Management Of Class 2 Malocclusion
Question 1. Give the causes of class 2 malocclusion. Describe treatment of a developing distocclusion with a functional appliance.
Or
Define Angle’s Class 2 malocclusion and give its etiology.
Or
Give the etiology of class 2 div. 1.
Give the etiology of class 2 div. 1.
Answer. According to Angle’s classification class 2 malocclusion indicates that the mandibular arch is in a distal relation to that of the maxilla.
Class 2 malocclusion is characterized by a class 2 molar relation where the distobuccal cusp of upper 1st molar occludes in the buccal groove of the lower Ist permanent molar.
It Can Occur in Two Main Form
- Class 2 div. 1.
- Class 2 div. 2.
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Question And Answers
Causes of Class 2 Malocclusion
- Prenatal factors.
- Natal factors.
- Postnatal factors.
Prenatal Factors
- Hereditary: Skeletal abnormalities like prognathic maxilla or retrognathic mandible due to hereditary cause.
- Teratogenesis: Certain drugs taken during pregnancy lead to abnormal skeletal development.
- Irradiation: Radiation exposure to a pregnant woman causes altered development of dentofacial complex.
- Intrauterine fetal posture: Abnormal fetal posture like hands across the face is found to affect mandibular growth.
Natal Factors
Trauma to the condylar region during forcep delivery leads to firosis or ankylosis of TMJ leading to under development of the mandible.
Postnatal Factors
- Trauma to mandible or TMJ.
- Long-term irradiation therapy of skeletal craniofacial region.
- Infectious conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can affect mandibular growth.
- Abnormal function—oral respiration, abnormal swallowing and habits such as thumb sucking.
Treatment of Developing Distocclusion with Functional Appliances.
Functional appliances are applied in growth modification.
- The abnormal skeletal pattern intercepted by functional appliances is to reduce severity of skeletal relationship.
- Functional appliances are usually applied during mixed or early permanent dentition period prior to the cessation of growth.
Mandibular Retrognathism
Retrognathic mandible with average FMA angle and lower facial height.
- Activator or FR – 1 is commonly used but bionator, biomodulator, cybernator, propulsor etc. are other functional appliances which are used less commonly.
- Functional appliance acts by placing the mandible in anterior position and also by eliminating the functional retrusion.
Retrognathic mandible with higher FMA angle and lower facial height
- Activator is used along with high pull headgear.
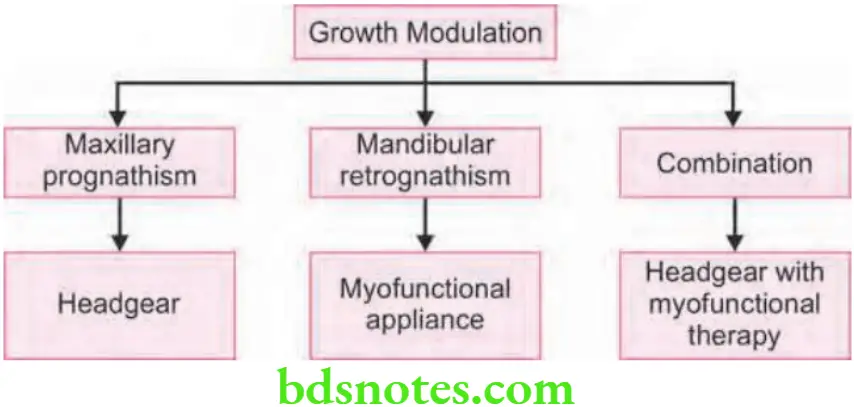
Maxillary Prognathism
- Growth inhibition of the maxilla for maxillary prognathism, with distalization of upper buccal segments is achieved by using extraoral orthopedic force.
- Headgears are recommended for orthopedic force.
- Patient wears the appliance for around 12–14 hours daily.
- Orthopedic force of 350–450 g/side is applied with the help of headgear.
- High pull or occipital pull headgear is used in case of patients whose maxilla is growing vertically.
- Cervical pull headgear is used for patients whose maxilla is growing horizontally.
- In cases of vertical maxillary excess, maxillary intrusion splints are used.
Combination of maxillary prognathism and mandibular retrognathism
- Combination of headgear and functional appliances is used for growth modification.
- Most commonly used combination is Activator with headgear.
Question 2. (1) Write the different skeletal combination of class 2, div. 1 malocclusion and write down facial and dental features of the same.
(2) Briefly mention the probable etiological factors for development of class II, div. 1 malocclusion.
Answer.
(1) Skeletal changes in class II, div. 1 malocclusion. The upper arch is narrower at the premolar and canine region thereby producing ‘V’ shaped upper arch.
- Maxilla is prognathic
- Mandible is retrognathic.
- Combination of prognathic maxilla and retrognathic mandible.
- Cases associated with receding chin.
Facial Features
- Profile is convex.
- Presence of posterior divergence.
- Presence of incompetent or potentially incompetent lips.
- Presence of short hypotonic upper lip.
- Increase in overjet causes lip trap.
- Lower lip is hyperactive.
- Presence of abnormal buccinator activity due to posterior placement of tongue.
Dental Features
- Presence of Class 2 molar relation.
- Presence of Class 2 incisor relation due to increase in overjet.
- Overbite is deep.
- If thumb sucking is involved there is incomplete overbite.
- Presence of deep curve of Speed.
- Presence of Class 2 canine relationship.
- Crossbite and scissor bite are occasionally present.
(2) Causes of Class 2 Div. 1 malocclusion
- Prenatal factors
- Natal factors
- Postnatal factors
Question 3. Discuss in brief the etiology, clinical features, cephalometric findings and the time of treatment in an Angle’s class II division 1 malocclusion case.
Answer.
Cephalometric Findings in Angle Class II div 1
Soft Tissue Analysis
Lips may locate beyond the ‘S’ line and give common profile.
Time of Treatment in Angle’s Class 2, Div. 1 Malocclusion
There are three basic approaches to the treatment of class 2, div. 1, depends upon the time of treatment.
- Growth modification.
- Camouflge.
- Surgical correction.
Growth Modification
In this the abnormal skeletal patterns can be corrected by functional and orthodontic appliances to reduce the severity.
These treatment procedures are usually carried out during the mixed or rarely permanent dentition period prior to the a cessation of growth.
Camouflge
In patients who are beyond growth, it is not possible to undertake growth modification. Thus, the underlying skeletal discrepancy can be camouflged by orthodontic tooth movement.
This is obtained by extraction of certain teeth and moving rest of the teeth.
Surgical Correction
Done after the completion of growth, in patient exhibiting severe skeletal malocclusion.
Question 4. Briefly describe class 2, division 2 malocclusion. Write the probable cause for its development.
Answer. Class 2, division 2 is a condition characterized by a class 2 molar relationship with retroclined upper centrals that are overlapped by the lateral incisor.
Features of Class 2 Division 2
It should be studied under the following headings:
Skeletal Features
- Pattern can be class 1 or 2
- In the vertical dimensions height of the lower anterior face is small.
- Frankfort horizontal plane is low.
- Severe to moderate deep bite is present.
- From transverse view maxillary arch is broader as compared to mandibular arch.
Soft Tissue Features
- Level of lower lip is high when compared to crown of maxillary incisor.
- Retroclined maxillary incisors because of high lower lip.
- Lower lip is hyperactive
- Mentolabial fold lies deep
- Profile can be straight due to chin prominence
- Lips are competent
- Musculature is strong
- Palatal gingiva gets traumatized because of close bite of lower incisor.
Occlusal Features
- Presence of Angle’s class 2 molar relationship
- Presence of class 2 division 2 incisor relationship
- Presence of class 2 canine relationship
- Mandibular anterior teeth are retroclined
- Presence of excessive deep overbite.
- Curve of Spee is increased
- Freeway space is increased
- Presence of mandibular anterior teeth crowding.
Functional Features
Mandible is posteriorly displaced because of overclosure, i.e. functional retrusion of mandible.
Path of closure of mandible lies upward and backward.
Treatment
- Correction of incisor relationship and buccal segment relationship
- Relief of the gingival trauma
- Relief of crowding and local irregularities
- Correction of buccal segment relationship
- Role of the extraction in treatment as well as correction of buccal segment relationship is same as for class 2 division 1 malocclusion.
- Deep anterior overbite and retroclination are characteristic of Class 2 division 2 malocclusion which is treated by reduction in incisal overbite and alteration in incisal inclination.
- Deep overbite is decreased by use of anterior bite plane or fixed appliances incorporating anchor bands or reverse curve of spee.
- Incisor inclination is treated by the use of torqueing springs to move maxillary incisor roots lingually and crown buccally.
- During the mixed dentition period, it is possible to procline the maxillary incisors by converting class 2 division 2 in malocclusion which resembles class 2 division 1. This is done by the use of functional appliances.
Question 5. How will you diagnose a case of class 2 div. 1 malocclusion.
- 1. Clinically
- 2. Cephalometrically
Answer. Class 2 Div 1 Malocclusion
Clinical Features
1. Skeletal Features
- Skeletal discrepancies are:
- Maxilla is prognathic
- Mandible is retrognathic
- Combination of prognathic maxilla and retrognathic mandible.
- Cases associated with receding chin.
2. Soft Tissue Features
- Profile is convex
- Presence of posterior divergence of teeth
- Lips are incompetent
- Upper lip is hypertonic and is short
- Lip trap is present
- Lower lip is hyperactive
- Activity of buccinators muscle is abnormal.
3. Occlusal Features
- Presence of Angle’s class 2 molar relationship
- Presence of class 2 incisor relationship
- Deep overbite
- Curve of Speed is deep
- Presence of canine relation is class 2.
4. Functional Features
- Swallowing pattern is abnormal.
- Mentalis muscle is hyperactive.
- Because of crossbite path of closure is changed.
Question 6. A male patient aged 11 years with the ANB angle of + 5° reported to the department of orthodontics. Discuss the management of the case.
Answer. ANB angle of +5° suggests the skeletal class 2 malocclusion. As the age of child is 11 years he is in growing stage so management of child is as follows.
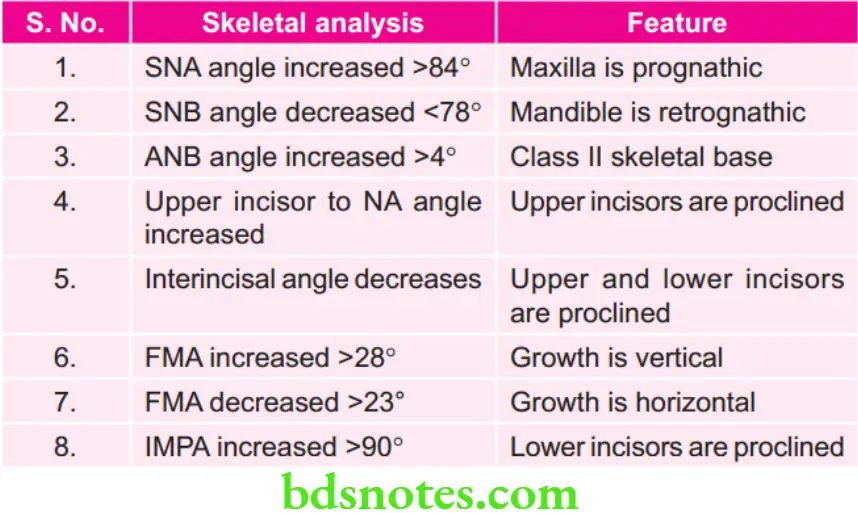
Management of Skeletal Class 2 Pattern
Management of Class 2 Skeletal Malocclusion.
- Growing patient with skeletal class 2 malocclusion is treated through growth modulation.
- Hands wrist radiographs and lateral cephalograms are taken to assess skeletal age and growth potential.
Maxillary Prognathism
- Growth inhibition of the maxilla for maxillary prognathism, with distalization of upper buccal segments is achieved by using extraoral orthopedic force.
- Headgears are recommended for orthopedic force.
- Patient wears the appliance for around 12–14 hours daily.
- Orthopedic force of 350–450 g/side is applied with the help of headgear.
- High pull or occipital pull headgear is used in case of patients whose maxilla is growing vertically.
- Cervical pull headgear is used for patients whose maxilla is growing horizontally.
Mandibular Retrognathism
- Retrognathic mandible with average FMA angle and lower facial height.
-
- Activator or FR – 1 is commonly used but bionator, biomodulator, cybernator, propulsor etc. are other functional appliances which are used less commonly.
- Functional appliance acts by placing the mandible in anterior position and also by eliminating the functional retrusion.
- Retrognathic mandible with higher FMA angle and lower facial height
-
- Activator is used along with high pull headgear.
Combination of Maxillary Prognathism and Mandibular Retrognathism
- Combination of headgear and functional appliances is used for growth modification.
- Most commonly used combination is Activator with headgear.
Question 7. What is distoocclusion. Describe the management of distoocclusion of 8–9 years old male child.
Answer. Disto-occlusion is the condition where the mandibular molar is positioned distally in relation to upper molar.
It is also known as class II malocclusion or postnormal occlusion.
Management of Distoocclusion of 8–9 Years Old Male Child
- The age of the male child is 8–9 years this indicates that the child is under the growing stage and is in mixed dentition period.
- Management plan of the child is divided into skeletal class 2 and dentoalveolar class 2.
Correction of Skeletal Class 2 Malocclusion
- Growth modulation is the treatment in patients with skeletal class 2 malocclusion.
- Growth modulation is done as:
In Maxillary Prognathism
- Distalization of maxillary buccal segment is done by using extraoral orthopedic force.
- Orthopedic appliances which apply the orthopedic force are headgears.
- Appliance should be worn for 12 to 14 hours a day.
- Patients exhibiting vertical growth should undergo therapy by occipital pull headgear.
- Patients exhibiting horizontal growth should undergo therapy by cervical pull headgear.
- In cases with vertical maxillary excess maxillary intrusion splint is used.
In Mandibular Retrognathism
- Retrognathic mandible with average FMA angle and lower facial height.
-
- Activator or FR – I is commonly used but bionator, biomodulator, cybernator, propulsor etc. are other functional appliances which are used less commonly.
- Functional appliance acts by placing the mandible in anterior position and also by eliminating the functional retrusion.
- Retrognathic mandible with higher FMA angle and lower facial height
-
- Activator is used along with high pull headgear.
In Combination of Prognathic Maxilla and Retrognathic Mandible
- Growth modification is carried out by combining headgear and myofunctional appliance.
- Most commonly used combination is activator with head gear.
Correction of Dentoalveolar Class 2 Malocclusion
- During early correction incisor and molar relationship is established.
- Crowding is corrected by space gaining methods such as extractions or distalization of molars.
- Deep bite is corrected by anterior bite plate in low angle cases.
- By utility arches incisor intrusion is carried out in high angle cases.
- Retroclination of incisors is done by fixed appliance mechanotherapy and labial bows.
- Posterior crossbite correction is done by crossbite elastics.
- If any habit is present it should be corrected.
Retention After Correction in Disto-occlusion
Tweed’s type B retention plan is implicated.
Question 8. Write down the treatment plan of a young growing child with skeletal class 2 div. 1 malocclusion with deep bite. The child exhibits positive VTO on mandibular advancement.
Answer. Flowchart depicts treatment plan for class 2 Div. 1 malocclusion with deep bite in a growing child.
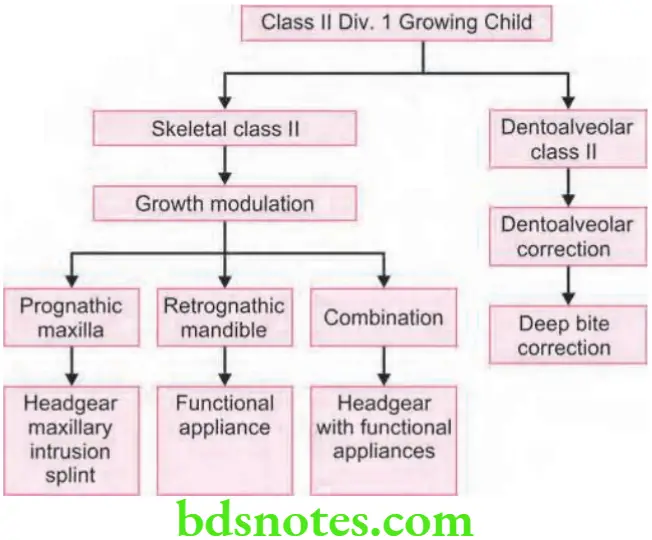
- Growing child with skeletal class 2 malocclusion should be treated by growth modulation.
- In this case positive VTO on mandibular advancement is suggestive of indication of myofunctional appliances in the treatment.
- Skeletal age and growth potential is assessed with handwrist radiograph.
- Lateral cephalograms helps to locate the skeletal problem.
Prognathic Maxilla
- Inhibition of growth of maxilla for prognathic maxilla, with distalization of maxillary buccal segments is achieved by the extraoral orthopedic force.
- For application of orthopedic force headgears are used.
- Patient wears the appliance for around 12 to 14 hours a day.
- Orthopedic force of 350-450 g/side is applied.
- For vertically growing patients high pull or occipital pull headgear is used.
- For horizontal growing patients cervical pull headgear is used.
- In patients with vertical maxillary excess maxillary intrusion splint is used.
Retrognathic Mandible
- Retrognathic mandible with average FMA angle and lower facial height.
- Activator or FR – 1 is commonly used but bionator, biomodulator, cybernator, propulsor etc. are other functional appliances which are used less commonly.
- Functional appliance acts by placing the mandible in anterior position and also by eliminating the functional retrusion.
- Retrognathic mandible with higher FMA angle and lower facial height
-
- Activator is used along with high pull headgear.
Combination of Prognathic Maxilla and Retrognathic Mandible
- By combination of headgear and functional appliances growth modification is done.
- Activator with headgear is commonly used.
Correction of Dentoalveolar Class 2
- In dentoalveolar class 2, the skeletal base is normal or orthognathic. Defect is in dentoalveolar part.
- Establishment of normal incisor and molar relationship is one of the aims of early correction.
- Deep bite correction is done by using anterior bite planes in low angle case while in high angle cases, incisor intrusion is achieved using utility arches.
- Correction of crowding is done by gaining space either by distalization of molars or extraction.
- Retraction of incisors is done by using labial bows or with fixed appliance mechanotherapy.
- Posterior crossbites should be corrected by using crossbite elastics

Leave a Reply