Methods Of Gaining Space
Question 1. Write about methods of gaining space in orthodontics.
Or
Describe briefly various methods of gaining space in orthodontics.
Or
Describe different methods of gaining space in orthodontics.
Or
What are the various methods of gaining space in the arch. Discuss about proximal stripping in detail.
Answer. Methods of gaining space are divided into two types:
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Question And Answers
- Procedures with reduction of tooth material
- Proximal stripping or slicing
- Extraction.
- Procedures without reduction of tooth material
- Expansion
- Labial proclination
- Distalization of molars
- Derotation
Proximal Stripping
- It is also known as reproximation, standardization, disking and proximal slicing.
- Proximal stripping is a method by which the proximal surfaces of the teeth are sliced in order to reduce mesiodistal width of teeth.
Investigations of Proximal Stripping
Carey’s/Arch Perimeter Analysis
- It provides the amount of arch length deficiency.
- This is indicated in minimum discrepancy cases where arch length tooth size discrepancy is less than 2.5 mm.
Bolton’s Analysis
- Discrepancy between maxillary and mandibular tooth material causes failure of establishment of normal interarch relationship.
- This analysis reveals the area of tooth material excess.
- Depending on location of problem, proximal reduction should be done.
- If discrepancy is normal than only proximal stripping is done.
Diagnostic Set up
- It helps in localization of problem.
- It helps in disclosing the amount of enamel reduction
- It helps in locating the site where space is needed.
Intraoral Periapical Radiograph
- It discloses the amount of enamel reduction.
- Extent of pulp horn should be studied by using IOPA.
Peck and Peck Ratio
- When labiolingual and mesiodistal ratio is altered, crowding occurs.
- It is calculated by Peck and Peck ratio
Procedure of Proximal Stripping
Armamentarium
- Use of metallic abrasive strips
- Safe sided carborundum or diamond discs
- Long thin tapered fisure burs.
Proximal Stripping Procedure
- It is of two types, i.e. localized reduction and generalized reduction.
- Localized reduction should be carried out in upper and lower anterior teeth.
- At times generalized interproximal reduction is done in moderate space discrepancy cases.
- Contact points are converted to contact areas taking care to establish proper contact between teeth.
- Not more than 50% of enamel thickness should not be reduced by the method of proximal stripping and is equally distributed all over the teeth.
- After inter – proximal reduction topical floride application should be done. This is done to reduce post proximal slicing sensitivity and to reduce the caries attack.
Proximal Stripping Advantages
- Proximal stripping establishes normal interarch relationship in patient with Bolton’s discrepancy.
- As contact area is wide, lower incisors remain stable in their new position. Contact points should be converted to contact areas which prevent slipping of contact.
- Extractions should be avoided
- Minor intraarch problems are corrected by proximal slicing.
Proximal Stripping Disadvantages
- It leads to hypersensitivity.
- Chances for proximal caries are more.
- Deposition of plaque and calculus causes gingivitis.
- Improper proximal reduction leads to loss of normal contact between teeth which results in impaction of food.
- If shape of tooth is grossly altered there is altered esthetics.
Proximal Stripping Indications
- It is indicated when the space required is minimum, i.e. 0 to 2.5 mm. In such cases it is possible to avoid extraction of teeth by performing reproximation.
- If Bolton’s analysis show mild tooth material excess in either of arches, it is possible to reduce tooth material by proximal stripping.
- It can be undertaken in lower anterior region as aid to retention.
- It is also indicated in cases where the individual tooth size prevent class I molar and canine relationship.
- For obtaining favorable overbite and overjet.
Proximal Stripping Contraindications
- It is not carried in young patients as they have large pulp chambers which increase risk of pulpal exposure.
- In patients susceptible to dental caries or those who have high caries index.
- On small teeth and teeth with enamel hypoplasia slenderization is avoided.
- It is avoided in the patients who refuse to accept slenderization as the treatment option.
- In patients with poor oral hygiene and high bacterial plaque index.
Proximal Stripping Expansion
- It is usually a non-invasive method of gaining space.
- It is usually undertaken in patient having constricted maxillary arch or in cases having unilateral or bilateral cross bite.
- Expansion is of two types i.e. skeletal or dentoalveolar.
- Skeletal expansion involves splittng of the midpalatine suture while the dentoalveolar expansion leads to the dental expansion with no skeletal change.
- Expansion is brought about by various appliances that incorporate jack screws or by use of springs.
Proximal Stripping Extraction
- Extraction of one or more teeth is undertaken as a part of orthodontic treatment called “therapeutic extraction”.
- Premolars are most frequently extracted teeth.
- Extraction of one premolar from each quadrant of the jaw provides suffient space to correct the confronting problem (crowding on proclination).
Proximal Stripping Distalization
- Distalization procedures are aimed at moving the molars in a distal direction so as to gain space.
- This approach is becoming popular due to the fact that extraction can be avoided.
- Distalization can be Brought About by Extraoral Method and Intraoral Method.
Proximal Stripping Extraoral Method
- Head gear deriving anchorage from the cervical or cranial region can be used to distalize molars.
- Head gear consists of face bow which is made up of an inner and an outer bow.
- Inner bow is attached to the buccal tubes present on molars and the outer bow is attached to the extraoral head cap or neck strap.
Intraoral Methods
These appliances are fied on teeth and therefore produces a continuous effct, e.g.
- Sagittal appliance—Removable appliances incorporating jack screw.
- Appliance consists of split acrylic plate joined together by a jack screw.
- These appliances are retained using Adam’s clasps on the molar and premolars.
- Distalization using intraoral magnets-
- These devices consist of repelling magnet placed on the molar to be distalized and tooth anterior to it.
- Use of open coil spring to distalize molars, i.e. Pendulum appliance.
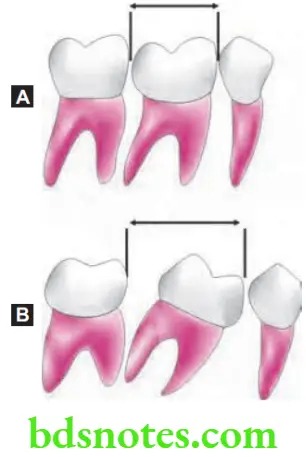
Uprighting of Molars
- By uprighting tipping molars certain amount of space can be recovered.
- Molar can be made upright by using molar uprighting springs or some form of space regainer.
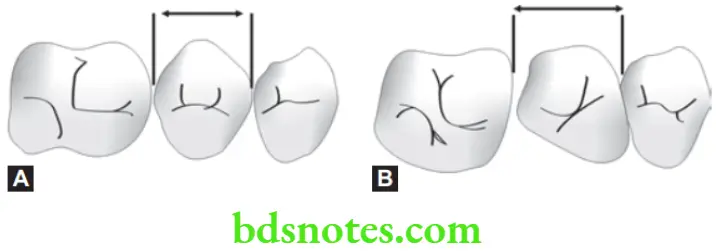
Derotation of Posterior Teeth
- Rotated posterior teeth occupy more space than normally placed posterior teeth.
- Derotation is best achieved with fixed appliances incorporating spring or elastics using a force couple.
Proclination of Anterior Teeth
- It is done in patients whose nasolabial angle is obtuse.
- It is also carried out in retroclined incisors.
Question 2. What are the various methods of gaining space in orthodontics? What do you think is the best method, justify your statement?
Answer.
Distalization
Distalization of molars is the best method to gain expansion.
- This method has gained a vast popularity as it was sometimes difficult to convince the patient for extraction of otherwise healthy teeth.
- The best time for molar distalization is during the mixed dentition period
- Basically, the procedures involved have one purpose, i.e. to push the maxillary and/ or mandibular terminal molars posteriorly.
- This increases the arch length by the same length as the amount of distalization achieved.
- The distalization procedures are usually undertaken before the eruption of the second permanent molars.
- It is definitely much easier to move one molar distally as compared to two (i.e. fist and second permanent molars).
- The appliances used for the purpose of distalization of molars can be classifid as Extraoral distalizing appliances and Intraoral distalizing appliances.
- Advantages of distalization of molars are that it helps in avoiding the extraction and it prevents collapse of arch.
Question 3. Write short note on expansion of arches for space gaining in orthodontics.
Answer. Expansion of arches is a noninvasive method of gaining space.
- It is usually undertaken in patient having constricted maxillary arch or in patient with unilateral or bilateral crossbite.Expansion can either be skeletal or dento-alveolar.
- Skeletal expansion involves splittng of the midpalatine suture while dentoalveolar expansion produces dental expansion with no skeletal change.
- Expansion is brought about by various appliances that incorporate jack screws or by use of springs.
Types of Expansions
They are of three types i.e.
- Orthodontic/dentoalveolar: It leads to dental expansion
- Result from the intrinsic forces exerted by the tongue.
- Skeletal/orthopedic: It results from splitting of midpalatal suture.
Type of Expansion Appliances
They are of two types i.e. maxillary and mandibular:
- Maxillary
- Slow
- Removable: For example, Coffin spring and Active plate with Screws or Z-springs
- Fixed: For example, W-arch, Quad helix, Fixed appliances with expansion screws
- Rapid
- Banded RME: For example, Hass, Isaacson, Derichsweiler
- Bonded RME: For example, Cast metal/acrylic splints
- Slow
- Mandibular: For example, Lower Schwarz plate.

Leave a Reply