Keratotic And Non-Keratotic White Lesions Question And Answers
Question 1. Write short note on Fordyce’s spot.
Answer. It is also known as Fordyce’s granule.
A Fordyce granule is a developmental anomaly characterized by heterotrophic collection of sebaceous glands at various sites in oral cavity, which is covered with intact mucosa.
Fordyce’s spot Pathogenesis
It is postulated that occurrence of sebaceous glands in oral cavity is due to inclusion of ectoderm inside the oral cavity, this ectoderm consists of some potentialities of skin in course of development of maxillary and the mandibular process in embryonic life.
Fordyce’s spot Clinical Features or Fordyce Spots Treatment
- It is seen at any age group with more prevalent in males.
- It is commonly found bilaterally in symmetrical pattern on mucosa of cheek, opposite to molar teeth.
- It is found on inner surface of lips, in retromolar areas lateral to anterior faucial pillar.
- They appear as small yellow spots, either discretely separated and forming relatively large plaques often projecting slightly above surface of tissues.
- On tongue, it appears as dome-shaped nodule on dorsum of tongue.
- It increases rapidly in number at puberty and continue to increase throughout adult life.
- They are sharply delineated and with smooth surface, which is not ulcerated.
- They have cheesy consistency.
- Granules occur either singly or in confluent sheets. Sometimes they occur in clusters and form plaque like lesions.
Read And Learn More: Oral Medicine Question And Answers
Fordyce’s spot Diagnosis or Fordyce Spots Treatment
- Clinical diagnosis: Small yellow colored discrete spots are present which are separated from oral mucosa.
- Histological diagnosis: It shows presence of sebaceous acini.
Fordyce’s spot Management
There is no requirement of treatment, if it leads to disfigurement, surgical removal can be done.
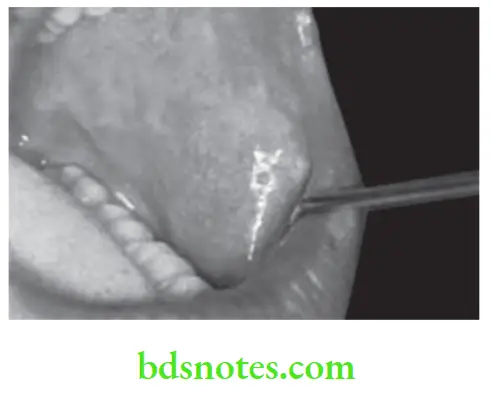
Fordyce Spots Treatment
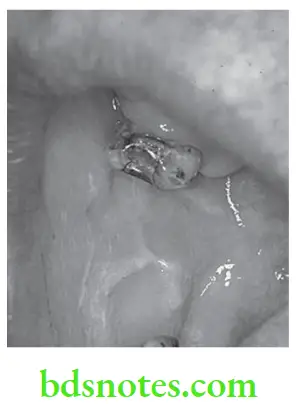
Question 2. Write short note on leukoedema.
Answer. It is abnormality of buccal mucosa which clinically resembles early leukoplakia.
Leukoedema Treatment
Leukoedema Etiology
- Use of tobacco: Seen commonly in smokers.
- Racial: Prevalent in blacks.
- Poor oral hygiene.
Leukoedema Clinical Features or Leukoedema Treatment
- It is common in age group of 15 to 35 years with prevalence in blacks. Male predilection is 2 : l.
- Most common sites of involvement are buccal mucosa and lip.
- Lesion is bilateral.
- It has mother of pearl appearance, i.e. lesion is diffuse and shows a filmy mother of pearl appearance often with delicate overlapping curtain like mucosal folds.
- Desquamation may occur which may leave surface of lesion eroded.
Leukoedema Diagnosis
Clinical diagnosis: Presence of faint milky folded appearance which is eliminated by stretching mucosa.
Leukoedema Differential Diagnosis
- Leukoplakia: Leukoedema has faint milky appearance, and wrinkled pattern as compared to whiteness of leukoplakia.Section 1: Oral Medicine 9
- Cheek-biting lesion: It is unilateral and not having typical appearance as seen in leukoedema.
- White sponge nevus: It is thicker and plaque like.
Leukoedema Diagnosis Treatment
No treatment is required.

Leave a Reply