Management Of Open Bite And Deep Bite
Question 1. Give causes and brief treatment planning on deep bite.
Or
Write briefly on management of deep bite.
Answer. The maxillary dental arch being larger than mandibular arch allows the maxillary anterior to overlap the mandibular anterior.
- Excessive vertical overlapping of the mandibular anterior by maxillary anteriors is called deep bite.
- Deep bite can be skeletal or dental type. Deep bite is a condition of excessive overbite, where the vertical measurement between maxillary and mandibular incisal margins is excessive when mandible is brought into the habitual or centric occlusion.
Etiology
Causes of Skeletal deep bite
This is caused due to the convergent rotation of skeletal jaw bases. The upward and forward rotation of mandible and as well downward and forward inclination of the maxilla leads to deep bite.
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Question And Answers
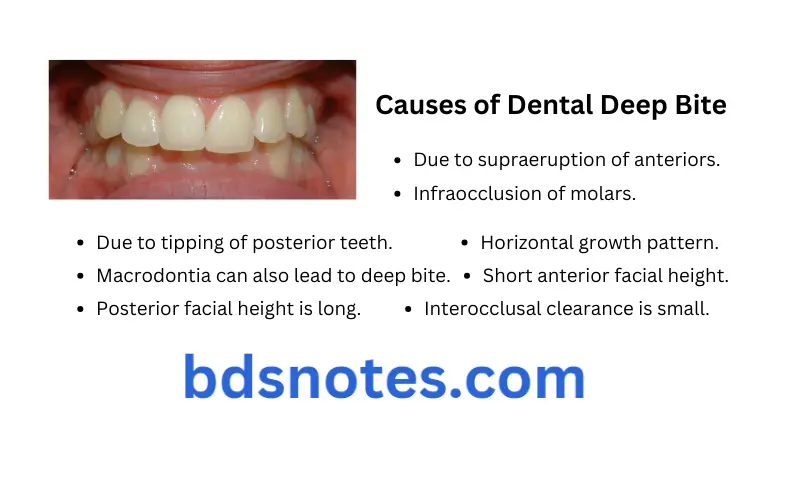
Causes of Dental deep bite
- Due to supraeruption of anteriors.
- Infraocclusion of molars.
- Due to premature loss of permanent teeth which leads to lingual collapse of anterior teeth.
- Due to tipping of posterior teeth.
- Macrodontia can also lead to deep bite.
- Horizontal growth pattern.
- Short anterior facial height.
- Posterior facial height is long.
- Upper facial height to lower facial height decreases.
- Interocclusal clearance is small.
Treatment of Deep Bite
Deep bite is treated by using removable, fixed or the myofunctional appliances
Removable appliances
- Anterior bite plane is the most commonly used appliance for treating the deep bite.
- Anterior bite plane is the modifid Hawley’s appliance with the flat ledge of an acrylic behind maxillary anteriors.
- As patient bites, mandibular incisors contact the bite planeand disclose the posteriors which are free to erupt.
- Height of anterior bite plane is just enough to separate the posteriors by 1.5 to 2 mm as posterior teeth erupts the height of bite plane increases.
Myofunctional Appliances
- Deep bite due to the infra-occlusion of molars can be treated by using the activator or the bionator.
- Design of the functional appliance is modified to allow extrusion of posterior teeth.
Fixed Appliances
Fixed orthodontic appliances may be used to intrude the anterior teeth
Anchor Bends
- Anchorage bends should be given in arch wire mesial to the molar tubes so the anterior part of arch wire lies gingival to the bracket slot.
- When the arch wires are pulled occlusally and engaged inside the brackets, a gingivally directed intrusive force is exerted on the incisors, which decreases the deep bite.
Arch Wires with Reverse Curve of Spee
- They intrude the anterior teeth.
- When there wires are inserted in molar tubes, anterior segment curves gingivally.
- Anterior segment is forced occlusally inside the bracket slot resulting in an intrusive force on incisors.
Use of Intrusion Arches
- Intrusion arch consists of two posterior stabilizing units in buccal segments which are made up of .0175 × .025 inch stainless steel wire.
- Anterior segment which consists of incisors is given a segmental wire of similar diameter.
- Intrusion arch is cantilever types of spring which is inserted into the auxiliary tube of molar tube and bypasses the premolars and the canines.
- It should given a 30 degree bend anterior to molar tube so that its anterior segment lies passively at depth of vestibule.
- Anterior segment is brought down incisally and is tied to anterior segment arch wire which causes intrusion of anteriors.
Role of Headgears in Treatment of Deep Bite
- Deep overbite due to overeruption of maxillary anterior teeth and be corrected by high pull headgear attached to the anterior segment of arch wire in attempt to intrude these teeth.
- Cervical headgear with downward vector if force increase lower facial height by extruding the molars.
Temporary Anchorage Device or Mini Screws in Treatment of Deep Bite
- Maxillary incisors are intruded by placing temporary anchorage devices or mini screws between upper lateral incisors and canines.
- Placement of these mini screws is delayed till leveling and alignment is complete to enable the adequate interradicular bone at the site of their placement.
Question 2. Give etiology and treatment modalities of anterior open bite.
Answer. Anterior open bite is a condition where there is no vertical overlap between upper and lower anterior.
Classification of anterior open bite
It is classified as:
- Skeletal anterior open bite: Open bite which develops due to the excessive vertical growth.
- Dental anterior open bite: They may close spontaneously in growing patient and are generally amenable to orthodontic treatment.
Etiology
- Digit sucking habits: Prolonged thumb sucking leads to open bite. A typical thumb sucker has malocclusion characterized by an asymmetric anterior open bite because of digit position and transverse constriction of maxillary arch due to lowered tongue posture. Thumb or a figer acts as a barrier and prevent the eruption of incisors and during same time allowing excessive eruption of posterior teeth.
- Lip and tongue habits: Habitual tongue thrusting leads to proclination and flring of upper anterior which causes anterior open bite.
- Airway obstruction: the most important factor is nasopharyngeal airway obstruction and the associated mouth breathing. Facial appearance of such patient is referred to as adenoid facies. In these, cheeks and nostrils are narrow, nostrils are pinched, lips are separated and there is exaggerated shadow beneath the eyes. They also have protruding teeth, an open mouth and dull expression.
- Skeletal growth abnormality: Various inherited factors such as size of tongue, abnormal skeletal growth pattern of maxilla and mandible leads to open bite. Genetic as well as the environmental factors which encourage the vertical growth in molar region are not compensated by growth at condyle or posterior ramus, this leads to anterior open bite.
- Iatrogenic causes: This is due to poor mechanics during fied appliance treatment which leads to extrusion of molar teeth or hanging palatal cusps, which opens the bite.
- Pathological causes: The causes are clef lip and palate, acromegaly or trauma to facial skeleton i.e. condylar fractures or Le Fort fractures of maxilla.
- Muscular dystrophy: Decrease in the tonic muscle activity which occur in the muscular dystrophy allow the mandible to rotate downward which lead to increase in anterior facial height, posterior growth rotation of mandible, excessive eruption posterior teeth, narrowing of maxillary arch and anterior open bite.
Clinical Features of Anterior Open Bite
Clinical Features of Skeletal Anterior Open Bite
- Increase in the lower anterior facial height.
- Increase in anterior and decrease in posterior facial height.
- Presence of steep mandibular plane angle.
- Patient often have long and the narrow face.
- Patient can have short upper lip with the excessive maxillary incisor exposure.
- Patient tends to have Class 2 malocclusion and mandibular deficiency.
- In some of the cases, upward tipping of maxillary skeletal base is observed.
Clinical Features of Dental Anterior Open Bit
- Maxillary anterior teeth are proclined.
- Patient may have narrow maxillary arch due to lowered tongue posture.
- Spacing may be seen in maxillary and mandibular anterior arches.
Cephalometric Features of Anterior Open Bite
- It reveals downward and backward rotation of mandible.
- Presence of upward tipping of maxillary skeletal base.
- Vertical maxillary increase is present.
- Presence of steep palatal plane and increased percentage of lower facial height.
- Excessive eruption of maxillary posterior teeth.
- Excessive eruption of maxillary and mandibular incisors.
- Cephalometric planes are divergent.
Treatment of Anterior Open Bite
- Removal of cause: Use a removable or fixed habit breaking appliance. E.g. palatal crib is used to intercept the habit.
- Myofunctional therapy: Skeletal anterior open bite at growth period should be treated with functional appliances such as Frankel IV or modified activator, which incorporates the bite block interposed between posterior teeth which has intrusive action on both upper and lower posterior teeth.
- Orthodontic therapy: Cases with mild to moderate open bites are managed successfully by the fixed orthodontic therapy along with box elastics, which brings extrusion of upper and lower anterior. Cases with severe skeletal open bite should not be treated by this method.
- Surgical correction: Skeletal open bites in adult are best treated by the surgical procedures which involve both maxilla and mandible.
Question 3. Write short note on open bite.
Or
Write briefly on open bite.
Or
Write short note on apertognathia.
Answer. Open bite is descriptive of a condition where a space exist between the occlusal or incisal surfaces of maxillary and mandibular teeth in buccal or anterior segments when mandible is brought in habitual or centric relation. Graber
Apertognathia is also known as open bite.
Classification of Open Bite
- Anterior open bite
- Skeletal
- Dental
- Posterior open bite
Posterior Open Bite
It is characterized by the lack of contact between posterior teeth nwhen teeth are brought in centric occlusion.
Etiology
- Mechanical interference with eruption
- Ankylosis of tooth because of trauma.
- Obstacles in eruption such as supernumerary teeth, non-resorbed deciduous tooth roots and the pressure from soft tissues which is interposed between the teeth.
- Due to failure of eruption mechanism of tooth.
Treatment
Here removal of etiological factors is the primary aim.
- In cases of lateral tongue thrusting habit, habit breaking appliance is given followed by removable or fixed orthodontic treatment.
- In cases of ankylosed teeth correction is done by forced extrusion of antagonistic teeth using fied orthodontic appliance or restoring normal occlusal level using crowns on submerged teeth.
Question 4. Definition, features, diagnosis and treatment of dental deep bite.
Answer. Dental deep bite is confied to the dentition where there is extrusion of anteriors and intrusion of molars. Dental deep bite is oftn seen in Angle’s class 2 division 2 malocclusion.
Features
- Extraoral Features
- Decrease in lower facial height
- Intraoral Features
- Increase in the overbite
- Decrease in the overjet
- Extruded maxillary anteriors
- Intruded maxillary posteriors
- Increased susceptibility to food impaction and resultant gingivitis in mandibular anterior region.
Diagnosis
Dental deep bite occurs when problem lies within the dentition. Extraoral and intraoral examinations of patients should be thoroughly done and history of oral habits is noted. Following are the diagnostic aids used:
- Clinical examinations.
- Orthodontic study models: To evaluate extent of severity of deep bite.
- Lateral cepahlograms: To evaluate height of ramus, interincisal angle and Frankfort mandibular plane angle.
- Here patient show decreased mandibular plane angle and decreased anterior facial height.
Extrusion
- Anterior bite plane is a modified Hawley’s appliance with a flat ledge of acrylic behind upper anteriors.
- Both removable and fied anterior bite planes are used.
- When patient bites, the mandibular incisors contact the bite plane thus distocclusion the posteriors which are free to erupt.
- Height of anterior bite plane should be such that it separates the posteriors by 1.5 to 2 mm.

Leave a Reply