Oral mucous membrane
Question 1. Classify oral mucous membrane and describe in detail about masticatory mucosa.
Answer:
Oral Mucous Membrane Classification:
- Based on the functional criteria, the oral mucous membrane is divided into:
- Masticatory mucosa-gingiva and hard palate.
- Lining mucosa – lop, cheek, vestibule, alveolar mucosa, the floor of the mouth, and soft palate.
- Specialized mucosa – dorsum of tongue and taste buds.
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
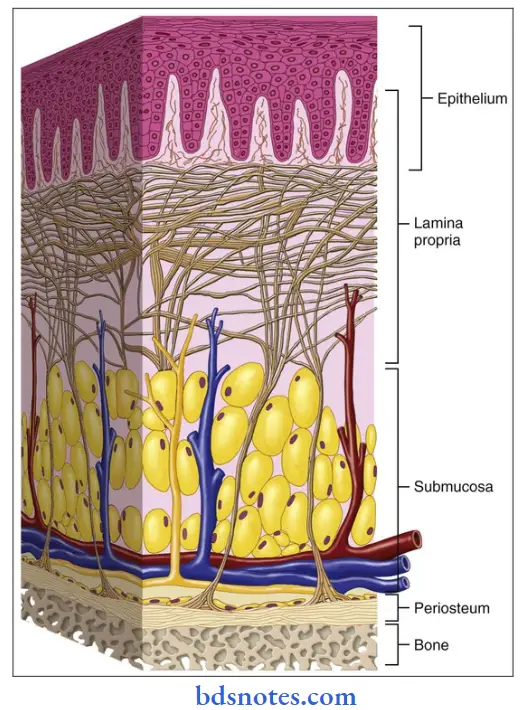
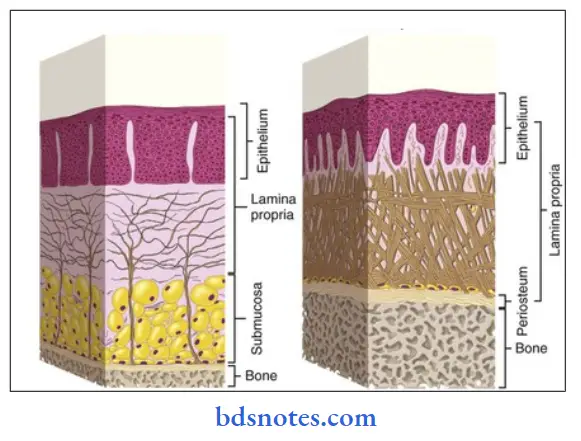
Masticatory mucosa:
- It covers those areas of the oral cavity such as the hard palate and gingiva that are exposed to compressive and shear forces and to abrasion during the mastication of food.
- It covers immobile structures.
- It is bound firmly to the structures directly by the attachment of the lamina propria to the periosteum of the underlying bone or indirectly by a fibrous submucosa.
Oral Mucous Membrane Significance:
1. Fibrous submucosa:
- Cushion the mucosa against mechanical loads.
- Protects the underlying nerves and blood vessels of the palate.
2. Firmness of mucosa:
- Ensures that it does not gape after surgical incision.
- Injections of local anesthesia become difficult and often painful.
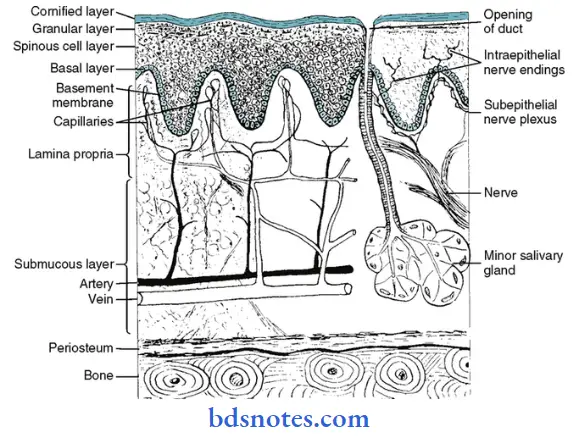
Histology:
1. Epithelium.
- Moderately thick.
- Orthokeratinised or para keratinized
- Well adapted to withstand abrasion.
2. Junction between epithelium and lamina propria.
- Convoluted.
- Presence of numerous elongated papillae.
Functions:
- Provide good mechanical attachment
- Prevent the epithelium from being stripped off.
3. Lamina propria.
- Thick
- Contain a dense network of collagen fibers.
4. Submucosa layer.
- Gingiva.
- No such distinct layer is present.
- It is because the mucosa is firmly attached by collagen fibers to the cementum and periosteum of the alveolar process.
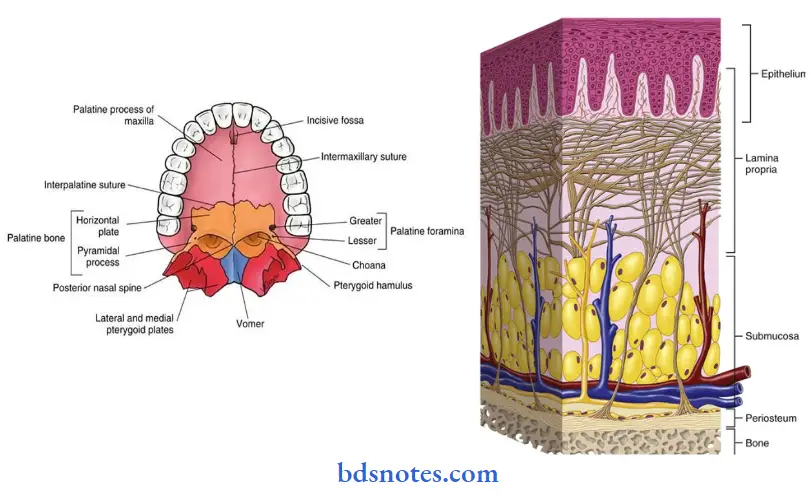
Palate:
- The submucous layer occurs in wide regions extending between the palatine gingiva and palatine raphe.
- The following zones are distinguished in the palate.
- Gingival region – adjacent to teeth.
- Palatine raphe – extending from the incisive papilla.
- Fatty zone – Anterolateral area between the raphe and gingiva.
- Glandular – zone – the posterolateral area between the raphe and gingiva.
- The submucous layer contains fat or glands for a cushioning effect.
Question 2. Describe the lining mucosa.
Answer:
- The oral mucosa covering the underside of the tongue, inside of the lips, cheeks, floor of the mouth vestibule, and alveolar mucosa are classified as lining mucosa.
- The mucous membrane is movably attached to the deep structures and does not restrict the movement of lips, cheeks, and tongue.
- Where the lining mucosa covers muscle, the mucosa is fixed to the fascia.
Lining Mucosa Clinical considerations:
- Surgical incisions require sutures for closure.
- Injections are easy due to the ready dispersion of fluids.
- Infections spread rapidly.
Lining Mucosa Histology:
1. Epithelium.
- Thick (400 pm)
- Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
- The surface is flexible to withstand stretching.
2. Junction between epithelium and lamina propria.
- Smooth
- Slender connective tissue papillae often penetrate into the epithelium.
3. Lamina propria.
- Thicker
- Contains fewer irregular collagen fibers.
- This helps the mucosa to be stretched to a certain extent.
- Also contains elastic fibers to control the extensibility of the mucosa.
4. Submucosa.
- The mucosa of the soft palate is separated from the loose and highly glandular submucosa by a layer of elastic fibers.
Attachments:
1. Lining mucosa covering the muscle.
- Attached by a mixture of collagen and elastic fibers
2. the alveolar mucosa and mucosa covering the floor of the mouth.
- Attached loosely to the underlying structures by a thick submucosa.
3. Mucosa of the underside of the tongue.
- Bound firmly to the underlying muscle.
Lining Mucosa Functions:
1. Collagen fibers.
- Helps to stretch the mucosa to a certain limit.
2. Elastic fibers.
- Tend to control the extensibility of the mucosa.
- During mastication.
- Retract the mucosa toward the muscle.
- Prevent it from bulging between the teeth and being bitten.
- Tend to restore the mucosa to its resting position after detention.
Question 3. Write about the specialized mucosa of the oral cavity.
Answer:
Specialized mucosa:
- The mucous membrane covering the dorsum of the tongue is called a specialized mucosa.
- It is covered by functionally highly extensible masticatory mucosa.
Dorsum of the tongue:
- It is rough and irregular.
- It is covered by a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium.
- It is divided by the V-shaped groove called sulcus terminals into:
1. Anterior two-thirds- the body of the papillary part.
- Mucosa is derived from the first pharyngeal arch.
- It is supplied by the lingual nerve.
2. Posterior one-third-base or lymphatic part.
- Derived from the third pharyngeal arch.
- It is supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Fungiform papillae:
- They are scattered between the numerous filiform papillae at the tip of the tongue.
- They are red, smooth, round structures.
- They are covered by thin, nonkeratinized epithelium.
- They have a rich capillary network.
- They contain one to three taste buds only on their dorsal surface.
Filiform Papillae:
- They are fine-pointed, cone-shaped papillae covering the anterior part of the tongue.
- Covered by a thick keratinized epithelium, containing a core of connective tissue.
- They form a tough, abrasive surface.
- They do not contain taste buds.
- They are involved in compressing and breaking food when the tire tongue is opposed to the tire hard palate.
Foliate papillae:
- They are leaflike papillae present on the lateral margins of the posterior part of the tongue.
- They consist of 4-11 parallel ridges separated by deep grooves.
- They contain few taste buds.
- They are more frequent in mammals.
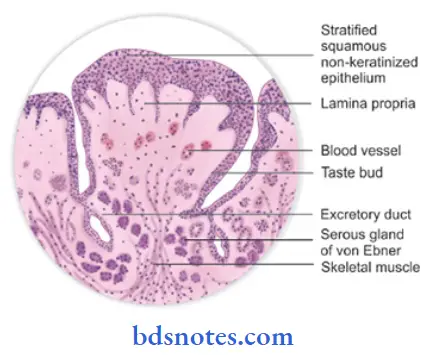
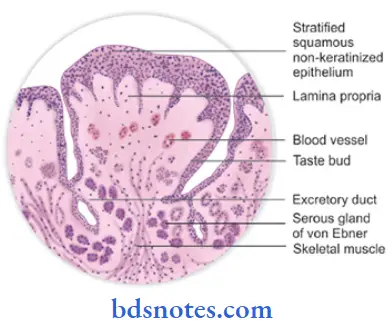
Circumvallate papillae:
- They are 8-12 large structures present just anterior to the sulcus terminalis.
- They are surrounded by a deep, circular groove for the opening of ducts of minor salivary glands.
- They contain a connective tissue core covered by a keratinized epithelium.
- Taste buds are present on its lateral surface.
- Its free surface shows numerous secondary papillae.
- They do not protrude above the surface of the tongue.
- Their function is to wash out the soluble food elements.
- They are also the main source of salivary lipase.
Posterior one-third of the tongue:
- It contains round or oval prominences – lingual follicles.
- Each of these has one or more lymph nodules.
- Lingual follicles have a small central pit called a lingual crypt lined with stratified squamous epithelium.
- Ducts of small mucous lingual glands open into the lingual crypt.
- The lingual follicles together form the lingual tonsil.
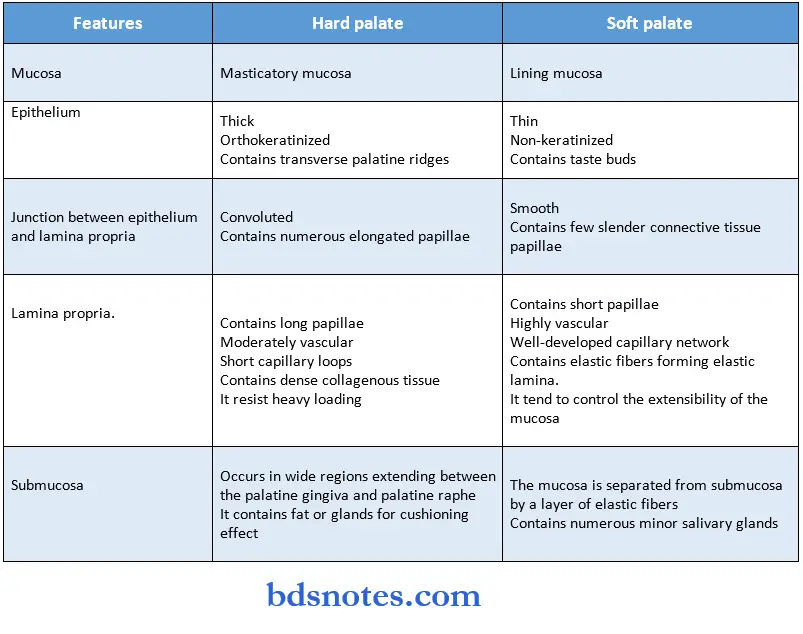
Question 4. Classify oral mucous membrane. Enumerate the histological differences between hard and soft palate.
Answer:
Classification:
- Based on the functional criteria, the oral mucous membrane is divided into.
- Masticatory mucosa – gingiva and hard palate.
- Lining mucosa – lip, cheek, vestibule, alveolar mucosa, the floor of the mouth, and soft palate.
- Specialized mucosa – dorsum of tongue and taste buds.
Differences between hard and soft palate:
Question 5. Classify oral mucous and describe keratinized mucosa.
Answer:
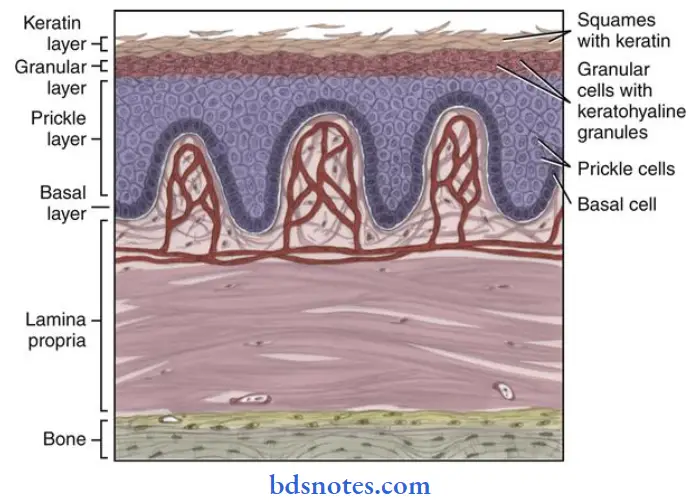
Keratinized mucosa:
- Keratinizing oral epithelium has keratinocytes arranged in four cell layers.
- Stratum basale
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratym corneum.
The mucosal surface results from the formation of a surface layer of keratin and the dying process of maturation is called keratinization.
1. Stratum basale:
- It is also called the proliferative or germinative layer.
- It is made up of a single layer of cuboidal cells that synthesize DNA and undergo mitosis to provide new cells.
- They contain bundles of tonofibrils and other cell organelles indicative of protein synthesis.
- The cells in this layer are capable of cell division.
- They divide and form two cell populations.
- One cell population migrate and form cells of the other layer.
- Other cell populations remain as stem cells.
- This layer contains desmosomes – connecting adjacent cells and hemidesmosomes – connecting cells to the basal lamina.
- They provide mechanical linkages.
- Gap junctions allowing electrical and chemical communications are also seen.
2. Stratum spinosum or prickle cell layer:
- Contains several rows of large elliptical or spherical cells.
- Membrane-coating granules appear in the upper part of this layer.
- The nuclei stain less intensely than those of the basal layer.
- They frequently shrink away from each other, remaining in contact only at points known as intercellular bridges.
- This gives the cells a spiny or prickle-like appearance.
- Cells of this layer are the most active in protein synthesis.
- Separation of cells occurs which is caused by loss of intercellular bridges – acantholysis.
- The basal and prickle cell layers together constitute from half to two-thirds of the thickness of the epithelium.
3. Stratum granulosum:
- This layer contains flattened cells containing basophilic keratohyalin granules associated with dense tonofibrils.
- Membrane-coating granules fuse with the cell membrane in the upper part.
- The nuclei of cells show signs of degeneration and pyknosis.
- The cell surfaces become more regular and more closely placed adjacent cell surfaces.
- This layer still synthesizes proteins.
- The membrane-coating granules are glycolipids that have an internal lamellated structure.
- This form an intercellular lamellar material that contributes to the formation of a permeable barrier.
4. Stratum corneum:
- This layer contains extremely flattened and dehydrated cells.
- Cell organelles have been lost.
- Cells are filled only with packed fibrillar material.
- Cells stain bright pink with eosin.
- The keratohyalin granules have disappeared.
- Cells do not synthesize proteins.
Orthokeratinization:
- Cells do not have any nuclei.
Parakeratinization:
- Cells retain pyknotic and condensed nuclei.
- Keratohyalin granules may be present in the cells.
- Cells also contain partially lysed cell organelles until they desquamate.
Question 6. Define oral mucosa. Write in detail the microscopic and macroscopic features of the gingiva.
Answer:
Definition:
- The moist lining of the oral cavity that communicates with the exterior is called oral mucosa.
Gingiva:
- It is defined as the tissue that covers the alveolus and encircles the necks of teeth.
- It extends from the dentogingivial junction to the alveolar mucosa.
- It is immovable and firmly attached to the periosteum of the alveolar bone.
Microscopic features:
1. Epithelium:
- Thick stratified squamous epithelium.
- The layers observed are:
- Stratum basale
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum corneum.
- It may be ortho-keratinized or para-keratinized.
- It shows stippled surface.
2. Junction between epithelium and lamina propria:
- Convoluted
- Presence of plenty of deep rete pegs that are closely placed.
- This prevents the epithelium from being stripped off.
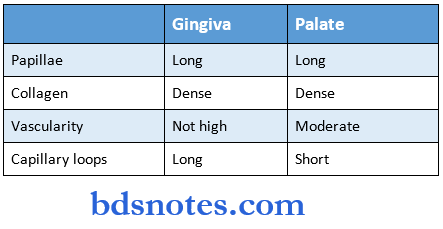
3. Lamina propria:
- Contains long and narrow connective tissue papillae.
It has a papillary layer and a reticular layer. - Not highly vascular.
- It is made up of collagen bundles, long capillary loops, lymphatics, nerve tissue, and cells like fibroblasts, histocytes, monocytes, mast cells, and lymphocytes.
4. Submucosa:
- A distinct submucosa layer is absent.
- Lamina propria is directly attached to the periosteum.
Fibers:

Macroscopic features:
- Colour- coral pink normally but it depends on.
- Thickness of epithelium
- Degree of keratinization
- Degree of pigmentation.
- Amount of circulation.
- Consistency – firm and resilient
- Contour – scalloped
- Surface -stippling surface.
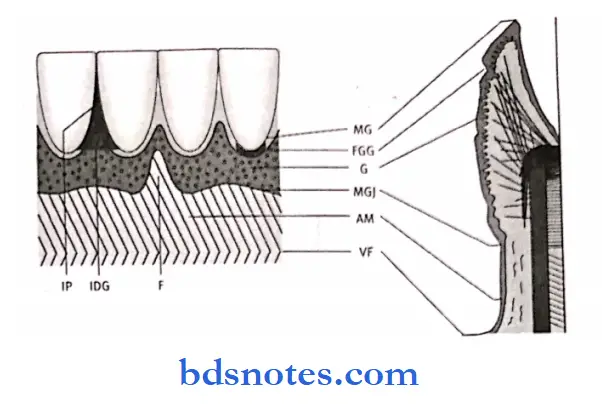
Parts of gingiva:
1. Free or marginal gingiva:
- Embraces the necks of the teeth.
- Width of free gingiva.
- 1 mm – in normal healthy gingiva
Increased in:
- Chronic marginal gingivitis.
- Chronic periodontitis.
- The dividing line between the free gingiva and the attached gingiva is the free gingival groove.
2. Attached gingiva:
- Part of the gingiva that is firmly bound to tire periosteum
- Boundaries.
- Superiorly – free gingival groove.
- Inferiorly – mucogingival line.
- It has a greater width in the maxilla compared to the mandible.
- It is about 4-6 mm.
- Its width decreases in pathological conditions.
- Due to the presence of pockets and gingival recession.
3. Interdental papilla:
- It is that part of the gingiva that fills the space between two adjacent teeth.
- The surface of the interdental papilla is triangular.
- The tip and margins are unattached and the central portion is attached.
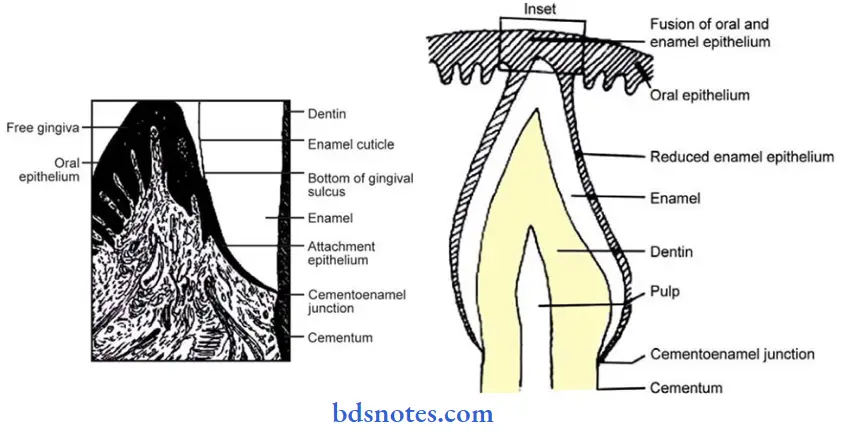
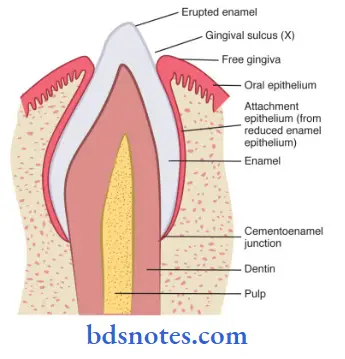
Gingival sulcus:
- It is a ‘ V’ shaped space between the marginal gingiva and the tooth surface.
- Its depth is about 0-2 mm normal.
- The base is formed by the superior end of the junctional epithelium.


Question 7. Write the development, structure, and different stages of the dentogingival junction.
Answer:
Dentogingival junction:
- It is the junction between the gingiva and the tooth.
- It represents a site of potential weakness in the continuous lining of the oral cavity.
Structure:
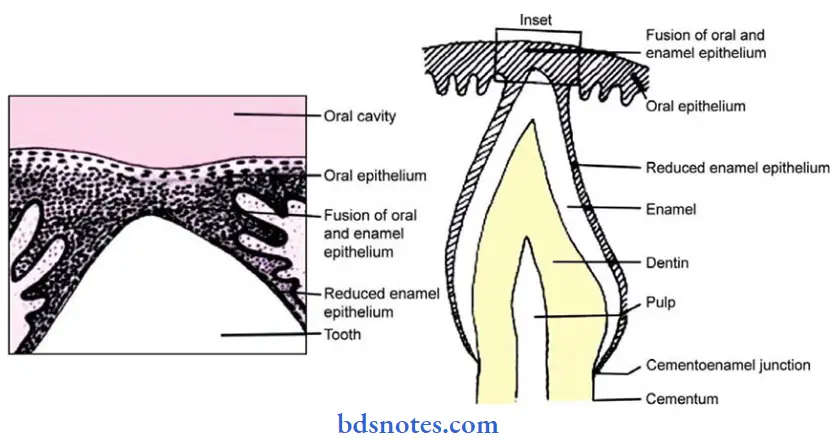
- The epithelium of the gingiva that attaches to the tooth is called junctional epithelium.
- The union between it and the tooth is called epithelial attachment.
- The junctional epithelium resembles reduced enamel epithelium.
- They have a basal layer and a few layers of flattened cells.
- It is non-differentiating, nonkeratinizing tissue.
- It is highly permeable with large intercellular spaces.
- Lymphocytes and plasma cells are seen in the connective tissue at the bottom of the gingival sulcus and below the attachment epithelium.
Development:
- After the formation of the enamel matrix, ameloblasts leave a thin membrane on the enamel surface, called the primary enamel cuticle.
- Then, the ameloblasts shorten and the epithelial enamel organ is reduced to a few layers of flat cuboidal cells called reduced enamel epithelium.
- It covers the entire enamel surface up to CEJ at the same time remains attached to the primary enamel cuticle.
- During the eruption, the tip of the tooth approaches the oral mucosa.
- By it, the reduced enamel epithelium and the oral epithelium meet and fuse.
- The remnants of the primary enamel cuticle are referred to as Nasmyth’s membrane.
- The epithelium covering the tip of the crown degenerates in its center through which it emerges into ora! cavity.
- Now, the reduced enamel epithelium is known as the primary attachment epithelium.
- At the margin of the gingival, the attachment epithelium becomes continuous with the oral epithelium.
- The reduced enamel epithelium gradually shortens due to which a shallow groove called gingival sulcus develops between the gingiva and the tooth surface.
- When the reduced enamel epithelium gets separated from the erupted tooth, the gingival sulcus further deepens.
- During the first and second stages, a clinical crown is smaller than the anatomic crown.
- During the third stage, a clinical crown is equal to an anatomic crown.
- During the fourth stage, the clinical crown is larger than the anatomic crown.
Question 8. Write briefly about epithelial attachment.
Answer:
Epithelial attachment:
- It is shown by Stem and confirmed by Listgarten and Schroeder,
- They showed the mode of attachment of the ameloblasts to the tooth, to be basal lamina to which hemidesmosomes are attached.
- This is referred to as epithelial attachment.
- Both reduced ameloblasts and gingival epithelial cells form basal lamina on enamel and cementum
- Hemidesmosomes of these cells attach to the basal lamina.
- This basal lamina is referred to as the internal basal lamina.
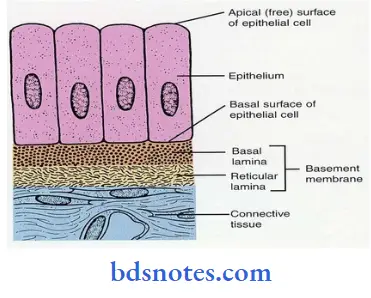
- The lamina propria below the junctional epithelium keeps the epithelial cells of the junctional epithelium immature so that it can develop hemidesmosomes and attach to the tooth.
- They then migrate over it, with their attachment being maintained by the hemidesmosomes.
- The hemidesmosomes hold the cells to the basal lamina so that the strength of the attachment is not diminished despite the migration.
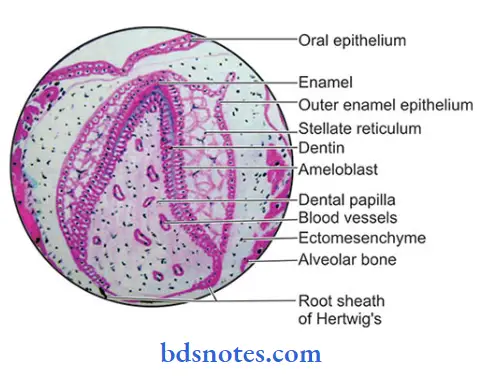
Question 9. Circumvallate papillae.
Answer:
- Location: Just anterior to the sulcus terininalis.
- Number: 8 – 12 in number.
Structure:
- Large round structures.
- They do not protrude above the surface
- They are surrounded by a deep, circular groove for the opening of ducts of minor salivary glands.
- They contain a connective tissue core covered by a keratinized epithelium.
Surfaces;
- Free surface – shows numerous secondary papillae covered by a thin, smooth epithelium.
- Lateral surface – contains numerous taste buds.
Functions:
- Wash out the soluble elements of food
- The main source of salivary lipase.
Question 10. Write briefly the development of three stages of detinogingival junction.
Answer:
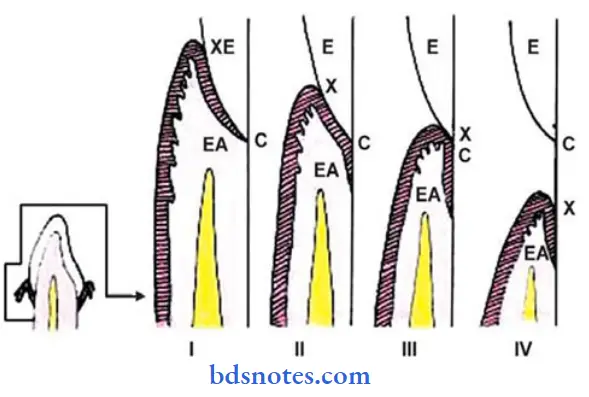
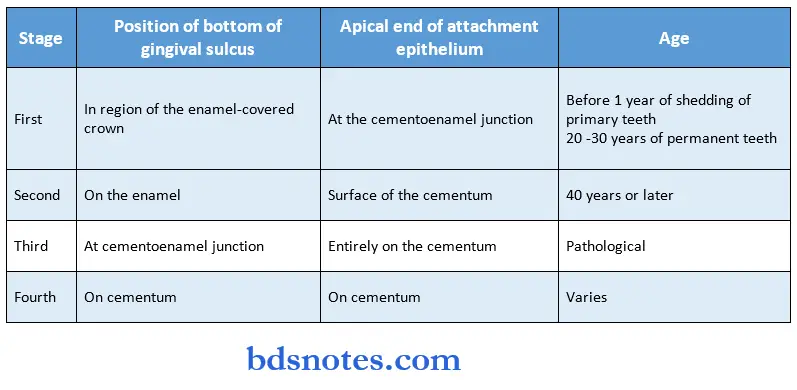
Stages of dentinogingival junction:
1. First stage physiologic:
- Position of the bottom of the gingival sulcus. In the enamel-covered crown.
- Position of the apical end of the attachment epithelium at tire cementoenamel junction.
- The clinical crown is smaller than the anatomic crown.
Age:
- Before 1 year of shedding of primary teeth.
- In permanent teeth, at the age of 20 – 30 years.
2. Second stage – physiologic:
- The bottom of the gingival sulcus is on the enamel.
- The apical end of the attachment epithelium is on the cementum.
- Fiber bundles present at the cervical parts of the cementum undergo dissolution.
- This part later gets covered by the epithelium.
- The apical shift of the gingival and transseptal fibers occurs.
- Fibers are destroyed by the enzymes secreted by the epithelial cells, by plaque or by immunologic reactions.
- The clinical crown is smaller than the anatomic crown.
- Age: 40 years or later.
3. Third stage – pathologic:
- The bottom of the gingival sulcus is at the cementoenamel junction.
- Epithelium attachment is entirely on the cementum.
- The tooth is exposed.
- The epithelium shifts along the tooth surface.
- The clinical crown is equal to the anatomic crown.
4. Fourth stage – pathologic:
- It represents a gingival recession.
- The entire attachment is on the cementum.
- May occur even in the absence of periodontitis.
- The clinical crown is longer than the atomic crown.
Age:
- Varies
- In some cases, occurs at the age of 20’s while absent even at the age of 50 or more.

Question 11. Inner enamel epithelium
Answer:
- Inner enamel epithelium is first seen during the cap stage
- Consists of a single layer of columnar cells called ameloblasts
- Present on the concave surface in the cap and bell stage
- Size
- 4-5 pm in diameter
- 40 pm high
- Attached to one another by junctional complexes and to the cells of stratum intermedium by desmosomes
- When the inner enamel epithelium is in contact with the dental papilla it receives its nutrient supply from the blood vessels of the dental papilla but dentin is formed, it cut off the ameloblasts from the source of nourishment.
- The inner enamel epithelium is supplied by the capillaries of the dental sac
Functions:
- It exerts influence on underlying mesenchymal cells of the dental papilla to differentiate into odontoblasts
- In the formation of cusps
- Inner enamel epithelial cells present in future cusp tip region stop differentiating
- Pressure is exerted on them by continuous division from other areas of the enamel organ
- As a result, these cells are pushed out of the enamel organ
- Thus cusp tip is formed
Question 12. Keratinized mucosa / Strata in keratinized mucosa
Answer:
- Basal layer
- Cells are cylindrical or cuboidal
- They are attached to the basement membrane
- Cells have the ability to divide
- One of the divided cells migrates to the superficial layer
- Basal cells are separated from connective tissue by the basement membrane
- Beneath the basal cell layer, the electro-lucent zone can be seen called lamina lucida
- Beneath it, there is electron dense zone called lamina densa
- Hemidesmosomes attach epithelium to the connective tissue
- Stratum spinosum
- Large cells are present with short processes called spines
This gives the cells a prickled appearance - Cells are attached to one another with the help of desmosomes
- Large cells are present with short processes called spines
- Stratum granulosum
- Keratohyalin granules are seen
- Stratum corneum
- The cytoplasm of cells in this layer is filled with keratin
- It can be
- Orthokeratinized- in this cells are devoid of nucleus
- Parakeratinized- In this cells contains the pinpoint nucleus
Question 13. Non keratinized mucosa
Answer:
Areas with non-keratinized mucosa:
- Lining mucosa
- Labial and buccal mucosa
- Alveolar mucosa
- Mucosa of ventral aspect of tongue
- Mucosa of the floor of the mouth.
- Soft palate
Histological features:
1. Epithelium
- Have high rates of mitosis
- Three layers are present
- Stratum basale
- Made up of a single layer of cuboidal cells
- These cells undergo mitosis, thus producing new cells
- Adjacent cells are attached by desmosomes
- Stratum intermedium
- Cells are larger
- Contains intermediate keratin filaments which are sparsely distributed within cells
- Cells are attached by desmosomes
- Stratum superficial
- Contains nucleated cells
- Contains less number of tonofilaments and lacks keratohyalin granules
- These cells desquamate
2. Lamina propria
- It is thin containing dense connective tissue and short irregular papillae
3. Submucosa
- It varies in different areas
Question 14. Specialized mucosa
Answer:
- The mucous membrane covering the dorsum of the tongue is called specialized mucosa
Dorsum of the tongue:
- It is rough and irregular
- It is divided by the V-shaped groove called sulcus terminals into
- Anterior two-third or papillary part
- Posterior one third or lymphatic part
Papillae of the tongue:

Posterior one-third of the tongue:
- It contains round or oval prominences called lingual follicles
- Each of these has one or more lymph nodules
- The lingual follicles together form lingual tonsil
Question 15. Lining mucosa
Answer:
- The oral mucosa covering the underside of the tongue, inside of the lips, cheeks, floor of the mouth, vestibule, and alveolar mucosa are classified as lining mucosa.
Histology:
1. Epithelium
- Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
- The surface is flexible to withstand stretching
2. Junction between epithelium and lamina propria
- Smooth
- Connective tissue papilla often penetrates into the epithelium
3. Lamina propria
- Thicker
- Contains fewer irregular collagen fibers and elastic fibers
4. Submucosa
- The mucosa of the soft palate is separated from the loose and highly glandular submucosa by a layer of elastic fibers
Functions:
- Collagen fibers help to stretch the mucosa to a certain limit
- Elastic fibers tend to control the extensibility of the mucosa
Question 16. Gingiva
Answer:
- It is defined as the tissue that covers the alveolus and encircles the necks of the teeth
- It is immovable and firmly attached to the periosteum of the alveolar bone
- Microscopic features
- Epithelium
- Thick stratified squamous epithelium
- Layers – stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum and stratum corneum
- Sulcular epithelium, junctional epithelium and interdental col are non-keratinized areas in the gingiva.
- Has stippled surface
- The junction between epithelium and lamina propria
- Convoluted
- The presence of plenty of deep rete pegs prevents epithelium from being stripped off
- Lamina propria
- Contains long and narrow connective tissue papillae
- It has a papillary layer and a reticular layer
- It is made up of collagen bundles, long capillary loops, lymphatics and nerve tissue, and cells like fibroblasts, histiocytes, monocytes, mast cells, and lymphocytes
- Fibers
- Denogingival
- Alveologingival
- Circular
- Dentoperiosteal
- Transseptal
- Epithelium
Macroscopic features:
- Color – coral pink
- Consistency – firm and resilient
- Contour – scalloped
- Surface – stapling
- Parts
- Free or marginal gingiva – embraces the necks of the teeth
- It is separated from the attached gingiva by a free gingival groove.
- Attached gingiva – part of the gingiva that is firmly bound to the periosteum
- It is separated from the alveolar mucosa by the mucogingival line
- Interdental papilla – part of the gingiva that fills the, space between two adjacent teeth
Gingival sulcus:
- V-shaped space between the marginal gingiva and tooth surface
- Depth is about 0-2 mm
Question 17. Vermillion zone of lip
Answer:
- The transitional zone between the skin of the lip and the mucous membrane of the lip is called the vermillion zone
- The line that separates the skin from the vermillion zone is called the vermillion border
- It is exposed to the atmosphere
Histological features:
Contains:
- Mildly keratinized epithelium
- Numerous, densely arranged long papillae of lamina propria
- It reaches deep into the epithelium
- Carries large capillary loops along with it close to the surface
- Thus it appears red in color
- There are no glands present to keep it moist thus lips require frequent moistening
Question 18. Difference between masticatory mucosa and lining mucosa
Answer:
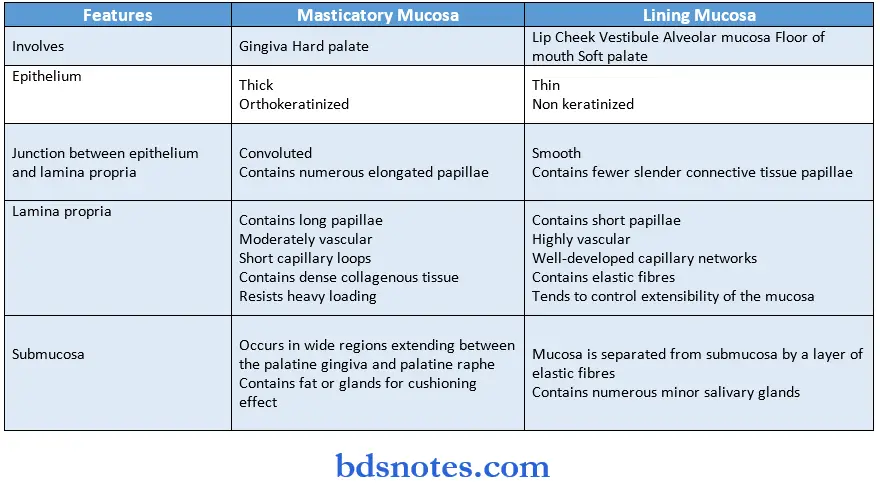
Question 19. Non-keratinocytes.
Answer:
These cells do not possess:
- Cytokeratin filaments
- Ability to keratinize
- Mitotic activity
- The ability of arranged in layers
- Desmosomal attachments.
- These cells migrate to the oral epithelium from the neural crest or from the bone marrow.
Question 20. Keratinocytes.
Answer:
- These are an epithelial cell that synthesizes keratin.
- They are part of each layer of keratinizing oral epithelium.
They contains:
- Cell organelles
- tonofilaments.
- Cytokeratin
- Tonofibrils.
- They show cell division, undergo maturation, and finally desquamate
- They, during their migration from the basal to the superficial layer, undergo biochemical and morphological changes.
- This results in the formation of keratinized squama.
- Keratinocytes increase in volume in each successive layer from basal to superficial.
Question 21. Col.
Answer:
It means a valley.
- Connecting the facial and lingual side of the interdental papilla on the proximal side is an epithelial surface called col.
Shape:
- Concave – in healthy gingiva.
- Dome-shaped – gingival recession and inflammation.
Structure:
- It is covered by thin non-keratinized epithelium.
Clinical importance:
- It is more vulnerable to periodontal disease.
- It is because its contours allow bacteria, food debris, and plaque to accumulate in it.
Question 22. Melanocytes.
Answer:
Origin:
- Embryologic neural crest cells.
Features:
- Dendritic cell.
- Do not possess desmosomes and tonofilaments.
- Stores melanin pigment in melanosomes.
- They are present in the basal layer of epithelium.
Function:
- Synthesize melanin pigment.
- Transfer to surrounding keratinocytes.
Question 23. Dentinogingival junction.
Answer:
- It is the junction between the gingiva and the tooth.
- It represents a potential weakness in the epithelial lining of the oral cavity.
- The firmness and mechanical strength of the dentinogingival junction are due to the connective tissue attachment.
- It is less resistant to mechanical forces and bacterial attacks.
- Firmness of it is maintained by the gingival portion of the periodontal ligament.
- The epithelium of the gingiva which gets attached to the tooth is called attachment epithelium.
- The adherence of epithelium to the tooth is the function of attachment epithelium.
Question 24. Changes In oral mucosa.
Answer:
- The oral mucosa becomes smooth and dry.
- Decreased salivary secretion.
Histological changes:
- Epithelium appears thinner
- Smoothing of the epithelium-connective tissue interface
- Flattening of epithelial ridges.
- Reduction in filiform papillae.
- Reduction in Langerhans cells.
- Development of varicosities.
- In lamina propria.
- Decreased cell hilarity
- An increased amount of collagen.
- Atrophy of minor salivary glands
- The decline in cell-mediated immunity
Changes in postmenopausal women:
- Dryness of the mouth
- Burning sensations
- Abnormal taste.
Nerve changes:
- Progressive loss of sensitivity to thermal, chemical, and mechanical stimuli.
- A decline in taste perception.
Question 25. Langerhans cells.
Answer:
Non-keratinocytes:
Origin: Bone marrow
Site: Suprabasal layer of epithelium.
Structure:
- Dendritic cell
- Has convoluted nucleus
- Has a small rod or flat-shaped granule called a Birbeck granule.
- Lacks desmosomal attachments.
- Appears as a clear cell histologically.
Functions:
- Recognizing and processing antigenic material.
Question 26. Junctional epithelium.
Answer:
- The epithelium of the gingiva which gets attached to the tooth is called the junctional epithelium.
- It resembles reduced enamel epithelium.
- It is non-differentiating, nonkeratinizing tissue
- It is highly permeable and has large intercellular spaces.
- It is formed by the fusion of reduced enamel epithelium and oral epithelium.
- It consists of flattened cells aligned parallel to the tooth surface.
- It has 3-4 layers apically and 15 – 30 layers coronally
Parts:
- Corona part – Thickest and has maximum permeability.
- Middle part – lias maximum adhesion
- Apical part – has maximum mitotic activity.
Question 26. Lamina propria.
Answer:
- The connective tissue supporting the oral epithelium is termed lamina propria.
Layers:
- The superficial papillary layer.
- Associated with the epithelial ridges Collagen fibers are thin and loosely arranged.
- Deeper reticular layer.
- Lies between the papillary layer and the underlying structures.
- Collagen fibers are arranged in thick bundles.
Consist of:
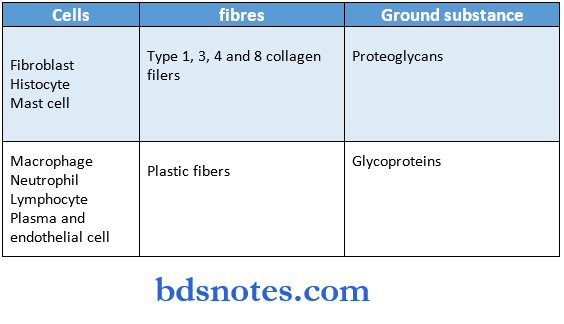
Question 27. Tastebuds.
Answer:
- They are small void or barrel-shaped interepithelial organs.
Size: 80 cm high, 40 cm thick.
Structure:
- Their outer surface is covered by a few flat epithelial cells surrounding taste pores.
- It is composed of 30 – 80 spindle-shaped cells.
- The outer supporting cells are arranged like the staves of a barrel.
- They are slender, dark-staining cells that carry finger-like processes at their superficial end.
- A rich nerve plexus is found below the taste buds.
Site:
- The inner wall of the trough surrounding the vallate papillae, In folds of the foliate papillae On the posterior surface of the epiglottis.
- At the tip of fungiform papillae.
- Lateral borders of the tongue.
Question 28. Vermillion border.
Answer:
- The transitional zone between the skin of the lip and the mucous membrane of the lip is called a vermillion zone.
- The line that separates the skin from the vermillion zone is called the vermillion border.
- It is characterized by a thicker mildly keratinized epithelium and numerous long papillae of the lamina propria.
- Large capillary loops are present close to the surface.
- It is exposed to the atmosphere but there are no glands to keep it moist thus lips require frequent moistening.
Question 29. Mucogingival groove.
Answer:
- It is the junction between the attached gingiva and alveolar mucosa.
- Clinically identified by the color change from the bright pink of the alveolar mucosa to the pale pink of the gingiva.
Histology:
- The epithelium of the attached gingival is keratinized or para-keratinized.
- Lamina propria of it contains numerous collagen bundles.
- The structure of mucosa changes at the mucogingival groove where alveolar mucosa has thicker, nonkeratinized epithelium and lamina propria with numerous elastic fibers.
Question 30. Epithelial attachment.
Answer:
- The attachment of ameloblasts to the tooth was shown to be basal lamina to which hemidesmosomes are attached.
- This mode of attachment is referred to as the epithelial attachment.
- It was first shown by Stern and confirmed by Listgarten and Schroeder.
- It is submicroscopic, approx, 40 nm wide
- The adhesive forces in this zone are molecular in nature.
- Such forces act across a distance smaller than 40 nm.
Question 31. Reduced enamel epithelium.
Answer:
- After the formation of the primary enamel cuticle, ameloblasts shorten.
- Then the epithelial enamel organ is reduced to a few layers of flat cuboidal cells, called reduced enamel epithelium.
- Under normal conditions it covers the tire’s entire enamel surface, extending to the tire cementoenamel junction.
- It is no longer involved in the secretion and maturation of enamel.
Function:
- It has a protective function.
- It protects the mature enamel by separating it from the connective tissue until the tooth erupts.
- If connective tissue comes in contact with the enamel, anomalies may develop.
- In the case of a premature break in tire epithelium, connective tissue cells come into contact with enamel and deposit cementum on the enamel.
Question 32. Clinical and microscopic features of palatal mucosa.
Answer:
Clinical features:
- The palate forms the roof of the oral cavity
- It is immovable and tightly fixed to the tire’s underlying periosteum.
- It is pink or color.
- 4 zones are identified.
- Gingival region – adjacent to the teeth.
- Palatine raphe – From incisive to palatine papilla.
- Anterolateral area – Between raphe and gingiva.
- Posterolateral area – Between raphe and gingiva.
Microscopic features:
- Epithelium.
- Thick, uniform.
- Orthokeratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
- Cells of the stratum corneum exhibit stacking.
- There is an increase in the number and length of desmosomes.
2. Junction between epithelium and lamina propria.
- Convoluted.
- Contains numerous elongated papillae.
3. Lamina propria.
Contains:
- Long papillae
- Short capillary loops.
- Dense collagenous tissue.
4. Submucosa.
- Extends between the palatine gingiva and palatine raphe.
- It contains fat or glands for a cushioning effect.
Question 33. Uvula.
Answer:
- It is a projection from the posterior edge of the middle of the soft palate.
- Its connective tissue contains a number of glands and muscle fibers.
- It plays a role in the articulation of some sounds.
- The muscles of it raise and retract the uvula.
- It is innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve.
- Uvula gets swollen under the following conditions.
- Dehydration
- Smoking
- Allergic reaction.
- Viral or bacterial infection.
Question 34. Rugae.
Answer:
They are ridges of mucous membranes extending laterally from the incisive papilla and the anterior part of the raphe.
Site:
- The over-hard palate immediately behind the upper anterior teeth.
Function:
- In speech.
- Facilitate the movement of food backwards towards the pharynx Histology:
- The epithelium is keratinized.
- Their core is made of a dense connective tissue layer with fine interwoven fibers.
Question 35. Incisive papilla.
Answer:
- It is formed by dense connective tissue.
- It contains the oral parts of the nasopalatine ducts.
- Ducts are lined by simple or pseudostratified columnar epithelium and surrounded by small, irregular islands of hyaline cartilage.
- Small mucous glands open into the lumen of the ducts.
- Ducts are rich in goblet cells.
Location:
- In the middle just behind the upper central incisors.
Question 36. Macrophages.
Answer:
It is cell,present in the lamina propria. n It is a stellate or fusiform cell.
Histology:
- Smaller and denser nuclei
- Less granular endoplasmic reticulum.
- The cytoplasm contains lysosomes and phagocytic vesicles.
Functions:
- Ingest damaged tissue or foreign material.
- Process it and present it to the lymphocytes.
- Stimulates fibroblast proliferation necessary for repair.
Question 37. Free gingival groove.
Answer:
- It is a dividing line between the free gingiva and the attached gingiva.
- It runs parallel to the margin of the gingiva.
- It is seen as a V-shaped shallow notch.
- It develops at or apical to the bottom of the gingival sulcus.
- Its base is formed by the superior end of the junctional epithelium.
- It is bound on one side by the tooth surface and on the other side by the sulcular epithelium.
Question 38. Membranaperformatica
Answer:
- It separates the enamel organ and dental papilla before the dentin formation
- It determines the morphology of the crown.
Question 39. Hemidesmosomes
Answer:
- Hemidesmosomes attach the cells to the basal lamina
- The lamina propria below the junctional epithelium keeps the epithelial cells of the junctional epithelium immature so that they can develop hemidesmosomes and attach to the tooth
- They then migrate with their attachment being maintained by hemidesmosomes
Function:
- Hemidesmosomes hold the cells to the basal lamina by this, the strength of the attachment is maintained despite migration
Question 40. Gingival group of fibers
Answer:


Leave a Reply