Question 1. Describe the Maxillary Nerve under the following headings. (or) Maxillary air sinus
- Origin, Course, Branches, Distribution, Applied anatomy
Maxillary Nerve Origin:
- It arises from the trigeminal ganglion
Maxillary Nerve Course:
- It runs forwards in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus below the ophthalmic nerve
- Leaves the middle cranial fossa by passing through the foramen rotundum
- It crosses the upper part of Pterygopalatine fossa
- Next it continues as the infraorbital nerve
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
Branches and their distribution:
1. In middle cranial fossa:
- Middle meningeal nerve to supply dura
2. In pterygopalatine fossa:
- Zygomatic nerve
- Passes anteriorly & laterally
- Divides into
- Zygomaticofacial nerve- Pierces the orbicularis oris & supplies prominence of cheek
- Zygomaticotemporal nerve
- Enters temporal fossa & supplies skin over the anterior temporal fossa region
- Pterygopalatine nerve: Branches:
- Orbital branches- By means of inferior orbital fissure, supplies periosteum of orbit, posterior ethamoid cells & sphenoid sinus
- Nasal branches: Divides into posterior superior lateral & medial or septal branches
- Palatine branches: Descends in pterygopalatine canal, divides into
- Greater or anterior palatine- supply hard palate
- Middle palatine-Sensory to soft palate
- Posterior palatine- Supplies mucous membrane to tonsil
3. Posterior superior alveolar nerve:
- Divides into many branches & descends downward to supply maxillary molars & their supporting gingivae
4. Branches in infraorbital groove & canal:
- Middle superior alveolar nerve:
- Supplies posterior part of maxillary sinus
- Descends downward
- Divides & supplies maxillary bicuspids
- Anterior superior alveolar nerve:
- Descend & divides
- Supplies maxillary anteriors
5. Terminal branches on face:
- Inferior palpebral- Supplies lower eyelid
- External or lateral nasal- Supplies side of nose
- Superior labial- Supplies upper lip
Maxillary Nerve Applied Anatomy:
- It carries the afferent limb fibres of the sneeze reflex
- Trigeminal neuralgia affecting maxillary nerve produces symptoms in the area of its distribution
- The nerve can be anaesthesized at the foramen rotundum
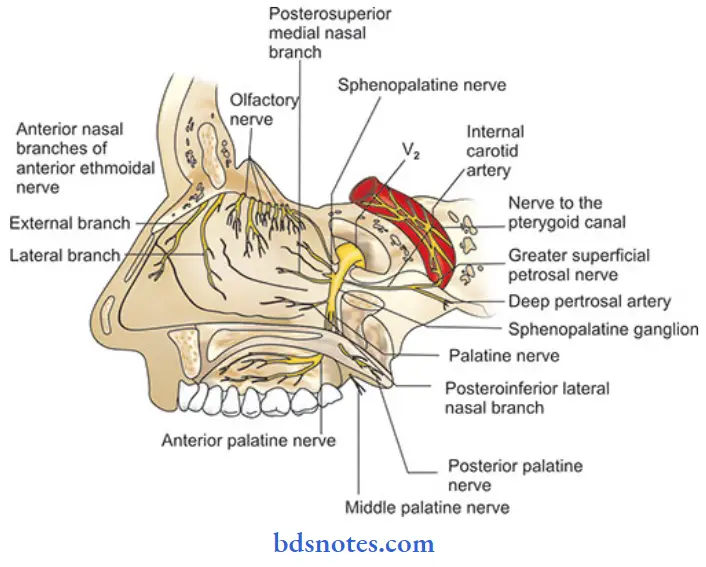
Question 2. Describe bone formation, features, opening, blood supply & nerve supply of lateral wall of nose (or) Lateral wall of nasal cavity. (or) Openings related to Lateral Wall of Nasal Cavity.
Answer:
Lateral wall of nose:
Lateral Wall of Nasal Cavity Bone formation:
- It is formed by following bones
- Nasal bone
- Frontal process of maxilla
- Lacrimal bone
- Labyrinth of ethamoid with superior & middle conchae
- Inferior nasal concha
- Perpendicular plate of palatine bone
- Medial pterygoid plate
Lateral Wall of Nasal Cavity Features:
- Bony wall is covered by mucous membrane & projects as three nasal conchae
- Inferior nasal concha
- It is separate bone, present horizontally
- Middle concha
- It is part of ethmoid labyrinth
- Superior concha
- It is smallest concha situated just above the posterior part of middle concha
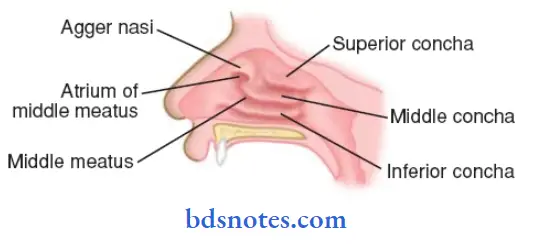
- The meatuses of the nose are passages beneath the overhariging conchae
- There are three meatuses
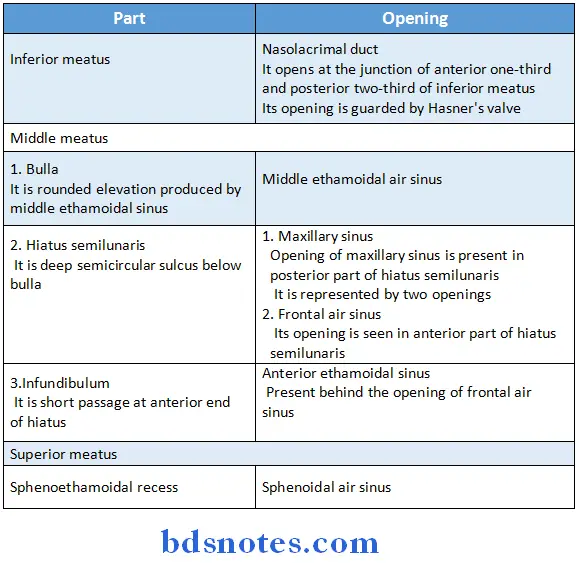
- Inferior meatus
- Lies underneath the inferior concha
- Middle meatus
- Lies beneath middle concha
- It presents
- Ethamoidal bulla
- Hiatus semilunaris
- Infundibulum
- Superior meatus
- Present below superior concha
- Area above superior concha is called sphenoethamoidal recess
- Inferior meatus
Lateral Wall of Nasal Cavity Openings:
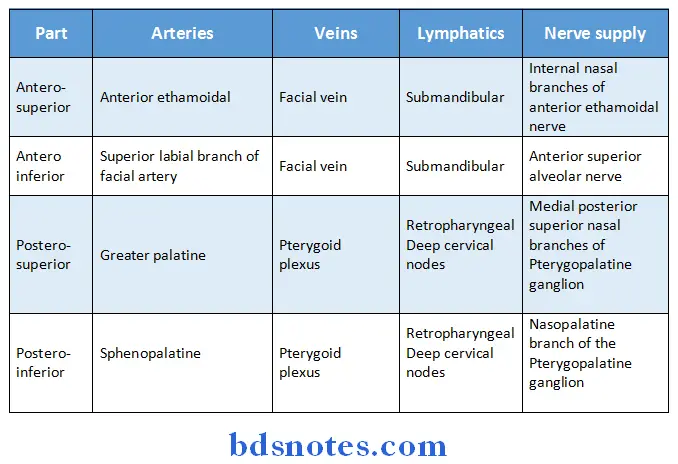
Lateral Wall of Nasal Cavity Blood supply & nerve supply:
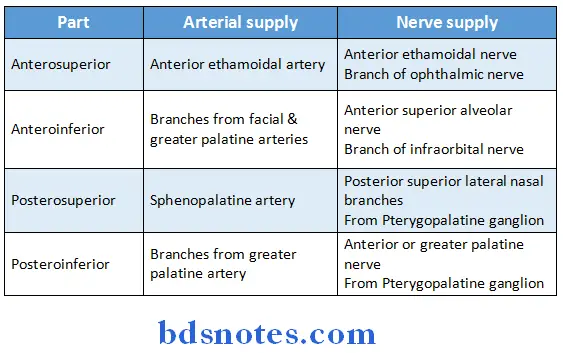
Nerve supply:
- General sensory nerves are from trigeminal nerve
- Special sensory nerves are olfactory nerves
Venous drainage:
- Anteriorly-drains into facial vein
- Posteriorly- drains into pharyngeal plexus
- Middle part- drains into pterygoid plexus of veins
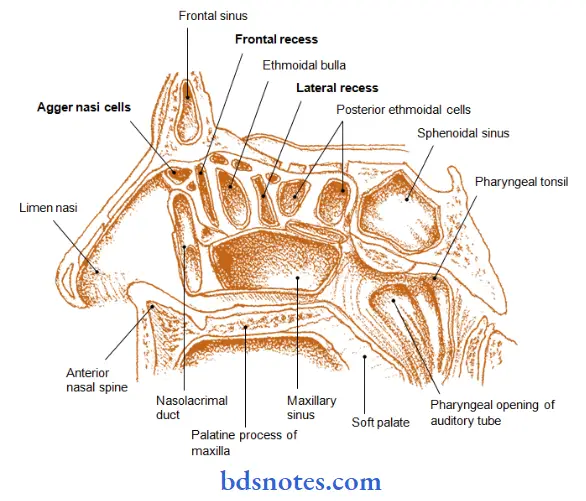
Question 3. Describe Maxillary Air Sinus & its relations
Answer:
Maxillary Sinus:
- It is largest of all sinuses
- It lies in the body of maxilla
Maxillary Air Sinus Size:
- Height-3.5 cm
- Width-2.5 cm
- Anteroposterior depth- 3.5 cm
Maxillary Air Sinus Boundaries:
- It is pyramidal in shape
- Base-directed medially towards lateral wall of the nose
- Apex-Directed laterally in the zygomatic process of the maxilla
- Roof- formed by Floor of the orbit
- Floor- Formed by alveolar process of maxilla
Maxillary Air Sinus Opening:
- It opens into middle meatus of nose in the lower part of the hiatus semilunaris
- A second opening is present at the posterior end of hiatus
- This opening is reduced in intact skull as it is overlapped by the following.
-
- Uncinate process of the ethamoid- from above
- Ethamoidal process of inferior nasal concha- from below
- Perpendicular plate of palatine bone- from behind
- Descending process of the lacrimal bone- from front
Maxillary Air Sinus Relations:
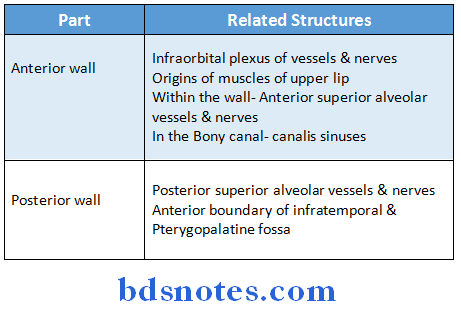
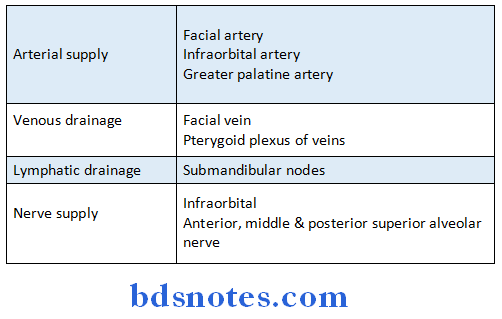
Maxillary Air Sinus Blood Supply:
Arterial Supply:
- Facial artery
- Infraorbital artery
- Greater palatine artery
Maxillary Air Sinus Venous Drainage:
- Facial vein
- Pterygoid plexus of veins
Maxillary Air Sinus Nerve Supply:
- Infraorbital nerve
- Anterior, middle & posterior superior alveolar nerve
Maxillary Air Sinus Lymphatic Drainage:
- Into Submandibular lymph nodes
Question 4. Describe gross anatomy of nasal septum. (or) Describe nasal septum. Give its blood supply, nerve supply, lymphatic drainage & applied anatomy (or) Nerve supply of septum of nose (or) Nasal septum
Answer:
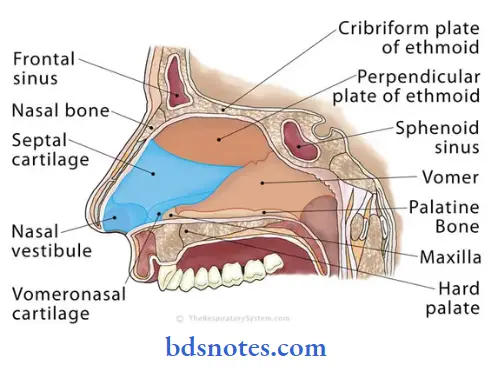
- It is a median osseocartilagenous partition between the two halves of the nasal cavity
Nasal Septum Formation:
- It is partly formed by bone & partly by cartilage
-
- Bony part
- It is formed by
- Perpendicular plate of ethmoid
- Vomer
- Accessory bones like
- Nasal spine of frontal bone
- Sphenoidal crest & rostrum
- Palatine processes of maxillae & horizontal parts of palatine bone
- It is formed by
- Cartilages are formed by
- Septal cartilage
- Septal process of lower nasal cartilage
- Vomeronasal cartilage
- Bony part
Nasal Septum Blood supply, nerve supply & lymphatic drainage:
- General sensory nerves arises from trigeminal nerve
- Special sensory nerves are olfactory nerves which are confined to the upper part of olfactory area
Nasal Septum Applied anatomy:
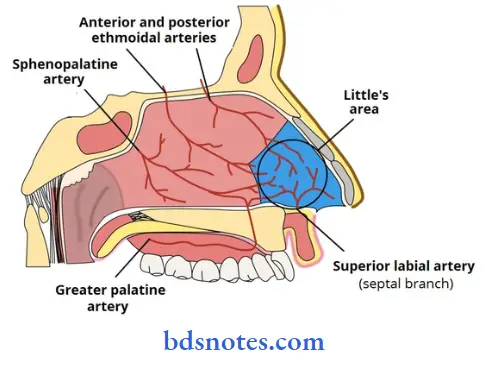
Little’s Area:
- It is common site of epitaxis
- It is an area of formation of large capillary network called the Kiesselbach’s plexus
- It is formed by anastomosis of five arteries
-
- Sphenopalatine artery
- Superior labial branch of facial artery
- Anterior ethmoidal artery
- Greater palatine artery
- Nasal branches of facial artery
- Pathological deviation of the nasal septum causes repeated attacks of common cold, allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, etc.
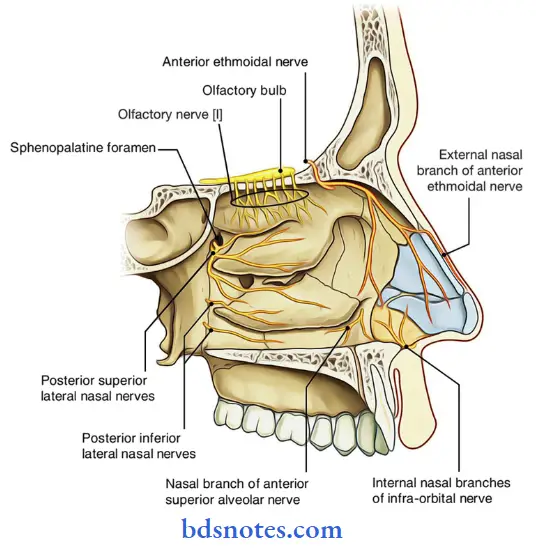
Question 5. Describe the lateral wall of Nasal Cavity under following headings:
- Parts
- Openings
- Blood supply
- Nerve supply
Answer:
Nasal Cavity Parts:
- Lateral wall of nasal cavity is divided into three parts
- Anterior part- vestibule
- Middle part- atrium of the middle meatus
- Posterior part-containing conchae
Nasal Cavity Openings:
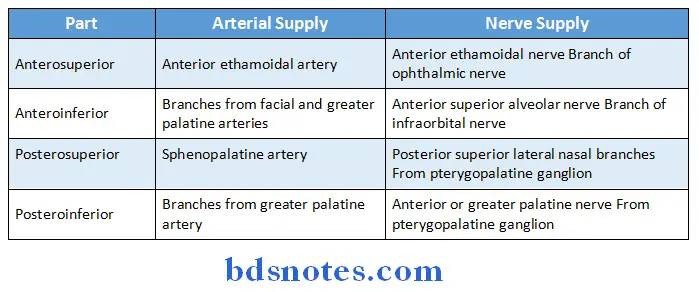
Nasal Cavity Nerve supply:
- General sensory nerves are from trigeminal nerve
- Special sensory nerves are olfactory nerves
Nasal Cavity Venous drainage:
- Anteriorly drains into facial vein
- Middle part drains into pterygoid plexus of veins
- Posteriorly drains into pharyngeal plexus
Question 6. Nasal septum
Answer:
Nasal septum Formation:
- It is partly formed by bone & partly by cartilage
1. Bony part:
-
-
- It is formed by
- Perpendicular plate of ethmoid
- Vomer
- Accessory bones like
- Nasal spine of frontal bone
- Sphenoidal crest & rostrum
- Palatine processes of maxillae & horizontal parts of palatine bone
- It is formed by
-
2. Cartilages are formed by:
- Septal cartilage
- Septal process of lower nasal cartilage
- Vomeronasal cartilage
- General sensory nerves arises from trigeminal nerve
- Special sensory nerves are olfactory nerves which are confined to the upper part of olfactory area
Question 7. Give boundaries, relations & applied anatomy of sphenoidal air sinus
Answer:
- It is a paired sinus
Sphenoidal Air Sinus Boundaries:
- Anteriorly-Roof of the orbit
- Posteriorly- Anterior margin of foramen magnum
- Laterally- pterygoid canal
Sphenoidal Air Sinus Relations:
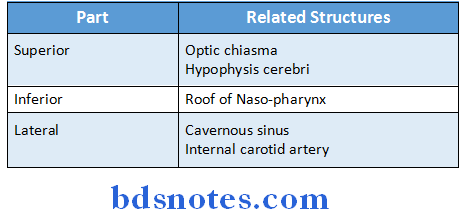
Sphenoidal Air Sinus Applied Anatomy:
- Infection of a sinus is known as sinusitis
- It causes headache & persistent, thick, purulent discharge from the nose
- It is diagnosed by transillumination & radiography
- A diseased sinus is opaque
- A surgical approach to pituitary gland is via sphenoidal sinus
Question 8. Paranasal air sinus
Answer:
They are air filled spaces present within some bones around the nasal cavities
Paranasal air sinus Types & Their Openings:
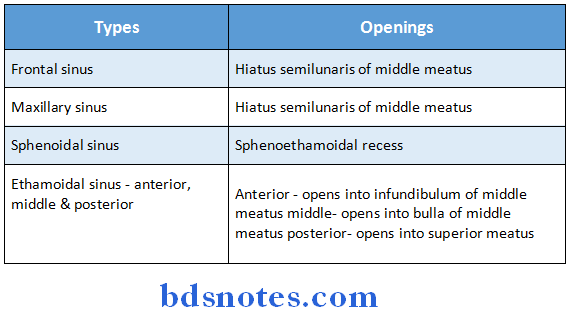
Paranasal air sinus Functions:
- Contained air of the sinuses adds humidity & temperature to the inspired air
- Serves as air-conditioning chambers
- Acts as resonating chambers for production of sounds
- Makes the facial bones lighter
- Establish adult contour of the face
- The mucous secretion of the sinuses is drained into the meatuses of the nose
Paranasal air sinus Growth:
- Rudimentary or absent- at birth
- Enlarges- during 6-7 years of age
- Next enlarges- due to
-
- Enlargement of bones in adults
- Resorption of the surrounding cancellous bone in old age
Question 9. Middle meatus of nose
Answer:
- Lies beneath middle concha
- It presents
- Ethamoidal bulla
- It is rounded elevation produced by middle ethamoidal sinus
- Hiatus semilunaris
- It is deep semicircular sulcus below bulla
- Infundibulum
- It is short passage at anterior end of hiatus
- Ethamoidal bulla
Middle meatus of nose Openings:
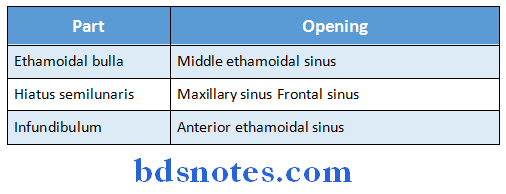
Question 10. Ethmoidal air sinuses
Answer:
- Ethmoidal sinuses are numerous small inter communicating spaces within the labyrinth of the ethmoid bone
- Bounded above by orbital plate of frontal bone, behind by sphenoidal conchae and the orbital process of the palatine bone and anterior by the lacrimal bone
- Sinuses are divided into anterior, middle and posterior groups
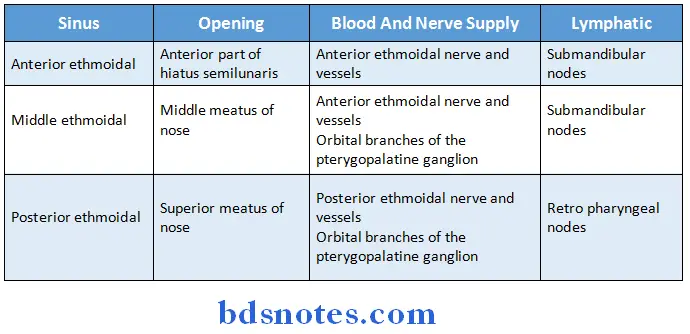
Question 11. Frontal sinus.
Answer:
- It lies in the frontal bone deep to the superciliary arch
- It is rudimentary at birth & develops at the age of 7-8 years
Frontal sinus Extend:
- Superiorly- Medial end of the eyebrow
- Posteriorly- Medial part of the roof of the orbit
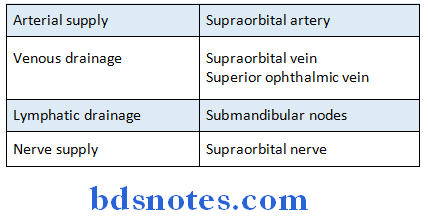
Question 12. Orbital nerve
Answer:
- It is a branch of Pterygopalatine nerve
- A branch of Maxillary nerve given in the Pterygopalatine ganglion
- By means of inferior orbital fissure, it supplies
-
- Periosteum of orbit
- Posterior ethmoid cells
- Orbitalis muscle
- Sphenoid sinus
Question 13. Maxillary sinus
Answer:
Maxillary Sinus:
- It is largest of all sinuses
- It lies in the body of maxilla
Maxillary Sinus Opening:
- It opens into middle meatus of nose in the lower part of the hiatus semilunaris
- A second opening is present at the posterior end of hiatus
Question 14. Lymphatic drainage of nasal septum
Answer:
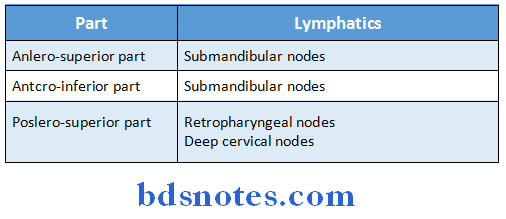
Question 15. Hiatus semilunaris
Answer:
- It is a deep semicircular sulcus below the bulla
- Openings present are
- Opening of frontal sinus – in anterior part
- Opening of maxillary sinus – in posterior part
- Opening of anterior ethmoidal sinus – behind frontal sinus
- Bounded by
- Inferior and anterior – concave margin of unicate process of ethmoid bone
- Superior ethmoidal bulla
- Posterior – inferior nasal concha
Question 16. Give the nerve supply of nasal cavity.
Answer:
1. General sensory nerves Part:
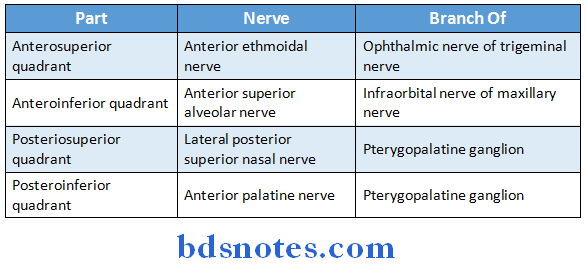
2. Special sensory nerves:
- Olfactory nerve carries sensory sensation.

Leave a Reply