving teeth is 10 to 200 gm
- Bone trabeculae line up in response to mechanical stress
Answer. 4. Bone trabeculae line up in response to mechanical stress
Question 2. Overjet is defined as:
- Horizontal overlap
- Vertical overlap
- Transverse plane discrepancy
- All of the above
Answer. 1. Horizontal overlap
Question 3. Abnormal thick labial frenum results:
- Midline diastema
- Imbrication
- Labial inclination of incisors
- All of the above
Answer. 1. Midline diastema
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Question And Answers
Question 4. Hyperactive mentalis muscle is the feature of:
- Class 1
- Class 2 div. 1
- Class 3 div. 2
- Class 3
Answer. 2. Class 2 div. 1
Question 5. If the force applied is through tooth’s center of resistance than tooth will:
- Tip
- Translate
- Move bodily
- Intrude
Answer. 2. Translate
Question 6. Anchorage is most effective in:
- Round roots
- Flat roots
- Triangular roots
- All of these equally
Answer. 4. All of these equally
Question 7. Examples of fixed functional appliance:
- Activator
- Frankel
- Bimler
- Herbst
Answer. 4. Herbst
Question 8. Elastics are used in fixed appliance:
- To correct Class 2 molar relation
- To correct Class 2I molar relation
- Directly attached to appliance component
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 9. Extraction of permanent molars is called:
- Balanced extraction
- Serial extraction
- Wilkinson’s extraction
- Compensated extraction
Answer. 2. Serial extraction
Question 10. Which of the following wires are called as shaping memory wires?
- Stainless steel round wire
- Multiflex round wire
- Nickel titanium wires
- Stainless steel edgewise wire.
Answer. 3. Nickel titanium wires
Question 11. Lip bumpers are used to move:
- Lower molar distally
- Lower incisor distally
- Upper incisor labially
- Upper molar distally
Answer. 1. Lower molar distally
Question 12. A tooth will translate when the center of rotation in at:
- The incisal edge
- The bracket
- Infinity
- The root apex
Answer. 3. Infinity
Question 13. The adam drap is made of:
1. 24 mil wire
2. 28 mil wire
3. 23 mil wire
4. 22 mil wire
Answer. 2. 28 mil wire
Question 14. Optimal orthodontic force according to Schwartz is:
- 30-36 grams per sq cm
- 20-26 grams per sq cm
- 20-26 grams per sq inch
- 20-26 grams per sq mm
Answer. 2. 20-26 grams per sq cm
Question 15. Denholtz appliance is used for:
- Correction of open bite
- Distalization of the upper molars
- Correction of deep bite
- Correction of anterior crossbite
Answer. 2. Distalization of the upper molars
Question 16. 18/8 stainless steel:
- 18% Nickel, 8% chromium
- 18% Chromium, 8% copper
- 18% chromium, 8% nickel
- None of the above
Answer. 3. 18% chromium, 8% nickel
Question 17. The main criteria for serial extraction is:
- Spacing
- Crowding
- Jaw relation
- Patient’s cooperation
Answer. 1. Spacing
Question 18. Orthodontic correction of which of the following is most easily retained:
- Anterior crossbite
- Crowding
- Diastema
- Spacing
Answer. 1. Anterior crossbite
Question 19. Which of the following cannot act on a space maintainer?
- Well restored tooth
- Lingual arch
- Nance holding arch
- Maxillary expansion device
Answer. 4. Maxillary expansion device
Question 20. A helix is placed for:
- Activation
- Increasing the flexibility and range
- Esthetics
- Retention
Answer. 2. Increasing the flexibility and range
Question 21. Cranium to face ratio at birth is:
- 40:1
- 5:1
- 8:1
- 2:1
Answer. 3. 8:1
Question 22. The major growth center of mandible is:
- Symphysis
- Condyle
- Alveolar bone
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Condyle
Question 23. With the growth of mandible from birth to the adult stage the gonial angle:
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains the same
- First increases then decreases
Answer. 2. Decreases
Question 24. The first ossification center of mandible in relation to Meckele’s cartilage develops:
- Mesial to Meckele’s cartilage
- Superior to Meckele’s cartilage
- Lateral to meckle’s cartilage
- Within the Meckele’s cartilage
Answer. 3. Lateral to meckle’s cartilage
Question 25. Which of the following structures do not contribute to cranial growth?
- Sphenoethmoidal synchondrosis
- Sphenooccipital synchondrosis
- Frontonasal suture
- Lambdoid suture
Answer. 4. Lambdoid suture
Question 26. The first evidence of dental lamina is seen at:
- 4th week of intrauterine life
- 6th week of intrauterine life
- 3rd month of intrauterine life
- 4th month of intrauterine life
Answer. 6th week of intrauterine life
Question 27. The incisal liability in maxillary arch and the mandibular arch is respectively:
- 10 mm and 8 mm
- 7 mm and 5 mm
- 3 mm and 6 mm
- 4 mm and 12 mm
Answer. 2. 7 mm and 5 mm
Question 28. According to Edward Angle the position of maxillary first permanent molar is fixed in relation to:
- Key ridge
- ANS
- PNS
- Pterygoid process
Answer. 1. Key ridge
Question 29. Tooth erupts into oral cavity when:
- One third root formation completed
- Two third root formation completed
- Root is fully formed
- Crown is fully formed
Answer. 4. Crown is fully formed
Question 30. A boy aged 8 years has lost his maxillary deciduous second molar on right side due to caries. Treatment by the dentist at this stage involves:
- Extraction of deciduous maxillary second molar on left side to maintain symmetry of maxillary arch.
- Mesial movement of maxillary first permanent molar on right side to close the space created by lost tooth.
- Immediate space maintainer
- None of the above
Answer. 3. Immediate space maintainer
Question 31. The six keys to normal occlusion was introduced by:
- Dewey
- Andrews
- Tweed
- Angle
Answer. 2. Andrews
Question 32. Enlow’s “V” principle of growth is found in:
- Cranial base
- Maxilla only
- Maxilla and mandible
- None of the above
Answer. 3. Maxilla and mandible
Question 33. As skeletal changes take place gonion moves:
- Downward and forward
- Downward and backward
- Upward and forward
- Upward and backward
Answer. 2. Downward and backward
Question 34. Sequence of eruption of permanent maxillary teeth:
- 6-1-2-4-3-5-7
- 6-1-2-4-5-3-7
- 6-1-2-3-4-5-7
- 1-2-3-4-5-6-7
Answer. 1. 6-1-2-4-3-5-7
Question 35. In occlusion the teeth have:
- Cusp-to-cusp contact
- Edge-to-edge contact
- Marginal contact
- Surface-to-surface contact
Answer. 4. Surface-to-surface contact
Question 36. Hyperactive mentalis muscle is a prominent feature of:
- Class 1
- Class 2 Div. 1
- Class 2 Div. 2
- Class 3
Answer. 2. Class 2 Div. 1
Question 37. Chin cup is used to correct:
- Skeletal Class 1 malocclusion
- Skeletal Class 2 malocclusion
- Skeletal Class 3 malocclusion
- Dental Class 1 malocclusion
Answer. 3. Skeletal Class 3 malocclusion
Question 38. Oral drive theory to explain thumb sucking habit was given by:
- Benjamin
- Sears and Wise
- Sigmund Freud
- Sheldon
Answer. 2. Sears and Wise
Question 39. Apertognathia means:
- Anterior crossbite
- Open bite
- Posterior crossbite
- Prognathism
Answer. 2. Open bite
Question 40. Prolonged retention is usually needed in:
- Diastema
- Mild crowding
- Anterior crossbite
- Deep bite
Answer. 1. Diastema
Question 41. Dolichocephalic refers to:
- Long wide faces
- Long narrow faces
- Short wide faces
- Short narrow faces
Answer. 2. Long narrow faces
Question 42. Calcification of first molar starts at:
- 2 weeks of IU life.
- At birth
- 6 months after birth
- 30 months after birth
Answer. 2. At birth
Question 43. In Sicher’s theory suture acts as:
- Has independent growth potential
- Dependent on cranial base
- Used for growth adjustment
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Has independent growth potential
Question 44. Following profile is more prone for fractures of maxillary incisors:
- Class 1
- Class 2 Div. 1
- Class 2 Div. 2
- Class 3
Answer. 2. Class 2 Div. 1
Question 45. The cause of pseudo class 3 malocclusion is:
- Developmental deficiency
- Increased mandibular growth
- Functional abnormality
- Hormonal disturbances
Answer. 3. Functional abnormality
Question 46. In Ackermann-Profit classification, outer envelop represents:
- Alignment
- Profile
- Transverse relation
- Vertical relation
Answer. 1. Alignment
Question 47. Fishman’s index is used in relation with:
- Population
- Hand-wrist radiograph
- Cephalogram
- Periodontal disease
Answer. 2. Hand-wrist radiograph
Question 48. Which of the following does not be on the mandible?
- Pogonion
- Menton
- Porion
- Gnathion
Answer. 3. Porion
Question 49. Angle of convexity:
- SNA
- SNB
- N-A- Pog
- ANB
Answer. 3. N-A- Pog
Question 50. The appliance used to treat thumb sucking:
- Crib appliance
- Frankel appliance
- Bionator
- Activator
Answer. 1. Crib appliance
Question 51. The term orthodontics coined by:
- Le Felon of France
- Hunter
- Carabelli
- Norman Kigsley
Answer. 1. Le Felon of France
Question 52. Oral and nasal capsule of functional growth is related to:
- Periosteal matrix
- Sutural matrix
- Capsular matrix
- None of the above
Answer. 3. Capsular matrix
Question 53. The ugly-duckling stage is seen at the age of:
- 6–7 years
- 9–10 years
- 10–12 years
- 12–14 years
Answer. 2. 9–10 years
Question 54. If dentition is placed close to Frankfort horizontal plane then it is called as:
- Protraction
- Attraction
- Abstraction
- Contraction
Answer. 2. Attraction
Question 55. Acromegaly is associated with:
- Class 1 malocclusion
- Class 2 malocclusion
- Class 3 malocclusion
- Class 1 crossbite
Answer. 3. Class 3 malocclusion
Question 56. The most anterior part of bony chin:
- Gonion
- Pogonion
- Menton
- Gnathion
Answer. 2. Pogonion
Question 57. The cells involved in bone resorption are:
- Osteoblasts
- Osteoclasts
- Osteocytes
- None of these
Answer. 2. Osteoclasts
Question 58. Maximum resistance to tooth movement is given by:
- Mandibular molar
- Maxillary molar
- Mandibular canine
- Maxillary canine
Answer. 1. Mandibular molar
Question 59. Example for fixed functional appliance:
- Activator
- Frankel
- Bimler
- Herbst
Answer. 2. Frankel
Question 60. Which of the following is the non-invasive method of gaining space?
- Slenderization
- Expansion
- Extraction
- All of the above
Answer. 2. Expansion
Question 61. Calcification of first permanent molar starts at:
- 11/2 week of IU life
- At birth
- 6 months after birth
- 21/2 years after birth
Answer. 2. At birth
Question 62. Eruption of teeth is delayed in all of the following except:
- Hypothyroidism and cleidocranial dysplasia
- Acromegaly and hyperthyroidism
- Rickets and cherubism
- Cretinism and dentigerous cysts
Answer. 1. Hypothyroidism and cleidocranial dysplasia
Question 63. The most reproducible relation of the jaws is:
- Centric occlusion
- Centric relation
- Protrusive contact position
- Lateral contact position
Answer. 2. Centric relation
Question 64. A pseudo class 3 is differentiated from true class 3 by:
- Presence of premature contacts
- Normal gonial angle
- Deviated path of closure
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 65. Abnormal muscular activity more often is result of:
- Bruxism
- Nail biting
- Tongue thrusting
- Tongue sucking
Answer. 3. Tongue thrusting
Question 66. Blanch test is used in the diagnosis of:
- Abnormal frenal attachments
- Pseudo Class 3
- Tongue thrusting
- Thumb sucking
Answer. 1. Abnormal frenal attachments
Question 67. Arch perimeter is measured with:
- Cephalogram
- Brass wire
- Vernier calliper
- Occlusal radiograph
Answer. 2. Brass wire
Question 68. Which of the following landmarks is present at the angle of mandible?
- Gnathion
- Gonion
- Pogonion
- Porion
Answer. 2. Gonion
Question 69. Carpal radiographs is used for assessment of:
- Bone condition
- Chronological age
- Treatment plan
- Skeletal maturation
Answer. 4. Skeletal maturation
Question 70. Y-axis is used to analyze:
- Maxillary growth
- Mandibular growth
- Both maxillary and mandibular growth
- To design appliance
Answer. 2. Mandibular growth
Question 71. In translation center of rotation is at:
- Apical 1/3rd
- Infinity
- Apex
- Coronal 1/3rd
Answer. 2. Infinity
Question 72. Baker’s anchorage is a type of:
- Intermaxillary anchorage
- Intramaxillary anchorage
- Extraoral anchorage
- Skeletal anchorage
Answer. 1. Intermaxillary anchorage
Question 73. Blanch test is used in diagnosis of:
- Abnormal frenal attachment
- Pseudo class 3
- Tongue thrust
- Thumb sucking
Answer. 1. Abnormal frenal attachment
Question 74. Posterior bite plane is used in correcting:
- Deep bite
- Anterior crossbite
- Posterior crossbite
- Crowding
Answer. 2. Anterior crossbite
Question 75. Anterior open bite is caused by:
- Bruxism
- Lip biting
- Thumb sucking
- Nail biting
Answer. 3. Thumb sucking
Question 76. Example of fixed functional applications:
- Activator
- Frankel
- Oral screen
- Herbst
Answer. 4. Herbst
Question 77. The process of securing arch wire to the bracket is known as:
- Separation
- Bonding
- Ligation
- Isolation
Answer. 3. Ligation
Question 78. Wilkinson’s extraction is:
- Extraction of 1st molars
- Extraction of 2nd molars
- Extraction of 3rd molars
- Extraction of 1st premolars
Answer. 1. Extraction of 1st molars
Question 79. Vestibular screen works on the principle of:
- Forces application
- Forces elimination
- Both of the above
- None of the above
Answer. 3. Both of the above
Question 80. Which of the following is not a type of a labial bow?
- Short
- Long
- Medium
- Reverse
Answer. 3. Medium
Question 81. Which branch of orthodontics is mostly related to mixed dentition period?
- Preventive
- Interceptive
- Corrective
- Surgical
Answer. 2. Interceptive
Question 82. The body tissue that grows rapidly but shows minimal growth after the age of 6 – 7 years is:
- Neural tissue
- Lymphoid tissue
- Genital tissue
- Skeletal tissue
Answer. 1. Neural tissue
Question 83. Servosystem theory of growth was given by:
- Scot
- Petrovic
- Limborgh
- Van der Klaw
Answer. 2. Petrovic
Question 84. Most of the mesenchymal structures of the face are formed from:
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
- Neural crest cells
- Mesoderm
Answer. 3. Neural crest cells
Question 85. At what age child is expected to have 12 primary teeth and 12 erupted permanent teeth:
- 4.5 years
- 6.5 years
- 8.5 years
- 11.5 years
Answer. 3. 11.5 years
Question 86. Most of the Leeway space is contributed by:
- Second primary molar
- Primary canine
- First primary molar
- Same by all
Answer. 1. Second primary molar
Question 87. The final form of dental arch is finally determined by:
- Facial type
- Growth pattern
- Angle’s classification
- Balance between intraoral and extraoral muscle force
Answer. 4. Balance between intraoral and extraoral muscle force
Question 88. In occlusion the teeth have:
- Cusp-to-cusp contact
- Edge-to-edge contact
- Marginal contact
- Surface-to-surface contact
Answer. 4. Surface-to-surface contact
Question 89. If the tooth has not erupted to the line of occlusion it is called:
- Supraversion
- Torsiversion
- Rotated
- Infraversion
Answer. 4. Infraversion
Question 90. Which one of the following has maximum familial tendency?
- Protruded maxillary incisors
- Open bite
- Deep bite
- Upper and lower crossbite
Answer. 3. Deep bite
Question 91. Rearward resorption is seen in:
- Application of light forces
- Application of heavy forces
- Both of the above
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Application of heavy forces
Question 92. A typical formulation of stainless steel wire for orthodontic use has:
- 18% chromium and 8% nickel
- 18% nickel and 8% chromium
- 18% chromium and 8% gold
- 8% gold and 18% palladium
Answer. 1. 18% chromium and 8% nickel
Question 93. Anchorage is:
- Resistance to unwanted tooth movement
- Resistance to wanted tooth movement
- Resistance to both wanted and unwanted tooth movement
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Resistance to unwanted tooth movement
Question 94. Tooth movement most likely to relapse unless adequate retention is applied is:
- Extrusion
- Intrusion
- Tipping
- Rotation
Answer. 4. Rotation
Question 95. Tongue blade is a simple device used for correction of:
- Lip sucking
- Finger sucking
- Tongue thrusting
- Incisor crossbite
Answer. 4. Incisor crossbite
Question 96. The following is not a component of fixed appliance:
- Bands
- Brackets
- Open coil spring
- Adam’s clasp
Answer. 4. Adam’s clasp
Question 97. The following is not a myofunctional appliance:
- Activator
- Begg’s appliance
- Frankel
- Oral screen
Answer. 2. Begg’s appliance
Question 98. Face mask therapy is used to:
- Push maxilla posteriorly
- Pull maxilla anteriorly
- Pull mandible anteriorly
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Pull maxilla anteriorly
Question 99. Which of the following condition should be treated as soon as it is seen?
- Proclination
- Crowding
- Anterior tooth crossbite
- Spacing
Answer. 3. Anterior tooth crossbite
Question 100. Intermaxillary elastics used in fixed orthodontics are worn:
- In same arch
- Between opposing arches
- Only in maxilla
- Only in mandible
Answer. 2. Between opposing arches
Question 101. Growth of condyle is by:
- Membranous growth
- Interstitial growth
- Cartilaginous growth
- Bony Apposition
Answer. 3. Cartilaginous growth
Question 102. Spheno-occipital synchondrosis closes at the age of:
- 6 year
- Early puberty
- Early adult age
- It never closes
Answer. 3. Early adult age
Question 103. Incisal liability in maxillary arch is:
- 7.6 mm
- 5 mm
- 1.7 mm
- 3.2 mm
Answer. 1. 7.6 mm
Question 104. What would be the treatment choice for adult with Class 2 skeletal malocclusion with recessive chin and normal maxilla:
- Fixed orthodontics only
- Functional appliance
- Surgical orthodontics
- All the above
Answer. 3. Surgical orthodontics
Question 105. Most common orofacial malformation producing malocclusion is:
- Ectodermal dysplasia
- Pierre Robin syndrome
- Clef lip and palate
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
Answer. 3. Clef lip and palate
Question 106. Mentalis muscle contraction causes lip to…………
- Retrede
- Protrude
- Inversion
- Eversion
Answer. 2. Protrude
Question 107. Normal nasolabial angle is:
- 110°
- 70°
- 55°
- 155°
Answer. 1. 110°
Question 108. Torsiversion refers to:
- Change in inclination
- Impaction of tooth
- Change in position
- Rotation around tooth axis
Answer. 4. Rotation around tooth axis
Question 109. Surgery of cleft lip is advocated at:
- 3 to 6 months
- 3 years
- 1 year
- 9 months
Answer. 1. 3 to 6 months
Question 110. Heavy forces on periodontal ligament cause:
- Hyalinization
- Gestalt bone reception
- Osteoclastic activity around tooth
- Osteoblastic activity
Answer. 1. Hyalinization
Question 111. First diagnostic setup was given by:
- Angle
- Kesling
- Tweed
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Kesling
Question 112. Normal value for FMA angle is:
- 45°
- 10°
- 25°
- 5°
Answer. 3. 25°
Question 113. Maxillary and mandibular incisor protrusion with spacing indicates:
- Mouth breathing habit
- Thumb sucking
- Tongue thrusting
- None of the above
Answer. 4. None of the above
Question 114. Angle’s classification of malocclusion was given in which year:
- 1899
- 1999
- 1909
- None of the above
Answer. 3. 1909
Question 115. Which will exhibit more flexibility:
- NiTi
- TMA
- Stainless steel
- None of the above
Answer. 1. NiTi
Question 116. If ANB angle is more than 40. It indicates:
- Class 1 malocclusion
- Class 2 malocclusion
- Class 3 malocclusion
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Class 2 malocclusion
Question 117. Timing for pubertal growth spurt in males is:
- 7 to 9 years
- 13 to 15 years
- 15 to 18 years
- Above 18 year
Answer. 2. 13 to 15 years
Question 118. Which is the most stable landmark in cephalogram:
- Sella
- Nasion
- Porion
- Point A
Answer. Sella
Question 119. Incline plane is constructed:
- 45° to occlusal plane
- 70° to occlusal plane
- 25° to occlusal plane
- None of the above
Answer. 1. 45° to occlusal plane
Question 120. After mixed dentition stage the arch length from first molar to first molar is usually:
- Decreases
- Increases
- Remains same
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Decreases
Question 121. Which is the supplemental diagnostic aid:
- Study casts
- Facial photographs
- Cephalogram
- Clinical examination
Answer. 3. Cephalogram
Question 122. Blanch test is used for diagnosis of:
- Pseudo class 3
- Abnormal frenal attachment
- Tongue thrusting
- Thumb sucking
Answer. 2. Abnormal frenal attachment
Question 123. In mixed dentition, which of the following may be considered as a self correcting problem with age:
- Unilateral loss of primary canine
- Lack of inter – dental spaces
- Distal step
- Open bite
Answer. 3. Distal step
Question 124. Baker’s anchorage is a type of:
- Intermaxillary anchorage
- Intramaxillary anchorage
- Extraoral anchorage
- Skeletal anchorage
Answer. 1. Intermaxillary anchorage
Question 125. Total mandibular arch contained in the maxillary arch is:
- Scissor bite
- Cross bite
- Deep bite
- Reverse bite
Answer. 3. Deep bite
Question 126. Fishman’s index is used in relation with:
- Population
- Hand wrist radiograph
- Cephalogram
- Orthodontic treatment index
Answer. 2. Hand Wrist radiograph
Question 127. Which of the following tells about the maxillomandibular relationship:
- SNA
- SNB
- IMPA
- ANB
Answer. 4. ANB
Question 128. Which is the example of reciprocal anchorage:
- Midline diastema correction
- Using Class 2 elastics
- Through the bite elastics
- Both a and c
Answer. 4. Both 1 and 3
Question 129. Which of the wire is called as shape memory wire:
- Stainless steel wire
- Multiflx wire
- Nickel titanium wire
- Coaxial wire
Answer. 3. Nickel titanium wire
Question 130. Optimum orthodontic force should not exceed the:
- Arterial blood pressure
- Venous blood pressure
- Capillary blood pressure
- Masticatory pressure
Answer. 3. Capillary blood pressure
Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. The pharyngeal muscle that forms the part of buccinator muscle is ……………
Answer. Superior constrictor
Question 2. Total Leeway space of Nance in mandibular arch is……………
Answer. 3.4 mm
Question 3. Concave profile is seen in…………… malocclusion.
Answer. Class 3
Question 4. Sphenooccipital synchondrosis closes at the age of…………… years.
Answer. 20
Question 5. Flush terminal plane is seen in relation to which tooth……………
Answer. Second primary molar
Question 6. The angle of convexity is measured as angle ……………
Answer. to the extent of maxillary basal arch at its anterior limit relative to the total facial profie
Question 7. The optimal orthodontic force is …………… gm/cm2 of root surface area.
Answer. 20 to 25
Question 8. The moment to force ratio (M/F) for translator tooth movement is ……………
Answer. 10:1
Question 9. …………… is an example of fied functional appliance.
Answer. Herbst appliance
Question 10. Pericision/CSF is done to prevent the relapse of ……………teeth.
Answer. Rotated
Question 11. Name of one commonly used cephalometric analysis is ……………
Answer. Steiner’s analysis
Question 12. Name of one commonly used mixed dentition analysis is ……………
Answer. Moyer’s analysis
Question 13. One common cephalometric reference plane is ……………
Answer. ANB
Question 14. Class 3 malocclusion have …………… profie.
Answer. Concave
Question 15. Andrews gave …………… keys of occlusion.
Answer. Six
Question 16. ………………….. is used to assess skeletal age.
Answer. Hand-Wrist radiograph
Question 17. Osteoclasts lie in …………… lacunae.
Answer. Howship’s
Question 18. Intermaxillary anchorage example is …………… Anchorage.
Answer. Baker’s
Question 19. …………… spring is used for maxillary expansion
Answer. Coffin
Question 20. …………… is the active component of fied appliance.
Answer. Arch wire
Question 21. Correction of ………………….. bite by cross elastics is known as Baker’s anchorage.
Answer. Cross
Question 22. Another name for infantile swallowing is ……………………. swallowing.
Answer. Visceral or Reverse infantile
Question 23. ……………….. Frankel appliance is used for correction of class 2 Div. 1 malocclusion.
Answer. FR1
Question 24. Target to source distance in a cephalostat is………………….. inches.
Answer. 60
Question 25. Closure of spheno-occipital synchondrosis takes place at the age of……………………..
Answer. 20 years
Question 26. Lip bumper is used for…………………
Answer. Distalization of lower molars
Question 27. Dentists act was framed in the year…………………….
Answer. 1948
Question 28. Posterior clearance in anterior bite plane is………………………
Answer. 2–3 mm
Question 29. Adam’s clasp is fabricated by ………………..mm stainless steel wire.
Answer. 0.7
Question 30. Father of modern orthodontics is……………………….
Answer. Edward Angle
Question 31. Hyrax is a type of ………………………. appliance.
Answer. Rapid maxillary expansion
Question 32. The most common cause of midline diastema is……………………..
Answer. Abnormal labial frenum attchment
Question 33. Caries control is a part of ……………… orthodontics
Answer. Preventive
Question 34. ANB angle in Steiner’s analysis is an indicator of ………………… relationship.
Answer. Maxilla and mandible
Question 35. ………………… is a type of self correcting malocclusion.
Answer. Ugly duckling
Question 36. Shape memory and superelasticity are two unique properties of ……………… arch wire.
Answer. Nickel – Titanium
Question 37. The term ugly duckling stage was coined by…………………
Answer. Broadbent
Question 38. The only malocclusion with monogenetic inheritance is Angle’s ………………. malocclusion.
Answer. Class 3
Question 39. Headgear is a type of ……………….. anchorage.
Answer. Extra-oral
Question 40. Adenoid face is seen in …………… habit.
Answer. Mouth breathing
Question 41. The ugly duckling stage is seen at the age of…………………. years.
Answer. 8 to 9
Question 42. Heavy forces on periodontal ligament cause……………..
Answer. Hyalinization
Question 43. In…………… cases the anchoraging unit should not more than 25%.
Answer. Maximum or critical anchorage
Question 44. ……………….. appliance is used for correction of anterior crossbite.
Answer. Inclined plane
Question 45. Hyperactive mentalis muscle is a prominent feature of………… malocclusion.
Answer. Class 2 Div. 1
Question 46. …………………. is defined as joining the parts of a metal by melting them by the application of heat/pressure without any intermediatory.
Answer. Soldering
Question 47. Total mandibular arch contained within maxillary arch is called…………….. bite.
Answer. Cross
Question 48. Carpal radiograph is used for assessment of……………… maturation.
Answer. Skeletal
Question 49. The age upto which thumb sucking is accepted………….year.
Answer. 31/2 to 4
Question 50. …………. forces best accomplish orthodontic tooth movement.
Answer. Light and continuous
Question 51. ………………………… is considered as the Father of Modern Orthodontics.
Answer. Edward Hartley Angle
Question 52. Serial extraction is a part of………………………orthodontics.
Answer. Interceptive
Question 53. …………………. Is the nerve of fist branchial arch.
Answer. Mandibular nerve
Question 54. The mean value of incisor mandibular plane angle (IMPA) in Tweed’s analysis is………………..
Answer. 90°
Question 55. Overall ratio of more than 91.3% indicates ………………….. tooth material excess in Bolton’s analysis.
Answer. Mandibular
Question 56. ………………… is the simplest type of tooth movement.
Answer. Tipping
Question 57. Intermaxillary anchorage is also termed as …………………. Anchorage.
Answer. Baker’s
Question 58. Edgewise appliance was given by…………………….
Answer. Edward Hartley Angle
Question 59. Herbst appliance is a type of …………………….. appliance.
Answer. Fixed functional
Question 60. Anterior bite plane can be used in correcting …………………….malocclusion.
Answer. Vertical
Question 61. Activator was designed by…………………..
Answer. Viggo Andresen (1908)
Question 62. The concept of expanding V principle was put forward by……………………
Answer. Enlow
Question 63. Localized spacing present mesial to upper canine and distal to lower canine are called as……………………
Answer. Primate space
Question 64. Leeway space in maxilla is……………………..and mandible is……………………
Answer. 1.8 mm and 3.4 mm
Question 65. Movement of tooth around its own axis is called as………………….
Answer. Rotation
Question 66. ………………….are used to create space between adjacent teeth for bonding procedures.
Answer. Separators
Question 67. …………………….is useful adjunctive surgical procedure in which the gingival fiers are incised to prevent relapse.
Answer. Edward’s procedure
Question 68. Intraoral elastics stretched between molars and anterior teeth of the same arch are called…………………… elastics.
Answer. Class 1
Question 69. Rotational tendency of the couple in orthodontics is called as…………………………..
Answer. Moment of the couple
Question 70. ……………………….is defied as the procedure for joining metals by the use of filer material.
Answer. Soldering
Question 71. Cephalometric radiography was introduced in 1931 by……………………………..
Answer. Holly Broadbent Sr. in USA.
Question 72. Resorption of alveolar bone by cells from adjacent marrow spaces is called …………………….
Answer. Undermining resorption or rearward resorption
Question 73. In…………………type of tooth movement only tension areas are present.
Answer. Extrusion
Question 74. Removable appliances produce…………………………. type of tipping.
Answer. Uncontrolled
Question 75. A single force through center of resistance of tooth will cause……………. type of tooth movement.
Answer. Bodily
Question 76. 9 theorums of retention was put forward by ……………………
Answer. Riedel
Question 77. ICON acrenym stands for……………………
Answer. Index of complexity, outcome and need
Question 78. …………………………… malocclusion in single largest group of malocclusion.
Answer. Class 1 (50 to 55%)
Question 79. Mandibular inter canine width completes by …………………………years of age.
Answer. 9
Question 80. Concept of functional matrix theory was given by………………………….
Answer. Melvin Moss (1960)
Question 81. Lymphoid tissue proliferates rapidly in late childhood and reaches almost………………% of about size.
Answer. 200
Question 82. Sutural theory was given by………………….
Answer. Sicher and Weinmann
Question 83. Gum pads usually lasts for ………………months after birth.
Answer. Six
Question 84. Ackerman Proffit classification is based on the ………………….diagram.
Answer. Venn
Question 85. Class 3 malocclusion patients generally have ………………profile.
Answer. Concave
Question 86. Serial extraction has been defied as active supervision of teeth by extraction by………………
Answer. Reducing crowding problems
Question 87. Pendulum appliance is used to………………… the molars.
Answer. Distalize
Question 88. Quad helix is used for……………..expansion.
Answer. Maxillary teeth
Question 89. Riedel has summarized the different concepts and philosophies existing into……………..theories.
Answer. Retention
Question 90. Catlan’s appliance is used to treat anterior……………….
Answer. crossbite
Question 91. The term “orthodontics” wascoined by……………………..
Answer. Sir James Murray
Question 92. FH plane is formed by joining……………………
Answer. orbitale and porion
Question 93. Rate of activation with slow expansion is…………………
Answer. 0.5 mm per week
Question 94. “Whip spring” is used for correction of…………….
Answer. Rotation
Question 95. Is extracted in Wilkinson extraction………………….
Answer. All permanent fist molars
Question 96. Anterior bite plane is used for correction of……………………
Answer. Extrusion
Question 97. P in and Tube appliance is a contribution of………………..
Answer. Angle (1910)
Question 98. Blanch test is used in diagnosis of………………………..
Answer. Midline diastema
Question 99. Adams is………………..component of removable orthodontic appliance.
Answer. Retentive
Question 100. Optimal orthodontic force is……………………g/sq inch
Answer. 129 to 166.7
Question 101. Bionator is developed by…………………..
Answer. Wilhelm Balters of Germany
Question 102. Early mesial shift is utilized by……………………..
Answer. Permanent mandibular and maxillary first molars
Question 103. Centre of resistance in case of multirooted teeth is located at 1 to 2mm apical to the……………….
Answer. Furcation
Question 104. Acid etch technique was introduced by……………….
Answer. Buonocore (1955)
Question 105. Mean value of mandibular plane angle in Steiner’s analysis is……………..
Answer. 32°
Question 106. Dissolves any surface impurities on metal to be joined is called………………..
Answer. Flux
Question 107. Most common etiological cause of midline diastema is abnormal or…………………..labial………….
Answer. Hypertrophic labial frenum
Question 108. Mid sagittal suture opening after rapid palatal expansion is assessed by……………….radiograph.
Answer. Occlusal
Question 109. Hyperactive mentalis muscle is a common fiding of…………………..malocclusion.
Answer. Class 2 division 1
Question 110. Most commonly used clasp is……………………………..
Answer. Adam
Additional Information
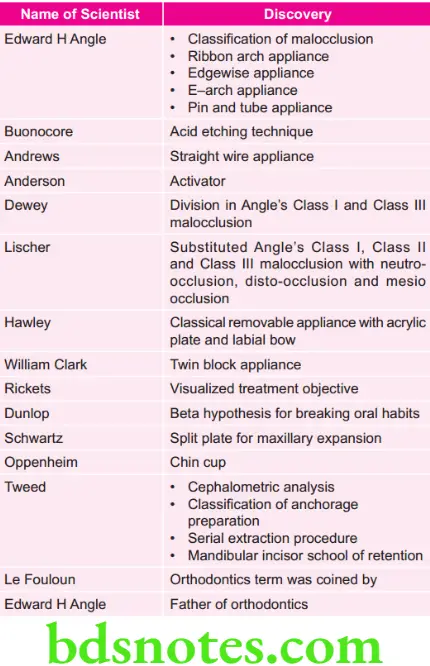
Various Scientists in Orthodontics Along with their Discoveries
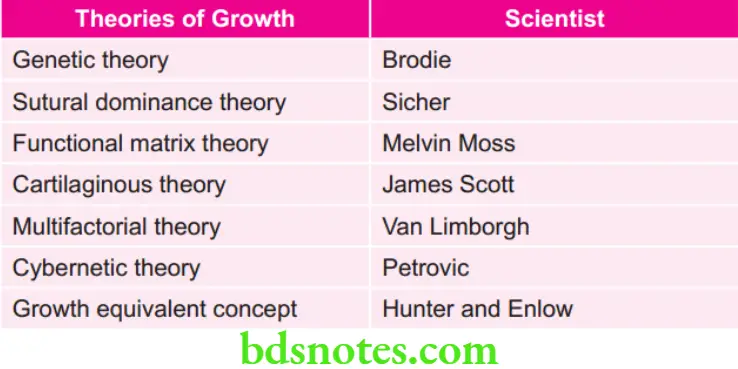
Various Theories of Growth and the Scientists who had Given Them
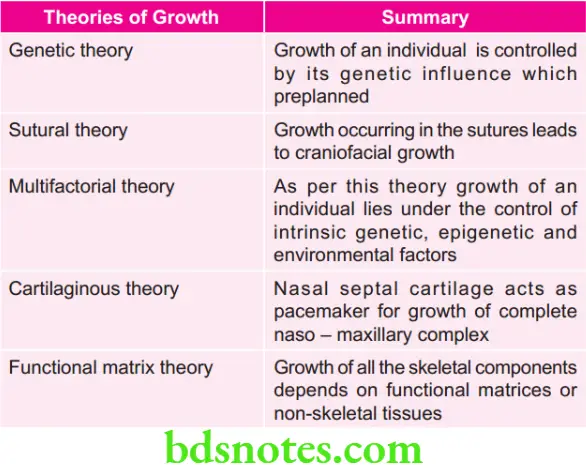
Various Theories of Growth and their Summary
Various Cartilages and their Derivatives
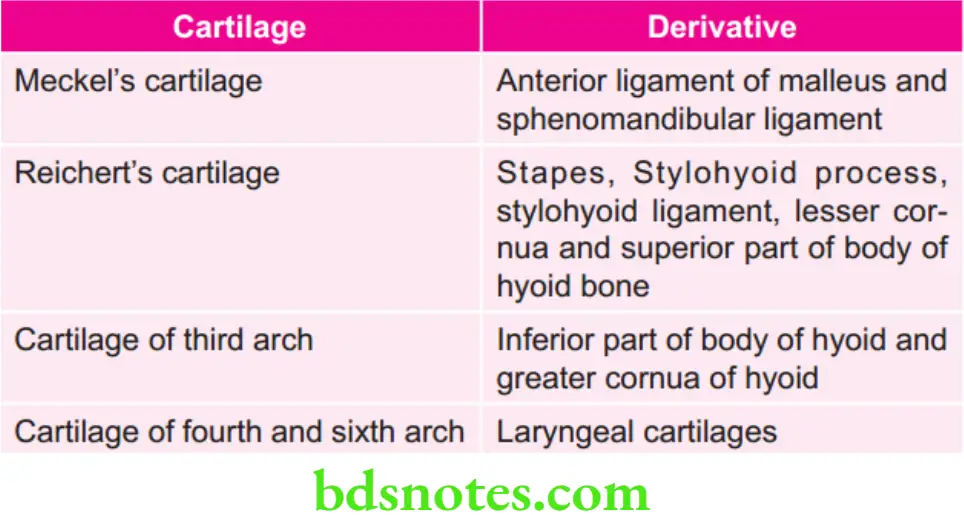
Timings of Cranial Base Growth
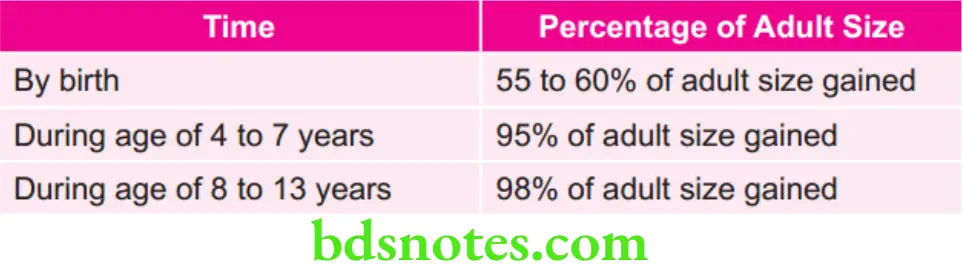
Various Synchondrosis and their Time of Ossification
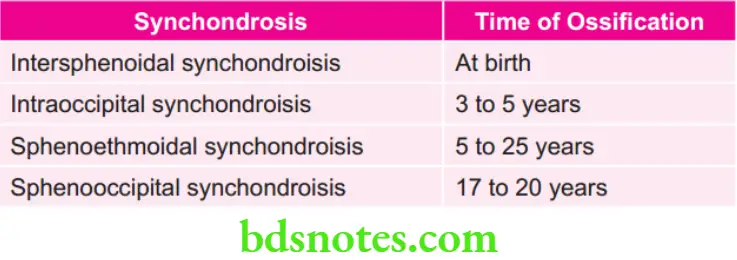
Various Stages in Development of Males and Females
Various Numbers of Bone Present in Body
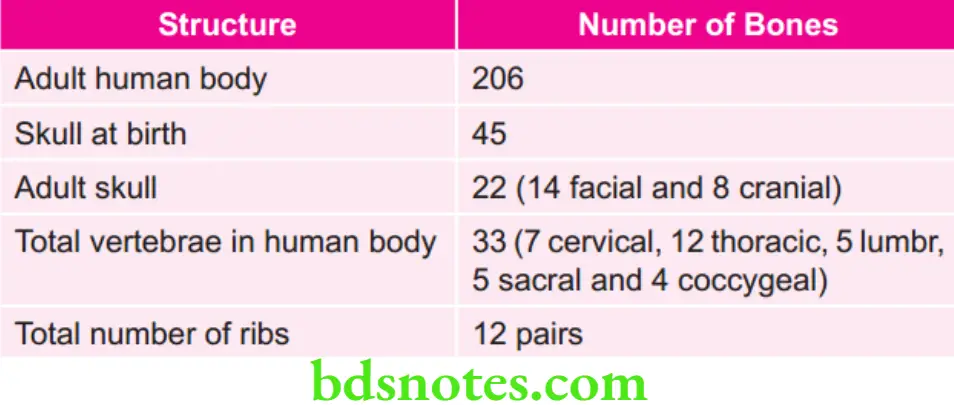
Various Types of Malocclusions and Their Meanings
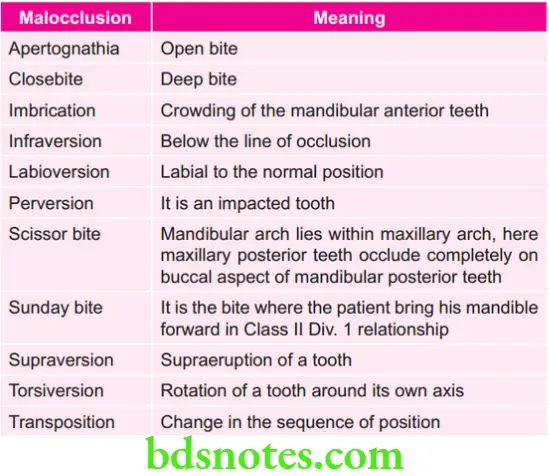
Various Malocclusions Along with their Percentages of Occurrence
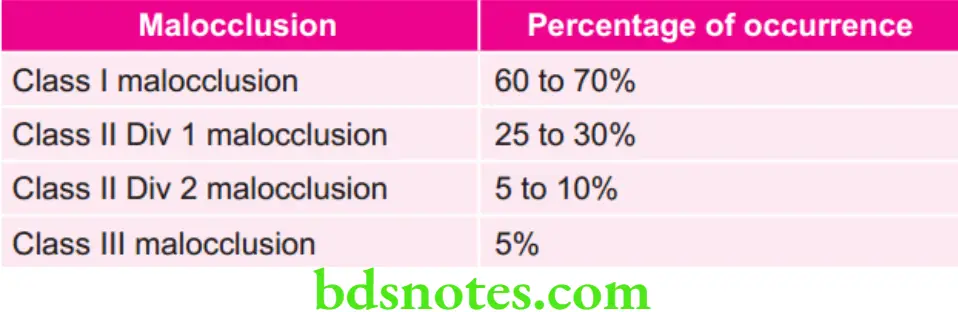
Various Diseases Leading to Jaw Abnormalities
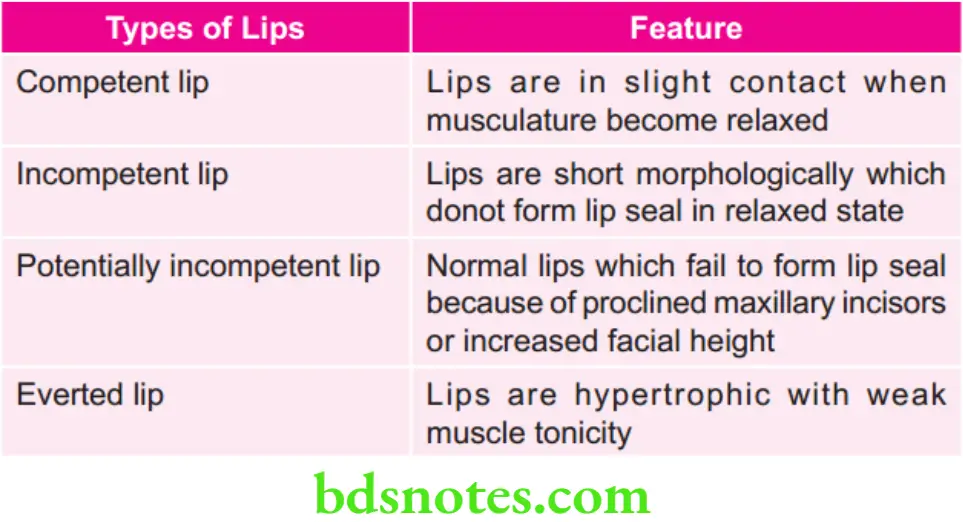
Types of Lips
Types of Head

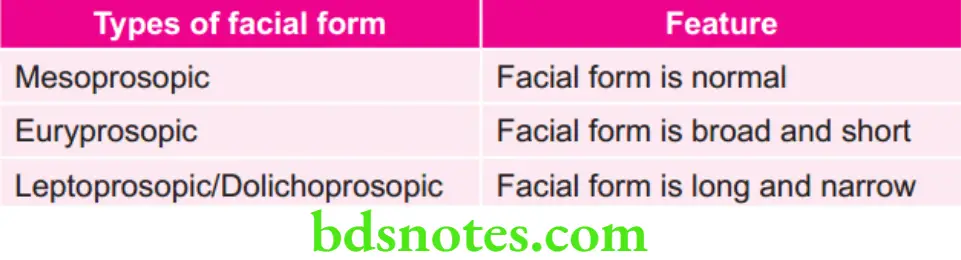
Types of Facial Form
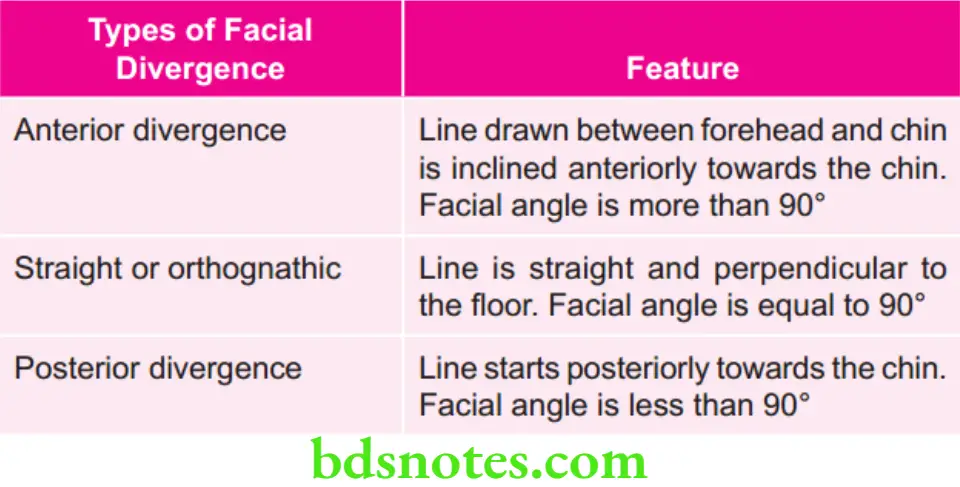
Types of Facial Divergence
Various Transient Malocclusions
- Transient skeletal Class 2
- Open bite in gum pads
- Flush terminal plane
- Ugly duckling stage
- First deep bite
- Second deep bite
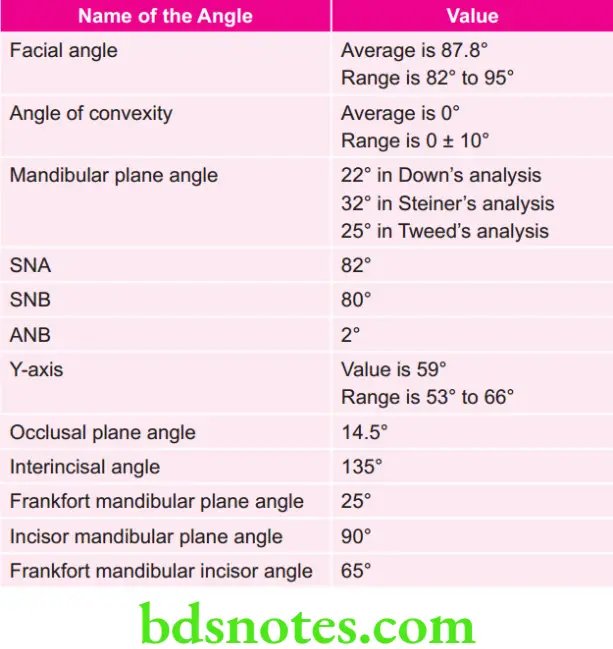
Various Angles and their values
Optimum Forces for Tooth Movement
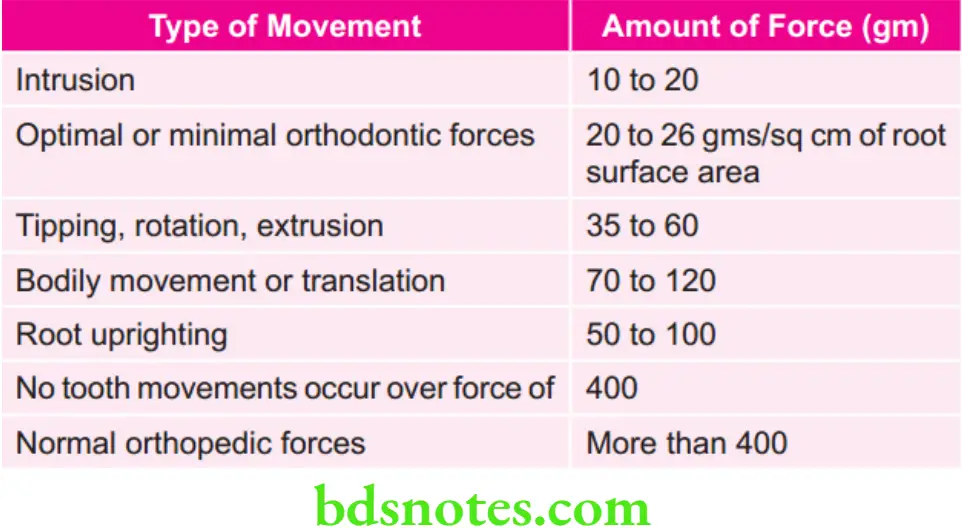
Various Types of Movements and their Center of Rotation
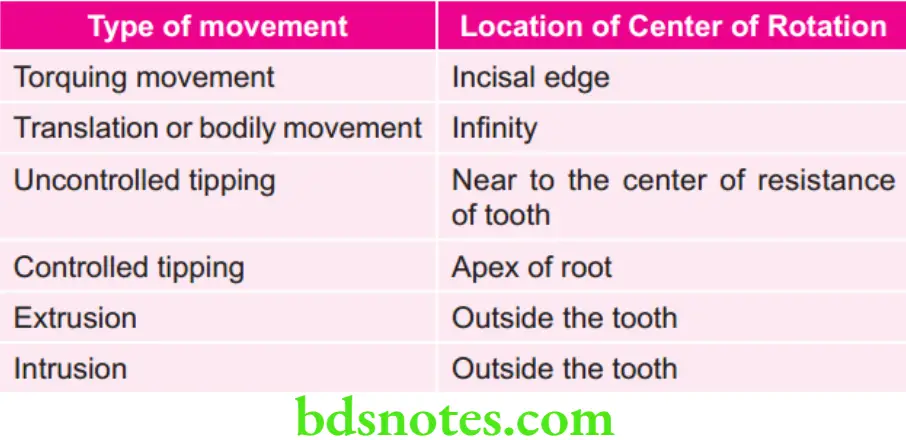
Various Types of Orthodontic Wires With their Modulus of Elasticity
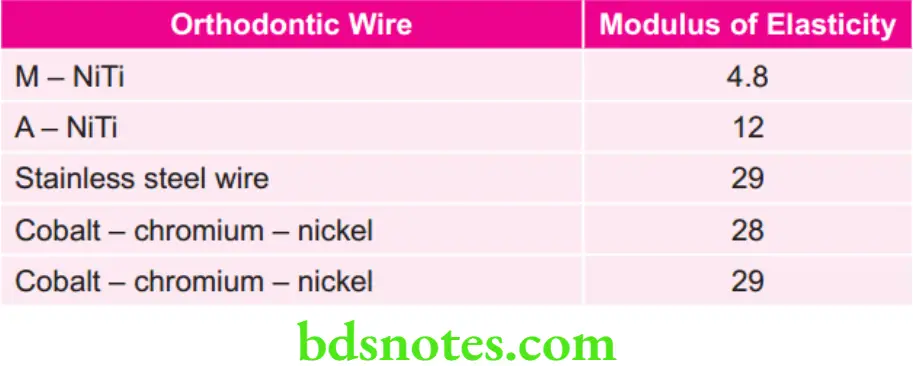
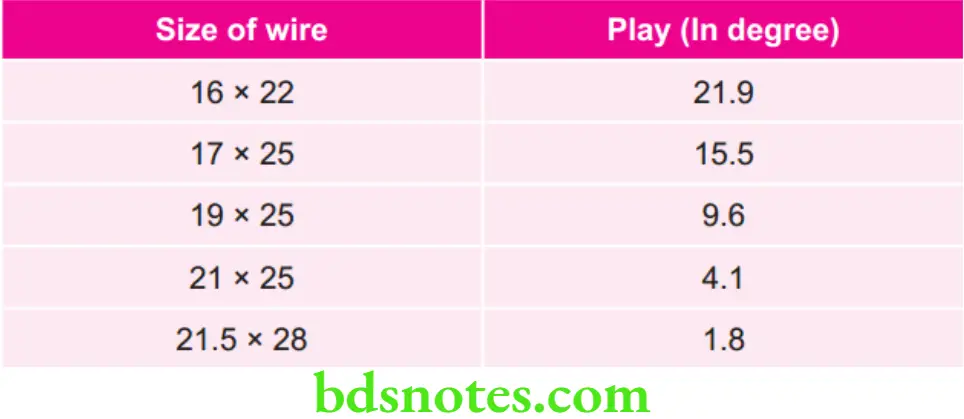
Various Sizes of Wire with Their Play
For 18 Slot Bracket
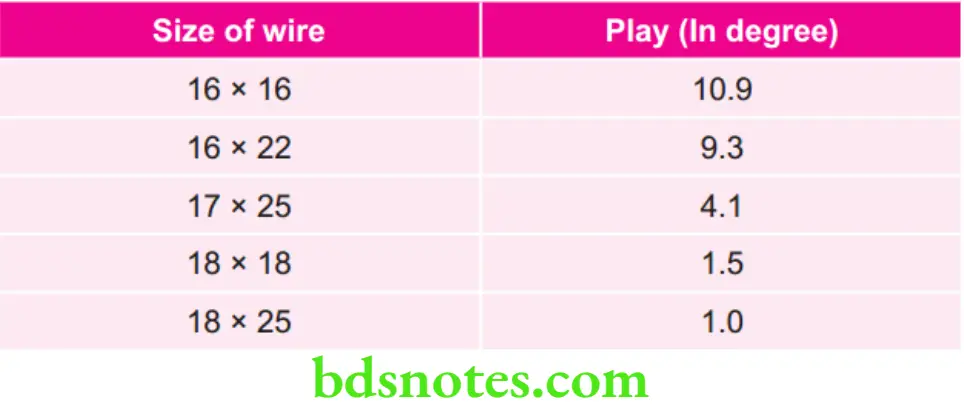
For 22 Slot Bracket
Enumeration of Slow Expansion Appliances
- Jack screw
- Coffin spring in maxilla
- Quad helix in maxilla
- Ni – Ti expander
- Schwartz appliance in mandible
Enumeration of Rapid Expansion Appliances
- Removable appliance incorporating jack screw
- Fixed tooth and tissue borne appliances
- Derichsweiler
- Hass type
- Fixed tooth borne appliances
- Isaacson type
- Hyrax type
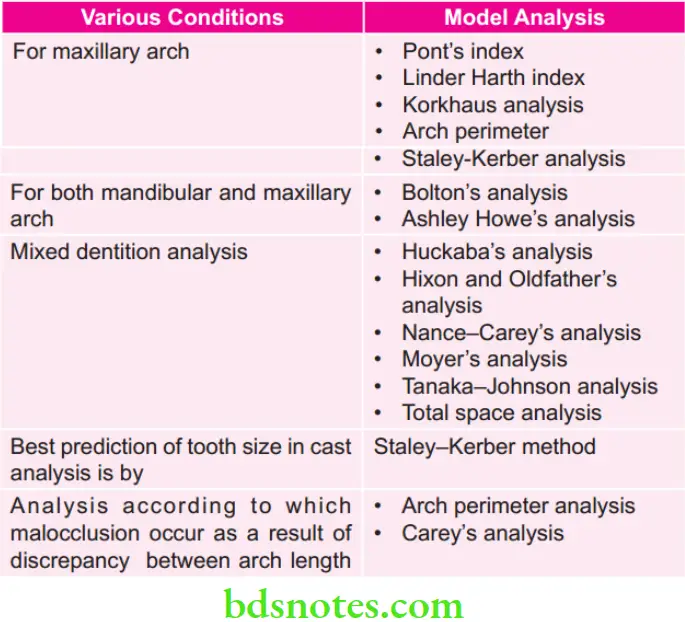
Various Analysis
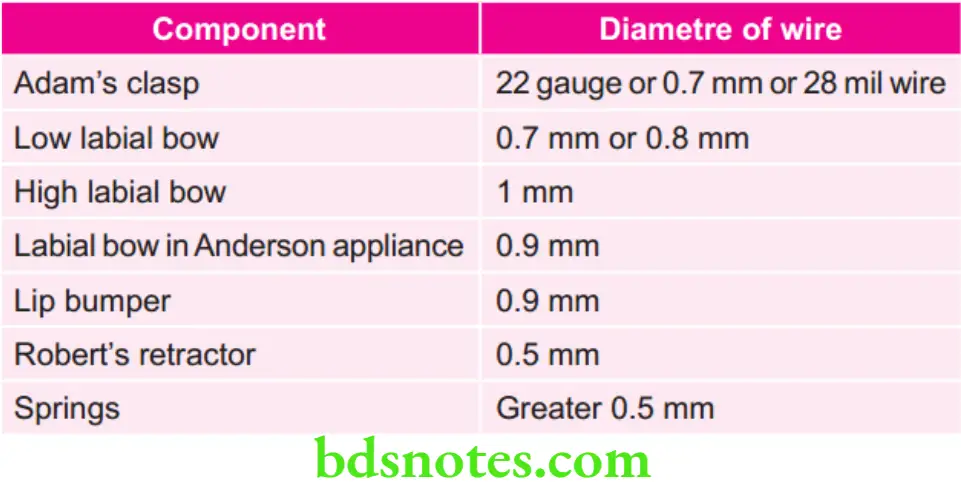
Various Components and Diameter of Wire used in Making Them
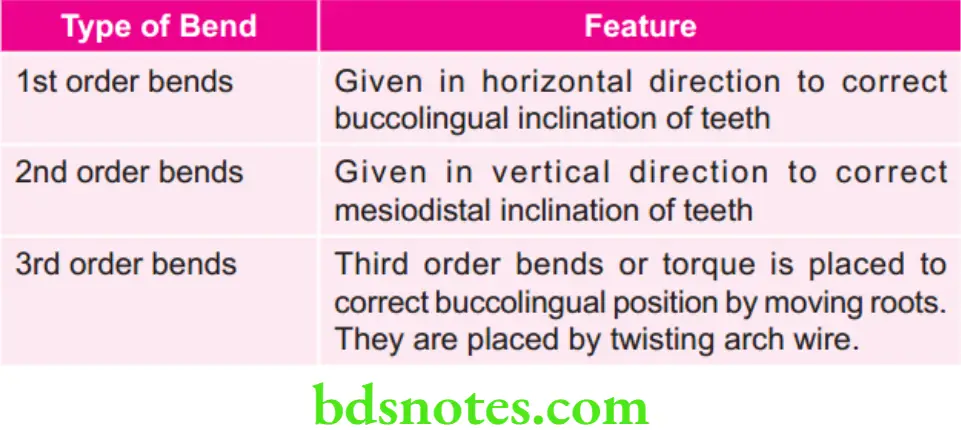
Various Bends in Edgewise Appliance
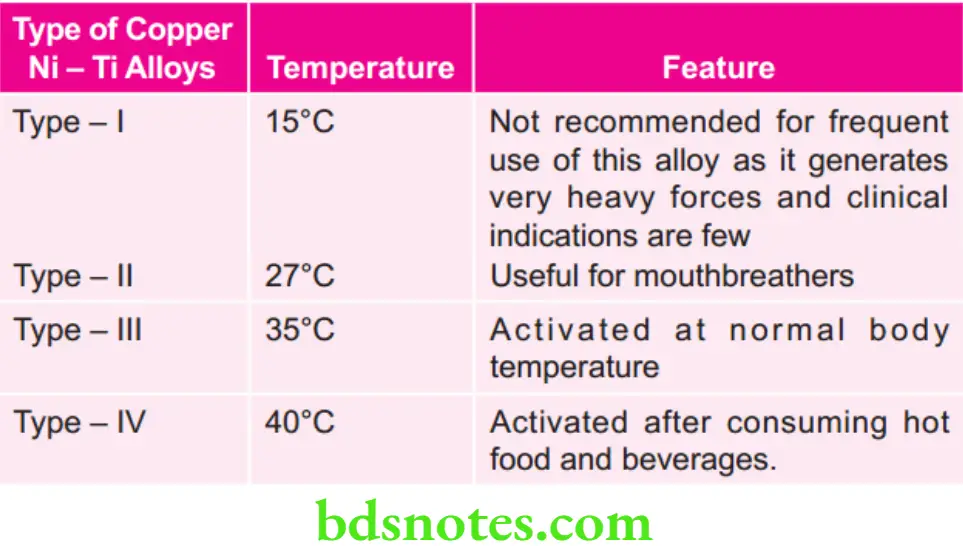
Type of Copper Ni–Ti Alloys
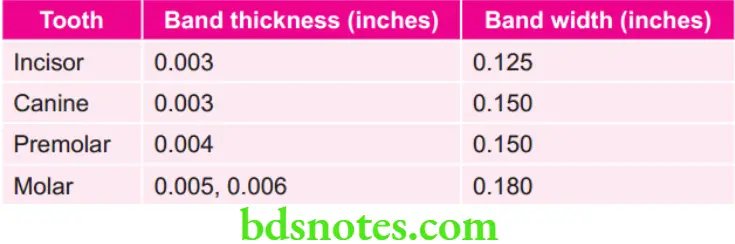
Various Teeth with Band Thickness and Band Width
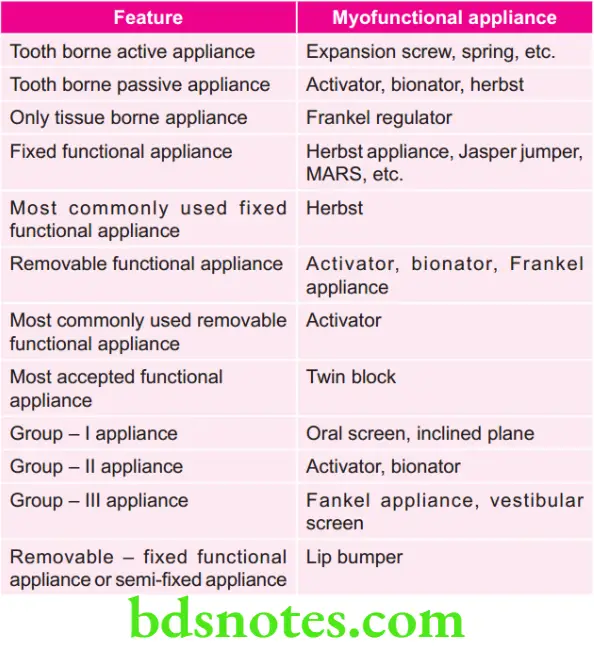
Some Important Points About various Myofunctional Appliances
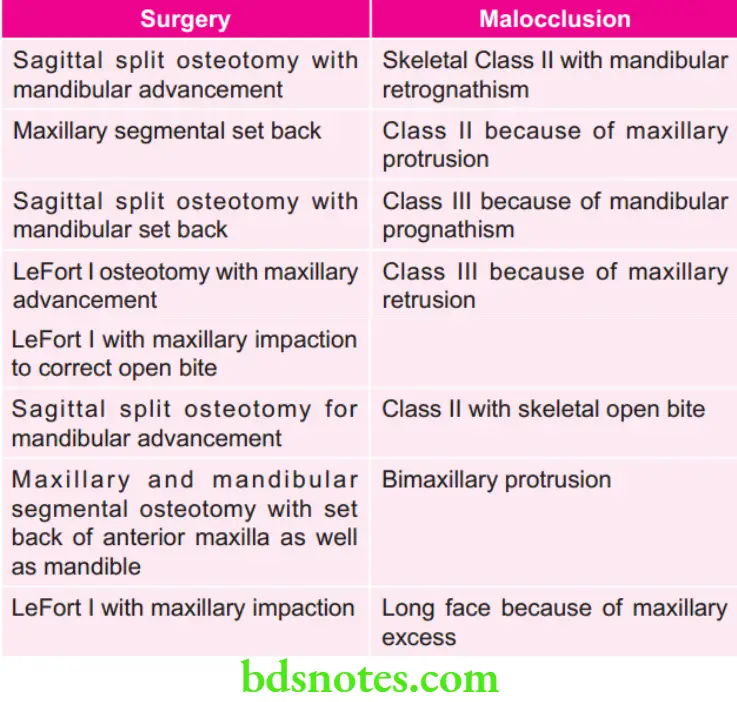
Various Surgeries Associated with Different Malocclusions
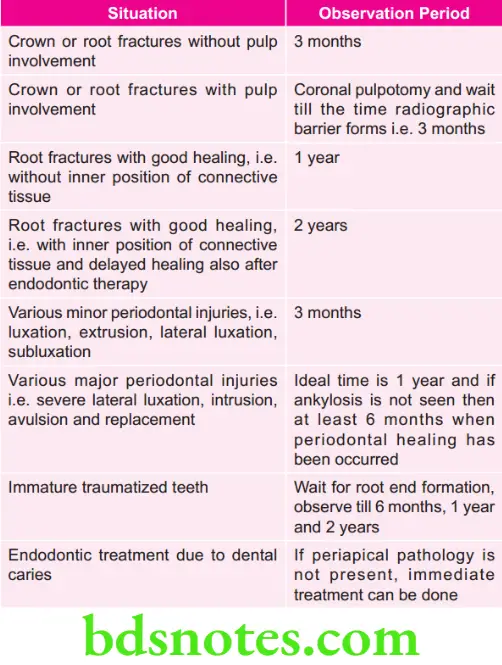
Various Recommended Observation Periods Before Orthodontic Treatment
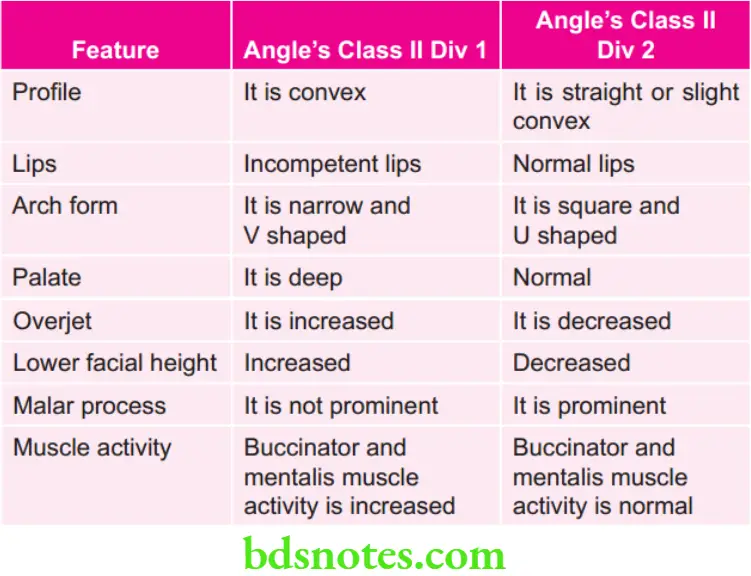
Difference Between Angle Class 2 Div And Div 2
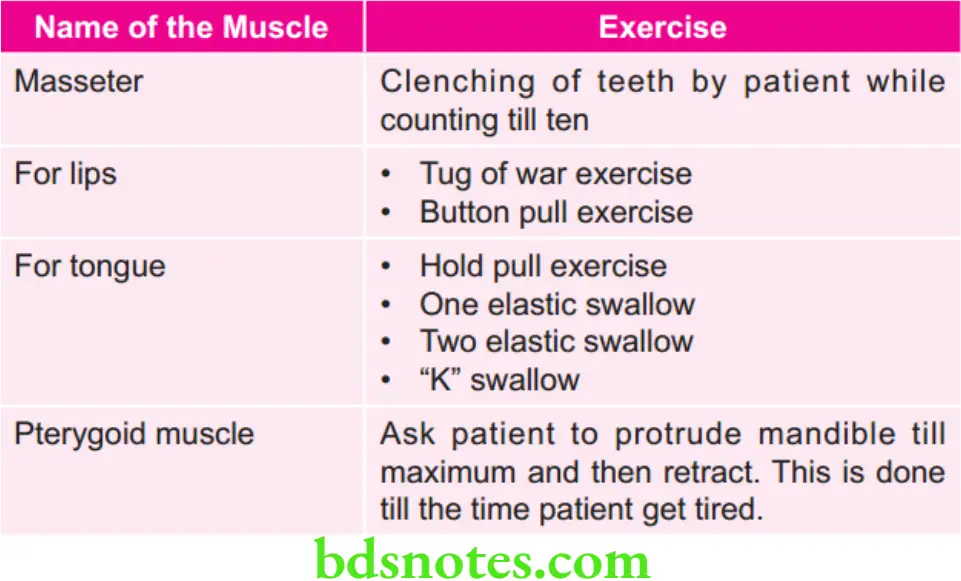
Various Exercises for Muscles in Orthodontics
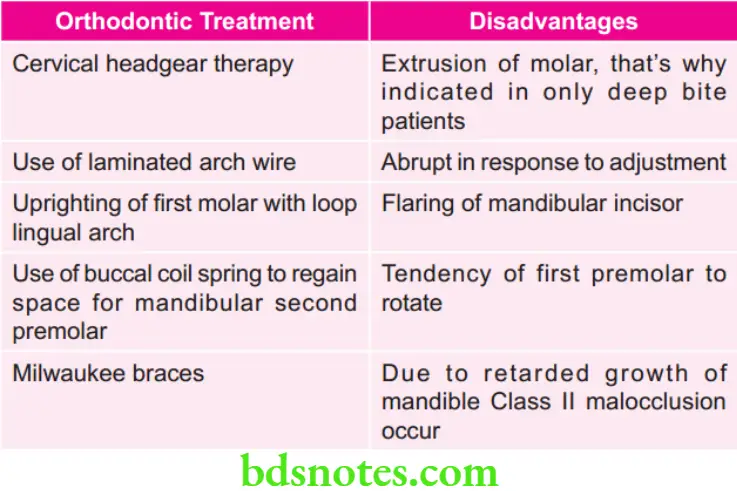
Various Treatment Procedures in Orthodontics with their Disadvantages
Component of Fixed Appliances
- Active components
- Separators
- Elastics
- Archwire
- Spring
- Passive components
- Brackets
- Ligature wire
- Lock pin
- Buccal tube
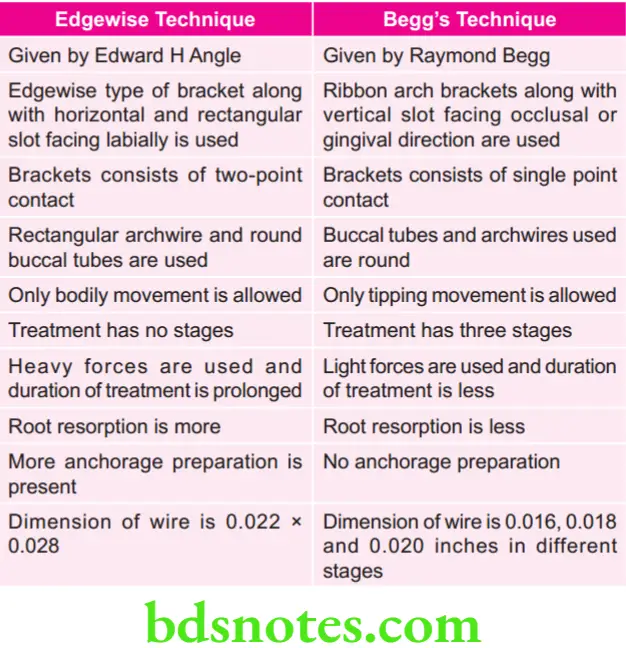
Difference Between Edgewise and Begg’s Technique
Various distances in a X-ray

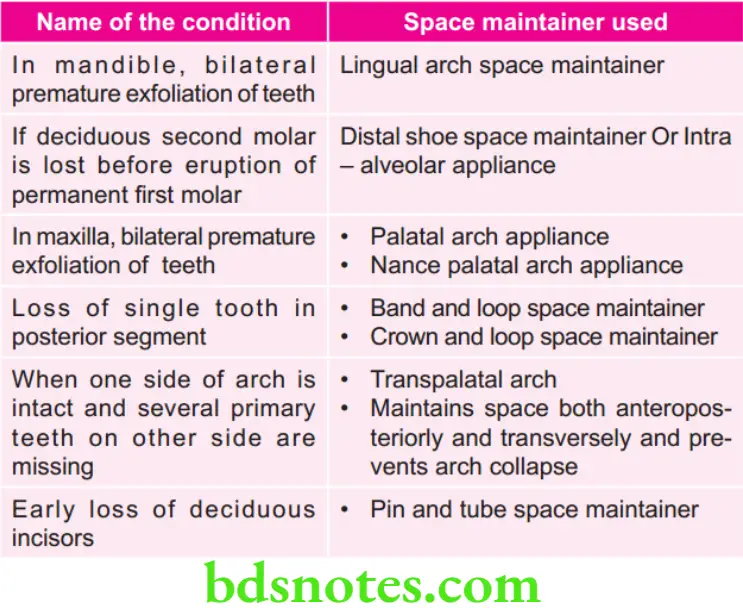
Various conditions and space maintainers used in them
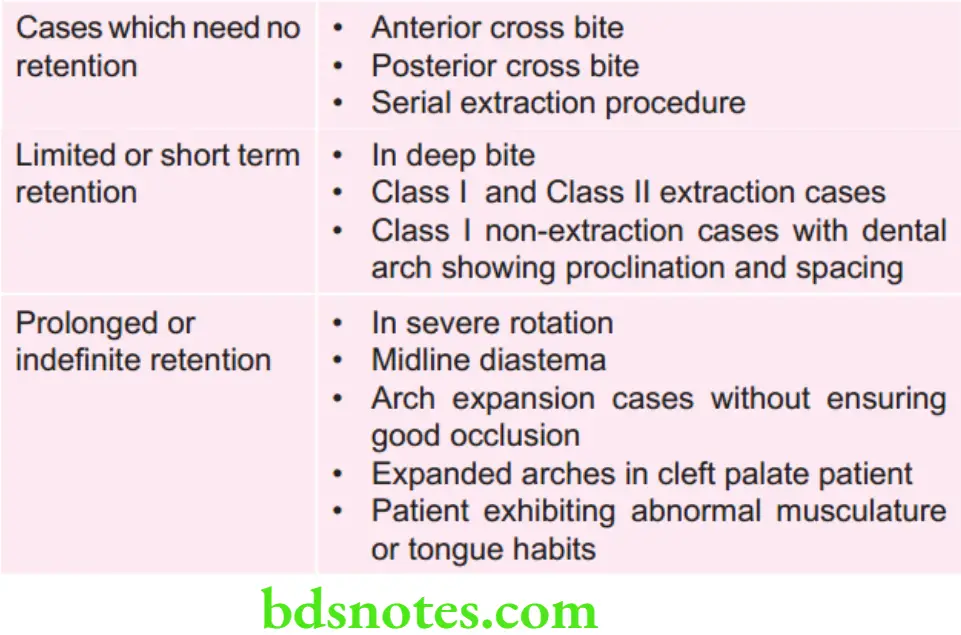
Retention in Various cases
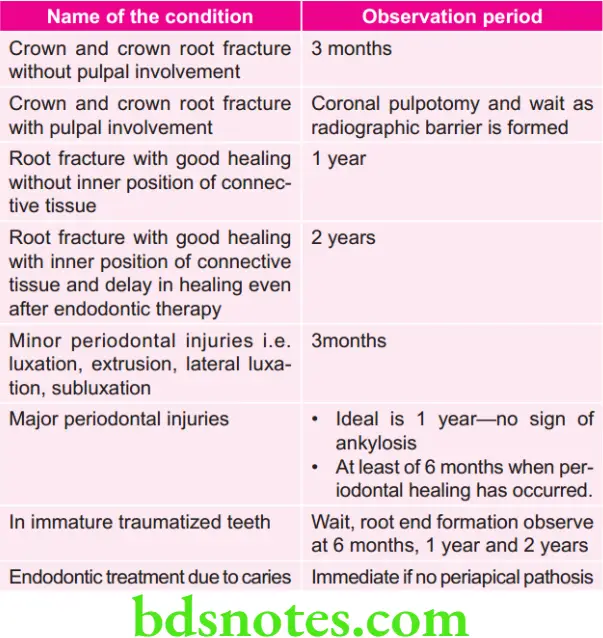
Recommended observation period before orthodontic treatment
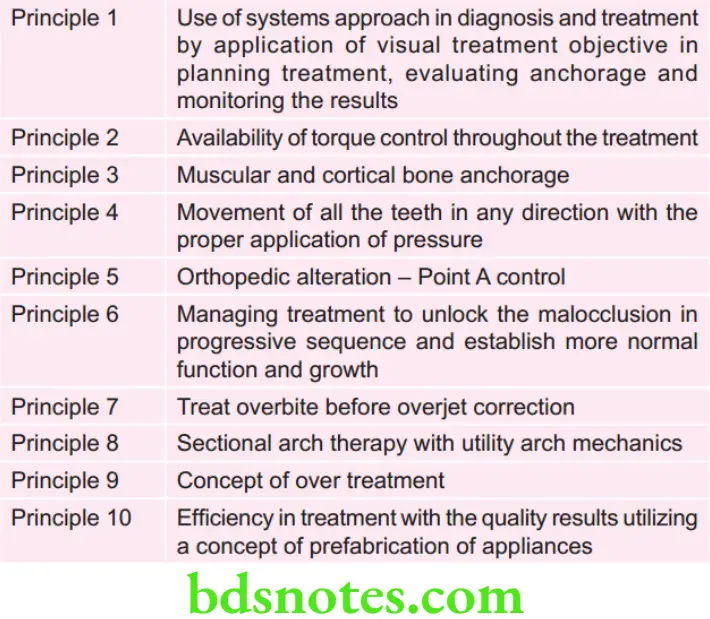
Principles of Bioprogressive therapy
Katz premolar classification
Premolar Class 1: It is identified when the most anterior upper premolar fis exactly into the embrasure created by the distal contact of the most anterior lower premolar. This definition applies when a full complement of premolars are present that is whether one upper premolar opposes two lower premolars or two upper premolar oppose one lower premolar or whether only one premolar is present in each quadrant in essence these relationships represent perfect interdigitations and the value is 0 millimeter on the calipers.
Premolar Class 2: Here the most anterior upper premolar is occluding mesial to the embrasure created by the distal contact of the most anterior lower premolar. The measurement has a plus sign.
Premolar Class 3: Here the most anterior upper premolar is occluding distal of the embrasure created by the distal contact of the most anterior lower premolar. The measurement has a negative sign.
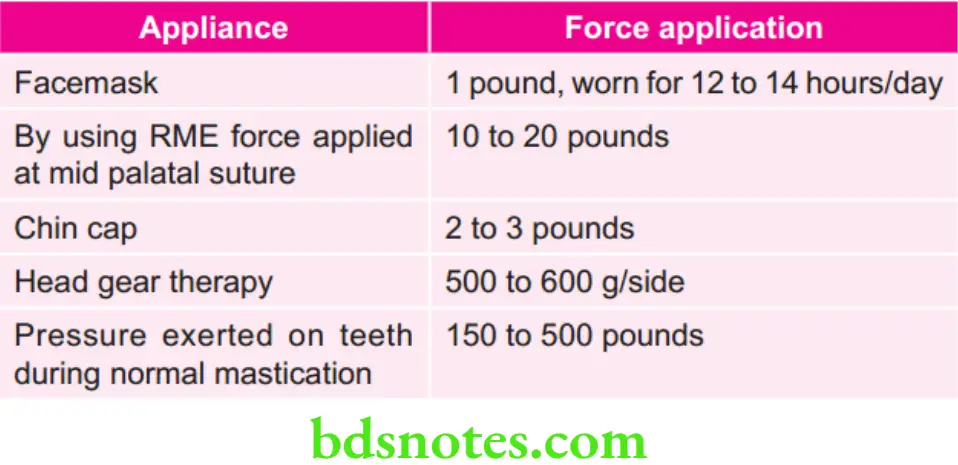
Various appliances and their force application
Root resorption index at the time of tooth movements
Grade 1: Irregular root contour
Grade 2: Root resorption at apex, less than 2 mm
Grade 3: Root resorption accounting to 2 mm to one-third of root length
Grade 4: Root resorption more than one third of root length

Leave a Reply