Question 1. Give an account of position, relations, blood supply & development of palatine tonsil. Add a note on its applied anatomy (or) Palatine tonsil (or) Name the lateral relations of palatine tonsil
Answer:
Palatine Tonsil:
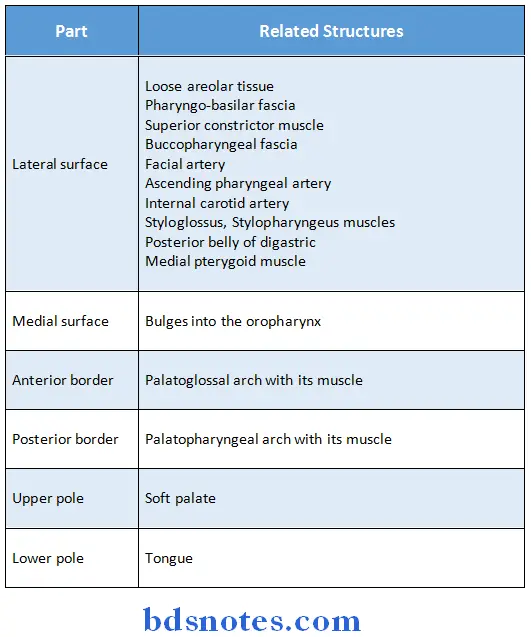
- Position:
- Each tonsil occupies the triangular tonsillar sinus or fossa between palatoglossus & palatopharyngeal arches
- Relations:
-
- It has two surfaces- medial & lateral, two borders- anterior & posterior & two poles- upper & lower
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
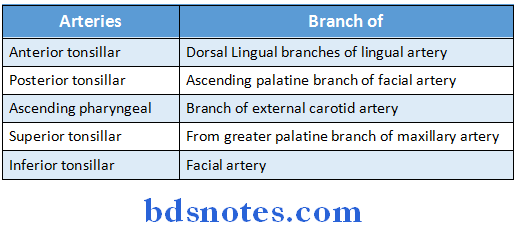
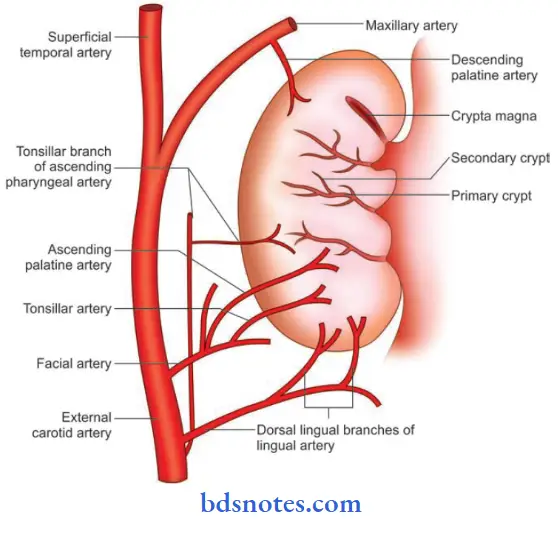
- Blood supply:
- Arterial supply
- Palatine Tonsil Venous drainage:
- Drains into pharyngeal venous plexus
- Palatine Tonsil Development:
- Each tonsil is developed from the ventral part of the second pharyngeal pouch
- Lymphocytes are mesodermal in origin
- Palatine Tonsil Applied anatomy:
- Tonsil is enlarged in children, while in adults it is diminished
- They are frequent sites of infections
- Infections in tonsil is called tonsilitis
- Tonsilitis may cause referred pain in the ear due to Glossopharyngeal nerve supply
- It requires surgical removal of tonsil called tonsillectomy
- Removal of tonsil is assessed by noticing the fibrous capsule
- During removal, the paratonsillar vein may be damaged producing excessive venous hemorrhage
- This is checked by removal of clot from the raw tonsillar bed
Question 2. Describe external features, muscles, nerve supply & blood supply of soft palate (or) Tensor palatine muscle (or) Muscles of soft palate
Answer:
Soft Palate:
- It is movable, muscular fold
- It separates the nasopharynx from the oropharynx
Soft Palate External Features:
- It has two surfaces- anterior & posterior, two borders- superior & inferior
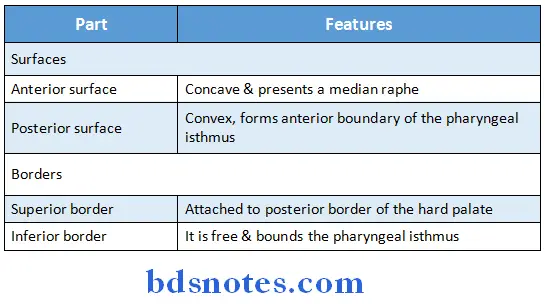
Soft palate contains:
- Palatine aponeurosis
- Five pairs of palatine muscle
- Nerves & vessels
- Palatine glands
Soft Palate Muscles:
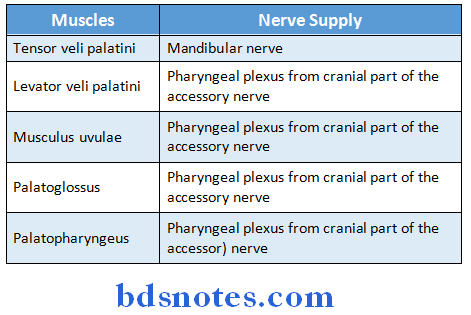
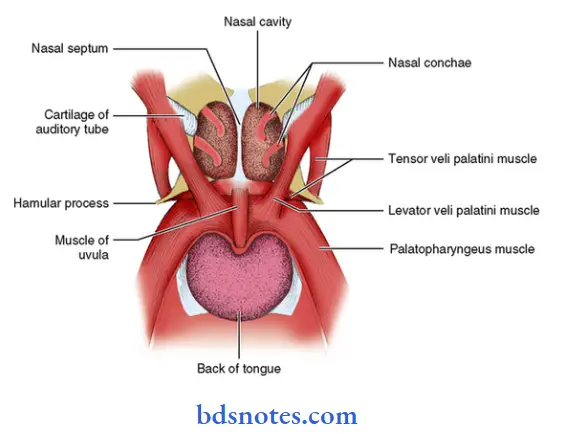
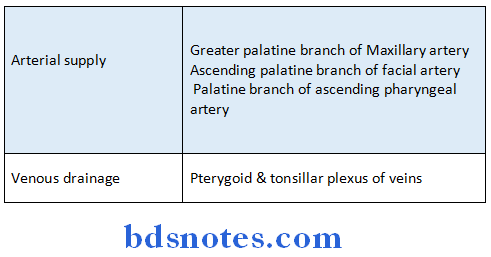
Soft Palate Blood supply:
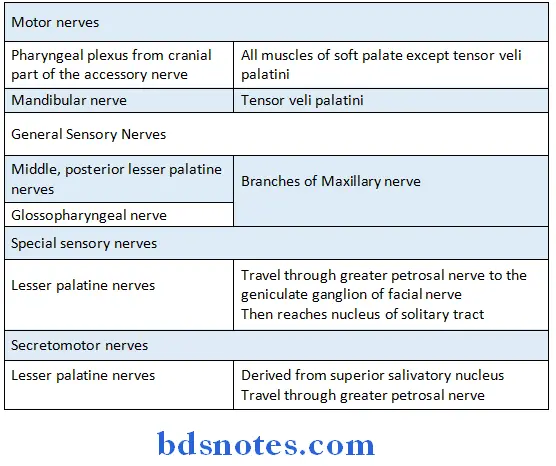
Soft Palate Nerves supply:
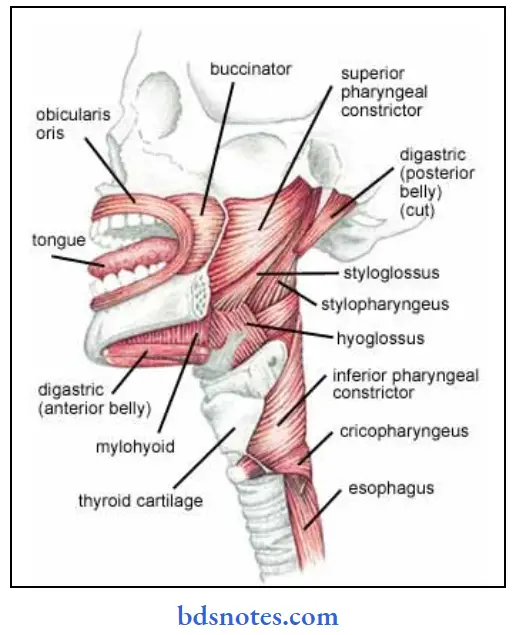
Question 3. Name the muscles of pharynx. Give origin, insertion & nerve supply of superior constrictor muscle of pharynx (or) Superior constrictor of pharynx
Answer:
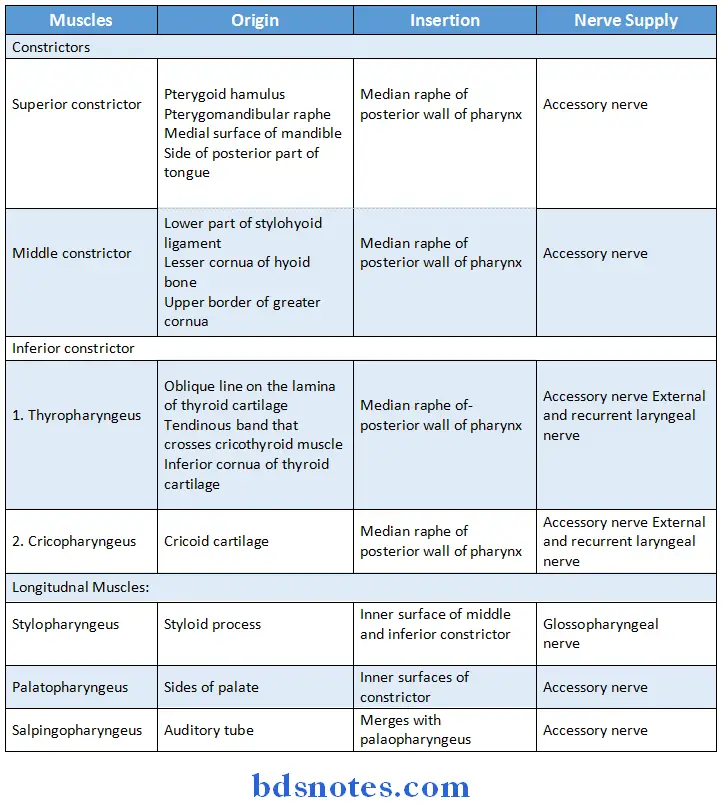
Muscles of pharynx:
1. Constrictor muscles:
- Superior constrictor
- Middle constrictor
- Inferior constrictor
2. Longitudinal muscles:
- Stylopharyngeus
- Palatopharyngeus Salpinopharyngeus
- Superior constrictor of pharynx:
Muscles of pharynx Origin:
- From the lower part of posterior border of medial pterygoid plate
- From the pterygoid hamulus
- From the posterior border of pterygomandibular raphe
- From posterior end of the mylohyoid line of mandible
- From the side of the tongue
Muscles of pharynx Insertion:
- Inserted into the median raphe on the posterior wall of the pharynx
Muscles of pharynx Nerve supply:
- It is supplied by the cranial part of accessory nerve through the pharyngeal plexus
Question 4. Oropharynx
Answer:
Oropharynx Situation:
- It is middle part of the pharynx situated behind the oral cavity
Oropharynx Extent:
- From soft palate to the upper border of the epiglottis
Oropharynx Communications:
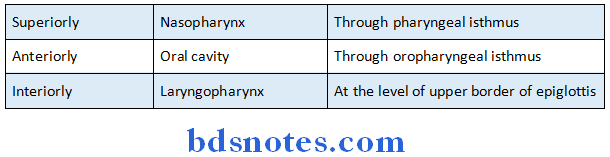
Oropharynx Relation:
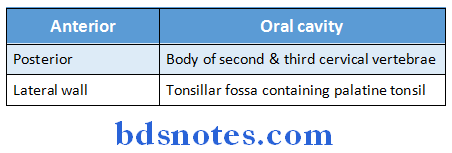
Oropharynx Function:
- Passage of air & food
Oropharynx Nerve Supply:
- IX & X cranial nerves
Question 5. Describe the features of lateral wall of nasopharynx (or) Soft palate
Answer:
- The lateral wall of the Nasopharynx presents the following features
- The pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube, at the level of the inferior nasal concha
- The Tubal opening bounded by the tubal elevation
- Behind the tubal elevation, there is a narrow vertical slit that leads into the pharyngeal recess or lateral recess or fossa of Rosenmuller
- The Salpinopharyngeus fold- It is vertical fold of mucous membrane running downwards from the posterior margin of the tubal elevation & gradually fading on the side wall of the pharynx
- The Levator veli palatini
Question 6. Nasopharynx (or) Boundaries and structures related to nasopharynx
Answer:
- Nasopharynx is the nasal part of pharynx
Nasopharynx Boundaries:
- Anterior wall-nasal conchae
- Posterior wall – free margin of soft palate
- Lateral wall – palato- pharyngeal arch
- Roof – body of sphenoid, basiocciput, anterior arch of atlas
- Floor – pharyngeal isthmus
Nasopharynx Relations:
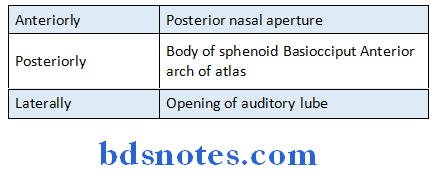
Nasopharynx Nerve supply:
- It is supplied by pharyngeal branches of pterygopalatine ganglion
Nasopharynx Function:
- Passage of air
Question 7. Muscles of pharynx
Answer:
Question 8. Laryngopharynx
Answer:
- It is laryngeal part of pharynx
Laryngopharynx Relations:
Laryngopharynx Anteriorly:
- Inlet of larynx
- Posterior surface of cricoid cartilage Arytenoid cartilage
Posteriorly:
- C4 &C5 vertebrae
Laterally:
- Piriform fossa
Laryngopharynx Nerve supply:
- Supplied by IX & X cranial nerves
Laryngopharynx Applied aspect:
- Removal of foreign bodies from piriform fossa may damage internal laryngeal nerve causing anaesthesia of supraglottic part of larynx
Question 9. Oropharynx
Answer:
- It is oral part of the pharynx
Oropharynx Relations:
- Anteriorly oral cavity
- Posteriorly body of C2 & C3 vertebrac
- Laterally tonsillar fascia
Oropharynx Nerve supply:
- Supplied by IX & X cranial nerves
Oropharynx Function:
- Passage of food and air
Question 10. Development of tooth
Answer:
1. Development of deciduous tooth
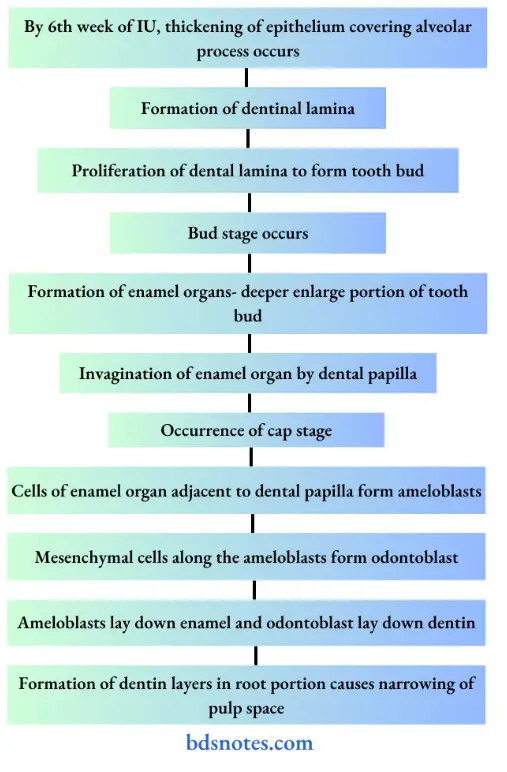
2. Development of permanent tooth
- Arises from tooth bud present on the medial side of each developing primary teeth.
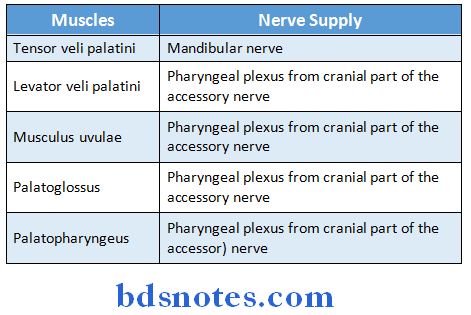
Question 11. Soft palate
Answer:
- It is movable, muscular fold
- It separates nasopharynx from oropharynx
Soft palate Muscles:
Question 12. Inferior constrictor
Answer:
Inferior constrictor Parts:
- Thyropharyngeus
- Cricopharyngeus
Inferior constrictor Origin:
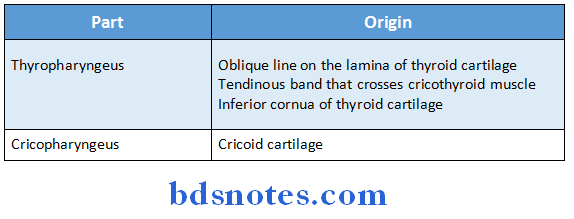
Inferior constrictor Insertion:
- Median raphe of posterior wall of pharynx
Inferior constrictor Nerve supply:
- Accessory nerve
- External and recurrent laryngeal nerve
Inferior constrictor Actions:
- Contracts reflexly during deglutition and induce a wave of peristalsis
- Thyropharyngeus causes propulsion
- Cricopharyngeus acts as sphincter
Question 13. Omohyoid muscle
Answer:
- Omohyoid is infrahyoid muscle
Omohyoid muscle Parts:
- Superior belly – insertion of muscle is by it
- Inferior belly origin of muscle is by it
- Common tendon
Omohyoid muscle Origin:
- Upper border of scapula
- Adjoining part of suprascapular ligament
Omohyoid muscle Insertion:
- Lower border of body of hyoid bone
Omohyoid muscle Action:
- Depresses hyoid bone following its elevation
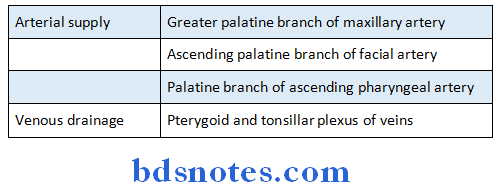
Question 14. Palatine tonsil
Answer:
Palatine tonsil Position:
Each tonsil occupies the triangular tonsillar sinus or fossa between palatoglossus and palatopharyngeal arches
Palatine tonsil Relations:
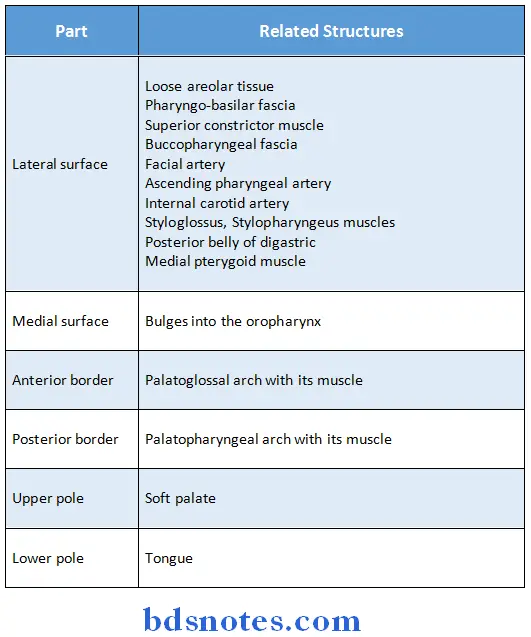
Palatine tonsil Blood supply:
Palatine tonsil Arterial supply:
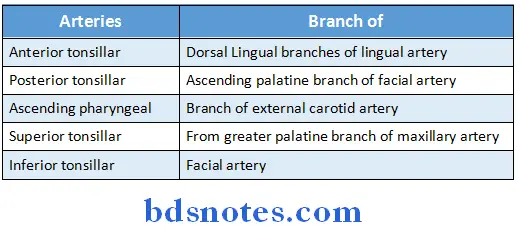
Palatine tonsil Venous drainage:
- Drains into pharyngeal venous plexus.
Question 15. Superior constrictor of pharynx
Answer:
Superior constrictor of pharynx Origin:
- From the lower part of posterior border of medial pterygoid plate
- From the pterygoid hamulus
- From the posterior border of pterygomandibular raphe
- From posterior end of the mylohyoid line of mandible
- From the side of the tongue
Superior constrictor of pharynx Insertion:
- Inserted into the median raphe on the posterior wall of the pharynx.
Superior constrictor of pharynx Nerve supply:
- It is supplied by the cranial part of accessory nerve through the pharyngeal plexus
Question 2. Nasopharynx
Answer:
Nasopharynx Situation:
- It is upper part of the pharynx situated behind the nose
Nasopharynx Extent:
- From base of skull to soft palate
Nasopharynx Communications:
- Anteriorly- nose
Nasopharynx Function:
- It resembles nose
- Passage of air
- Its walls are rigid & non-collapsable, so that air passage is kept patent
Nasopharynx Nerve Supply:
- Pharyngeal branches of Pterygopalatine ganglion
Question 16. Pharyngobasilar fascia
Answer:
- It forms the bed of the tonsil
- It is fibrous sheet internal to the pharyngeal muscles
- The posterior border of medial pterygoid plate gives attachment to it
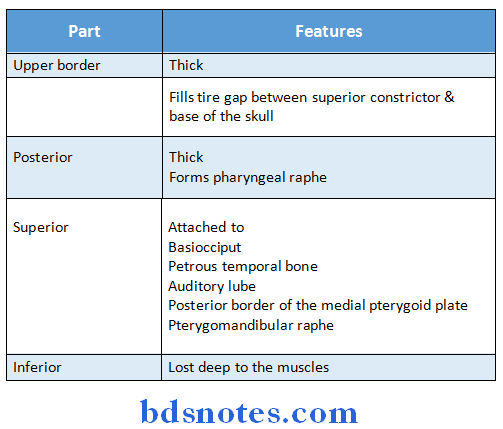
Question 17. Lymphatic drainage of tonsil.
Answer:
- Lymphatics from the tonsil pass to the Jugulodigastric nodes
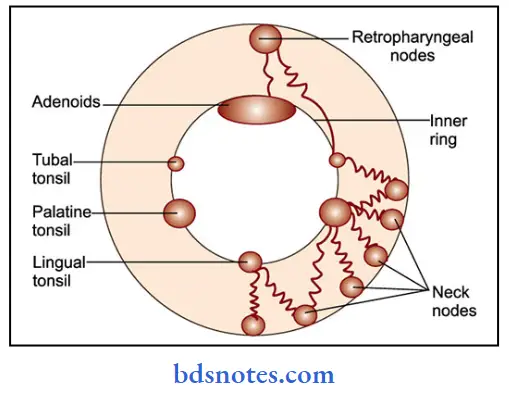
Question 18. List the lymphatic nodules in Waldeyer’s ring
Answer:
Waldeyer’s lymphatic ring consists of:
- Retropharyngeal node
- Pharyngeal tonsil- posteriorly & above
- Pharyngeal tonsil
- Tubal tonsil-Laterally & above
- Lingual tonsil- Inferiorly
- Submandibular nodes
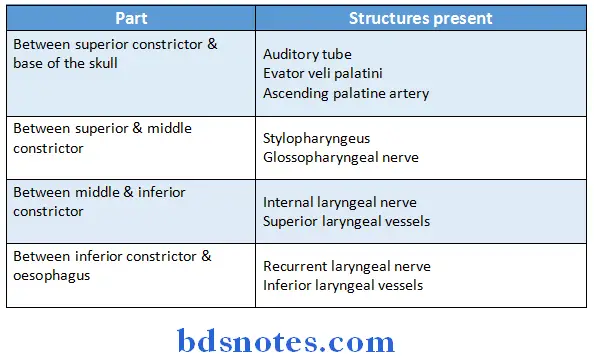
Question 19. Enumerate four relations of constrictor muscle of pharynx
Answer:
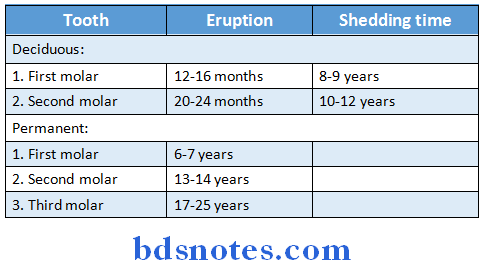
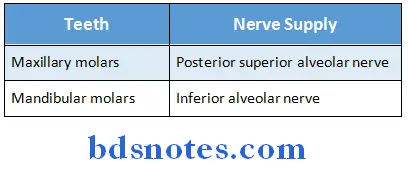
Question 20. Molar teeth
Answer:
- Molar teeth are grinding teeth
- They have square crowns with four or five cusps over it
- Deciduous molars are two in each half of each jaw While permanent molars are three in each half of each jaw
Molar teeth Eruption:
Question 21. Temporary teeth
Answer:
- They are 20 in number
- There are
- Two incisors- cutting teeth
- One canine- holding & tearing teeth
- Two molars- grinding teeth, in each half of the jaw
- They begin to erupt at about six months of age
- All get erupted by the end of the second year
- Falling of deciduous teeth to get replaced by permanent teeth is called shedding
Question 22. Premaxilla
Answer:
- It is the embryonic unit of bone lying anterior to the incisive foramen of hard palate
Premaxilla Contents:
- Upper four incisors
- Nasal spine
- Maxillary crest
Premaxilla Applied anatomy:
- Soft tissues in the region of premaxilla could be systematically elevated by detaching the soft tissue & mucosa that could be easily detached from this area
- Tumors involving the floor of the nasal cavity can spread through premaxilla
Question 23. Oral diaphragm
Answer:
- It comprises of two bilateral Mylohyoid muscles
- It provides structural support to the floor of the mouth
- It is attached to hyoid bone so that it can pull larynx forward during swallowing & opening of mouth
Question 24. Structure of tooth
Answer:
Each tooth is composed of:
1. Pulp
- It is central core of tooth
- It is loose, fibrous connective tissue
- Vessels, nerves, lymphatics reaches pulp through apical foramen
2. Dentin
- It is calcified material covering pulp
- Contains dentinal tubule
3. Enamel
- Hardest substance of body
- Covers dentin in crown portion of tooth
- Composed of crystalline prisms
4. Cementum
- Covers dentin in root portion
- It either overlaps enamel or just meet or is short of enamel
5. Periodontal ligament
- It holds the tooth in its socket
Question 25. Development of tooth
Answer:
Development of tooth:
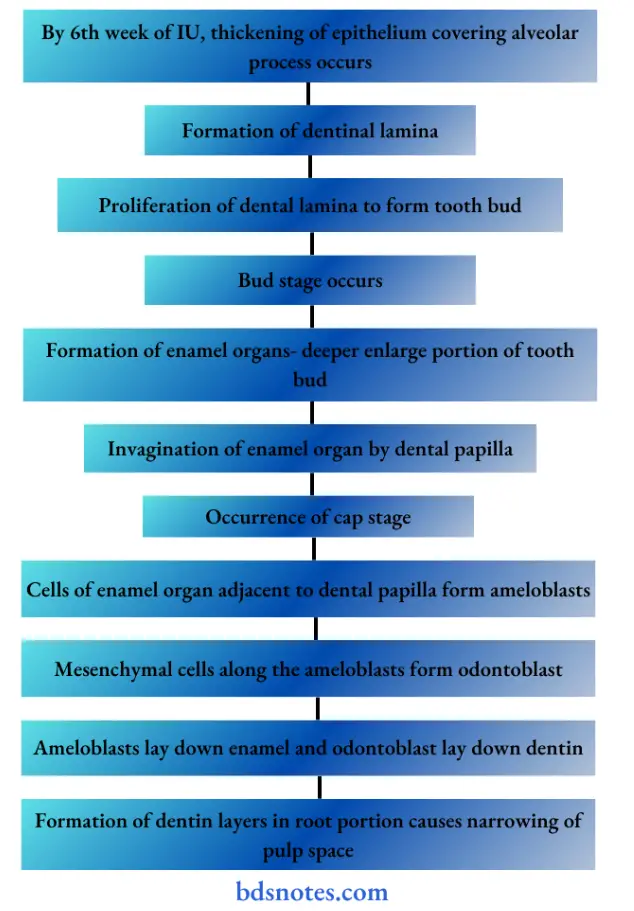
Question 26. Enumerate structures between middle and inferior constrictor of pharynx.
Answer:
Structures between middle and inferior constrictor of pharynx are
- Internal laryngeal nerve
- Superior laryngeal vessels

Leave a Reply