Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Sun-burst appearance is the radiographic feature of:
1. Multiple myeloma
2. Ewing’s sarcoma
3. Burkitt’s lymphoma
4. Osteosarcoma
Answer 4. Osteosarcoma
Question 2. Generalized hypercementosis can be seen in:
1. Hypothyroidism
2. Paget’s disease
3. Trauma
4. Ameloblastoma
Answer 2. Paget’s disease
Question 3. Cementum is not apparent radiographically because:
1. It has high mineral content
2. It has low contrast compared to dentin
3. It has low mineral content
4. It has high contrast compared to dentin
Answer 2. It has low contrast compared to dentin
Read And Learn More: Oral Radiology Question And Answers
Question 4. Which of the following is not a true cyst?
1. Radicular cyst
2. Primordial cyst
3. Aneurysmal bone cyst
4. Dentigerous cyst
Answer 3. Aneurysmal bone cyst
Question 5. Which of the following conditions is associated with non-vital tooth?
1. Periapical cemental dysplasia
2. Hypercementosis
3. Cementoblastoma
4. Periapical condensing osteitis
Answer 4. Periapical condensing osteitis
Question 6. Which of the following cells are more radioresistant?
1. Basal cell of oral mucosa
2. Spermatocytes
3. Vascular endothelial cells
4. Striated muscle cells
Answer 4. Striated muscle cells
Question 7. Target in the X-ray tube is made of:
1. Aluminium
2. Copper
3. Molybdenum
4. Tungsten
Answer 4. Tungsten
Question 8. Which of the following mandibular landmarks can be seen in maxillary posterior intraoral periapical radiograph?
1. Lingula
2. Coronoid process
3. External oblique ridge
4. Inferior alveolar canal
Answer 2. Coronoid Process
Question 9. Snow-driven appearance is characteristic radiographic feature of:
1. Pindborg tumor
2. CEOC
3. AOT
4. Chronic sclerosing osteomyelitis
Answer 1. Pindborg tumor
Question 10. Which of the following is not a PA view?
1. 0° occipitomental
2. Towne’s view
3. Reverse Towne’s view
4. 30° Occipitomental
Answer 3. Reverse Towne’s view
Question 11. Panoramic radiograph can be useful to view all of the following except:
1. Mandibular condyles
2. Symphysis
3. Ramus
4. Body of mandible
Answer 1. Mandibular condyles
Question 12. Basal cell nevus syndrome is associated with:
1. Odontogenic keratocyst
2. Pindberg tumor
3. Dentigerous cyst
4. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic cyst
Answer 1. Odontogenic keratocyst
Question 13. Which of the following views is not useful for maxillary sinuses?
1. Waters
2. OPG
3. Submentovertex
4. Reverse Towne’s
Answer 4. Reverse Towne’s
Question 14. Which of the following is best method to protect operator from occupational radiation exposure?
1. Leave the room
2. Use suitable lead barrier
3. Use lead apron and thyroid collar
4. Follow position and distance rule
Answer 3. Use lead apron and thyroid collar
Question 15. Primary source of X-ray photons from X-ray tube is:
1. Bremsstrahlung radiation
2. Characteristic radiation
3. Photoelectric interaction
4. None of the above
Answer 1. Bremsstrahlung radiation
Question 16. Which of the following acts as anti-fog agent in developing solution?
1. Developer
2. Activator
3. Preservative
4. Restrainer
Answer 4. Restrainer
Question 17. ‘Sjögren syndrome’ on sialography will show:
1. Driven-snow appearance
2. Ball-in-hand appearance
3. Branchless fruit laden appearance
4. Cauliflwer appearance
Answer 3. Branchless fruit laden appearance
Question 18. Inverted Y line on maxillary IOPA forms due to crossing of:
1. Floor of nasal cavity and maxillary sinus
2. Zygomatic bone and maxillary sinus
3. Coronoid process and tuberosity
4. Mental ridges bilaterally
Answer 1. Floor of nasal cavity and maxillary sinus
Question 19. Target in X-ray tube is made of:
1. Aluminum
2. Copper
3. Molybdenum
4. Tungsten
Answer 4. Tungsten
Question 20. Brown tumors can be seen in:
1. Hyperthyroidism
2. Hypothyroidism
3. Hypoparathyrodism
4. Hyperparathyroidism
Answer 4. Hyperparathyroidism
Question 21. Cathode in X-ray tube is made of:
1. Tungsten and copper
2. Copper and molybdenum
3. Tungsten and molybdenum
4. Copper and lead
Answer 3. Tungsten and molybdenum
Question 22. X-rays were discovered by:
1. Edmund C Kells
2. WA Price
3. WC Roentgen
4. HR Raper
Answer 3. WC Roentgen
Question 23. Which one of the following cells are more radiosensitive?
1. Erythrocyte
2. Neuron
3. Nephron
4. Basal cells of oral mucosa
Answer 4. Basal cells of oral mucosa
Question 24. Which one of the following cyst has pericoronal radiolucency?
1. Radicular cyst
2. Dentigerous cyst
3. Aneurysmal bone cyst
4. Para dental cyst
Answer 2. Dentigerous cyst
Question 25. Which of the following radiographic view to visualize fractures of zygomatic aids?
1. PNS view
2. OPG
3. AP view
4. Jug handle view
Answer 4. Jug handle view
Question 26. Phalangioma is:
1. Processing error
2. Exposure error
3. Positioning error
4. None of the above
Answer 4. None of the above
Question 27. Branchless fruit laden tree and cherry blossom appearance are sialographic appearance of:
1. Sjögren’s syndrome
2. Sialolithiasis
3. Sialadenosis
4. Mumps
Answer 1. Sjögren syndrome
Question 28. The function of grid in extraoral radiography:
1. Reduces the exposure
2. Reduces the contrast
3. Increases the density
4. Improves the contrast and sharpness
Answer 4. Improves the contrast and sharpness
Question 29. Onion-peel appearance is classical features of:
1. Periapical abscess
2. Osteosarcoma
3. Garre‘s osteomyelitis
4. Periapical cyst.
Answer 3. Garre‘s osteomyelitis
Question 30. Which one of the following is not the example of electromagnetic radiations?
1. X-rays
2. Visible rays
3. UV rays
4. Cathode rays
Answer 4. Cathode rays
Question 31. Anode in X-ray tube is made of:
1. Tungsten and copper
2. Tungsten and molybdenum
3. Tungsten and lead
4. Lead and copper
Answer 1. Tungsten and copper
Question 32. Father of dental radiology:
1. WC Rontgen
2. Edmund G kellis
3. Marie Curie
4. HR Rapes
Answer 2. Edmund G Kellis
Question 33. Tyre track appearance is a:
1. Processing error
2. Exposure error
3. Positioning error
4. None of the above
Answer 4. None of the above
Question 34. Which one of the following is best radiographic view to visualize maxillary sinus?
1. OPG
2. Submentovertex view
3. Lateral skull view
4. PNS view
Answer 4. PNS view
Question 35. Film badge is a type of:
1. Dosimeter
2. Sonometer
3. Thermometer
4. Any of the above
Answer 1. Dosimeter
Question 36. Intensifying screen in extraoral radiography is used for:
1. Increasing the sharpness
2. Reducing the exposure
3. Increasing the contrast
4. Increasing the density
Answer 2. Reducing the exposure
Question 37. Size of fims in occlusal radiography:
1. 31 × 41 mm
2. 61 × 71 mm
3. 57 × 76 mm
4. 27 × 54 mm
Answer 3. 57 x 76 mm
Question 38. Ground-glass appearance is classical feature of:
1. Cherubism
2. Osteopetrosis
3. Periapical cemental dysplasia
4. Fibrous dysplasia
Answer 4. Fibrous dysplasia
Question 39. Cells which are most radioresistant:
1. Basal cells of oral mucosa
2. Pleuripotent stem cells
3. Neurons
4. Nephrons of kidney
Answer 3. Neurons
Question 40. Multilocular radiolucency is a classical feature of:
1. Ameloblastoma
2. Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
3. Complex odontome
4. Odontogenic myxoma
Answer 1. Ameloblastoma
Question 41. Total fitration is a path of a dental X-ray beam upto 70 kVp should be:
1. 2 mm aluminum
2. 1.5 mm aluminum
3. 3.5 mm aluminum
4. 0.5 mm aluminum
Answer 2. 1.5 mm aluminum
Question 42. The cells which are most sensitive to radiation is:
1. Matured erythrocyte
2. Neuron
3. Basal cells of oral mucosa
4. JG cells of kidney
Answer 1. Matured erythrocyte
Question 43. Multiple punched-out radiolucencies of the jaw are seen in:
1. Odontogenic myxoma
2. Multiple myeloma
3. SCC
4. Osteosarcoma
Answer 2. Multiple myeloma
Question 44. The clearing agent in the fier solution is:
1. Hydroquinone
2. Ammonium thiosulphate
3. Aluminum sulphate
4. Ammonium sulphate
Answer 2. Ammonium thiosulphate
Question 45. Which are not photons?
1. Ultrasound
2. Gamma ray
3. X-rays
4. None of the above
Answer 1. Ultrasound
Question 46. Extraoral projection of zygomatic fracture:
1. Water’s view
2. Submentovertex
3. Zimmer’s projection
4. Reverse Towne’s
Answer 2. Submentovertex
Question 47. The optimal developing temperature in manual processing:
1. 60°F
2. 68°F
3. 70°F
4. 62°F
Answer 2. 68°F
Question 48. The quantity of X-rays produced is controlled by:
1. Kilovoltage
2. Milliampere
3. Exposure time
4. Angulation to cone
Answer 2. Milliampere
Question 49. Normal appearance of sialogram of parotid gland is:
1. Tree in winter
2. Sausage link
3. Cheery Blossom
4. Snow storm
Answer 1. Tree in winter
Question 50. X-rays were discovered by:
1. Madam Marie Curie
2. WC Roentgen
3. EC Kelli
4. WC Price
Answer 2. WC Roentgen
Question 51. Collimation reduces:
1. Size of X-ray beam
2. Size of X-ray fim
3. Low energy photons
4. None
Answer 1. Sixe of x-ray beam
Question 52. Dark radiograph is caused by:
1. Increase developing time
2. Decrease exposure time
3. Decrease exposure parametres
4. None
Answer 1. Increase developing time
Question 53. CBCT is commonly used for:
1. Implant planning
2. Intra-articular disc
3. Parotid gland
4. Sof tissue pathology
Answer 1. Implant Planning
Question 54. Distance of safe light from working area:
1. 4 feet
2. 7 feet
3. 8 feet
4. 9 feet
Answer 1. 4 feet
Question 55. Size of an adult IOPA film:
1. 24 × 40 mm
2. 57 × 75 mm
3. 31 × 41 mm
4. 22 × 35 mm
Answer 3. 31 x 41 mm
Question 56. Most radiosensitive cells are:
1. Neuron
2. Acinar cells
3. Endothelial cells
4. Basal cells
Answer 4. Basal cells
Question 57. Filters are made up of:
1. Lead
2. Plastic
3. Aluminum
4. Copper
Answer 3. Aluminum
Question 58. Ball in hand appearance in sialography is seen in:
1. Parotitis
2. Benign tumor
3. Malignancy
4. Sialolithiasis
Answer 2. Benign tumor
Question 59. Generalized loss of lamina dura is seen in:
1. Anemia
2. Paget’s disease
3. Fibrous dysplasia
4. Hypothyroidism
Answer 4. Hypoparathyrodism
Question 60. Safe distance of the operator from patient during radiation exposure:
1. 6 feet
2. 9 feet
3. 4 feet
4. 12 feet
Answer 1. 6 feet
Question 61. Examples of electromagnetic radiation are the following except:
1. X-rays
2. Gamma rays
3. Infra-red radiation
4. Microwaves
Answer 2. Gamma rays
Question 62. Component parts of the tube head do not include:
1. Insulating oil
2. Extension arm
3. Metal housing
4. Tube head seal
Answer 2. Extension arm
Question 63. Ideally in the darkroom safe light must be placed from:
1. 2 feet
2. 4 feet
3. 6 feet
4. 8 feet
Answer 4. 8 feet
Question 64. The best way of detecting dental caries by:
1. IOPA
2. Panoramic
3. Occlusal
4. Bitewing
Answer 4. Bitewing
Question 65. Generalized loss of lamina dura is not seen in:
1. Leukemia
2. Hyperparathyroidism
3. Osteomalacia
4. Multiple myeloma
Answer 3. Osteomalacia
Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. The process of converting an atom into ion is known as ……………
Answer. Ionization
Question 2. Multiple myeloma patient …………… eaten appearance on lateral skull radiograph.
Answer. Moth
Question 3. Determination of the quantity of radiation exposure or dose is known as ……………
Answer. Dosimetry
Question 4. The supernumerary tooth that is located in between maxillary central incisors is known as ……………
Answer. Mesiodens
Question 5. The three-dimensional curved zone in which the structures lying within are clearly demonstrated on panaromic radiograph is known as ……………
Answer. Topography
Question 6. The focal spot to film distance in cephalometric radiography is …………… feet.
Answer. 6
Question 7. Reflcting layer of intensifying screen is made up of……………
Answer. Titanium dioxide
Question 8. The intensity of X-ray photon at 1 meter is 4 KeV. The intensity will be…………… at 4 meter.
Answer. 16 KeV
Question 9. The …………… appearance is characteristic radiographic feature of pleomorphic adenoma.
Answer. Ball in hand
Question 10. The …………… is most common source of radiation used in treatment of oral ulcer.
Answer. LASER
Question 11. State the formula for maximum accumulated dose……………
Answer. MAD=(N-18) X 5 rems/year Or MAD=(N-18) X 0.05 Sv/year
Question 12. X-rays were discovered in the year……………
Answer. 1895
Question 13. The overall blackness or darkness of dental radiography is termed as……………
Answer. Density
Question 14. Safe light must be placed a minimum of ………………… feet distance from the fim.
Answer. 4
Question 15. The optimum temperature for developer solution is ……………
Answer. 68°F
Question 16. Hypoxia, hypocellularity and hypovascularity of bone following irradiation leads to……………
Answer. Osteoradionecrosis
Question 17. The ideal radiograph to visualize the mediolateral expansion of a jaw is……………
Answer. Occlusal radiograph
Question 18. Onion-peel appearance in a radiograph is a typical feature of ……………
Answer. Chronic osteomyelitis, eosinophilic granuloma and Ewing’s sarcoma
Question 19. Fracture of the zygoma can be best visualized in a…………… view.
Answer. Submentovertex
Question 20. The image receptor used in an intraoral direct digital radiography is called……………
Answer. Solid state detectors, i.e. Charged, coupled device
Question 21. Restrainer used in developer solution is……………
Answer. Potassium or sodium bromide
Question 22. SI unit of absorbed dose is……………
Answer. Gray
Question 23. The intensity of X-ray photon at 1 meter is 4KeV. The intensity at 4 meter will be……………
Answer. 16 KeV
Question 24. Wattge of safe light bulb used in dark room is……………
Answer. 15 Wat
Question 25. XCP instruments are used in……………
Answer. Film or sensor holding
Question 26. Least sensitive cell for radiation……………………..
Answer. Fixed post-mitotic cells
Question 27. Radiographic appearance of osteosarcoma is …………………….
Answer. Sunburst appearance
Question 28. Most radiosensitive cell to radiation are of ……………………glands.
Answer. Salivary
Question 29. The basic purpose of using intensifying screens is to …………………….
Answer. Intensify the effct of the X-ray photon by producing a larger number of light photons. It decreases the mAs required to produce a particular density, and hence decreases the patient dose signifiantly.
Question 30. Localization of object is done by…………………… technique.
Answer. Tube shif
Question 31. Cyst associated with impacted tooth is ……………………….cyst.
Answer. Dentigerous cyst
Question 32. Honey-comb/Soap-bubble radiographic appearance commonly seen with benign tumor………………….
Answer. Hemangioma
Question 33. Tennis-racquet-like radiographic appearance is seen with……………….
Answer. Odontogenic myxoma
Question 34. Primary indication of bitewing radiograph is to diagnose………………..
Answer. Early inter – proximal carious lesions
Question 35. Charge-coupled device (CCD) sensor is used in………………….
Answer. Intraoral imaging
Question 36. Pear shaped radiolucency in anterior maxilla with splaying apart roots is suggestive of………………………
Answer. Globulomaxillary cyst
Question 37. Dentigerous cyst transformed to most common tumor is……………..
Answer. Ameloblastoma
Question 38. Most common radiographic technique used for submandibular sialolithiasis is………………..
Answer. Sialography
Question 39. Sequestration in chronic osteomyelitis is …………………….
Answer. Infected dead bone
Question 40. Generalized loss of lamina dura with increased calcium serum and alkaline phosphatase is seen in ………………….
Answer. Hyperparathyroidism
Question 41. Radiographic features seen in Garre’s osteomyelitis is……………..appearance.
Answer. Onion skin
Question 42. Copper beaten appearance is seen in………………… syndrome
Answer. Apert syndrome and Crouzon syndrome
Question 43. ………………..radiograph is best for diagnosing periapical cyst.
Answer. IOPA
Question 44. ………………….fiters are used in safe lights in dark room.
Answer. GBX-2 safelight
Question 45. Disc of TMJ is best visualized in………………….. imaging modality.
Answer. MRI
Question 46. The collimator is made up of……………………
Answer. Lead
Question 47. The hardening agent in the fixer solution is…………………….
Answer. Potassium alum
Question 48. The radiolucent mark in the periapical region of lower central incisor is………………
Answer. Lingual foramen
Question 49. In digital radiography, the image receptor is called………………..
Answer. Image sensors
Question 50. Sec ondary infection of irradiated bone is called…………………
Answer. Osteoradionecrosis
Additional Information
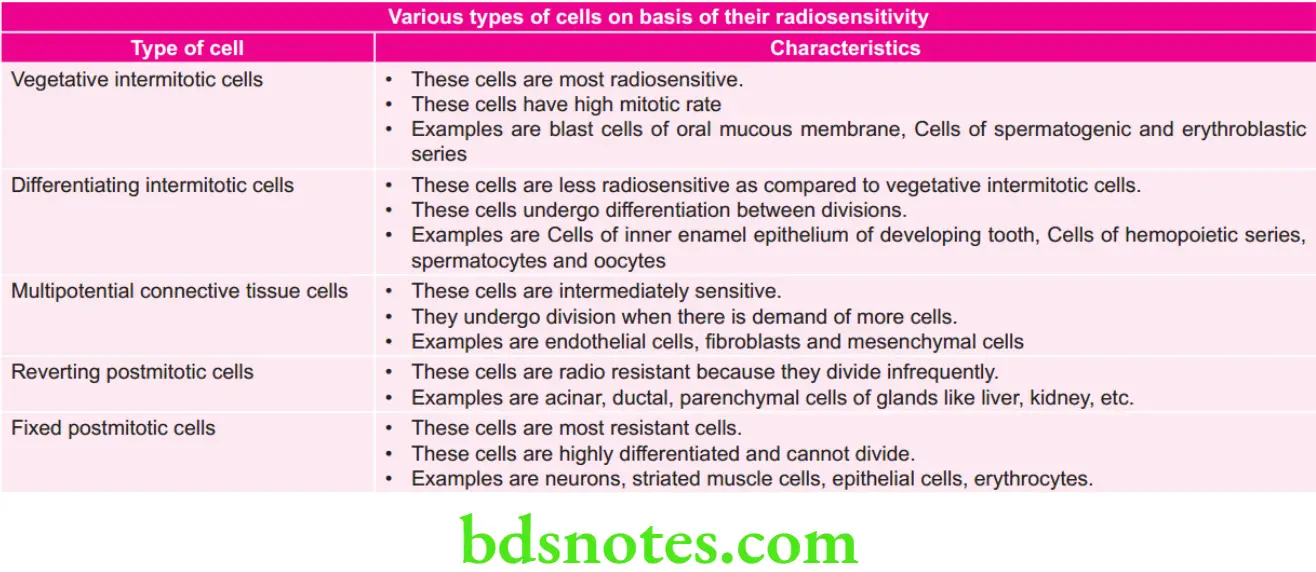
Radio sensitivity of Various Organs
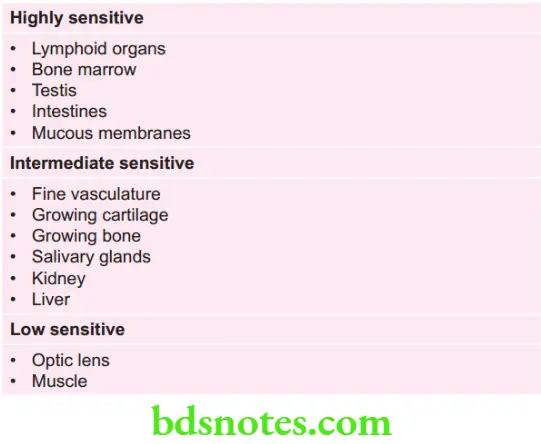
Harmful Whole Body Exposure Values
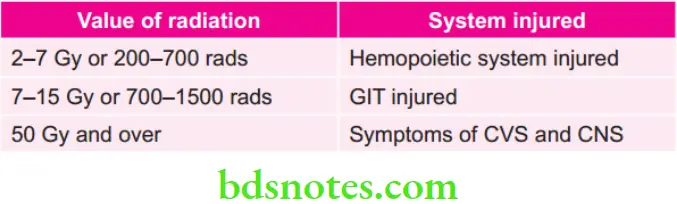
Susceptibility of Various organs to Radiation-induced Cancer

Various cell division Phases and their Sensitivity
M phase and Late G2 phase and G2M interphase (premitosis or RNA synthesis) are most sensitive
Early S and G1 phase are intermediately sensitive
S phase is least sensitive
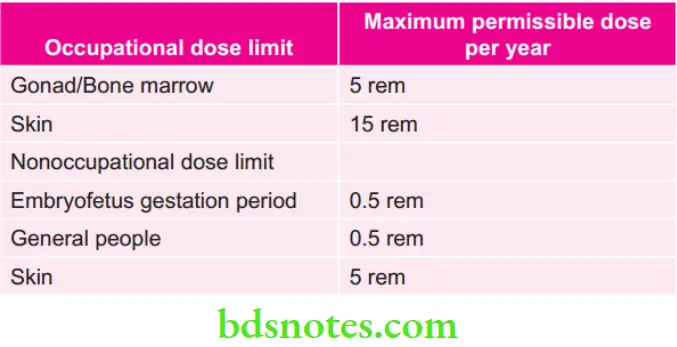
Various Maximum Permissible Dose per Year
Enumeration of Various things and Factors Which Decreases Patient Radiation Exposure
- E-speed fims
- Intensifying screens
- Collimation
- Filtration
- Lead aprons
- Thyroid collars
- Increasing focal spot to fim distance
- Increasing KVp and optimal exposure time
Radiation dose by NCRP (national council on Radiation Protection)
- Occupational dose is 50 mSV annually and 10 mSV in a year
- Non – occupational dose is 5 mSV annual effctive dose limit for infrequent exposure or 1 mSV annual dose for continuous exposure.
Radiation dose by ICRP (international commission of Radiation Protection)
- Occupational dose is 50 mSV annually and 100 mSV in 5 year cumulative effctive dose limit.
- Non occupational dose is 1 mSV annually, if higher not to exceed annual average of 1 mSV over 5 years.
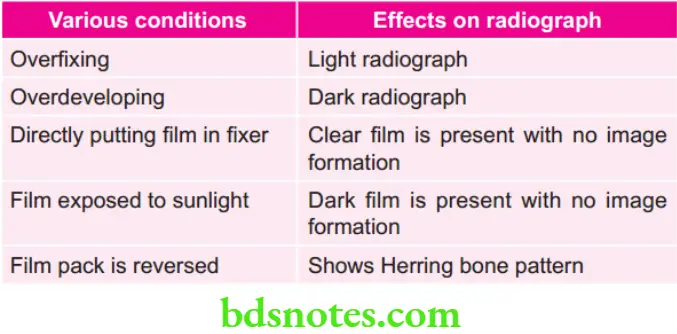
Various conditions and their Effects on Radiograph
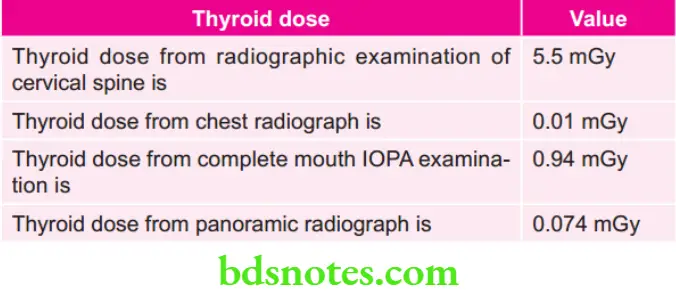
Various Thyroid Doses
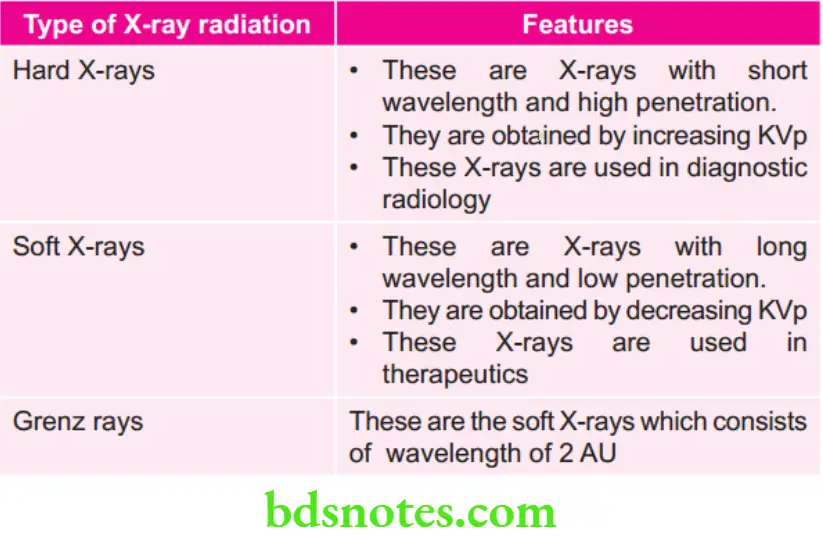
Various Types of X-ray Radiation

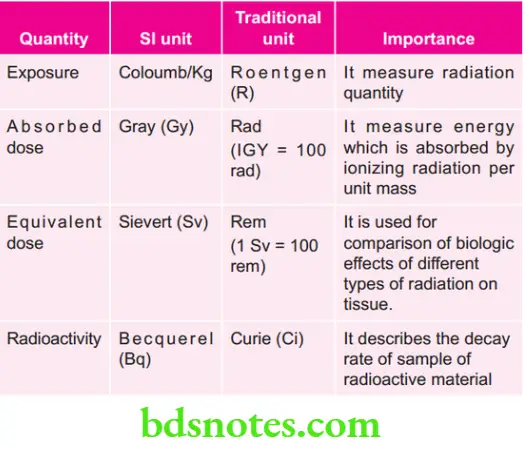
Various Quantities their Units and Importance
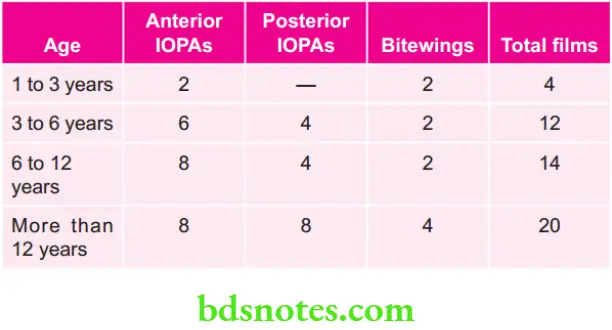
According to FINN, Number of Radiographs Required According to Age
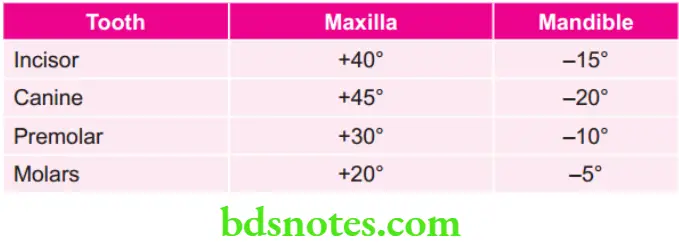
Various Angulations for Bisecting Angle Projections
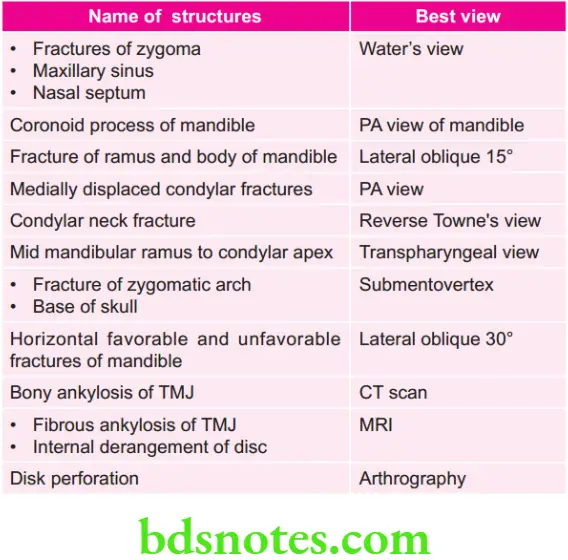
Various Views for Various Structures
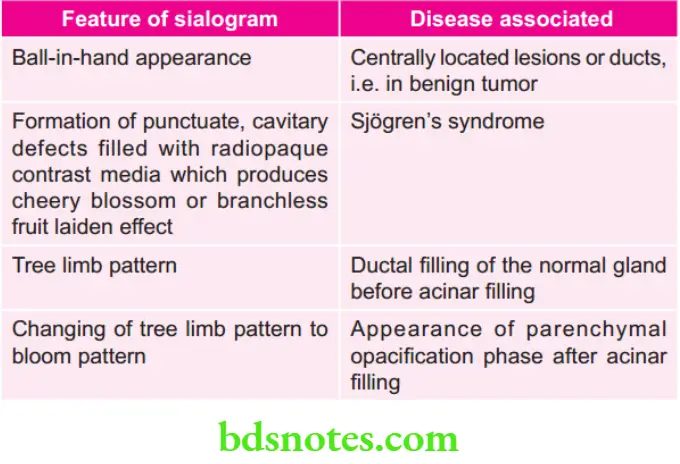
Various Features of Sialogram and Associated Disease
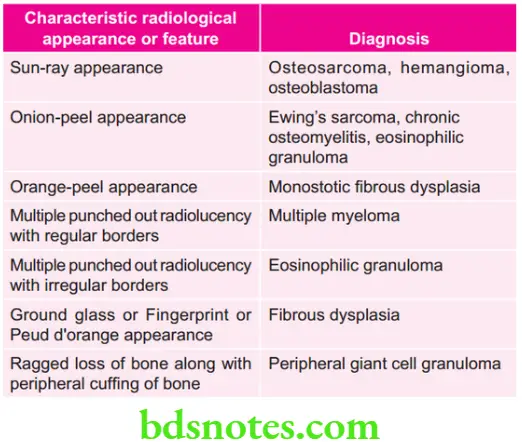
Various characteristic Radiologic Features and Their Diagnosis
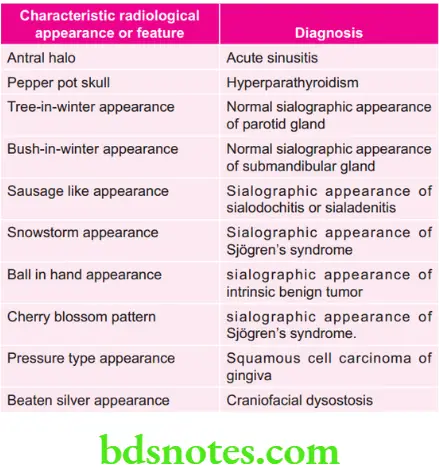
Various Pericoronal Radiolucencies
- Dentigerous cyst
- Pericoronal space
- Ameloblastoma
- Unicystic ameloblastoma
- Calcifying odontogenic cyst
- Ameloblastic firoma
- Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
- Developmental primordial cyst
Various Periapical Radiolucency
- Acute apical periodontitis
- Benign and malignant tumor including secondary metastatic deposit
- Periapical abscess
- Periapical granuloma
- Periapical cyst
- Dentigerous cyst
- Periapical scar
- Osteomyelitis
- Giant cell granuloma
- Lymphoreticular tumors of bone
- Langerhans cell disease
- Periapical cemental dysplasia
- Surgical defect
Various Monolocular Radiolucency
- Radicular cyst
- Residual cyst
- Dentigerous cyst
- Simple bone cyst
- Lateral periodontal cyst
- Nasopalatine duct cyst
- Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
- Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor
- Primary bone tumors
- Multiple myeloma
- Eosinophilic granuloma
- Stafne’s bone cyst
- Fibrocementoosseous lesion
Various Multilocular Radiolucency
- Keratocystic odontogenic tumor
- Ameloblastoma
- Ameloblastic firoma
- Ameloblastic firo odontoma
- Odontogenic myxoma
- Central giant cell granuloma
- Cherubism
- Aneurysmal bone cyst
- Metastatic tumor of jaw
- Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor
- Burkitts lymphoma
- Fibrous dysplasia
- Squamous odontogenic tumor
Lesions consisting of Loss of Lamina dura
- Normal anatomical variation
- Periapical infections
- Paget’s disease
- Fibrous dysplasia
- Osteoporosis
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Leukemia
- Osteomalacia
- Multiple myeloma
- Osteomalacia
- Hypophosphatasia
- Cushing’s syndrome
Generalized Rarefaction of Jaws
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Osteoporosis
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Hypervitaminosis D
- Diabetes
- Osteomalacia
- Leukemia
Periapical Radiopacities
- True
- Foreign bodies
- Hypercementosis
- Periapical idiopathic osteosclerosis
- Condensing osteitis
- Mature periapical cementoma
- Projected
- Retained root tip
- Sialoliths
- Phleboliths
- Tori
- Periapical osteoma
- Arterial calcifications
Campbell’s Line
These lines are drawn on occipitomental radiograph to interfere with maxillofacial trauma. These are basically the fie lines to have an orientation of bone after trauma

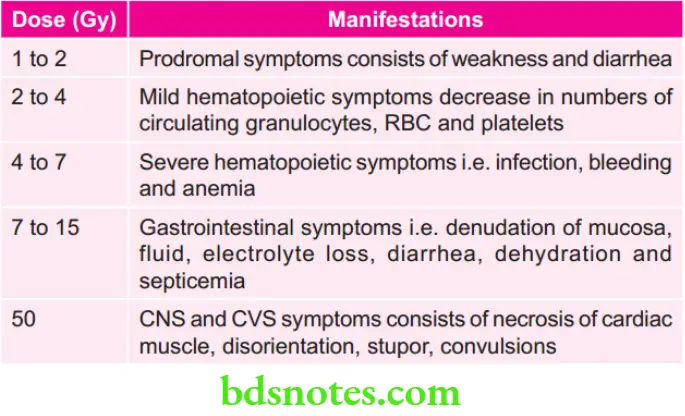
Various doses of Radiation and their Manifestations
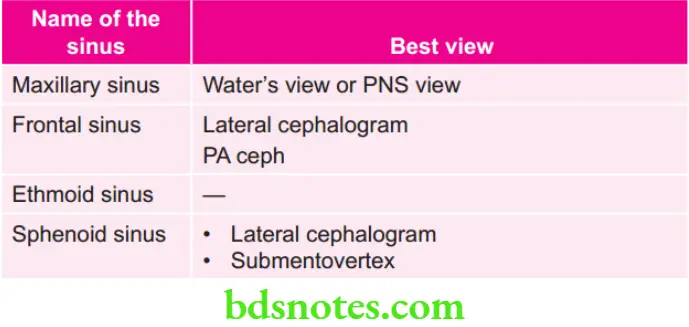
Various sinuses and their Views

Leave a Reply