Mechanical Properties Of Dental Materials
- Stress: Force per unit area within a structure subjected to an external force on pressure.
- Shear stress: Ratio of force to the original cross-sectional area parallel to the direction of the force applied to a test specimen.
- Tensile stress: Ratio of tensile force to the original cross-sectional area perpendicular to the direction of applied force
- Compressive stress: Ratio of compressive force to cross-sectional area perpendicular to the axis of applied force
- Strain: Change in length per unit initial length.
- Elastic Strain: Deformation that is recovered upon removal of an externally applied force or pressure.
- Plastic strain: Deformation that is not recoverable when the externally applied force is removed
- Strength: Maximum stress that a structure can withstand without sustaining a specific amount of plastic strain or stress at the point of fracture.
- Tensile strength: Tensile stress at the point of fracture.
- Yield strength: The stress at which a test specimen exhibits a specific amount of plastic strain.
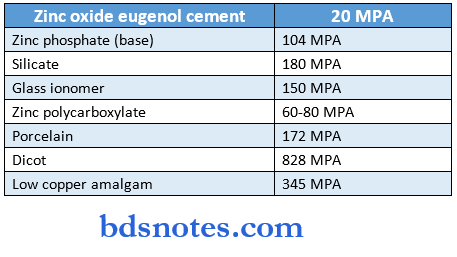
- Compressive strength: Compressive stress within a compression test specimen at the point of fracture.
- Elastic modulus or Young’s modulus: Relative stiffness of material or ratio of elastic stress to elastic strain.
- Proportional limit: Maximum stress at which stress is directly proportional to strain and above which plastic deformation occurs.
- Resilience: The relative amount of elastic energy per unit volume released on unload- ing of a test specimen
- Ductility: Relative ability of a material to deform plastically under tensile stress before it fractures.
- Malleability: Ability of a material to sustain considerable permanent deformation without rupture under compressions as in hammering or rolling into a sheet. Gold is the most ductile and malleable pure metal., 2nd silver.
- Brittleness: Relative to the ability of a material to deform plastically.
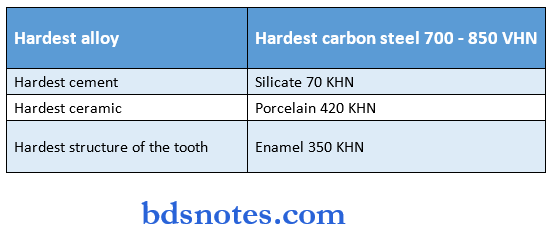
- Hardness: Resistance of a material to plastic deformations typically measured under an indentation load.
- Toughness: Ability of a material to absorb elastic energy to deform plastically before Fracturing.
- Average max. sustainable biting force is approximately 756 N (170 Pounds)
Classification: based on:
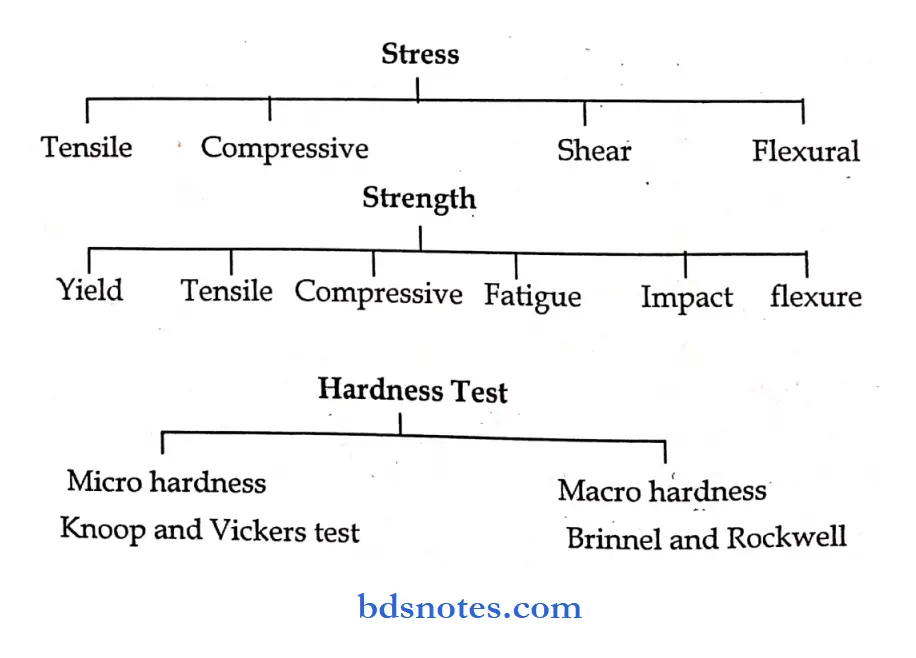
Hard ness:
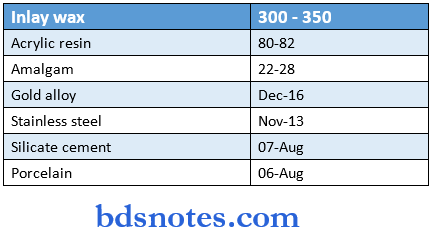
Compressive strength:
Linear coefficient of thermal expansion(X10-6/0c)
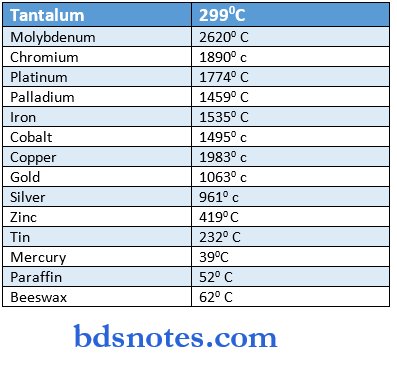
Melting Points


Leave a Reply