Management Of Cross Bite
Question 1. Give the etiology and treatment modalities of incisor crossbite.
Answer. Crossbite is defied as the condition where one or more teeth may be abnormally malposed buccally or lingually or labially with reference to the opposing tooth or teeth. Graber
Etiology of Incisor Crossbite
Skeletal Factors
Skeletal incisor crossbite results due to excessive mandibular growth. It is genetic or inherited malocclusion.
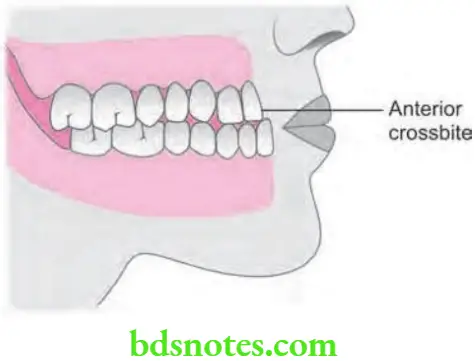
Dental Factors
- A dental incisor crossbite is because of abnormal axial inclination of the maxillary incisors.
- Abnormal axial inclination is due to following factors, i.e.
- Inadequate arch length which leads to lingual eruption of permanent tooth.
- Labial position of supernumerary tooth.
- Over retained primary tooth.
- Lip biting habit.
- Trauma to primary teeth or to the permanent tooth bud.
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Question And Answers
Functional Factors
An incisor crossbite also occurs due to functional interference of the mandible during closure. It is due to premature tooth contact and results in peudo-class 3 malocclusion.
Treatment of Incisor Crossbite
Correction of incisor Crossbite in the preadolescent age group
Following appliances are used:
- Tongue Blade
- Tongue blade therapy is used to treat the developing incisor crossbite by placing the wooden tongue blade behind the tooth in crossbite at an angle of about 60 degrees to the occlusal plane. The patient should exert force by biting on it using the lower teeth as a fulcrum for a period of 5-10 minutes. Usually the tooth will erupt into normal position over a period of time.
- Catalan’s Appliance or Lower Anterior Inclined Plane
- Catalan’s appliance is also called as “lower anterior inclined plane”, which explains the design of this appliance. Catalan’s appliance consists of an inclined plane cemented to the lower incisor.
- Fabrication
- Acrylic resin or cast metal is used to fabricate Catalan’s appliance. The lower anterior inclined plane is designed in such a way that, it is at 45 degree angle to the maxillary occlusal plane. Catalan’s appliance can be fabricated on a single lower anterior tooth for the correction of single tooth crossbite or for the whole anterior segment.
- Removable Orthodontic Appliances
- Removable orthodontic appliances with “z” spring. Incisor crossbite involving one or two maxillary teeth can be treated by using a double cantilever spring or “z” spring.
- In case of single tooth incisor crossbite, “Z” spring on tooth involved in crossbite can be used for correction of such a condition.
- In case of anterior crossbites involving two teeth in crossbite, “Z” spring on two teeth is used to correct the anterior crossbite by involving group of teeth by labial movement.
- Removable orthodontic appliances with expansion screw:
- Removable orthodontic appliance incorporates expansion screw of various types, which can be used to correct either single tooth crossbite or segmental tooth crossbite.
- Removable orthodontic appliances with “z” spring. Incisor crossbite involving one or two maxillary teeth can be treated by using a double cantilever spring or “z” spring.
- Orthopedic Appliances
- Face mask along with RME
- Face mask (reverse headgear) is used in the treatment of skeletal anterior crossbite during growth period, before cessation of growth. Face mask helps in protraction of the retrognathic premaxilla, thereby normalizing the skeletal crossbite.
- Chin-cup appliance
- Chin-cup appliance is one of the orthopedic, orthodontic appliance and is used to redirect the growth of the mandible to prevent or correct the anterior crossbite due to excessive mandibular growth. Chin cup appliance tends to rotate the mandible posteriorly and inferiorly.
- Face mask along with RME
- Myofunctional Appliances
- Frankel 3 appliance may be used to correct a developing class 3 skeletal jaw in relation with anterior crossbite.
Correction of Incisor Crossbite in Adolescent and Adults
Removable orthodontic appliance incorporated expansion screw of either mini or medium, which may also be used to correct anterior crossbite; involving single tooth or group of teeth in adults.
- Removable orthodontic appliances
- Removable orthodontic appliances with mini screw:
- Removable orthodontic appliance with incorporated mini screw type of expansion screw, which are used to correct the anterior crossbite involving up to two teeth in crossbite.
- Removable orthodontic appliances with medium screw:
- Removable orthodontic appliance with incorporated medium screw can be used to treat anterior crossbite involving up to 4-6 teeth in crossbite.
- Removable orthodontic appliances with 3D screw:
- Removable orthodontic appliance with incorporated three-dimensional expansion screws in the midline can be used in the treatment of anterior crossbite associated with pseudo class 3 malocclusion.
- Removable orthodontic appliances with mini screw:
- Fixed orthodontic appliances
- Fixed orthodontic appliance can be used to correct incisor crossbite involving single tooth or group of teeth.
- The in-locked teeth are pulled into their correct labial position by fixed appliances.
Question 2. Discuss the deleterious effects of crossbite. Write a note about its management.
Answer. Following are deleterious effects of anterior crossbite:
- Teeth become excessively weared.
- As adjacent teeth migrate there is presence of loss of arch length.
- Unlocked tooth undergo traumatic occlusion.
- Pseudo class 3 malocclusion develops.
- Following are deleterious posteffcts of anterior crossbite
- Presence of abnormal wearing of teeth.
- Muscle spasm leads to pain.
- Periodontium get damaged.
- Normal growth and the development of dental arches get interfered.
Question 3. Describe in detail etiology, clinical features and management of crossbite.
Or
Write short note on crossbite.
Answer. Crossbite is defied as the condition where one or more teeth may be abnormally malposed buccally or lingually or labially with reference to the opposing tooth or teeth. Cross bite is of two types, i.e. anterior and posterior cross bite.
Classification
- According to their location in the arch
- Anterior crossbite
- Single tooth crossbite
- Segmental crossbite.
- Posterior crossbite
- Single tooth crossbite
- Segmental crossbite.
- Anterior crossbite
- Classification of posterior crossbite on the basis of its presence on one or both sides of arch
- Unilateral posterior crossbite
- Bilateral posterior crossbite.
- According to the extent of crossbite
- Simple posterior crossbite
- Buccal non-occlusion Or scissor bite
- Lingual non-occlusion.
- Classification of crossbite based on structure involved
- Dental crossbite
- Skeletal crossbite
- Functional crossbite.
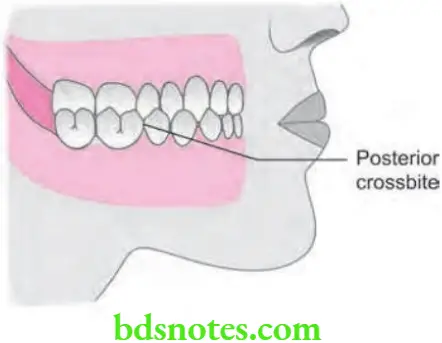
Etiology of Anterior Crossbite
Skeletal Factors
Skeletal incisor crossbite results due to excessive mandibular growth. It is genetic or inherited malocclusion.
Dental Factors
- A dental incisor crossbite is because of abnormal axial inclination of the maxillary incisors.
- Abnormal axial inclination is due to following factors, i.e. Inadequate arch length which leads to lingual eruption of permanent tooth.
- Labial position of supernumerary tooth.
- Over retained primary tooth.
- Lip biting habit
- Trauma to primary teeth or to the permanent tooth bud
Functional Factors
An incisor crossbite also occurs due to functional interference of the mandible during closure. It is due to premature tooth contact and results in peudo-class 3 malocclusion.
Etiology of Posterior Crossbite
Dental Crossbite
- Anomalies of tooth size, i.e. Microdontia and macrodontia
- Anomalies of tooth number, i.e. Supernumerary teeth and missing teeth.
- Anomalies of tooth shape, i.e. germination, fusion skeletal crossbite.
- Oral habits like thumb sucking, mouth breathing, etc.
- Trauma at birth
Clinical Features of Anterior Crossbite
An abnormal labiolingual relationship, i.e. reverse overjet is present between one or more maxillary and mandibular anterior teeth.
Clinical Features of Posterior Crossbite
An abnormal buccolingual relationship of teeth in maxilla and mandible when two dental arches are brought into centric occlusion.
Management of Posterior Crossbite
Single tooth dental crossbite
- It involves the molars which are treated by crossbite elastics.
- Such elastics are stretched between maxillary palatal surface and the mandibular buccal surfaces.
- Such elastics to be worn in both day and night. Treatment is not continued for more than 6 weeks as elastics causes extrusion of teeth.
Dentoalveolar contraction and crossbite
- First of all any of the functional interference which is present should be eliminated by occlusal equilibration i.e. a dental bilateral lingual crossbite in deciduous or the mixed dentition is simply corrected by removing occlusal interferences mainly in cuspid areas. This sometimes needs to be accompanied by some of the appliances.
- Various appliances which are to be given after occlusal equilibration are:
- Coffin spring: It is a removable appliance which consists of an omega shaped wire of 1.25 mm diameter which is placed in mid palatal region. Free ends of an omega are embedded in an acrylic plate which covers slopes of the palate. Spring causes dentoalveolar expansion. It causes skeletal changes when used in young patients.
- Quad helix: This spring consists of four helices. It causes dentoalveolar expansion of both molar and premolar region. It causes skeletal expansion when used in younger patients.
- Removable plates
- Removable appliances incorporating jackscrew is used to treat unilateral crossbite.
- The appliance consists of a split acrylic plate, a jack screw and Adam’s clasp on posterior teeth to retain the plate. Labial bow can also be incorporated into the appliance for minor space closure and retraction.
- Fixed appliances: Unilateral crossbite can also be treated by using fixed appliances.
Skeletal Crossbite
It is either due to presence of narrow maxilla or narrow mandible.
- In patients with narrow maxilla which have mild skeletal crossbite quad helix or W arch is used while in the severe cases RME or Minnesota expander is beneficial.
- In patients with narrow mandible functional appliances are used.
- If skeletal crossbite is very severe surgical treatment is done.
Question 4. Write short note on management of single incisor crossbite.
Answer. Single incisor crossbite is a condition where there is overlapping of one of the mandibular incisor over one of the maxillary incisor.
Management of single incisor crossbite:
Correction of incisor crossbite in the preadolescent age group.
Following appliances are used.
Tongue Blade
Tongue blade therapy is used to treat the developing incisor crossbite by placing the wooden tongue blade behind the tooth in crossbite at an angle of about 60 degrees to the occlusal plane. The patient should exert force by biting on it using the lower teeth as a fulcrum for a period of 5-10 minutes. Usually the tooth will erupt into normal position over a period of time.
Catalan’s Appliance or Lower Anterior Inclined Plane
- Catalan’s appliance is also called as “lower anterior inclined plane”, which explains the design of this appliance. Catalan’s appliance consists of an inclined plane cemented to the lower incisor.
- Fabrication
- Acrylic resin or cast metal is used to fabricate Catalan’s appliance. The lower anterior inclined plane is designed in such a way that, it is at 45 degree angle to the maxillary occlusal plane. Ctalan’s appliance can be fabricated on a single lower anterior tooth for the correction of single tooth crossbite or for the whole anterior segment.
Removable Orthodontic Appliances
- Removable orthodontic appliances in case of single tooth incisor crossbite, “Z” spring on tooth involved in crossbite can be used for correction of such a condition.
- Removable orthodontic appliances with expansion screw:
- Removable orthodontic appliance incorporates expansion screw of various types, which can be used to correct single incisor crossbite.
Correction of Incisor Crossbite in Adolescent and Adults
Removable orthodontic appliance incorporated expansion screw of either mini or medium, which may also be used to correct anterior crossbite involving single tooth in adults.
- Removable Orthodontic Appliances
- Removable orthodontic appliances with mini screw:
- Removable orthodontic appliance with incorporated mini screw type of expansion screw, which are used to correct the anterior crossbite involving single to two teeth in crossbite.
- Removable orthodontic appliances with mini screw:
- Fixed Orthodontic Appliances
- Fixed orthodontic appliance can be used to correct incisor crossbite involving single tooth.
- The in-locked teeth are pulled into their correct labial position by fixed appliances.
Question 5. Write short note on scissors bite.
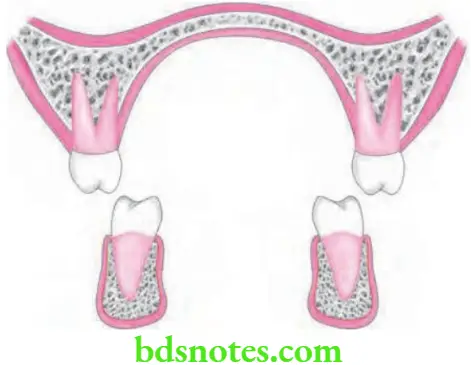
Answer. It is also called as buccal non-occlusion or buccal crossbite.
- Scissors bite is a form of posterior crossbite where the maxillary posteriors occlude entirely on the buccal aspect of mandibular posteriors.
- It can involve a single tooth or group of teeth and may be unilateral or bilateral.
Scissors Bite Diagnosis
It is done via thorough clinical or study model examination.
Scissors Bite Treatment
- It is done by placing the cross elastics which are placed across the bite.
- Cross elastic should be stretched from the buccal aspect of maxillary tooth to the lingual of mandibular tooth involving the scissor bite.
- Various lingual attchments such as lingual buttn are used to engage the elastic on lingual aspect of lower tooth involved in the scissor bite.
- Bite block should be needed to provide the occlusal clearance for jumping or clearing the bite.

Leave a Reply