Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Tubercle bacilli were first demonstrated by
- Robert Koch
- Antony Ven Leeuwenhoek
- Edward Jenner
- Louise Pasteur
Answer: 1. Robert Koch
Question 2. One millimeter is equal to
- 10 micrometer
- 100 micrometer
- 1000 micrometer
- 10,000 micrometer
Answer: 3.1000 micrometer
Read And Learn More: Microbiology Question And Answers
Question 3. In bacteria, flagella act as:
- Organ of reproduction
- Organ of locomotion
- Organ of respiration
- Organ of digestion
Answer: 2. Organ of locomotion
Question 4. Plasmodium is a
- Virus
- Protozoa
- Bacterium
- Mycoplasma
Answer: 2. Protozoa
Question 5. MacConkey agar is a
- Selective medium
- Selective and indicator medium
- Liquid medium
- Nutrient medium
Answer: 2. Selective and indicator medium
Question 6. Methicillin-resistant Staph. aureus is
- Sensitive to penicillin
- Typable with phage typing
- Predominant hospital-resistant strain
- Gram-negative pyogenes
Answer: 3. Predominant hospital-resistant strain
Question 7. In streptococcal infection, the common route of entry is
- Gastrointestinal
- Urinary
- Upper respiratory
- Genitourinary
Answer: 3. Upper respiratory
Question 8. Tubercle bacilli cannot survive in
- Dust
- Milk
- Sunrays
- Saliva
Answer: 3. Sunrays
Question 9. Malignant pustule is
- Cutaneous anthrax lesion
- Cancerous lesion
- Benign lesion
- Autoimmune lesion
Answer: 1. Cutaneous anthrax lesion
Question 10. Clostridium tetani are
- Gram-negative non-sporing bacilli
- The causative organism for Lock Jaw
- Usually resistant to penicillin
- Non-motile
Answer: 2. Causative organism for Lock Jaw
Question 11. All these are dir infection + except
- AgNO3
- Mercuric chloride
- Brilliant green
- Methylene blue
Answer: 3. Brilliant green
Question 12. Antibodies in the primary response to an antigen is due to
- lgG
- IgM
- lgE
- lgD and lgA
Answer: 2. IgM
Question 13. All these factors take part in innate immunity, except
- Complement C1
- Macrophages
- Neutrophils
- NK- lymphocytes
Answer: 1. Complement C1
Question 14. All these cells have phagocytic property, except
- Macrophages
- Neutrophils
- Monocytes
- Lymphocytes – CD4+
Answer: 4. Lymphocytes – CD4+
Question 15. Malignant cells are killed by
- B-lymphocytes
- Neutrophils
- CD4 lymphocytes
- NK-lymphocytes
Answer: 2. Neutrophils
Question 16. All these organisms can have superantigen effect except
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Staphylococcus epidermidis
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- HIV
Answer: 2. Staphylococcus epidermidis
Question 17. An example of an anaerobic medium is
- Wilson and B lair medium
- MacConkey broth
- Robertson’s cooked meat medium
- EMB agar
Answer: 3. Robertson’s cooked meat medium
Question 18. Hepatitis B virus is:
- dsDNA
- ssDNA
- Partial dsDNA
- Partial dsRNA
Answer: 1. dsDNA
Question 19. Antiretroviral antibodies (anti-HIV) may be about in
- Full-blown AIDS at the terminal stage
- AlDS-related complex (ARC)
- Persistent generalized lymphadenopathy (PCL)
- Acute AlDS syndrome
Answer: 4. Acute AlDS syndrome
Question 20. So-called central dogma of molecular biology is
- DNA-DNA-RNA axis
- DNA-RNA-Peptides axis
- RNA-DNA-Peptides axis
- mRNA-DNA—RNA axis
Answer: 2. DNA-RNA-Peptides axis
Question 21. Multiple antibiotic resistance is mediated by
- Episome
- Plasmid
- Colplasmid
- Both b and c
Answer: 2. Plasmid
Question 22. Endotoxins are
- Glycoprotein
- Lipoprotein
- Lipopolysaccharides
- Nucleoproteins
Answer: 3. Lipopolysaccharides
Question 23. A viable count of bacteria is best arrived at by
- Direct microscopy
- Electron microscopy
- Colter-counter device
- Dilution and plating method
Answer: 1. Direct microscopy
Question 24. For Staphylococcus saprophyticus, virulence and pathogenicity is due to
- Coagulase enzyme
- Urease
- Exotoxin A to E
- Exopolysaccharides
Answer: 2. Urease
Question 25. The following all are true for diphtheriae, except
- Bacteria spread through the blood
- Gram variable
- Pleomorphic on microscope
- Produce exotoxin
Answer: 2. Gram variable
Question 26. the AMP test is positive in
- Streptococcus Gr. A
- Streptococcus Gr. B
- Streptococcus Gr. C
- Streptococcus Gr. D
Answer: 2. Streptococcus Gr. B
Question 27. Cerebral malaria is caused by
- Plasmodium vivax
- P. ovale
- P. falciparum
- P. malaria
Answer: 3. P. falciparum
Question 28. All are true for Clostridium tetanus, except
- Pathogenicity due to exotoxins
- Produce relatively heat-resistant spores
- They grow on cooked meat broth
- Antibiotics destroy toxin in tetanus
Answer: 2. Produce relatively heat-resistant spores
Question 29. All are true for episomes, except
- They are bacteriophage
- Carry drug-resistant gene
- Transfer from one to other bacteria by transduction
- Transfer from one to other bacteria by conjugation
Answer: 3. Transfer from one to other bacteria by transduction
Question 30. All of these are dimorphic fungal species, except
- Candida
- Histoplasma
- Coccidiodies imitis
- Cryptococcus neoformans
Answer: 4. Cryptococcus neoformans
Question 31. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- Amplifies DNA
- Utilizes polymerase
- Detects viruses like Hepatitis B
- Does all of the above
Answer: 4. Does all of the above
Question 32. In microbiology, filters are used for sterilization of
- Glasswares
- Disposable gloves
- Serum
- Bacteriological media
Answer: 3. Serum
Question 33. Widal test is done for diagnosis of
- Cholera
- Tuberculosis
- Tetanus
- Typhoid
Answer: 4. Typhoid
Question 34. In hypersensitivity reactions, T lymphocytes are associated with
- Anaphylactic reaction
- Immune complex status
- Cytotoxic reaction
- Cell mediatéd immunity
Answer: 4. Cell mediatéd immunity
Question 35. Streptococci associated with dental caries are
- S. equi
- S. bovis
- S. mutans
- S. avium
Answer: 3. S. mutans
Question 36. Bacillus anthracis
- Motile, non-encapsulated and non-sporing organism
- Has the tremendous capacity to infect the handler
- Causes primary disease in human
- Is resistant to penicillin
Answer: 4. Is resistant to penicillin
Question 37. In diphtheria
- Domestic animals are a reservoir of infection
- Men are the source and reservoir of infection
- Endotoxin produces a local lesions
- The schick test is negative
Answer: 2. Men are the source and reservoir of infection
Question 38. Mycobacterium can ideally be demonstrated with the highest sensitivity and specificity by
- Acid-fast stain
- PCR
- Culture
- Biopsy
Answer: 2. PCR
Question 39. Opportunistic fungal infection usually occurs in
- Young healthy person
- Immunocompromised person
- Old person
- Children
Answer: 2. Immunocompromised person
Question 40. The viruses
- Can be grown on artificial media
- Have rigid cell wall
- Have both RNA and DNA together
- Cannot be activated by antibiotics
Answer: 3. Have both RNA and DNA together
Question 41. Pentamer antibody is
- IgG
- IgM
- IgA
- IgE
Answer: 2. IgM
Question 42. The virulence factor of Pneumococcus is
- Fimbria
- Slime layer
- Toxin
- Capsule polysaccharide
Answer: 4. Capsule polysaccharide
Question 43. Which of the following media is transport media?
- Pike’s media
- Crystal violet pectate media
- Stuart’s media
- Saboraud’s media
Answer: 3. Stuart’s media
Question 44. Nagler’s test is done for testing the toxin production in
- Diphtheria
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Group B Streptococcus
- Clostridium welchii
Answer: 4. Clostridium welchii
Question 45. R+ factor is transmitted by
- Conjugation
- Mutation
- Transduction
- Transformation
Answer: 1. Conjugation
Question 46. All of the following are gram-positive anaerobic bacilli, except
- Propionibacterium
- Mobiluncus
- Fusobacterium
- Bifidobacterium
Answer: 3. Fusobacterium
Question 47. Trichophyton species affect
- Skin and nails
- Skin and hair
- Nails and hair
- Skin, nails, and hair
Answer: 4. Skin, nails, and hair
Question 48. DNA hepatitis virus is
- Hepatitis A virus
- Hepatitis B virus
- Hepatitis C virus
- Hepatitis E virus
Answer: 2. Hepatitis B virus
Question 49. Which of the following staining techniques cannot be used for Treponema palladium?
- Giemsa staining
- Gram staining
- Immunofluorescence staining
- Silver impregnation staining
Answer: 2. Gram staining
Question 50. Which of the following bacteria is/are involved in the production of dental caries?
- Streptococcus mutants
- Streptococcus sanguis
- Both of the above
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both of the above
Question 51. Following are the nonstructural genes of HIV 1 virus, except:
- Tat
- Nef
- Vif
- Vpx
Answer: 4. Vpx
Question 52. All the following are the features of Pneumococcus except
- Bile insolubility
- Optochin sensitivity
- Gram positivity
- Encapsulation
Answer: 1. Bile insolubility
Question 53. The toxigenicity of Corynebacterium diphtheriae is due to
- Lambda phage
- T-4 phage
- Beta phage
- T-2 phage
Answer: 3. Beta phage
Question 54. In bacterial growth culture bacteria have the maximum cell size towards the end of
- Lag phase
- Log phase
- Stationary phase
- Phase of decline
Answer: 1. Lag phase
Question 55. The major component of complement is
- C 1
- C 2
- C 3
- C 4
Answer: 3. C 3
Question 56. Grafts between two genetically non-identical members of the same species are called:
- Autograft
- Isograft
- Allograft
- Xenograft
Answer: 3. Allograft
Question 57. Cary Blair is
- Transport medium
- Liquid medium
- Enriched medium
- Differential medium
Answer: 1. Transport medium
Question 58. Incineration means
- Sterilization of glassware
- Sterilization of media
- Burning to ashes
- Disinfection
Answer: 3. Burning to ashes
Question 59. Mycobacterium intracellular is
- Photochromogen
- Scotochromogen
- Non-photochromogen
- Rapid growth
Answer: 3. Non-photochromogen
Question 60. TCBS medium is used for the growth of
- Salmonella typhi
- Escherichia coli
- Vibrio cholera
- Shigella dysenteriae
Answer: 3. Vibrio cholerae
Question 61. All are the methods of transmission of genetic material except
- Transformation
- Conjugation
- Transduction
- Transportation
Answer: 4. Transportation
Question 62. The infective form of E. histolytica is
- Binucleate cyst
- Mononucleate cyst
- Trophozoite form
- Quadrinucleate cyst
Answer: 4. Quadrinucleate cyst
Question 63. In diphtheria:
- Domestic animals are a reservoir of infection
- Men are the source and reservoir of infection
- Endotoxin produces local lesions
- The schick test is negative
Answer: 2. Men are the source and reservoir of infection
Question 64. The causative agent of syphilis is
- Treponema pallidum
- Clostridium species
- Corynebacterium
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Answer: 1. Treponema pallidum
Question 65. Streptococcus pyogenes causing pyogenic infections
- Has the characteristic to be localized
- Has the characteristic to spread
- Both of the above
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both of the above
Question 66. Only immunoglobulin is transported through the placenta and provide passive immunity to newborn
- IgG
- IgM
- IgE
- IgD
Answer: 1. IgG
Question 67. Immunoglobulin involved in anaphylaxis reaction is
- IgG
- IgM
- IgE
- IgD
Answer: 3. IgE
Question 68. A commonly used cultural medium for the cultivation of viruses is
- NAME
- Chocolate agar
- SDA
- Macconkey agar
Answer: 1. NAM
Question 69. Taenia solium and Taenia saginata are similar in many ways, but Taenia solium is more dangerous. Which of the following makes Taenia solium more dangerous
- It has an armed scolex
- It has fewer uterine branches than T. saginata
- Man can be infected as an intermediate host by eating eggs from T. solium.
- It produces more eggs than T. saginata.
Answer: 1. It has an armed scolex
Question 70. Virulence factors include
- Toxins
- Capsule
- Enzymes
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 71. Ascaris lays
- Only fertilized eggs
- Only unfertilized eggs
- Only decorticated eggs
- Fertilized, unfertilized and decorticated eggs
Answer: 4. Fertilized, unfertilized, and decorticated eggs
Question 72. White plaques in the mouth, tongue, gums, and palate indicate infection caused by
- Streptococcus
- Staphylococcus
- T. palladium
- Candida albicans
Answer: 4. Candida albicans
Question 73. Most of the fungi with medical importance belong to
- Phycomycetes
- Ascomycetes
- Basidiomycetes
- Deuteromycetes
Answer: 4. Deuteromycetes
Question 74. Antigens commonly involved in allergies are
- Pollen grains
- House dust
- Ingestants like milk and eggs
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 75. Which of the following is a live attenuated vaccine?
- BCG
- TAB
- Rabies vaccine
- Cholera vaccine
Answer: 1. BCG
Question 76. When a tissue or organ is transplanted in genetically unrelated members of the same species, such type of transplantation is called as
- Xenograft
- Allograft
- Autograft
- Isograft
Answer: 2. Allograft
Question 77. Robertson’s cooked meat media is
- Anaerobic media
- Aerobic media
- Both of the above
- None of these
Answer: 1. Anaerobic media
Question 78. Corynebacterium diphtheriae produces
- Exotoxin
- Endotoxin
- Mycotoxin
- Streptolysin ‘O’
Answer: 1. Exotoxin
Question 79. Streptolysin ‘O’ produced by S. pyogenes is
- Oxygen labile
- Oxygen stable
- Heat stable
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Oxygen stable
Question 80. Which of the following is a common cause of nosocomial infections?
- T. palladium
- Candida albicans
- tetani
- Staphylococcus spp.
Answer: 2. Candida albicans
Question 81. Immunoglobulin which can cross the placenta
- IgG
- IgM
- IgA
- IgE
Answer: 1. IgG
Question 82. Plasmodium is a
- Fungus
- Parasite
- Virus
- Bacteria
Answer: 2. Parasite
Question 83. Bacteria flagella act as a
- Organ of reproduction
- Organ of locomotion
- Organ of respiration
- Organ of digestion
Answer: 2. Organ of locomotion
Question 84. MacConkey media is
- Selective media
- Liquid media
- Nutrient media
- Selective and indicator media
Answer: 1. Selective media
Question 85. In streptococcal infection the common route of entry is
- Respiratory
- Gastrointestinal
- Genitourinary
- All above
Answer: 1. Respiratory
Question 86. Clostridium tetani are
- Gram-negative cocci
- Non-mobile
- The causative organism of lockjaw
- All above
Answer: 3. Causative organism of lockjaw
Question 87. The toxigenicity of Corynebacterium diphtheriae is due to
- Lambda phage
- T4 phage
- Beta phage
- T2 phage
Answer: 3. Beta phage
Question 88. All are dimorphic fungus except
- Sporothrix
- Histoplasma
- Cryptococcus
- Rhinosporidium
Answer: 4. Rhinosporidium
Question 89. The Hepatitis B virus is a
- dsDNA
- ssDNA
- Partial dsDNA
- Partial dsRNA
Answer: 1. dsDNA
Question 90. Cell-mediated immunity is caused by
- Plasma cell
- B lymphocyte
- T lymphocyte
- All above
Answer: 3. T lymphocyte
Question 91. UV radiation is best suited for among which of the following
- Syringes
- Endoscopies
- Vaccines
- Culture media
Answer: 3. Vaccines
Question 92. Drug resistance or resistance transfer factor is transmitted by which of the following
- Conjugation
- Transformation
- Transposition
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Conjugation
Question 93. All the following cells take part in innate as well as adaptive immunity except
- Macrophages
- B-Lymphocytes
- NK cells
- T-Lymphocytes
Answer: 1. Macrophages
Question 94. If CD4 dysfunction occurs, which of the following process is affected
- IgM and IgG production is decreased
- Antigen presentation is defective
- Deficiency of complement C3 is decreased
- IgM to IgG switchover is disturbed
Answer: 1. IgM and IgG production is decreased
Question 95. Mantoux test (Mx test) is invariably negative in which clinical condition of tuberculosis
- Iris tuberculosis
- Post Iris tuberculosis
- Extrapulmonary tuberculosis
- Miliary tuberculosis
Answer: 4. Miliary tuberculosis
Question 96. Pathogenicity of Streptococcus pneumonia is mostly due to which of the following
- Cell wall
- Autolytic enzymes
- Hemolysin
- Capsules
Answer: 4. Capsules
Question 97. Commonest cause of gas gangrene is due to
- Clostridium septicum
- Clostridium nori
- Clostridium perfringens
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Clostridium perfringens
Question 98. Nocardia and actinomycetes are filamentous higher bacteria with similar morphologically. Which stains differ from?
- Gram stain
- Acid-fast stain
- Giemsa stain
- Culture on blood agar media
Answer: 2. Acid-fast stain
Question 99. HIV infection mostly destroys which cells
- CD4 T-lymphocytes
- CD8 T-lymphocytes
- NK-lymphocytes
- Dendritic cells
Answer: 1. CD4 T-lymphocytes
Question 100. Kerion’s clinical condition happens due to
- Candida
- Pseudomonas
- Herpes simplex virus
- Dermatophytes
Answer: 4. Dermatophytes
Question 101. In malaria, the form of plasmodium transmitted to a man from a mosquito is:
- Sporozoite
- Gametocytes
- Merozoites
- Trophozoites
Answer: 2. Gametocytes
Question 102. The host that harbors the adult or sexually mature parasite is called
- Intermediate host
- Commensal host
- Symbiotic host
- Definitive host
Answer: 4. Definitive host
Question 103. Which of the following statements is not correct regarding hookworm infestation
- Hookworm infection causes anemia
- Man acquires infection when filariform larvae penetrate the skin
- Hookworm infection may sometimes be acquired by oral route
- Hookworm infection can be diagnosed by finding trophozoites in the stool
Answer: 4. Hookworm infection can be diagnosed by finding trophozoites in the stool
Question 104. Which of the following bacterial substance binds to the Fc portion of immunoglobulin molecules
- Endotoxin
- Coagulase
- Lipoteichoic acid
- Protein A
Answer: 4. Protein A
Question 105. Which of the following components enhances the binding of the antigen-antibody complex to macrophages
- C1
- C3a
- C3b
- C8
Answer: 3. C3b
Question 106. Two tests are used to detect the presence of HIV infection are
- Agglutination and neutralization reactions
- Complement fixation and immunofluorescence tests
- ELISA and Western blot
- Hemagglutination and Coombs test
Answer: 3. ELISA and Western blot
Question 107. Which of the following is an RNA virus?
- Human papilloma virus
- Human T cell leukemia virus
- Hepatitis B virus
- Epstein-Barr virus
Answer: 2. Human T cell leukemia virus
Question 108. The most reliable method for diagnosis of primary syphilis is
- VDRL test
- FTA-ABS
- Microhemagglutination test
- Darkfield examination of chancre material
Answer: 3. Microhemagglutination test
Question 109. The antiphagocytic property of the Group A Streptococcus is associated with which of the following
- Hyaluronidase
- Streptolysin S
- M protein
- Peptidoglycan
Answer: 3. M protein
Question 110. Which of the following test does not correspond with the respective disease?
- Casoni’s test for hydatid disease
- Frei’s test in infectious mononucleosis
- Schick test for diphtheria
- Wasserman test for syphilis
Answer: 2. Frei’s test in infectious mononucleosis
Question 111. The variable portion of the antibody molecule is
- C-terminal
- B-terminal
- A-terminal
- N-terminal
Answer: 4. N-terminal
Question 112. “Vi” antigen of Salmonella is helpful to find out
- Carrier stage
- Infective stage
- Immunity
- Susceptibility
Answer: 1. Carrier stage
Question 113. The Streptococcus pneumoniae produced on blood agar
- Alpha hemolysis
- Beta hemolysis
- Gamma hemolysis
- No hemolysis
Answer: 1. Alpha hemolysis
Question 114. In malaria, the form of Plasmodium transmitted to man from mosquitoes is
- Sporozoites
- Gametocytes
- Merozoites
- Trophozoites
Answer: 1. Sporozoites
Question 115. The host that harbors the adult or sexually mature, parasite is called as
- Intermediate host
- Commensal host
- Symbiotic host
- Definite host
Answer: 4. Definite host
Question 116. Which of the following bacterial substance binds to the Fc portion of immunoglobulin molecules
- Endotoxin
- Coagulase
- Lipoteichoic acid
- Protein A
Answer: 4. Protein A
Question 117. The infected form of E. histolytica is
- Binucleate cyst
- Quadrinucleate cyst
- Mononucleate cyst
- Trophozoite form
Answer: 2. Quadrinucleate cyst
Question 118. The paul-Bunnell test is useful in the diagnosis of
- Cytomegalovirus infection
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Herpes simplex infection
- ECHO virus infection
Answer: 2. Infectious mononucleosis
Question 119. Chlamydospores are present in
- Macrosporium
- Epidermophyton
- Candida albicans
- Microsporum
Answer: 3. Candida albicans
Question 120. Which of the following components enhances the binding of the antigen-antibody complex to macrophages?
- C1
- C3a
- C3b
- C8
Answer: 3. C3b
Question 121. The Streptococcus pneumoniae produces on blood agar
- Alpha hemolysis
- Beta hemolysis
- No hemolysis
- Gamma hemolysis
Answer: 1. Alpha hemolysis
Question 122. The infective form of E. histolytica is
- Quadrinucleate cysts
- Commensal host
- Definite host
- Symbiotic host
Answer: 1. Quadrinucleate cysts
Question 123. The most reliable method for diagnosis of primary syphilis is
- FTA-ABS
- VDRL test
- Microhemagglutination test
- Dark field examination
Answer: 1. FTA-ABS
Question 124. Double-stranded RNA is seen in
- Retrovirus
- Reovirus
- HIV virus
- Rhabdovirus
Answer: 2. Reovirus
Question 125. The variable portion of the antibody molecule is
- B-terminal
- C-terminal
- N-terminal
- A-terminal
Answer: 3. N-terminal
Question 126. The paul-Baunnel test is used for the diagnosis of
- Cytomegalovirus infection
- Herpes simplex infection
- Infectious mononucleosis
- ECHO virus
Answer: 3. Infectious mononucleosis
Question 127. The antiphagocytic property of Group A streptococcus is associated with which of the following
- Hyaluronidase
- M protein
- Streptolysin S
- Peptidoglycans
Answer: 2. M protein
Question 128. Two tests are used to detect presence of HIV infection are
- Agglutination and neutralization reaction
- Compliment fixation and immunoflorescence test
- ELISA and Western blot
- Hemagglutination and Coombs test
Answer: 3. ELISA and Western blot
Question 129. Which of the following is an RNA virus?
- Human papilloma virus
- Human T cell leukemia virus
- Hepatitis B virus
- Epstein-B arr virus
Answer: 2. Human T cell leukemia virus
Question 130. Darting movements are seen in
- Salmonella
- Vibrio cholerae
- Treponema
- Clostridium
Answer: 1. Salmonella
Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. Widal test is due for serodiagnosis of ……………….
Answer: Enteric fever
Question 2. VDRL is a type of test ……………….
Answer: Non-specific test
Question 3. Candidiasis is caused by the organism ……………….
Answer: Candida albicans
Question 4. Complement is obtained from ……………….
Answer: Macrophages and other host cells
Question 5. Blackwater fever is caused by ……………….
Answer: P. falciparum
Viva-Voce Questions For Practical Examination
Question 1. Who had discovered the microscope?
Answer: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek.
Question 2. Who had named the term vaccine?
Answer: Louis Pasteur
Question 3. Who has discovered blood groups?
Answer: Landsteiner
Question 4. Which bacteria appear as spherical or oval cells?
Answer: Cocci
Question 5. Who appear as rod-shaped cells?
Answer: Bacilli
Question 6. Which microscopic organism appears as comma-shaped bacteria?
Answer: Vibrio
Question 7. Name the bacteria which possess both capsule and slime layers.
Answer: Streptococcus salivarius
Question 8. Name the organ of adhesion of bacteria.
Answer: Fimbriae
Question 9. Name the phase in which there is no increase in number but there is an increase in the size of the cell.
Answer: Lag phase
Question 10. Name the phase where there is nutritional exhaustion and toxic accumulation which causes cell death.
Answer: Stationary phase
Question 11. Name the bacteria which are aerobic but are able to grow in the presence of oxygen.
Answer: Facultative anaerobes
Question 12. Name the method of sterilization which kills organisms by protein denaturation and oxidative damage.
Answer: Dry heat
Question 13. Name the spores which are used to check efficiency of the hot air oven.
Answer: Clostridium tetani
Question 14. Which is the most appropriate method to sterilize operation theater?
Answer: UV radiation
Question 15. Which bacteria test the efficiency of ionizing radiation?
Answer: Micrococcus radiodurans
Question 16. Which agent is used universally for preparing solid media?
Answer: Agar
Question 17. Name the example of nutrient broth.
Answer: Simple media
Question 18. If blood serum or egg is added to basal media, what does it become?
Answer: Enriched media
Question 19. Name the media which allows the growth of only one type of bacteria.
Answer: Enrichment media
Question 20. If an inhibiting substance is added to the solid medium what it is known as?
Answer: Selective media
Question 21. Which agent is used to test efficacy of disinfectants?
Answer: Phenol
Question 22. MacConkey medium is an example of this media.
Answer: Differential media
Question 23. Robertsons’s cooked meat media is an example of this media.
Answer: Anaerobic media
Question 24. Which cells synthesize immunoglobulins?
Answer: Plasma cells
Question 25. Which is the major serum immunoglobulin?
Answer: IgG
Question 26. How much is the half-life of IgG?
Answer: 23 days
Question 27. Which is the only maternal immunoglobulin which is normally transported across the placenta and provides natural passive immunity in the newborn?
Answer: IgM
Question 28. Which immunoglobulin has the longest half-life?
Answer: IgG
Question 29. Which is the major immunoglobulin in saliva and tears?
Answer: IgA
Question 30. Which antibody is known as a millionaire molecule?
Answer: IgM
Question 31. Which is the earliest immunoglobulin to be synthesized by a fetus?
Answer: IgM
Question 32. Which immunoglobulin is intravascular?
Answer: IgD
Question 33. Which immunoglobulin mediates hypersensitivity?
Answer: IgE
Question 34. Name the protein seen in multiple myeloma.
Answer: Bence-Jones protein
Question 35. Which type of test is the VDRL test?
Answer: Slide agglutination test
Question 36. Where does Hassal’s corpuscles are seen?
Answer: Thymus
Question 37. Which is the largest lymphoid organ?
Answer: Spleen
Question 38. Where does white pulp, red pulp, and Malphigian corpuscles are seen?
Answer: Spleen
Question 39. Which cell show the cartwheel appearance of its nucleus?
Answer: Plasma cell
Question 40. What do macrophages know in the liver, lungs, and spleen?
Answer: In the liver as Kupffr cells, in the lung as alveolar macrophages, and in spleen as sinus histiocytes
Question 41. Which is the most important vasoactive amine in human anaphylaxis?
Answer: Histamine
Question 42. Which type of hypersensitivity do Arthus reaction and serum sickness represent?
Answer: Type III hypersensitivity reaction
Question 43. Which reaction is known as a delayed hypersensitivity reaction?
Answer: Type IV reaction
Question 44. Which test detects hypersensitivity?
Answer: Patch test
Question 45. In which disease antibodies against acetylcholine receptors present on myoneural functions of striated muscles?
Answer: Myasthenia gravis.
Question 46. If an organ or tissue is taken from an individual and is grafted on himself, what does it known as.
Answer: Autograft
Question 47. If an organ or tissue is taken from an individual and is grafted on another person of the same genetic constitution, what does it know as.
Answer: Isograft
Question 48. What does graft between two genetically non-identical members of the same species is known as?
Answer: Allograft
Question 49. What does graft between members of different species is known as?
Answer: Xenograft
Question 50. Which blood group is commonly associated with duodenal ulcers?
Answer: O
Question 51. Which blood group is commonly associated with stomach cancer?
Answer: A
Question 52. Which type of colonies are produced by most of the staphylococcal strains from pyogenic lesions?
Answer: Golden yellow colonies
Question 53. Which type of appearance is produced by S. aureus on nutrient agar?
Answer: Oil paint appearance
Question 54. Which are the most resistant non-sporing bacteria?
Answer: Staphylococcus
Question 55. Name the toxin produced by staphylococci which produce pathogenecity.
Answer: Alpha toxin
Question 56. Which toxin is responsible for staphylococcal food poisoning?
Answer: Enterotoxin
Question 57. Name the test which leads to differentiation of S. aureus and other staphylococci.
Answer: Coagulase test
Question 58. Name the common deep infection caused by staphylococci.
Answer: Osteomyelitis
Question 59. Name the type of streptococci which causes green discoloration with partial hemolysis around the colonic.
Answer: α hemolytic
Question 60. Name the type of streptococci which produces sharp defied clear colorless zone of hemolysis.
Answer: β hemolytic
Question 61. Name the microorganism which causes scarlet fever.
Answer: S. pyogenes
Question 62. What is the shape of pneumococci?
Answer: Flame shape
Question 63. Which microorganism produces draughtsman or carrom coin appearance on blood agar?
Answer: Pneumococci
Question 64. Which is the most serious pneumococci infection?
Answer: Meningitis
Question 65. Which microorganism shows metachromatic granules or Babes Ernst granules or polar bodies?
Answer: Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Question 66. Which strain is used universally used for toxin production?
Answer: Park-William strain
Question 67. Which was the first pathogenic bacterium to be seen under the microscope?
Answer: Bacillus anthracis
Question 68. Which are the largest pathogenic bacteria?
Answer: Bacillus anthracis
Question 69. Which is the most important causative agent of gas gangrene?
Answer: Clostridium welchi
Question 70. Which toxin is responsible fortoxemia ofgas gangrene?
Answer: Alpha toxin
Question 71. Which disease is known as malignant edema?
Answer: Gas gangrene
Question 72. Name the bacilli with a drumstick appearance.
Answer: Clostridium tetani
Question 73. Name the important toxin of Clostridium tetani.
Answer: Tetanospasmin
Question 74. What does tetanus toxin block in the spinal cord?
Answer: Synaptic transmission
Question 75. What is the first symptom of tetanus?
Answer: Trismus
Question 76. Which bacteria cause food poisoning?
Answer: Clostridium botulinum
Question 77. On which system does botulinum toxin act?
Answer: Parasympathetic system
Question 78. Which are the most common anaerobe isolated from clinical specimens?
Answer: Bacteroides
Question 79. Which is the most common bacteria which leads to urinary tract infections?
Answer: E. coli
Question 80. Salmonella typhi causes which disease?
Answer: Typhoid fever
Question 81. Which are the differential media for salmonella?
Answer: MacConkey’s media and Wilson-Blair media
Question 82. Which is a good culture medium for S. typhi?
Answer: Bile
Question 83. Which disease shows step ladder fever and rose spots?
Answer: Typhoid
Question 84. Which bacteria show fish in stream appearance?
Answer: Vibrio cholera
Question 85. On which enzyme does cholera toxin act on?
Answer: Adenyly cyclase
Question 86. Which bacteria demonstrate a safety pin appearance?
Answer: Yersinia pestis
Question 87. Which is the most common form of plague.
Answer: Bubonic form
Question 88. Where does kill vaccine in India is prepared?
Answer: Haffke institute Mumbai
Question 89. What does Bacillus pertussis lead to?
Answer: Whooping cough
Question 90. Which disease is known as familial Mediterranean fever?
Answer: Brucellosis
91. Which bacilli is known as acid-fast bacilli?
Answer: Mycobacterium
Question 92. Why there is a presence of acid-fastness in bacterial cell wall?
Answer: Due to mycolic acid
Question 93. Which solid media is used for the culture of M. tuberculosis?
Answer: Lowstein-Jenson media
Question 94. Which type of vaccine is BCG?
Answer: Live attenuated vaccine
Question 95. Lepra bacilli arranged in parallel rows of globe shows which type of appearance?
Answer: Cigar bundle
Question 96. Which stage of syphilis shows hard chancer?
Answer: Primary stage
Question 97. Which is the most infectious stage of syphilis?
Answer: Secondary stage
Question 98. In which stage gumma is seen?
Answer: Tertiary stage
Question 99. Lumpy jaw is associated with which disease?
Answer: Actinomycosis
Question 100. Name the most common form of actinomycosis in human
Answer: Cervicofacial
Question 101. What does an extracellular infectious virus particle is known as?
Answer: Virion
Question 102. Which is the largest virus?
Answer: Pox virus
Question 103. Which is the smallest virus?
Answer: Parvovirus
Question 104. Name the agent by which viral protein is made up of.
Answer: Lipoprotein
Question 105. In which disease Negri bodies are seen?
Answer: Rabies
Question 106. Name the viruses which infect bacteria.
Answer: Bacteriophages
Question 107. Name the intranuclear inclusion bodies seen in herpes.
Answer: Lipschut
Question 108. Which is the most common virus infection in hum?
Answer: Herpes simplex
Question 109. Herpes virus Type I remain latent in which ganglion.
Answer: Trigeminal ganglion
Question 110. In which disease Tzanck cells are seen?
Answer: Herpes
Question 111. Name the virus causing chickenpox.
Answer: Varicella zoster
Question What does herpes zoster also know as?
Answer: Shingles and zona
Question 113. Name the largest virus of the herpes family.
Answer: Cytomegalovirus
Question 114. Name the virus causing mumps.
Answer: Paramyxovirus
Question 115. Warthin–Finkeldey giant cells are seen in which disease?
Answer: Measles
Question 116. Which disease is known as infective hepatitis?
Answer: Hepatitis A
Question 117. Which disease is known as serum hepatitis?
Answer: Hepatitis B
Question 118. Which is the most common mode of transmission of the hepatitis virus?
Answer: Parenteral
Question 119. Hepatitis B virus belongs to which family of viruses.
Answer: Hepadnaviridae family
Very Short Questions
Question 1. Define immunity.
Answer: Immunity is defined as state of resistance or insusceptible- ability which is exhibited by the host towards injury caused by microorganisms or their products. This is the collective effort of cells, tissues, and various molecules of the immune system to recognize and defend against infectious
disease.
Question 2. The selective medium for Mycobacterium tuberculosis is
Answer: Lowenstein-Jensen medium
Question 3. The diagnostic test for typhoid fever is
Answer: Widal test
Question 4. Defie pyemia and toxemia
Answer: Pyemia: It is septicemia caused by pyogenic bacteria with multiple abscesses in internal organs such as the spleen, liver, kidneys, etc.
- Toxemia: It is the condition where bacterial toxins circulate inside the blood.
Question 5. Clostridium tetani grown in which medium?
Answer: Robert’s cooked meat media
Question 6. What are the stages of syphilis?
Answer: Following are the stages of syphilis:
- Primary syphilis
- Secondary syphilis
- Tertiary syphilis
Question 7. Flagellae are organs for
Answer: Locomotion
Question 8. Enumerate diffrent immunoglobulins
Answer: Following are the immunoglobulins:
- IgG
- IgA
- IgM
- IgD
- IgE
Additional Information
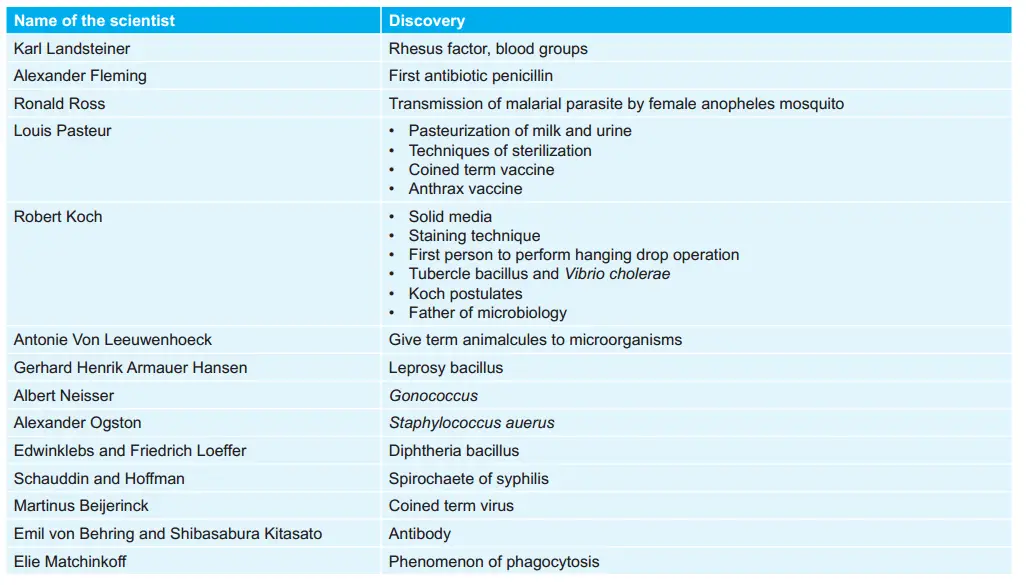
Scientists and their Discoveries:
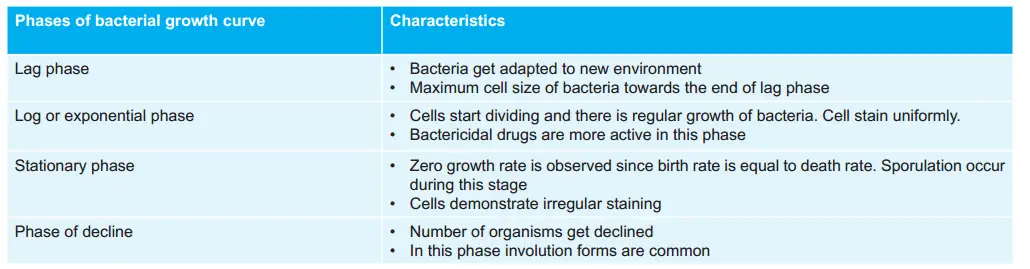
Various Phases of Bacterial Growth Curve:
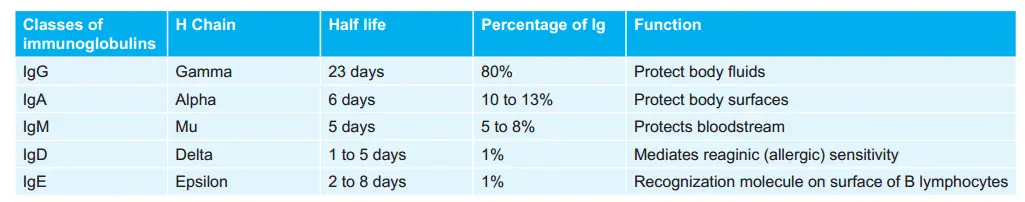
Various Immunoglobulins:
Various Types Of Staining:

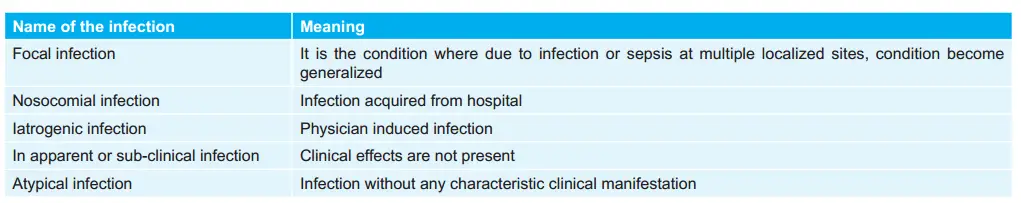
Types of Infections:
Various carriers:

Various cultural media and organisms are associated with:
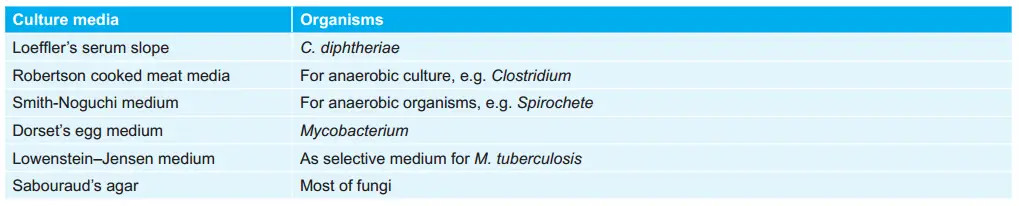
Shape and Arrangement of Various Bacteria:
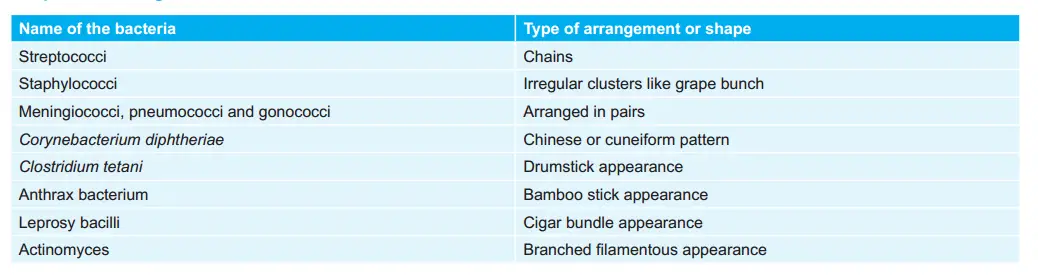
Various Materials and their Methods of Sterilization:
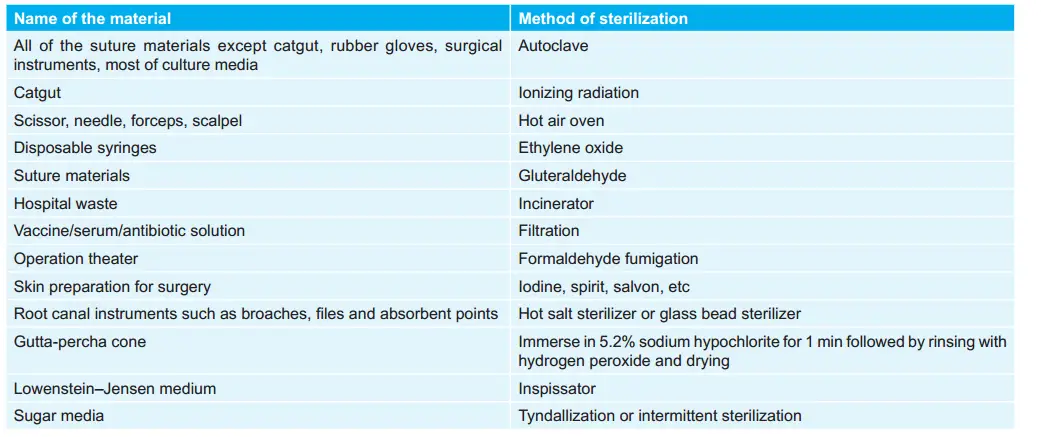
Pasteurization of Milk:
- Holder’s method: 63°C for 30 minutes
- Flash process: 72°C for 15 to 20 seconds
Various Interleukins and Names of Their Secreting Cells:
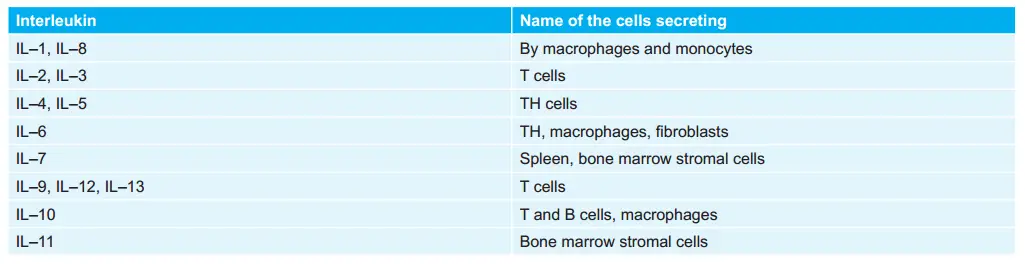
Various Interleukins and Names of Their Secreting Cells:

Name of Various Cytokines and their Functions:
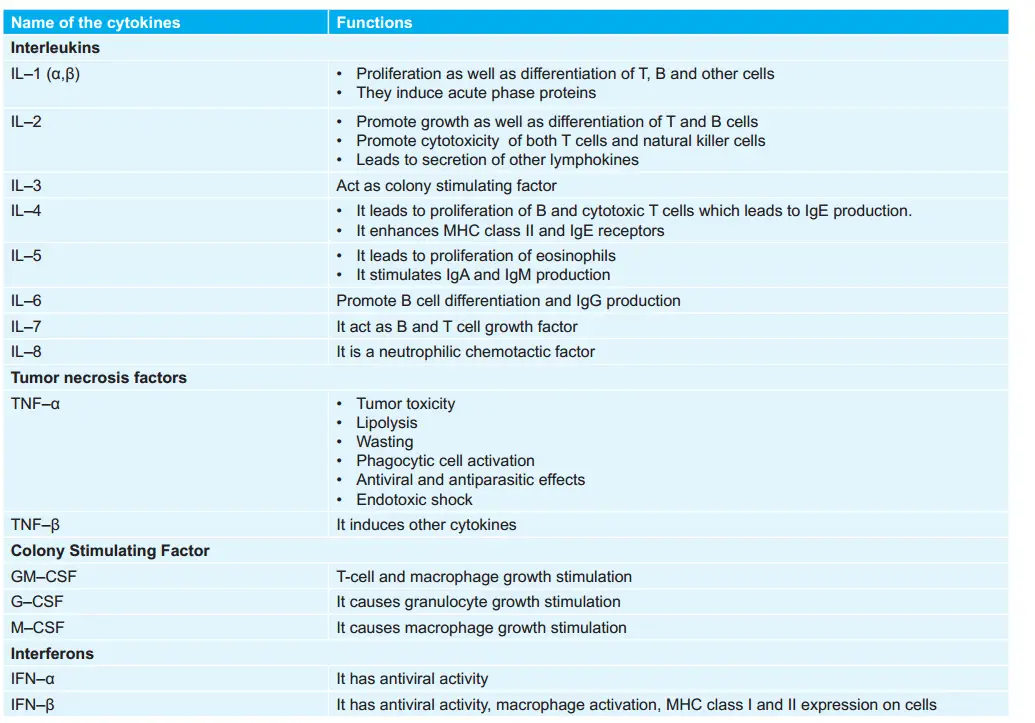
Various Tests and Category to which they belong:
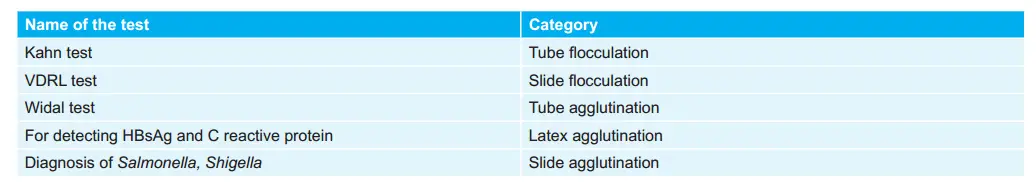
The differential between two bacteria by Various Tests:
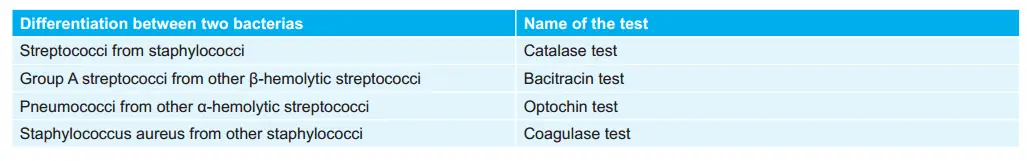
Identification Tests for Various Bacteria:
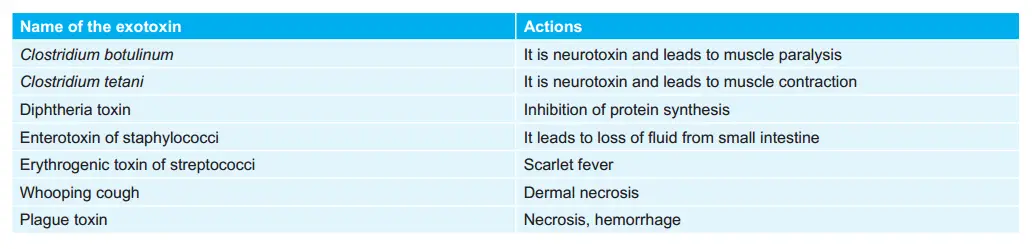
Various Exotoxins Produced By Bacteria and Their Actions:
Various Bacteria and their Growth in Various Environments:

Various Gram-positive and Gram-negative Microorganisms:

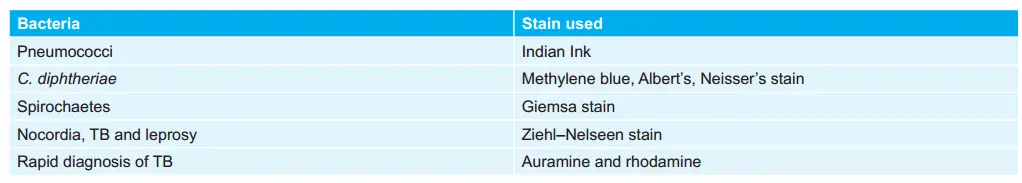
Various Bacteria and their Staining:
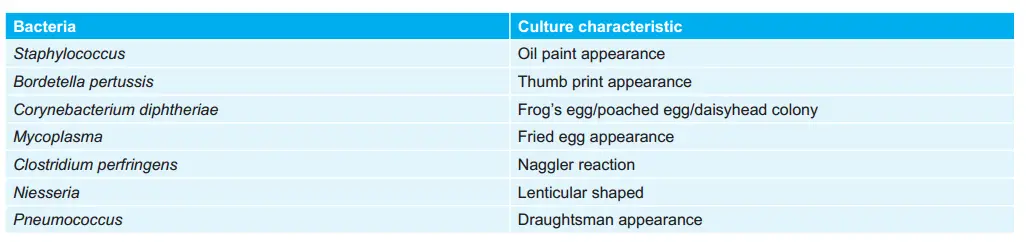
Various Bacteria and their Cultural Characteristic:
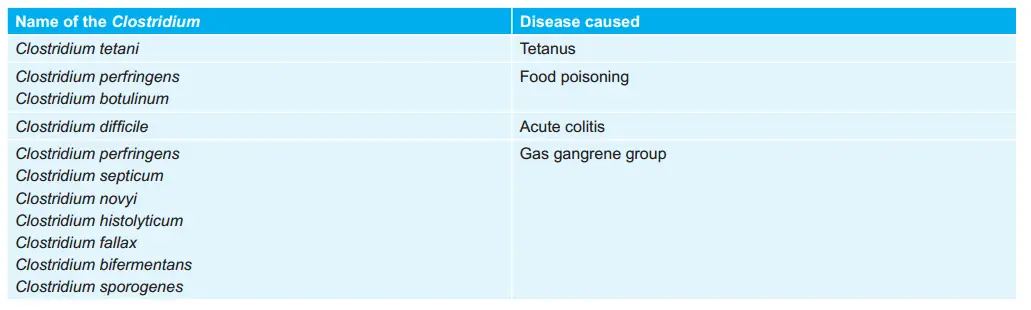
Various Clostridium and Diseases Caused by Them:
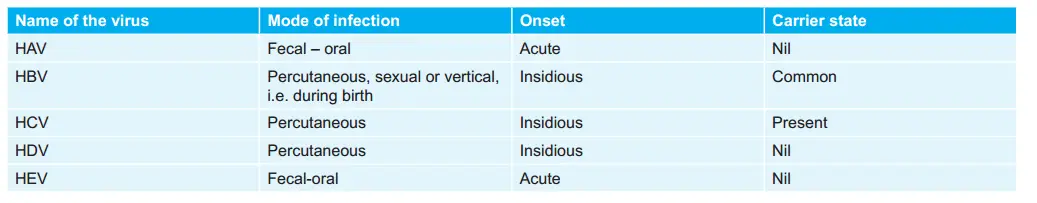
Various Hepatitis Viruses:
Various DNA Viruses:
- Poxviridae, for example, Smallpox, molluscum contagiosum
- Herpesviridae, for example, Herpes simplex, Varicella zoster, Epstein-B arr virus, cytomegalovirus
- Adenoviridae
- Papovaviridae (consists of single-stranded RNA), for example, Human papillomavirus
- Hepadnaviridae, for example, the Hepatitis B virus
- Parvoviridae, for example, Parvovirus
Various RNA Viruses:
- Picornaviridae, for example, Polio, Coxsackie, Rhinovirus, Hepatitis A
- Orthomyxoviridae, for example, Influenza
- Paramyxoviridae, for example, Measles, Mumps
- Reoviridae (consists of double-stranded RNA)
- Retrovirus, for example, HIV
- Togaviridae, for example, Rubella
- Rhabdoviridae, for example, Rabies virus
- Flaviviridae, for example, Hepatitis C and G
- Hepeviridae/calciviridae, for example, Hepatitis E
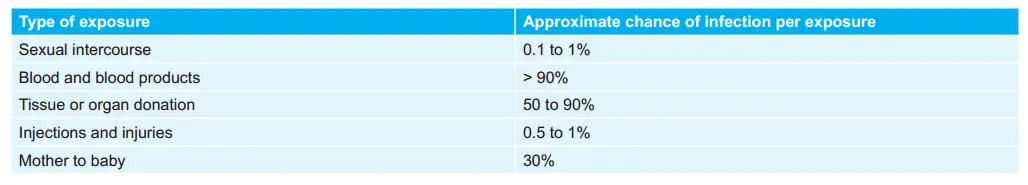
The tendency of Exposures that Carry Maximum Risk of Transmission of HIV:
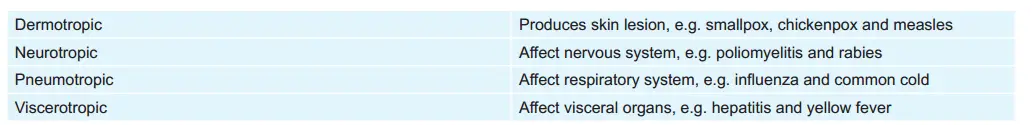
Classification of Human Viruses based on their Affinity to Different systems:
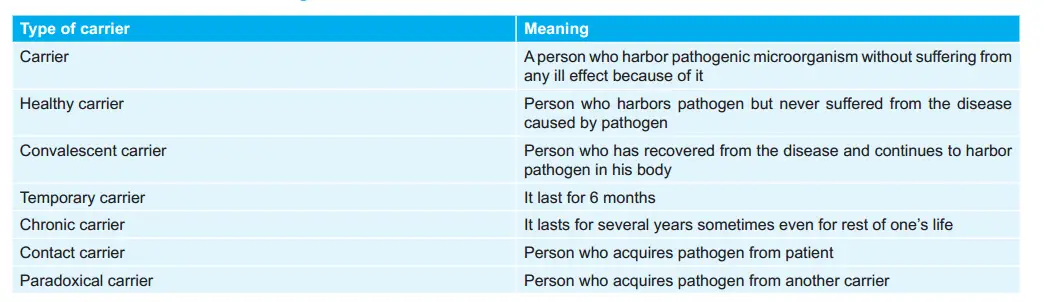
Various Carriers and their Meanings:
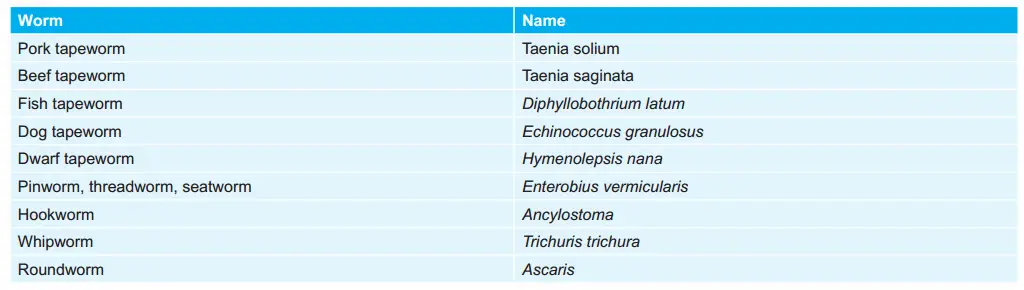
Various Worms and their Names:
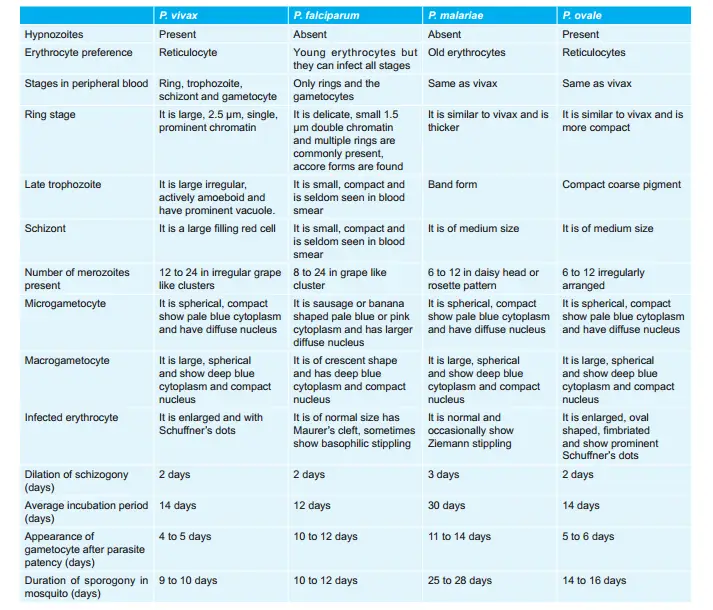
Characteristics of Various Plasmodia Leading to Malaria:
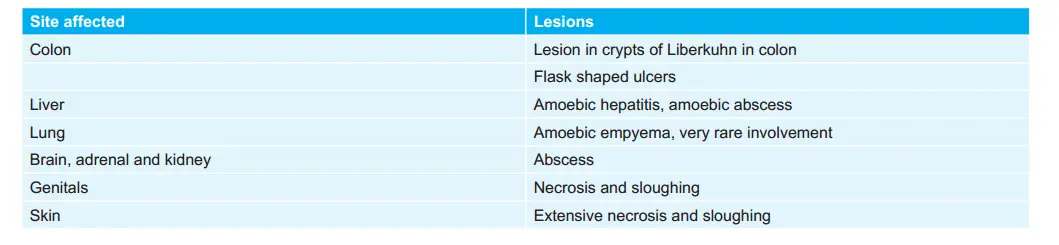
Sites Affected by Amoebiasis:
Various Arthopods and Diseases Caused by them:

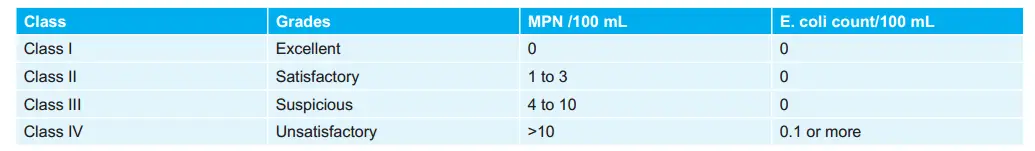
Drinking Water Classification as per Bacteriological Tests:
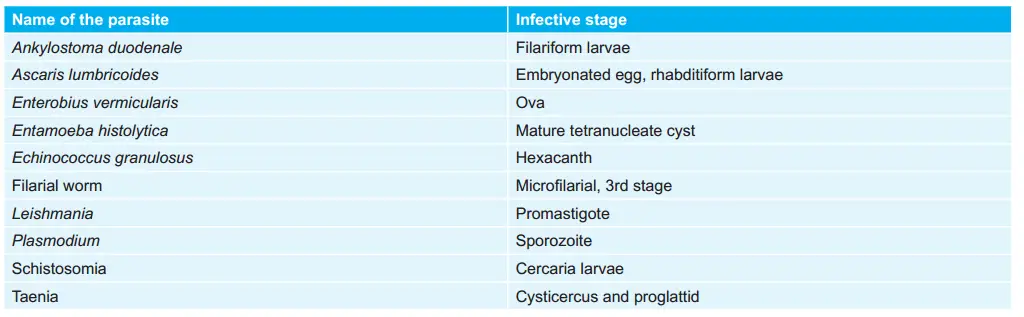
Important Microorganisms and diseases caused by them:
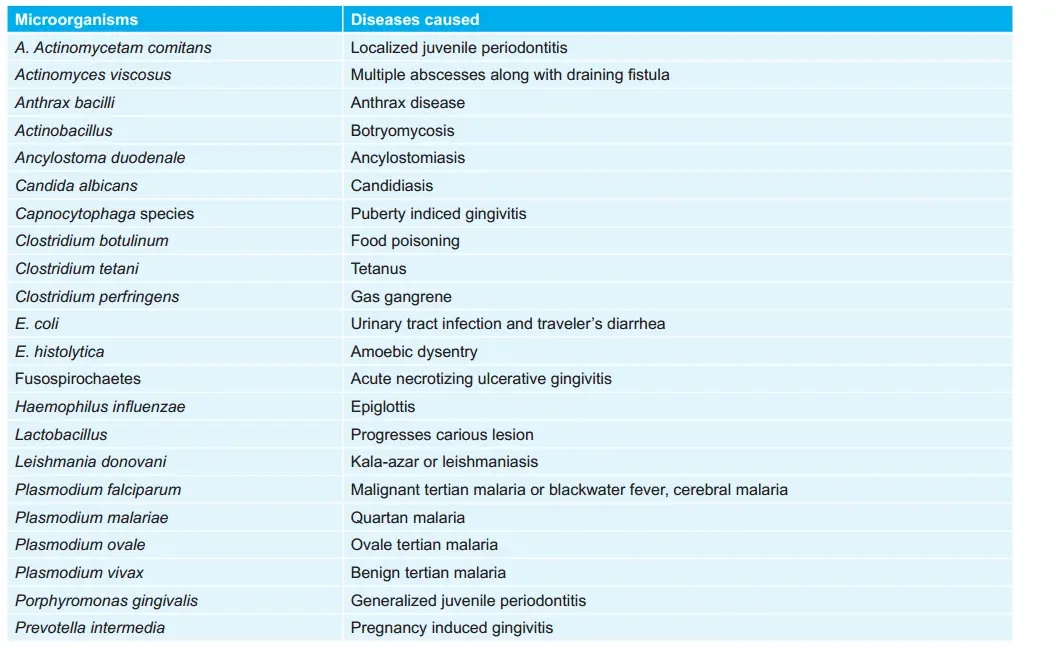
Various Diseases and their incubation periods:
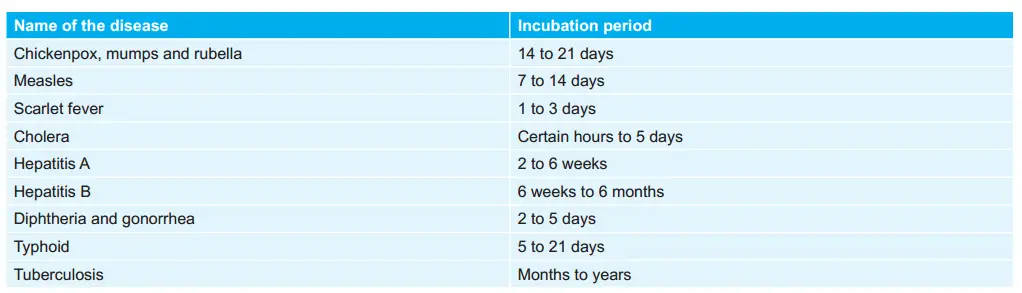
Inclusion Bodies and Organisms Associated with it:
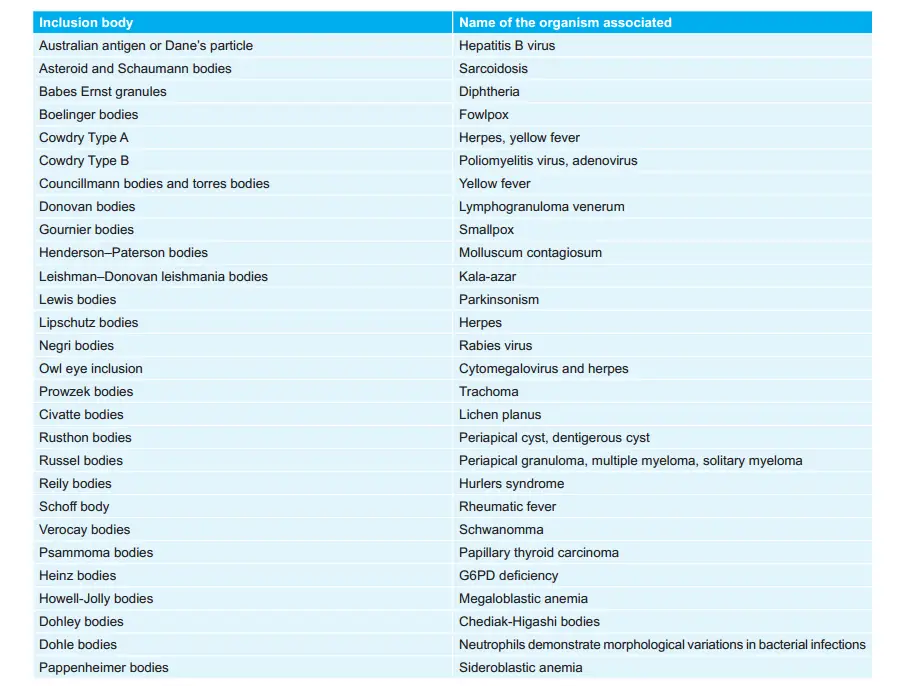
Infective Stages of Various Parasites:
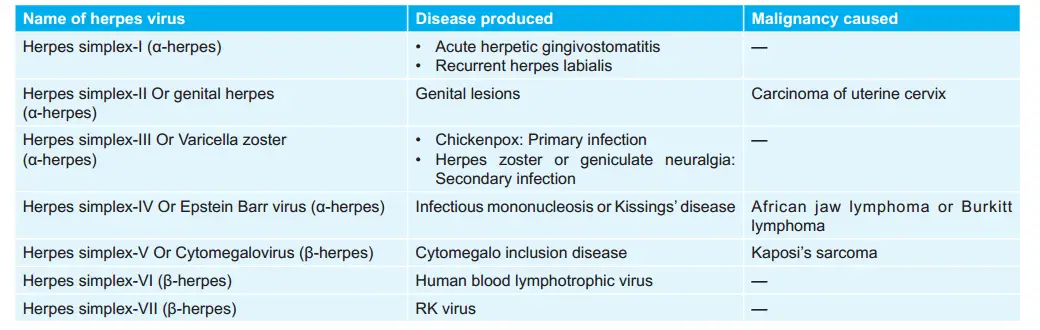
Types Of Herpes Viruses and Diseases caused by them:

Leave a Reply