Oral Aspects Of Metabolic Diseases
Question.1.Write short note on pathologic calcification.
Answer. Pathologic calcification is abnormal deposition of the calcium in various tumors and organs of the body.
They are of three types:
1. Dystrophic calcification
2. Metastatic calcifiation
3. Calcinosis
Dystrophic Calcification
- It is a type of pathologic calcifiation in which calcium salts are deposited in the dead or degenerating tissue of the body.
- It is not associated with increased level of serum calcium and is related to change in local environment.
- This is the most frequent type of pathological calcification found in wide variety of tissues.
- In oral cavity dystrophic calcification is found in gingiva,tongue, cheek and pulp.
- One of the most common intraoral dystrophic calcification found in the pulp of the teeth, i.e. “Pulp Stone.”
Read And Learn More: Oral Pathology Question And Answers
Metastatic Calcifiation
- Abnormal deposition of calcium in the tissue due to increase in amount of serum calcium.
- It occurs particularly in diseases like hyperparathyroidism which depletes the bone calcium and causes high level of blood calcium.
- Metastatic calcifiation also occurs in hypervitaminosis D.
In this type of calcification, deposit of calcium occurs in kidney, lung, gastric mucosa and media of blood vessels.
Metabolic Syndrome
Calcinosis
- Abnormal deposition of calcium under the skin is also known as calcinosis.
- There are two forms of calcinosis:
1. Calcinosis circumscripta: It is circumscribed form.
2. Calcinosis universalis: It is generalized form and is associated with scleroderma and dermatomyositis.
Question.2. Write short note on scurvy.
Answer. Scurvy is prolonged deficiency of vitamin C and is characterized by:
- Microvessels having least muscular support.
- Defective synthesis of osteoids.
- Impaired wound healing.
Scurvy Clinical Features
- Lassitude, anorexia, painful limbs, and enlargement of costochondral junction.
- Hair follicle rises above the skin and there is perifollicular hemorrhage.
- Hemorrhage may occur in the joint in the nerve sheath under the nails or conjunctiva.
- Scorbutic child usually assumes the frog-like position.
Scurvy Oral Manifestations
- It occurs chiefly in gingival and periodontal region.
- Interdental and marginal gingiva is bright red, swollen, smooth, shiny surface producing scurvy bud.
- There is presence of typical fetid breath of the patient with fusospirochetal stomatitis.
- In severe cases, hemorrhage and swelling of periodontal ligament membrane occurs followed by loss of bone and loosening of teeth which are exfoliated.
Scurvy Treatment
Vitamin C 250 mg TDS daily is given.
Metabolic Syndrome
Question.3. Write short note on hyperpituitarism.
Answer. It results from hyperfunction of anterior lobe of pituitary gland, most significantly if increases production of growth hormone.
Types
1. Gigantism: If the increase occur before the epiphysis of long bones are closed, gigantism results.
2. Acromegaly: If the increase occur later in the life after epiphysis, closure results in acromegaly.
Oral Manifestations Of Hyperpituitarism
- Teeth in gigantism are proportional to size of jaw and the rest of the body and the root may be longer than the normal.
- Mandibular condylar growth is very important, overgrowth of mandible leads to prognathism.
- Mandible may be of extraordinary proportions creating a major discrepancy between the upper and lower jaw and class III malocclusion.
- The palatal vault is flttned and tongue increases in the size and causes crenation on its lateral border.
- In edentulous patients, enlargement of alveolus may prevent the comfortable fi of complete denture.
- The lip becomes thick and Negroid.
Hyperpituitarism Treatment
- Transsphenoidal surgery should be done.
- Octreotide lowers the growth hormone.
- Dopamine antagonists are used.
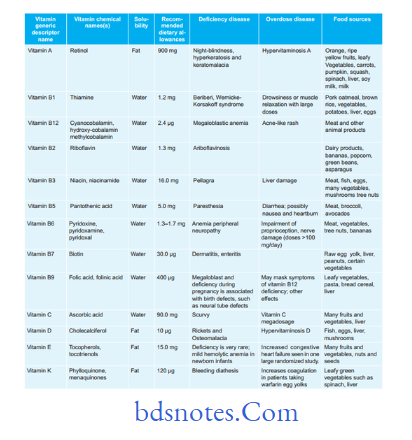
Question.4. Write short note on vitamins.
Answer. Each vitamin is typically used in multiple reactions, and,therefore, most have multiple functions.
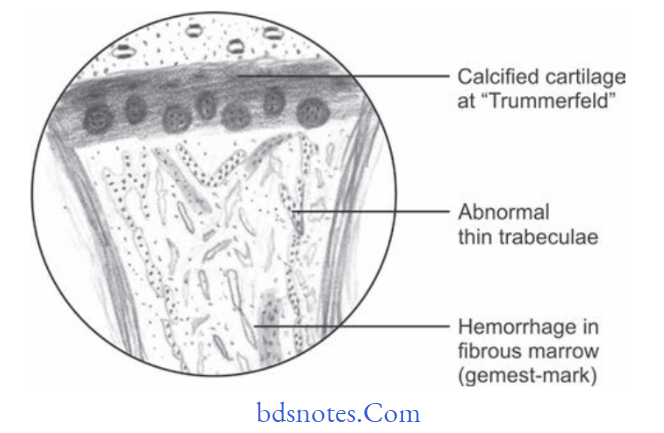
Question.5. Describe histologic features with diagram of scurvy.
Answer. Following are the histologic features of scurvy:
- In scurvy osteoblasts fail to form osteoid on spicules of calcified cartilage matrix.
- Cartilage cells of epiphyseal plate proliferate normally and salts are deposited in matrix between column of cartilage cells.
- A wide zone of calcified but non-ossified matrix known as scorbutic lattice develops in metaphysis.
- As scorbutic lattce increases in width more fragile zone develops which leads to complete fracture of spicules with separation and deformity of cartilage shaft junction.
Fracture of calcified matrix material lead to the classic picture of scurvy known as Trummerfeld zone. - Area beneath Trummerfeld zone is free of hematopoietic cells and is formed of connective tissue cells known as Gemestmark.
Question.6. Write short note on hyperparathyroidism.
Answer. Hyperparathyroidism is an endocrine disorder in which there is secretion of excess of circulating parathyroid hormone.
- Excess of parathyroid hormone stimulate osteoclast and mobilize calcium from bone which causes hypercalcemia.
Types Of Hyperparathyroidism
- Primary hyperparathyroidism: In this excess secretion of parathyroid hormone is present because of parathyroid adenomas.
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism: It occurs when parathyroid continuously produced in response to low levels of serum calcium.
This is related to chronic renal diseases. Kidney utilizes vitamin D which is important for calcium absorption from gut.
So in patient with chronic renal disease active form of vitamin D is not produced and there is less calcium absorption from gut which results in low serum calcium levels. - Tertiary hyperparathyroidism: As secondary hyperparathyroidism remains for longer time it is known as tertiary hyperparathyroidism.
Hyperparathyroidism Clinical Features
- It occurs mainly from 3rd to 6th decade of life.
- Female predilection is seen with male to female ratio of 1:3
- Patient has classic triad of kidney stones, resorption of bone and duodenal ulcers.
- Patient usually complains of back pain and blood in urination.
- Patient also suffrs from emotional unstability.
- Presence of gastrointestinal problems is present, i.e.nausea, vomiting, anorexia.
- In severe cases, there is presence of headache, bone pain, pathological fractures and comma.
Hyperparathyroidism Oral Lesions
- A tumor-like swelling is present either intraorally or extraorally which is known as Brown’s tumor.
- Mandible is affected more commonly.
- Presence of jaw bone fractures is present.
- There is presence of drifting, loosening, and exfoliation of the teeth.
- Fetid odor or halitosis is present.
- Malocclusion is present because of the drifting and spacing of the teeth.
Histopathology
- There is presence of osteoclastic resorption of multiple boney trabeculae and there is also formation of new bone by osteoblast cells.
- Areas of excessive hemorrhage and hemosiderin pigmentation are present.
- Multiple multinucleated osteoclast type of giant cells are often seen in tumors.
- At places, bone marrow is replaced by fibrous connective tissue.
- As disease progresses osteoclastomas develop which are characterized by masses of fibroblasts growing in loose syncytium.
Histopathology Treatment
- Administration of vitamin D and dietary phosphate supplements.
- Parathyroidectomy should be done if patient does not respond to the medicinal treatment.

Leave a Reply