Opioid Analgesics
Question 1. Write A Short Note On Opioid Analgesics.
Or
Write A Short Note On Opioids.
Or
Write In Brief About General Pharmacological Effects Of Opioid Analgesics.
Answer:
The opioid term includes all naturally occurring, synthetic, and semisynthetic drugs which have morphine-like actions and relieves pain without affecting consciousness.
- Opioid Analgesics Classifiation
- Natural opium alkaloid: Morphine and codeine
- Semisynthetic opiates: diacetylmorphine and pholcodine
- Synthetic opioids: Pethidine, fentanyl, methadone tramadol, and dextropropoxyphene.
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question And Answers
Question 2. Describe The Actions And Uses Of Morphine. In What Respect Pentazocine Diffrs From Morphine?
Answer:
Morphine Pharmacological Actions
1. CNS
Morphine produces two types of pharmacological actions, i.e. CNS depressant actions and CNS stimulant actions.
Depressant Actions
The following are the CNS depressant actions:
- Analgesia: This is mediated via the μ receptors at both spinal and supraspinal sites. At the spinal level, the drug reduces the release of neurotransmitters in substantia gelatinosa of the dorsal horn and inhibits the excitation transmitter released from fiers carrying main impulses.
- Sedation: Morphine produces euphoria, sedation, indifference to surroundings, and drowsiness. At higher doses, it induces sleep and still higher causes coma.
- Respiratory system: It depresses the respiratory center based on the dosage given. Both rates of respiration and tidal volume get decrease. If drug poisoning occurs, death is due to respiratory failure. It also causes a decrease in cough by acting on the cough center in the medulla.
- Mood and subjective effects: These effects are also known as euphoria. Morphine leads to loss of apprehension, feelings of detachment, lack of initiation, mental clouding, and inability to concentrate.
- Temperature regulating center: Morphine leads to the depression of the cough regulating center.
- Vasomotor center: On giving high doses vasomotor center get depressed at high doses and causes a fall in blood pressure.
Stimulating Actions
- Nausea and vomiting: Morphine stimulates CTZ in the medulla which leads to nausea and vomiting.
- Miosis: By the stimulating action of morphine on the Edinger Westphal nucleus of the third cranial nerve morphine leads to constriction of the pupil and decreases intraocular tension.
- Vagal center: Morphine stimulates the vagal center and leads to bradycardia.
2. CVS
Morphine leads to three actions viz depression of vasomotor center; histamine release and act directly on blood vessels which leads to vasodilatation and this causes a decrease in blood pressure.
3. GIT
Constipation occurs due to:
- Increase muscle tone and decrease propulsive movements of the intestine.
- Spasms of pyloric ileocaecal and anal sphincters
- Decrease gastrointestinal secretions which cause a decrease in the transfer of water and electrolytes from mucosa to lumen.
4. Neuroendocrine
- The influence of the hypothalamus on the pituitary is reduced due to which follicular stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, and ACTH levels decreased while prolactin and growth hormone levels get increased.
- Morphine can also lead to the release of ADH and decreases urine volume.
5. Biliary Tract
Morphine raises the intrabiliary pressure by increasing the tone of the sphincter of Oddi.
6. Action On Other Smooth Muscles
- In the urinary bladder, morphine raises the tone of the urethral sphincter which can lead to retention of urine.
- In the uterus, it can prolong labor.
- Morphine causes the release of histamine which causes bronchoconstriction.
7. Autonomic Nervous System
Morphine leads to mild hyperglycemia as it stimulates the central sympathetic system.
Morphine Uses
- As an analgesic, it provides symptomatic relief and is indicated in severe pain of any type, i.e. myocardial infarction, fractures of the mandible and long bones, burns, terminal stage of malignancy, postoperative pain, etc.
- Preanesthetic medication: Morphine in its dosages of 10 mg IM reduces the anxiety and apprehension of surgery. It causes preoperative as well as postoperative analgesia and leads to smooth induction.
- In acute left ventricular failure IV morphine decreases breathlessness by reducing preload on the heart due to peripheral vasodilatation; shifting blood from pulmonary to systemic circulation; decreases anxiety, fear, and apprehension related to illness.
- Morphine can also be used as a sedative.
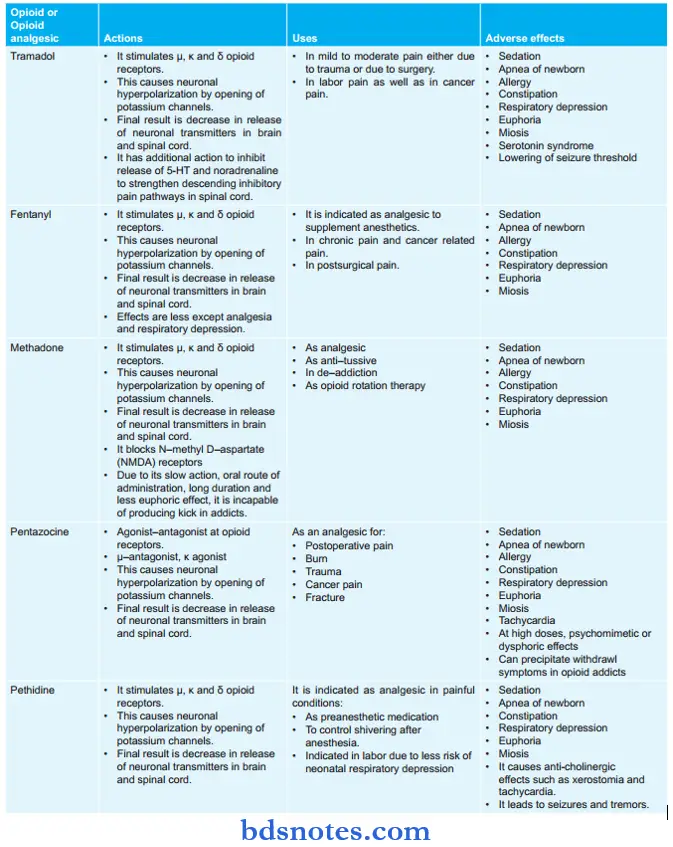
Differences Between Pentazocine And Morphine Are

Question 3. Write A Note On Pethidine.
Answer:
Pethidine is an opioid analgesic.
Pethidine Mechanism Of Action
- It stimulates µ, κ, and δ opioid receptors.
- This causes neuronal hyperpolarization by the opening of potassium channels.
- The final result is a decrease in the release of neuronal transmitters in the brain and spinal cord.
Pethidine Uses
- It is indicated as an analgesic in painful conditions.
- As pre-anesthetic medication
- To control shivering after anesthesia.
- Indicated in labor due to less risk of neonatal respiratory depression.
Pethidine Adverse Effects
- Sedation
- Apnea of newborn
- Constipation
- Respiratory depression
- Euphoria
- Miosis
- It causes anticholinergic effects such as xerostomia and tachycardia.
- It leads to seizures and tremors.
Question 4. Give A Description Of Pentazocin.
Answer:
Pentazocine is the first agonist-antagonist to be used as an antagonist.
Pentazocine Mechanism of Action
- Agonist–antagonist at opioid receptors.
- µ – antagonist, κ agonist
- This causes neuronal hyperpolarization by the opening of potassium channels.
- The final result is a decrease in the release of neuronal transmitters in the brain and spinal cord.
Pentazocine Uses
- As an analgesic for:
- Postoperative pain
- Burn
- Trauma
- Cancer pain
- Fracture.
Pentazocine Adverse Effects
- Sedation
- Apnea of newborn
- Constipation
- Respiratory depression
- Euphoria
- Miosis
- Tachycardia
- At high doses, psychomimetic or dysphoric effects i.e. euphoria, hallucinations, and nightmares.
- Can precipitate withdrawal symptoms in opioid addicts.
Pentazocin Contraindications
In hypertensive patients and in patients with ischemic heart disease.
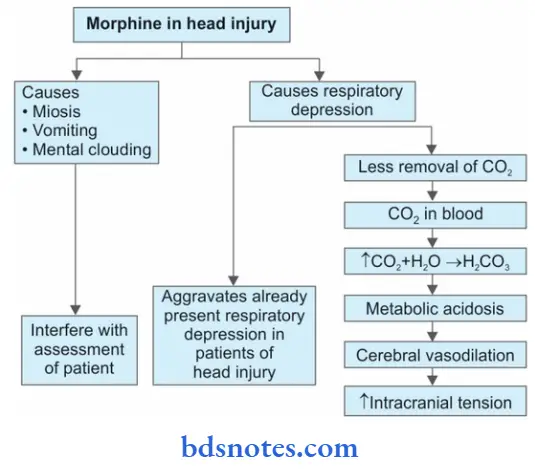
Question 5. Explain The Pharmacological Basis For Morphine Is Contraindicated In Head Injury Cases.
Answer:
Morphine is contraindicated in head injury because of the following reasons:
- Morphine produces effects like miosis, vomiting, and mental clouding. These are important signs in following up the clinical course of a patient with a head injury. It may lead to interference with the assessment and prognosis of a patient with a head injury.
- It can cause severe respiratory depression. It reduces the hypercapnic drive (stimulation of the respiratory centers by increased carbon dioxide levels) while having minimal effect on the hypoxic drive. It may exacerbate the already present respiratory depression in a patient with a head injury.
- Due to the respiratory depression action of morphine, it leads to the retention of carbon dioxide. This is followed by an increase in the cerebral blood flow which causes increased intracranial tension. The latter action is harmful in patients with head injuries.
Question 6. Write Short Note On Therapeutic Uses And Contraindications Of Morphine.
Answer:
Therapeutic Uses Of Morphine
- As an analgesic, it provides symptomatic relief and is indicated in severe pain of any type, i.e. myocardial infarction, fractures of the mandible and long bones, burns, terminal stage of malignancy, postoperative pain, etc.
- Preanesthetic medication: Morphine in its dosages of 10 mg IM reduces the anxiety and apprehension of surgery. It causes preoperative as well as postoperative analgesia and leads to smooth induction.
- In acute left ventricular failure IV morphine decreases breathlessness by reducing preload on the heart due to peripheral vasodilatation; shifting blood from pulmonary to systemic circulation; decreases anxiety, fear, and apprehension related to illness.
- Morphine can also be used as a sedative.
Morphine Contraindications
- Morphine can precipitate bronchial asthma
- Morphine is contraindicated in cases of head injury because:
- By retaining carbon dioxide it increases the intracranial tension.
- Therapeutic doses cause marked respiratory depression in these patients.
- It causes vomiting, miosis, and altered mental state which interfere with assessment of progress in head injury cases.
- Hypotensive states and hypovolemia exaggerate falls in BP due to morphine.
- In elderly males chances of urinary retention is high.
- Hypothyroidism, liver, and kidney disease patients are more sensitive to morphine.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease should be avoided as it has respiratory depressant action and this disease have a low respiratory reserve.
- It should not be given in undiagnosed abdominal pain as it has a spasmogenic effect which can aggravate the pain.
Question 7. Classify Analgesics. Write The Mechanism Of Action, Adverse Effects, And Therapeutic Uses Of Opioids.
Or
Classify Opioid Analgesics. Describe the Important Uses And Adverse Effects Of Opioid Analgesics.
Answer:
Classifiation Of Analgesics
Generally, there are two types of analgesics, i.e. opioids, and NSAIDs.
Oploid Analgesics
- Natural opium alkaloid: Morphine and codeine
- Semisynthetic opiates: Diacetyl morphine and pool codeine
- Synthetic opioids: Pethidine, tramadol, fentanyl, methadone.
Oploid Analgesics NSAIDs
- Non-selective COX inhibitors:
- Salicylates: Aspirin
- Propionic acid derivatives: I buprofen, ketoprofen, naproxin
- Mephenamic acid
- Diclofenac
- Piroxicam, tenoxicam
- Ketorolac
- Indomethacin
- Phenyl butazone.
- Preferential COX-2 inhibitors: Nimesulide, meloxicam, nabumetone
- Selective COX-2 inhibitors: Celecoxib, rofecoxib, valdecoxib, etoricoxib
- Analgesic, antipyretic with poor anti-inflammatory action:
- Paracetamol (acetaminophen)
- Metamizol, propiphenazone
- Nefopam.
Mechanism Of Action Of Opioids
- They stimulate µ, κ, and δ opioid receptors.
- This causes neuronal hyperpolarization by the opening of potassium channels.
- The final result is a decrease in the release of neuronal transmitters in the brain and spinal cord.
Opioid Analgesics Therapeutic Uses
- As analgesic: Morphine and other opioids are potent and efficacious analgesics, so they are indicated in moderate to severe painful conditions, such as acute myocardial infarction, burns, pulmonary embolism, fracture of mandible and long bones, bullet wounds, etc. Opioids are also indicated in severe pain in terminal stages of cancer. In renal and biliary colic, atropine is used with morphine to counteract the spasmogenic effect of morphine. Opioids are the preferred analgesics in severe painful conditions.
- Preanesthetic medication: Opioids such as morphine and pethidine are used about half an hour before anesthesia as their sedative, analgesic and euphoric effects reduce the dose of anesthetic required.
- Acute pulmonary edema: Intravenous morphine relieves breathlessness associated with acute left ventricular failure.
- Postanesthetic shivering: Pethidine is very effective in eliminating post-anesthetic shivering.
- Cough: Codeine and dextromethorphan are indicated for suppressing dry cough.
- Diarrhea: Synthetic opioids such as loperamide and diphenoxylate are used for symptomatic treatment of diarrhea.
- Neurolept analgesia and anesthesia: Fentanyl is used.
- Deaddiction: Methadone is used as substitution therapy in addicts.
Opioid Analgesics Adverse Effects
- Common adverse effects of opioids are:
- Sedation
- Apnea of newborn
- Allergy
- Constipation
- Respiratory depression
- Euphoria
- Miosis
- Pethidine can lead to tachycardia so it is avoided in myocardial infarction. Pethidine can also precipitate seizures.
- Pentazocine at high doses leads to psychomimetic or dysphoric effects. It also precipitates withdrawal symptoms in opioid addicts.
- Tramadol leads to serotonin syndrome and lowering of seizure threshold.
- Codeine leads to constipation and sedation.
- Buprenorphine shows postural hypotension and less constipation.
- Pentazocine leads to sympathetic stimulation and increases heart rate and blood pressure.
- Butorphanol leads to cardiac stimulation.
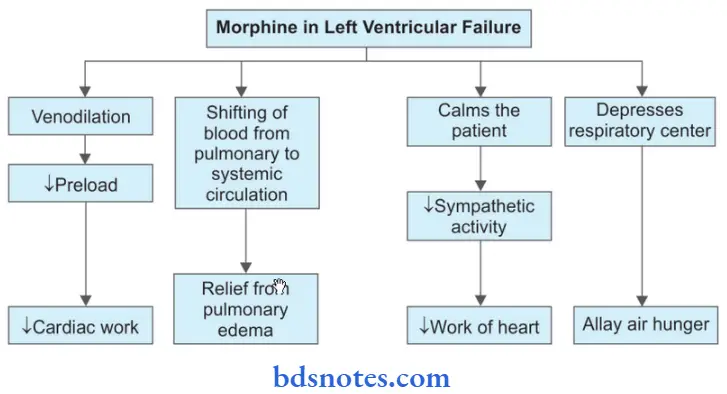
Question 8. Write A Short Note On Morphine In Left Ventricular Failure.
Answer:
Morphine is administered in patients having left failure because of the following reasons:
- On intravenous administration, morphine causes peripheral pooling of the blood and thereby reduces the venous return. This reduction in the preload is
beneficial in a failing heart as it reduces the work of the heart. - Morphine causes a shift of blood from the pulmonary to the systemic circulation. This relieves pulmonary congestion and edema thereby affording
dramatic symptomatic relief for the patient. - It calms the patients which decreases the sympathetic stimulation and further benefits the patient by decreasing cardiac work.
- It causes a depression of the respiratory center which causes a reduction in the air hunger associated with left ventricular failure.
Question 9. Write About The Mechanism Of Action, Uses, And Adverse Effects Of Morphine.
Answer:
Morphine is an opioid analgesic
Morphine Mechanism Of Action
- It stimulates µ, κ, and δ opioid receptors.
- This causes neuronal hyperpolarization by the opening of potassium channels.
- The final result is a decrease in the release of neuronal transmitters in the brain and spinal cord.
Morphine Uses
- As an analgesic, it provides symptomatic relief and is indicated in severe pain of any type, i.e. myocardial infarction, fractures of the mandible and long bones, burns, terminal stage of malignancy, postoperative pain, etc.
- Preanesthetic medication: Morphine in its dosages of 10 mg IM reduces the anxiety and apprehension of surgery. It causes preoperative as well as postoperative analgesia and leads to smooth induction.
- In acute left ventricular failure IV morphine decreases breathlessness by reducing preload on the heart due to peripheral vasodilatation; shifting blood from pulmonary to systemic circulation; decreases anxiety, fear, and apprehension related to illness.
- Morphine can also be used as a sedative.
Morphine Adverse Effects
- Sedation
- Apnea of newborn
- Allergy
- Constipation
- Respiratory depression
- Euphoria
- Miosis
- It causes the release of histamine.

Leave a Reply