Nucleic Acids And Nucleotides
Question 1. DNA&RNA
Answer:
DNA:
- It is deoxyribonucleic acid
- It was discovered in 1869 by Johann Friedrich Miescher
- It contains
- Bases- adenine, guanine, cytosine & thymine
- Sugars- D-deoxyribose
- It is composed of monomeric units namely deoxy adenylate, deoxy guanylate, deoxycytidylate & deoxy thymidylate
- It has a right-handed double helix structure
- The transition between different helical forms of DNA plays a significant role in regulating gene expression
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
RNA:
- It is ribonucleic acid
- It contains
- Bases- adenine, guanine, cytosine & uracil
- Sugars- D-ribose
- It is usually a single-stranded polynucleotide
Types:
- Messenger RNA-5-10%
- Transfer RNA- 10-20%
- Ribosomal RNA- 50-80%
- RNA is synthesized from DNA
- They are involved in the process of protein biosynthesis
Question 2. Structure & functions of tRNA
Answer:
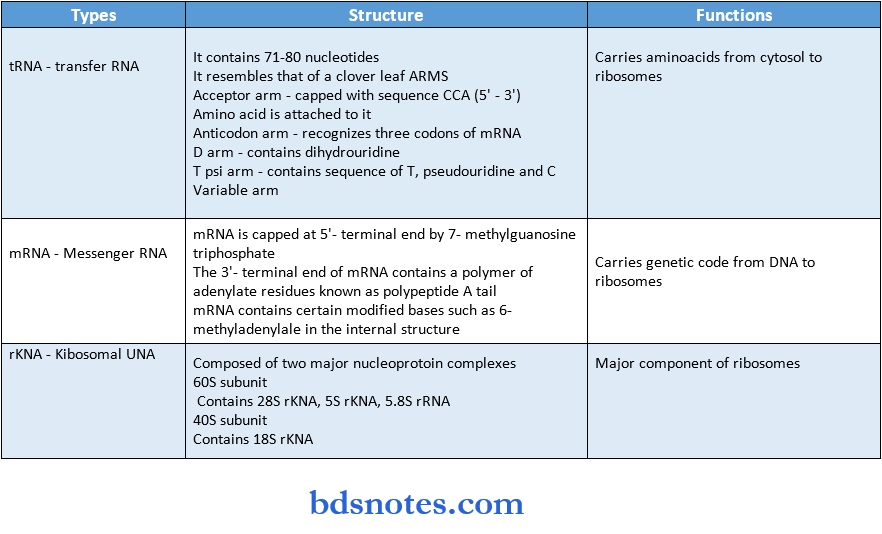
Structure:
- It contains 71-80 nucleotides
- It resembles a cloverleaf
- It contains four arms
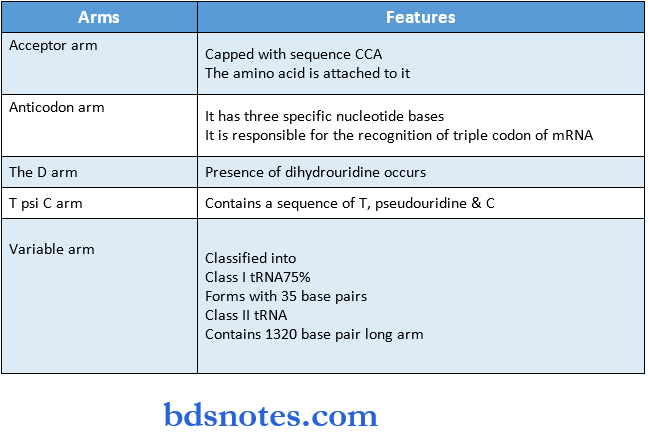
Functions:
- Carries amino acids from the cytosol to ribosomes
Question 3. Ribonucleic acid
Answer:
- It is ribonucleic acid.
- It contains
- Bases- adenine, guanine, cytosine & uracil
- Sugars- D-ribose
- It is usually a single-stranded polynucleotide
- RNA is synthesized from DNA
- They are involved in the process of protein biosynthesis
Types:
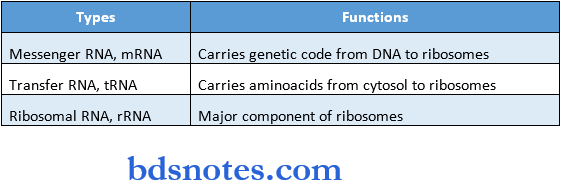
Question 4. Structure & functions of DNA
Answer:
Structure:
- It is a right-handed double helix
- The width of a double helix is 20 Armstrong
- Each turn of the helix is 34 Armstrong
- Helix consists of two polydeoxyribonucleotide chains twisted around each other on a common axis
- The two strands are anti-parallel
- Each strand has a hydrophilic deoxyribose phosphate on the outside while the hydrophobic bases are inside
- The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds
- Hydrogen bonds are formed between a purine & pyrimidine only
- The two dinucleotide chains are not identical but complementary to each other
- Genetic information resides on the template strand or sense strand
- Opposite strand is antisense strand
Functions:
- DNA is the chemical basis of hereditary
- It may be regarded as the reserve bank of genetic information
- It is exclusively responsible for maintaining the identity of different species of organisms
- Every aspect of cellular function is under the control of DNA
- It is organized into genes which are THE fundamental units of genetic information
- These genes control protein synthesis through the mediation of RNA
Question 5. Nucleotides and their Functions
Answer:
- Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate
- They are monomeric units in the nucleic acid
Functions:
- They are building blocks in DNA & RNA str culture
- They are structural components of several coenzymes of the vitamin B complex
- They serve as carriers of high-energy intermediates in the biosynthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
- They are involved in the energy reactions of the cell
- They control several metabolic reactions by their action as allosteric regulators
- Cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP are the second messengers in hormonal function
Question 6. Types of RNA
Answer:
Types of RNA:
Question 7. Watson and Crick’s model of DNA structure
Answer:
Double Helical Structure of DNA:
- Proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953
Features:
- It is a right-handed double helix
- Consists of two polydeoxyribonucleotide chains twisted around each other
- The bases present are adenine
- (A), Guanine(G), Cylosine(C) and Thymine(T)
- Two strands are antiparallel, one running from 5′ to 3′ and the other vice versa Width is 20 A°
- Each turn of helix is 34 A° with 10 pairs of nucleotides
Two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds - The A-T pair has 2 hydrogen bonds, G-C pair has 3 hydrogen bonds
Content of adenine equals thymine and guanine equals cytosine – Char gaff’s rule
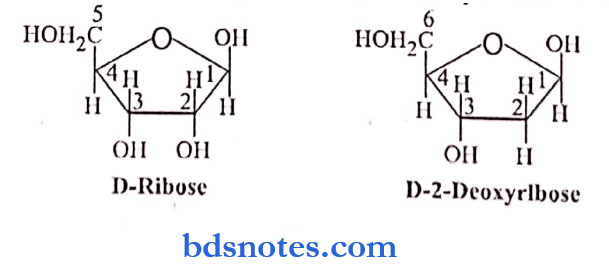
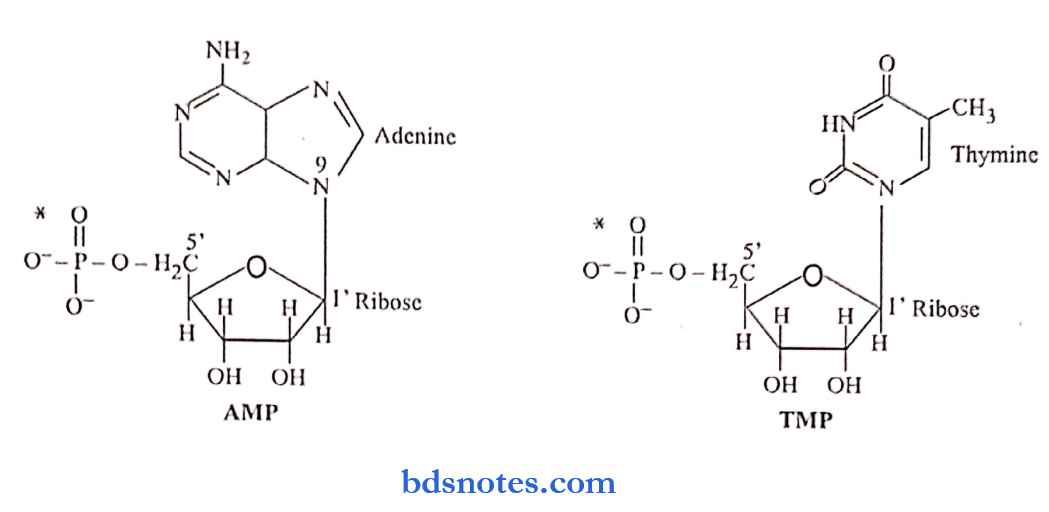
Question 8. What are nucleosides & nucleotides? Give examples of each
Answer:
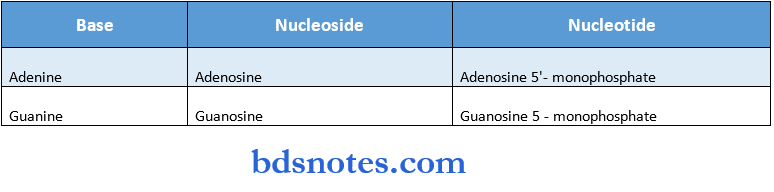
Nucleotide:
- They are composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar & a phosphate
- They are monomeric units in the nucleic acid
Nucleoside:
- Nucleoside is a nucleotide without esterified phosphate groups
- Examples
Question 9. Name different types of RNA & their functions
Answer:
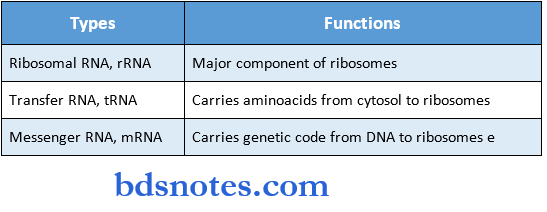
Question 10. Structures & functions of mRNA
Answer:
Structure:
- mRNA is capped at the 5′- terminal end by 7-methylguanosine triphosphate
- This helps to prevent the hydrolysis of mRNA by 5′-exonucleases
- The 3-terminal end of mRNA contains a polymer of adenylate residues known as polypeptide A tail
- This provides stability to mRNA
- mRNA contains certain modified bases such as 6-methyl adenylate in the internal structure
Functions:
- Carries genetic code from DNA to ribosomes
Question 11. Base pairing & its importance for the function & structure of DNA
Answer:
- Base pairing in DNA structure occurs between purine & pyrimidine
- If two purines face each other, they would not fit into allowable spaces
- Two pyrimidines would be too far for hydrogen bonds
Thus, base pairing in DNA structure occurs only between purines & pyrimidines - It occurs between
- Adenine and thymine or uracil
- Two hydrogen bonds occur between them
- Guanine and cytosine
- Three hydrogen bonds occur between them
- Adenine and thymine or uracil
Question 12. Describe the features of genetic code (or) Characteristics of genetic code
Answer:
1. Universality
- The same codons are used to code for the same amino acids in all the living organisms
2. Specificity
- A particular codon always codes for the same amino acids
3. Non-overlapping
- Genetic code is read from a fixed point as a continuous base sequence
4. Degenerate
- Most of amino acids have more than one codon
- This is because there are 61 codons for 20 amino acids
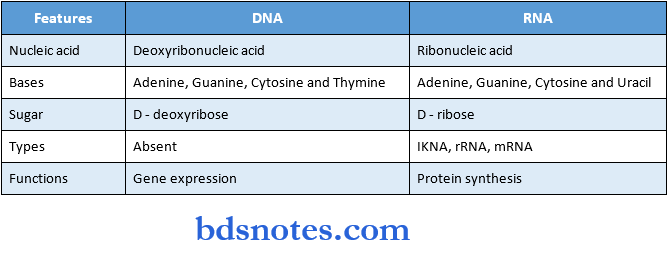
Question 13. Differences between DNA &. RNA.
Answer:
Question 14. Gout
Answer:
- Gout is a metabolic disorder associated with the overproduction of uric acid
- Due to excess uric acid, forms crystals of sodium really
- This gets deposited in the soft tissues, particularly in joints resulting in inflammation of joints and painful gouty arthritis
Types:
1. Primary gout
- It is an inborn error of metabolism due to the overproduction of uric acid
2. Secondary gout
- Occurs due to various diseases like various cancers, psoriasis, and increased tissue breakdown.
Treatment:
- Allopurinol is a drug of choice
- It is oxidized to alloxanthine by xanthine oxidase
- Alloxanthine is an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase
- Thus allopurinol acts by suicide inhibition mechanism

Leave a Reply