Question 1. Maxillary sinus.
Answer:
Maxillary sinus Definition:
- The maxillary sinus is the pneumatic space that is lodged inside the body of the maxilla and communicates with the environment by way of the middle meatus and the nasal vestibule.
Maxillary sinus Anatomy:
- The maxillary sinus is a four-sided pyramid in structure.
- Base – faces medially towards the nasal cavity.
- Apex – faces laterally toward the body of the zygomatic bone.
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
Maxillary sinus Sides:
- Anterior – facial surface of maxilla.
- Inferior – alveolar and zygomatic process of maxilla.
- Superior – orbital surface of the maxilla.
- Posterior – infratemporal surface and meet at an obtuse angle.
Recesses: Expansion of processes of the maxilla that have become invaded by air space. They are
-
- Zygomatic recess
- Frontal recess
- Alveoloplatine recess.
Maxillary sinus Histology:
- The maxillary sinus is lined by a mucosa that is firmly bound to the underlying periosteum.
- Layers lining the space of the maxillary sinus are
- Epithelial layer
- Basal layer
- Subepithelial layer.
Maxillary sinus Cells:
- Basal cells
- Columnar nonciliated cells.
- Mucous-producing secretory goblet cells
- Ciliated cells.
- myoepithelial cells.
Maxillary sinus Functions:
- Olfactory function
- Respiratory function
- Resonance of voice
- Lightening of skull weight
- Humidification of air
- Enhancement of the faciocranial resistance to mechanical shock.
- Bacteriocidal activity.
Maxillary sinus Relations:
- Roof – infraorbital nerve.
- Anterior – anterosuperior alveolar nerve.
- Lateral – middle superior alveolar nerve
- Posterior – posterosuperior alveolar nerve
- Posteromedial – greater and lesser palatine nerve
- Floor- roots of maxillary posterior teeth.
Question 2. Write briefly about the functions of the maxillary sinus.
Answer:
Functions of the maxillary sinus:
1. Olfactory and respiratory function.
- It is due to the maxillary sinus being regarded as an accessory space to the nasal cavity.
2. Humidification of air.
- It is due to the presence of ostium.
- Ostium may be large, situated in the hiatus semilunaris or it may be small, hidden in the depth of hiatus semilunaris.
3. Protects internal structures like the brain and eyeball.
- Air is arrested in the sinus which is then brought to body temperature.
- As a result, the sinus protects the internal structure from exposure to cold.
4. Bacteriocidal activity.
- The maxillary sinus produces bacteriocidal lysozyme in the nasal cavity.
5. Resonance of voice.
6. Lightening of skull weight.
7. Enhancement of faciocranial resistance to mechanical shock.
Question 3. Boundaries of the maxillary sinus
Answer:
The maxillary sinus is a four-sided pyramid
- The anterior-facial surface of the body of the maxilla
- Inferior – alveolar and zygomatic processes
- Superior – orbital surface
- Posterior – infratemporal surface
- Base – faces medially towards the nasal cavity
- Apex – faces laterally towards the body of the zygomatic bone
Question 4. Maxillary sinus. (or) Functions of the maxillary sinus.
Answer:
Synonym: Antrum of Highmore
maxillary sinus Definition:
- It is the pneumatic space that is lodged inside the body of the maxilla and communicates with the environment by way of the middle meatus.
maxillary sinus Anatomy:
- It is pyramidal in shape with a base facing nasal cavity and apex facing zygomatic bone.
maxillary sinus Nerve supply:
- Superior alveolar nerve
- Infraorbital nerve
- The greater palatine nerve.
maxillary sinus Blood supply:
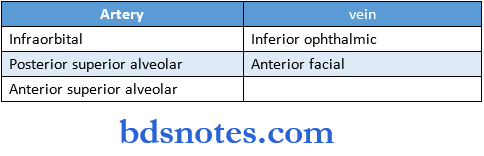
Question 5. The lining of the maxillary sinus.
Answer:
The maxillary sinus is lined by 3 layers.
1. Epithelial layer.
- It is pseudostratified, columnar ciliated.
- It contains basal cells, columnar nonciliated cells, and goblet cells.
2. Basal layer
3. Subepithelial layers.
- It consists of blood capillaries, fibroblasts, fibrocytes, collagen bundles, and other connective tissue elements.
Question 6. Goblet cells.
Answer:
- They are mucous-producing secretory cells.
- Basal segment – it contains the nucleus
- Cytoplasm. It contains rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus.
- Zymogenic granules transport the mucopolysaccharide produced by the Golgi apparatus to the epithelial surface.
Question 7. Anomalies of the maxillary sinus.
Answer:
- Agenesis, aplasia, hypoplasia.
- They are a rare condition.
- Often associated with anomalies involving the face or palate.
- Supernumerary sinuses.
- It is a condition of occurrence of two completely separated sinuses on the same side.
- Results due to out pocketing of the nasal mucosa.
- Associated with other disorders.
- In pituitary gigantism, it appears large.
- In congenital syphilis, it is suppressed.

Leave a Reply