Organ Functions Tests
Question 1. Explain the van den Bergh test
Answer:
- Van den Bergh test is used to identify an increase in serum bilirubin
Reagent Used:
- A mixture of equal volumes of sulfanilic acid in dilute HCI & sodium nitrate
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
Principle:
- Diazotized sulfanilic acid reacts with bilirubin to form a purple-colored azobilirubin
Reactions:
1. Direct reaction
- Detects conjugated bilirubin
- Conjugated bilirubin is water soluble
- Thus it immediately gives purple color with the van den Bergh reagent
- This is referred to as a direct reaction
2. Indirect reaction
- Detects Unconjugated bilirubin
- Unconjugated bilirubin is water insoluble
- The addition of methanol makes it water soluble after which it gives a positive van den Bergh reaction
- This is called an indirect reaction
3. Biphasic
- Useful when serum contains both conjugated & Unconjugated bilirubin
- It gives an immediate reaction
Reactions to Jaundice:

Question 2. Write the tests to identify the following in urine Sugar, Ketone bodies, Proteins
Answer:
Test to detect sugar in urine:
1. Benedict’s test
- Used to detect reducing sugar in the urine
- Enediol forms of sugar reduce cupric ions of copper sulfate to cuprous ions
- The color of the precipitate indicates the approximate amount of glucose present

2. Glucose oxidase test
- Glucose oxidase oxidizes glucose to liberate hydrogen peroxide
- This is converted to nascent oxygen
- The compound O-diansidine combines with nascent oxygen to form a colored complex
Test to detect ketone bodies in urine
1. Rothera’s test
- In this test, nitroprusside reacts with the keto group of ketone bodies
- Results in the formation of the purple ring
Test to detect proteins in urine:
1. Sulfosalicyclic acid test
- On reacting with Sulfosalicyclic acid, proteins get precipitated as protein-sulfosalicylic
2. Heat coagulation test
- Used to detect Albumin & globulin
- Based on the principle of denaturation of proteins followed by coagulation
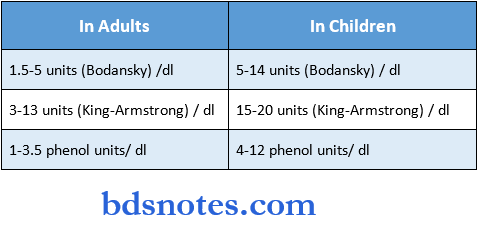
Question 3. The normal value of serum alkaline phosphatase\
Answer:
- The normal value of serum alkaline phosphatase is
Question 4. Enzymes of diagnostic importance in liver diseases
Answer:
- Enzymes used to detect liver diseases are
- Serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase (SGPT)
- Serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (SGOT)
- Alkaline phosphatase
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
- 5-5-Nucleotidase
- Serum isocitrate dehydrogenase
- Isoenzymes of lactate dehydrogenase
Question 5. The normal value of blood urea
Answer:
The normal value of blood urea is 10-40 mg/dl
Question 6. Standard urea clearance
Answer:
Clearance:
- It is defined as the volume of plasma that would be completely cleared of a substance per minute
Standard Clearance:
- The urea clearance drastically changes when the volume of urine is less than 2 ml/min
- This is called standard urea clearance
Value:
- Its normal value is around 54 ml/min
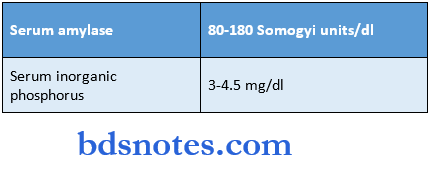
Question 7. Give normal levels of
- Serum amylase
- Serum inorganic phosphorus
Answer:
- Normal levels are as follows
Question 8. Gastric function tests
Answer:

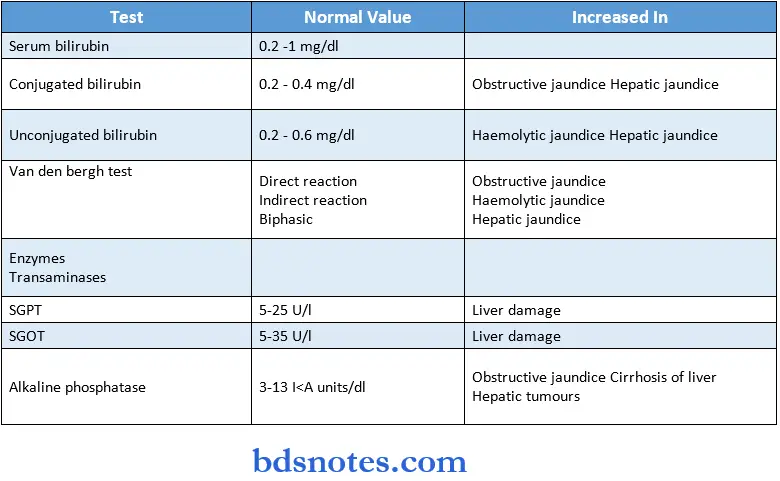
Question 9. Liver function tests
Answer:
Uses:
- Assess the capacity of the liver to function
- Detects abnormalities and extent of damage
Tests:
Question 10. Creatinine clearance value
Answer:
- Creatinine is an excretory product derived from creatine phosphate
Definition:
- It is defined as the volume of plasma that would completely clear of creatinine per min
Calculation:
- Creatinine content of 24-hour urine is collected
- Plasma concentration is estimated
U = creatinine concentration in urine (mg/ml)
V = urine excreted per min in ml
P = creatinine concentration in plasma (mg/ml)
Normal value:
- Its value is close to GFR and is sensitive
- Normal range is 120-145 ml/min
Significance:
- Used for early detection of kidney impairment
- A value below 75% of normal -indicates decreased GFR, renal damage
Question 11. Vanderbegh test
Answer:
- Van den Bergh test is used to identify an increase in serum bilirubin
Reagent used:
- A mixture of an equal volume of sulfanilic acid in dilute HCl and sodium nitrate
Reactions:
- Direct reaction
- Detects conjugated bilirubin
- Indirect reaction
- Detects unconjugated bilirubin
- Biphasic
- Useful when serum contains both conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin
Question 12. Briefly write on the urea clearance test
Answer:
- Urea is the end product of protein metabolism
Definition:
- It is defined as the volume of plasma that would completely clear of urea per min
Calculation:
\(C_m=\frac{U^* \mathrm{~V}}{\mathrm{P}}\)Cm = Maximum urea clearance output of urine more than 2 ml/min U urea concentration in urine (mg/ml)
V urine excreted per min in ml
P = urea concentration in plasma (mg/ml)
Normal value:
75 ml/min
Significance:
- A value below 75% of normal indicates renal damage
- A value below 50% of normal indicates an increase in blood urea level
Question 13. Write normal values for
Answer:
- Blood urea, Random blood glucose, Serum creatinine
- Blood urea-10-40 mg/dl
- Random blood glucose 80-140 mg/dl
- Serum creatinine 0.6-1 mg/dl

Leave a Reply