Impression Materials
Question 1. Classify impression materials. Describe the composition, setting reaction, and manipulation of alginate impression material.
Or
Classify impression materials. Give composition and setting reaction of sodium alginate material.
Or
Classify impression material. Describe the composition and manipulation of irreversible hydrocolloids.
Or
Classify impression material.
Or
Classify impression materials, composition, setting reaction, and uses of alginate impression material.
Or
Write a short note on alginate.
Or
Write briefly on irreversible hydrocolloid.
Answer:
A dental impression is a negative record of the tissues of the mouth. The material used for taking impressions is called impression material.
Read And Learn More: Dental Materials Question And Answers
Classification of Impression Material
- Impression materials are classified on the basis of:
- On the basis of mode of setting and elasticity (Skinner)
- On the basis of tissue displacement during the impression procedure
On the basis of use in dentistry. - Based on the type of tray.
On the Basis of Mode of Setting and Elasticity (Skinner):
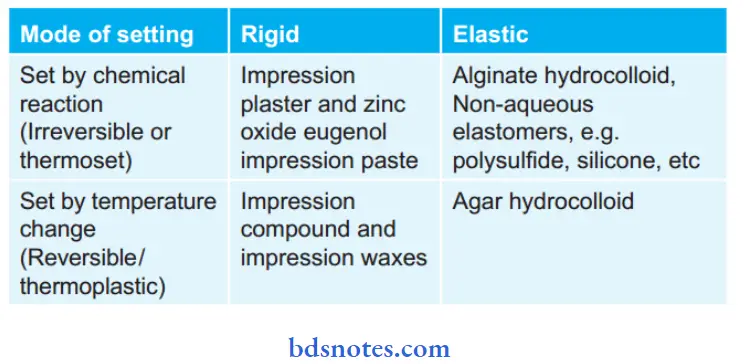
On the Basis of Tissue Displacement:
According to the tissue displacement impression materials are mucostatic and mucocompressive.
- Mucostatic materials: They produce minimum displacement of tissue during the impression.
- For example: Impression plaster, zinc oxide eugenol, low viscosity alginates, high viscosity elastomers, etc.
- Mucocompressive materials: They are more viscous and displace the tissues while recording them.
- For example: Impression compounds, high-viscosity alginates, high-viscosity elastomers, etc.
On the Basis of their use in Dentistry Impression material used for complete denture prosthesis:
Impression plaster, impression compound, and impression paste. These materials have rigid mass and are not removed from undercuts without being fractured. Hence, these materials are used for an edentulous mouth.
Impression material used for the dentulous mouth: Alginate and rubber base impression materials are elastic and can easily be withdrawn from undercuts. These impression materials are suitable for impression for fabrication of removable and field partial denture prostheses.
Based on the Type of Tray:
- Perforated metal tray: Alginate hydrocolloid
- Water-cooled metal tray: Agar hydrocolloid
- Custom tray: Zinc oxide eugenol, impression plaster, elastomeric impression material
Alginate of Impression Material:
- Irreversible hydrocolloid.
- The word alginate comes from ‘Algin’ which is a peculiar
mucous extract yielded by certain brown seaweeds (Algae).
Composition of Impression Material:
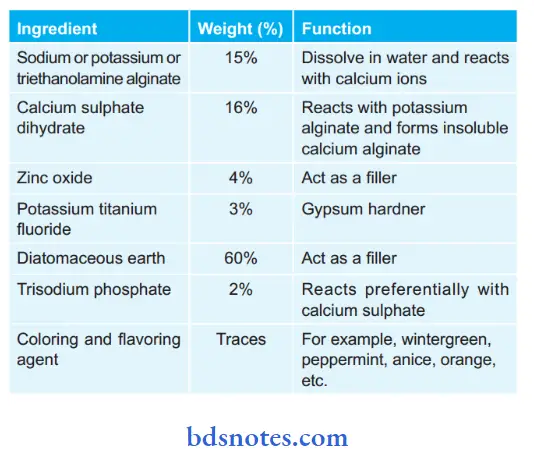
Chemistry of Setting / Setting Reaction:
When alginate powder is mixed with water a sol is formed which later sets to a gel by a chemical reaction. The final gel, i.e. insoluble calcium alginate is produced when soluble sodium alginate reacts with calcium sulfate. However, this reaction proceeds too fast. There is not enough working time. So the reaction is delayed by the addition of a retarder (trisodium phosphate)First sodium phosphate reacts with the calcium sulphate to provide adequate working time.
Next, after the sodium phosphate is used up, the remaining calcium sulphate reacts with sodium alginate to form insoluble calcium alginate, which forms a gel with water.
- First reaction:
2 Na3PO4 + 3CaSO4→ Ca3(PO4)2 + 3 Na2SO4
- Second reaction:
Sod. alginate + CaSO4+ H2O → Ca alginate + Na2SO4
(Powder) (Gel)
Gel Structure:
The final gel consists of a brush heal of calcium alginate fibril network enclosing unreacted sodium alginate sol, excess water, filer particles, and reaction by-products. It is a cross-linked structure and calcium leads to cross-linking.
Manipulation: For manipulation, the requirements are:
- A clean flexible plastic bowl.
- A clean wide-bladed, reasonably stif metal spatula (curved).
The steps for the manipulation are:
Fluf the powder by inverting the cane several time, this ensures uniform distribution of filer before mixing.
- The proper water/powder ratio should be used.
- The measured quantity of the powder is sprinkled in the measured amount of water in the rubber-mixing bowl.
- The mixing is started with a stirring motion to wet the powder with water.
- Once the powder has been moistened rapid speculation by swiping or stropping against the side of the bowl is done.
- A vigorous force of eight motion can be used with the mix being swiped against the wall of the bowl while rotating the bowl 180 degree.
- A proper mix is smooth and creamy with minimum voids and does not drip of the spatula when it is raised from the bowl.
Finally, the formed gel structure consists of brush heap of calcium alginate firil network which consists of unreacted sodium alginate sol, excess water, filer particles and reaction by-products.
Question 2. Describe the uses, advantages and disadvantages of irreversible hydrocolloid impression material.
Or
Explain in detail about irreversible hydrocolloids.
Answer:
Uses of Irreversible hydrocolloid impression:
- It is used for impression making
- When there are undercuts
- In the mouth with excessive flow of saliva
- For partial denture with clasps.
- For making a preliminary impression for complete dentures.
- For impressions to make study models and working casts.
- For duplicating models
Advantages of Irreversible hydrocolloid impression:
- Easy to mix and manipulate.
- Minimum requirement of equipment.
- The flexibility of the set impression.
- Accuracy if properly handled.
- Low cost.
- Comfortable to the patients.
- It gives a good surface detail even in the presence of saliva.
Disadvantages of Irreversible hydrocolloid impression:
- Cannot be electroplated so metal dies are not possible.
- It cannot be corrected.
- Poor dimensional stability cannot be stored for the long time due to the syneresis and imbibitions.
- Poor tear strength.
- Silica particles in dust cause possible health hazards.
Question 3. Give composition, the role of such ingredient, and properties of zinc oxide eugenol impression paste.
Or
Describe the chemistry, manipulation, and uses of zinc oxide eugenol impression paste.
Answer:
Zinc Oxide Eugenol Impression Paste:
- The ZOE impression paste is a rigid, irreversible material.
- It is mainly used for making an impression of an edentulous mouth.
Composition:
- Base Paste
- Zinc oxide 87%
- Fixed vegetable or mineral oil 13%
- Accelerator Paste or Catalyst Paste:
- Oil of clove or eugenol (70 to 85%) – 12%
- Gum or polymerized rosin – 50%
- Filler (Silica type) – 20%
- Lanolin – 03%
- Resinous balsam – 10%
- Accelerator solution (CaCl2) and coloring agents – 05%
Role of Each Ingredient
- Zinc oxide: Main ingredient to react with the catalyst. It should be finally divided and should contain slight amount of water.
- Fixed vegetable or mineral oil: Acts as a plasticizer and also aids in masking the action of eugenol as an irritant.
- Oil of clove: It contains 70–85% eugenol. It reduces the burning sensation or irritant effect of eugenol.
- Gum or polymerized rosin: Speeds the reaction and improves homogeneity.
- Canada or Peru balsam: Improves flow and mixing properties.
- Filler: It provides proper consistency of the mix.
- Calcium chloride: Acts as an accelerator of setting reaction.
- Other Accelerators:
- Zinc acetate
- Primary alcohol
- Glacial acetic acid.
Uses of Zinc Oxide Eugenol Impression Paste:
- As cementing and insulating medium
- As temporary filling material
- As root canal filling material
- As surgical pack in periodontal surgeries
- For bite registration
- As temporary relining material for dentures
- For taking an impression in edentulous patients.
Properties of Zinc Oxide Eugenol Impression Paste:
- Consistency and flow: A thin free flowing material copies the tissues without distorting them. Clinically these materials have very good flow. According to ADA specification No. 26, the spread is:
- Type I paste: 30 to 50 mm
- Type II paste: 20 to 45 mm.
- Detail reproduction: It registers surface details quite accurately due to the good flow.
- Rigidity and strength: The impression should resist fracture and be unyielding when removed from the mouth.
- The compressive strength of hardened ZOE is 7 MPa two hours after mixing.
- Biological consideration: Some patients may experience a burning sensation in the mouth due to eugenol. It can also cause tissue irritation.
Question 5. Describe the manipulation of ZOE. Explain the setting reaction in detail.
Or
Write in detail about the manipulation of zinc oxide eugenol impression paste.
Or
Write in detail about zine oxide eugenol impression paste.
Or
Describe the chemistry, manipulation, and uses of zinc oxide eugenol impression paste.
Answer:
Manipulation of ZOE:
- Requirements:
- Oil-impervious paper or glass slab.
- Flexible stainless steel spat
- Mixing time —1 minute:
- Procedure: Two ropes of paste of the same length and width, one from each tube are squeezed onto the mixing slab in order to ensure the correct proportioning. Mixing is done with a flexible stainless steel spatula using circular motion until a streak-free mix is obtained. Setting Reaction The setting reaction is a typical acid-base reaction to form a chelate.
When the two pastes are mixed a acid-base reaction takes place which is known as “chelation” and the product is called “Zinc Eugenolate”.
ZnO + H2 O → Zn (OH)2
Zn (OH)2 + 2HE → ZnE2 + 2H2
Base Acid (eugenol) Salt (Zinc eugenolate)
The chelate (zinc eugenol) forms a matrix surrounding a core of zinc oxide particles. The chelate is thought to form as an amorphous gel that tends to crystallize giving strength to the set mass.
Advantages of ZOE Impression Paste:
- It has enough working time to complete border molding.
- It registers accurate surface details.
- It is dimensionally stable.
- It can be checked in the mouth repeatedly without deforming.
- It does not require any separating media since it does not stick to the cast material.
- The minor defect can be corrected locally without discarding a good impression.
Disadvantages of ZOE Impression Paste:
- It requires a special tray for impression-making.
- It is sticky in nature and adheres to tissue.
- Eugenol can cause a burning sensation and tissue irritation.
- It cannot be used for making impressions of teeth and undercut areas, as it is inelastic in nature.
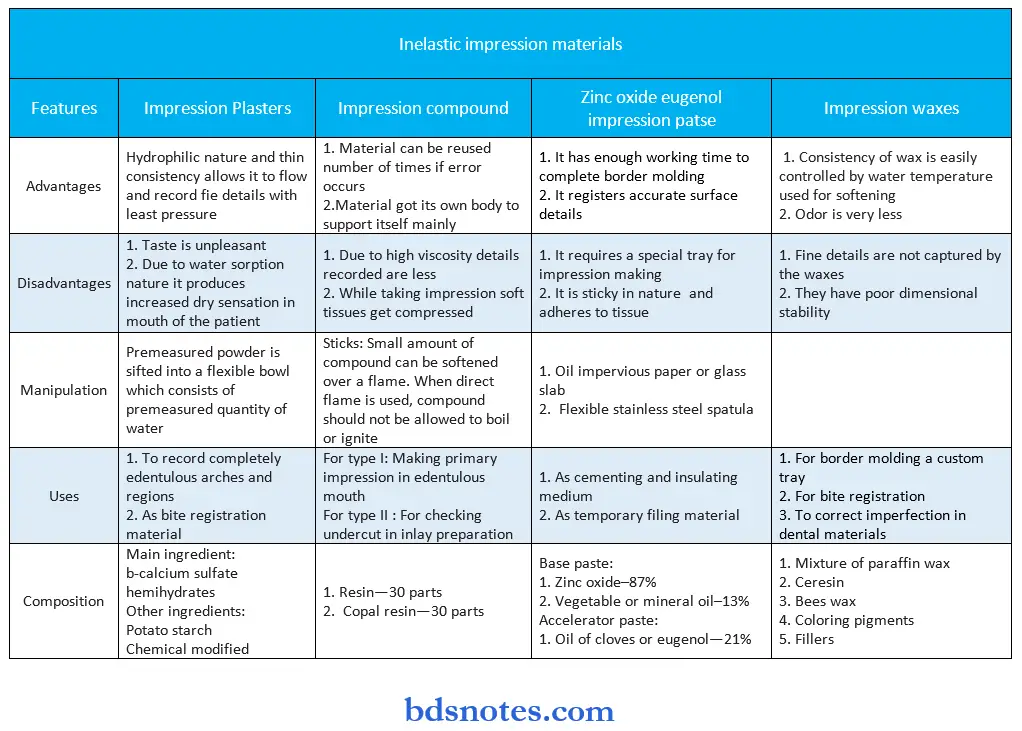
Question 6. Write in short about inelastic impression material and specially its advantages, disadvantages and manipulation, etc.
Answer:
Inelastic impression materials are known as rigid impression materials.
Inelastic impression materials are set to a hard rigid mass and hence cannot be removed from undercuts without the impression being fractured or distorted therefore these materials are best suited for edentulous mouths.
Following are the inelastic impression materials:
- Impression compound
- Impression plaster
- Zinc oxide eugenol impression paste
- Impression waxes.
Question 7. What are hydrocolloids
Answer:
Hydrocolloids are polysaccharide materials such as agar and alginate which form cross-link networks by hydrogen bonding. Both agar and alginate are sensitive to water gain or loss. For composition and manipulation of irreversible hydrocolloid, i.e. alginate refer to
Question 8. Describe the composition and manipulation of polysulphide rubber base impression material and its advantages and disadvantages.
Answer:
Polysulphide Rubber-base Impression Material:
- This was the first elastomeric impression material.
- It is also known as “Mercaptan” and “Thioko”
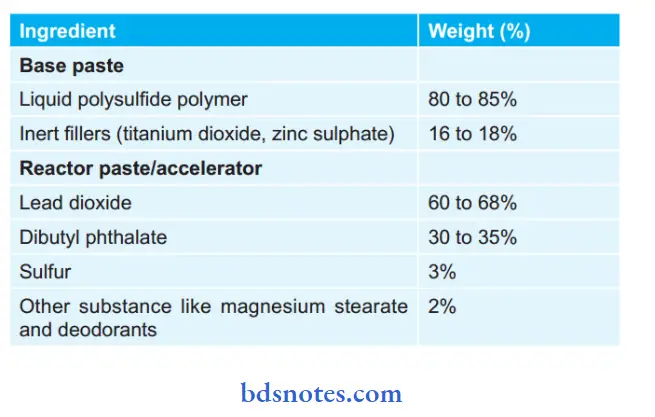
Composition of Polysulphide Rubber-base Impression Material:
- Base Paste
- Liquid polysulphide polymer – 80 – 85%
- Inert filer (titanium dioxide, zinc sulphate, copper carbonate, and silica) -16 – 18%
- Reactor Paste
-
- Lead oxide – 60 – 68%
- Dibutyl phthalate – 30 – 35%
- Sulfur – 03%
- Other substances like (magnesium stearate (retarder) and deodorants) – 02%
Manipulation Polysulphide Rubber-base Impression Material:
- High viscosity material, i.e. Put is usually supplied in small tubs with different colored scoops for identification and dispensing.
- Equal quantities of both the pastes are taken. Mixing is done by hand by kneading the material together to obtain a uniform mix without any streaks.
- Manufacturers also supply base and catalyst in separate tubes with a much smaller diameter opening for a catalyst to enable dispensing equal lengths of base and catalyst, though the volume is different.
- For polysulphide, mixing of low viscosity material is accomplished by taking equal lengths of base and catalyst on a paper pad and manipulating by stiff bladed spatula
in a circular motion for 45 seconds till the mix is free from streaks. - Mixing is done in a large area to dissipate the heat.
Advantages of Polysulphide
- Excellent reproduction of surface detail as fie as 0.025 mm wide
- It can be electroplated more with silver than copper
- The shelf-life is good (2 years)
- It has good flexibility (7%)
- It has high tear strength (4,000 g/cm) thus making it more resistant to tearing even when the impression is in thin section.
Disadvantages of Polysulphide:
- Unpleasant odor and color.
- These materials are extremely viscous and sticky. Mixing is difficult.
- It has long setting time which adds to the patient discomfort.
- Dimensional unstability: It has high permanent deformation. The curing shrinkage is high, and loss of byproduct (water) also causes shrinkage.
- Staining is present due to lead dioxide.
Question 9. Classify rubber base impression materials. Describe in detail.
Or
Classify elastomeric impression materials used in dentistry. Give the composition, properties, and advantages of any two elastomeric impression materials.
Or
Classify rubber base impression materials.
Or
Classify impression materials.
Or
Describe elastomeric impression materials in detail
Or
Write in detail about elastomeric (rubber base) impression materials.
Answer:
Rubber base impression materials are another group of elastomeric impression materials. They are soft and rubber-like and are known as elastomers or synthetic rubbers. Elastomeric materials contain large molecule with weak interaction between them. They are tied together at certain points to form a three-dimensional network.
Classification of Rubber Base Impression Materials:
- On the basis of their chemistry
- Polysulfide
- Condensation polymerizing
- Addition polymerizing silicones
- Polyether.
- On the basis of their viscosity (ISO 4823:2015)
- Type 0—Putt consistency (very heavy)
- Type 1—Heavy bodied consistency (tray consistency)
- Type 2—Medium bodied consistency (regular-bodied)
- Type 3—Light bodied (syringe consistency).
- On the basis of wettability or contact angle:
- Hydrophilic, if their contact angle is from 800 to 1050
- Hydrophobic, if their contact angle is from 400 to 700.
- According to ADA specification: As per the elastic property and dimensional stability of set material, ADA has classified elastomers as:
- Type – 1
- Type – 2
- Type – 3
Polysulphide Elastomeric Impression Material:
This was the first elastomeric impression material to be introduced. It is also known as “Mercaptan or Thiokol”.
Composition of Polysulphide Elastomeric Impression Material:
- Base Paste:
- Liquid polysulfide polymer 80 – 85%
- Inert filer (titanium dioxide, zinc sulfate or silica) 16 – 18%
- Reactor Paste:
- Lead dioxide 60 – 68%
- Dibutyl phthalate 30 – 35%
- Sulfur 3%
- Other substances like magnesium 2% stearate and deodorants
Setting Reaction of Polysulphide Elastomeric Impression Material:
As base and accelerator pastes are mixed, they undergo both polymerization by oxidation of terminal SH groups and the cross-linking of pendant SH groups. Reaction occur between polymer with free mercaptan, i.e.–SH groups, and the oxidizing agent lead dioxide, which lengthen and cross-link the chain through reaction of terminal and pendant –SH group. The whole reaction is exothermic which increases the temperature from 3°C to 5°C and formation of water as by-product.
Mercaptan + Lead dioxide → Polysulfied +Water
Properties of Elastomeric Impression Material:
It has an unpleasant odor and color. It stains linen and is messy to work with.
These materials are extremely viscous and sticky. Mixing is difficult.
- It has a long setting time of 12.5 minute.
- Excellent reproduction of surface detail.
- Dimensional stability: The curing shrinkage is high and continuous even after setting. It has the highest permanent deformation among the elastomers, i.e. 3 to 5%.
- It has high tear strength (4,000 g/cm).
- It has good flexibility (7%) and low hardness.
- It is hydrophobic so the mouth should be dried before making an impression.
- It can be electroplated more with silver than copper.
- Shelf-life is good, i.e. 2 years.
Advantages of Polysulphide:
- Excellent reproduction of surface detail as fie as 0.025
mm wid - It can be electroplated more with silver than copper
- The shelf-life is good (2 years)
- It has good flexibility (7%)
- It has high tear strength (4,000 g/cm) thus making it more resistant to tearing even when the impression is in thin section.
Disadvantages of Polysulphide:
- Unpleasant odor and color.
- These materials are extremely viscous and sticky. Mixing is difficult.
- It has a long setting time which adds to the patient’s discomfort.
- Dimensional unstability: It has high permanent deformation. The curing shrinkage is high, and loss of byproduct (water) also causes shrinkage.
- Staining is present due to lead dioxide.
Condensation Silicone
It is also known as conventional silicone.
Composition of Condensation Silicone :
![]()
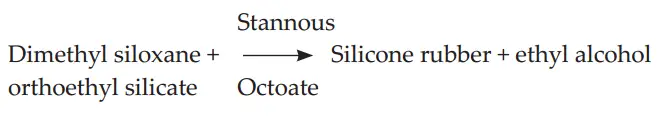
Setting Reaction of Condensation Silicone :
It is a condensation reaction. Polymerization occurs as a result of cross-linkage between the ortho-ethyl silicate and terminal hydroxy group of dimethylsiloxane to form a three-dimensional network. Ethyl alcohol is the by-product of the reaction which evaporates causing contraction of the set condensation silicone impression. The reaction is exothermic with a temperature rise of 1°C.
Properties of Condensation Silicone:
- It has pleasant color and odor.
- Its setting time is 6 to 9 minutes while the mixing time is 45 seconds.
- It is non-toxic but direct skin contact should be avoided.
- Excellent reproduction of surface details.
- Dimensional stability is comparatively less because of high curing shrinkage (0.4 to 0.65).
- Tear strength (3,000) g/cm is lower than the polysulfides.
- It is stiffer than polysulfide.
- It is hydrophobic so field should be dried before making an impression.
- It can be plated with silver/copper.
- Shelf-life is slightly less than polysulfide.
Advantages of Condensation Silicone:
- It does not consist of a bad odor of polysulphides.
- Basic advantages of elastomeric impression materials are present.
Disadvantages of Condensation Silicone:
- Shelf life is limited.
- As by-products are formed after the chemical reaction, the impression cannot be kept for an extended period of time.
- Due to evaporation of ethyl alcohol dimensional stability is affected.
Addition Silicone
It has better properties than condensation silicones. It is also known as “Polyvinyl siloxane”.
Composition of Addition Silicone :
- Base:
- Poly (methyl hydrogen siloxane)
- Other siloxane prepolymers
- Fillers (amorphous silica or fluorocarbon)
- Palladium or hydrogen absorber
- Retarders.
- Accelerator:
- Divinyl polysiloxane
- Other siloxane prepolymers
- Platinum salt-catalyst
- Fillers.
Setting Reaction of Addition Silicone :
It is an additional reaction. In this, the base polymer is terminated with vinyl groups and is cross-linked with silane. The reaction is activated by platinum salt. There are no by-products as long as, there is a balance between the vinyl siloxane and silane siloxane. If unbalanced, hydrogen gas is produced causing air bubbles in stone models. To avoid this palladium is added to absorb hydrogen.
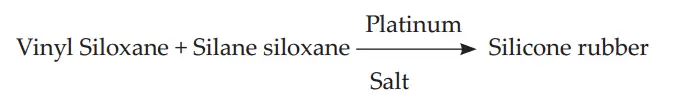
Properties of Addition Silicone:
- Its odor and color is pleasant.
- It can lead to allergic reactions.
- The reproduction of surface details is excellent.
- Setting time is 5 to 9 minutes. The mixing time is 45 seconds.
- Working time is extended by chilling the tubes.
- Dimensional stability is good. Curing shrinkage is low (0.17%) and permanent deformation is very low, i.e. 0.05 to 0.3%.
- Tear strength is good, i.e. 3,000 g/cm.
- Material is hydrophobic so care should be taken while pouring impression.
- It can be electroplated from silver or copper
- Flexibility is low. Extra spacing should be provided in impression tray. Care should be taken at time of removing stone cast from impression to avoid breakage.
- Its shelf-life ranges from 1 to 2 years.
Advantages of Addition Silicone :
- Most dimensionally stable impression material.
- These impressions can be kept for 7 days after taking impression.
- They are available in various consistency so can be used in various clinical situations.
Disadvantages of Addition Silicone :
- They are inherent and have hydrophobic nature. A rounded margin with loss of detail in impression is caused by moisture contamination of prepared tooth.
- Sulfur contamination from latex gloves inhibit setting reaction of additional silicones.
- As residual hydrides in set material react with moisture present in the atmosphere and evolve hydrogen gas, due to this cast cannot be poured readily.
- It should be poured after 30 minutes for gypsum casts and only after 24 hours for epoxy dies.
Polyether Rubber Impression Material
It has good mechanical properties and dimensional stability.
Composition of Polyether Rubber Impression Material:
- Base:
- Polyether polymer 80 – 85%
- Colloidal silica—filer
- Glyco ether or Phthalate — Plasticizer.
- Accelerator Paste:
- Aromatic sulfonate ester — cross-linking agent
- Colloidal silica — Filer
- Phthalate or glycol ether — Plasticizer.
Setting Reaction of Polyether Rubber Impression Material:
It is cured by the reaction between aziridine rings which are at the end of branched polyether molecules.The main chain is a copolymer of ethylene oxide and tetrahydrofuran. Cross-linking is brought about by the aromatic sulphonate ester via the imine end groups. The reaction is exothermic. No by-product is formed.
Polyether + Sulfonic ester→ Crosslinked rubber
Properties of Polyether Rubber Impression Material
- Its taste and odor are pleasant.
- It can lead to skin reactions due to presence of sulfonic ester.
- Thorough mixing is done before making an impression.
- Its setting time is 6 to 8 minutes. Mixing is done quickly, i.e. in 30 seconds. Heat decreases the setting time.
- Dimensional stability is good. Curing shrinkage is low, i.e. 0.24%.
- Permanent deformation is low, i.e. 0.8 to 1.6%. Polyether absorbs water and can change dimension, so prolonged contact with water and humid climate is not recommended.
The material is stiff and it is difficult to remove it from undercuts so additional spacing is required.
- Tear strength is good, i.e. 3000 g/cm.
- Since the material is hydrophilic, moisture in the impression field is not critical. It has the best compatibility with stone among
all elastomers. - Its shelf-life is excellent, i.e. more than 2 years.
- It can be electroplated with silver or copper.
Uses of Rubber Base Impressions Materials:
- In fixed partial dentures for an impression of prepared teeth.
- Impressions of dentulous mouths for removable partial dentures.
- Impressions of edentulous mouths for complete dentures
- Polyether is used for border molding of special trays.
- For bite registration.
- Silicone duplicating material is used for making refractory casts during cast partial denture condensation.
Manipulation of Rubber Base Impression Materials:
Following are the methods of manipulating rubber base or elastomeric impression materials, i.e.
- Hand mixing
- Static auto-mixing system
- Dynamic mechanical system
Hand Mixing:
- High-viscosity material, i.e. putt is usually supplied in small tubs with different colored scoops for identification and dispensing.
- Equal quantities of both the pastes are taken. Mixing is done by hand by kneading the material together to obtain a uniform mix without any streaks.
- Manufacturers also supply base and catalyst in separate tubes with a much smaller diameter opening for a catalyst to enable dispensing equal lengths of base and catalyst, though the volume is different.
- For polysulfides and additional silicone mixing of low-viscosity material is accomplished by taking equal lengths of base and catalyst on a paper pad and manipulating by stiff bladed spatula in a circular motion for 45 seconds till the mix is free from streaks.
For condensation silicone the quantity of reactor paste needed is very little
- So the base and reactor pastes are extruded on a mixing pad with unequal lengths of base and catalyst on a paper pad and manipulated by stif bladed spatula in a circular motion for 45 seconds till the mix is free from streaks.
- In polyether rubber base impression material the quantity of reactor paste needed is very little.
- So the base and reactor pastes are extruded on mixing pad with unequal lengths without touching each other.
- Required amount of thinner when supplied is added to the base and accelerator depending on the viscosity needed.
- Reactor paste is incorporated into base paste. Mixing is done by using tapered stiff bladed metal or plastic spatula. A streak-free mix is obtained in 45 seconds.
Static Automixing System:
These days many of the materials are now dispensed by an extruder gun with a mixing tip.
- Base and catalyst are stored or supplied in separate cylinders of the plastic cartridge.
- Extruder gun contains two plungers on which these cylinders are placed.
- Now the base and catalyst are forced through the mixing tip.
- It consists of a stationary plastic internal spiral that brings together the correct volume of both base and catalyst, and dispenses it premixed.
- Apply the mixed material directly over the prepared teeth and/or impression tray.
- The advantages of the mixing tip include dispensing of the correct ratio of base and catalyst, and uniform mixing without incorporation of air bubbles.’
- Addition and condensation silicones, and polyethers are available in these systems.
Dynamic Mechanical System:
It is also known as automated mixing system.
- It consists of a separate mixing machine with cartridges for the base and catalyst, and a plastic mixing tip.
- Base and catalyst are supplied in collapsible plastic bags.
- After housing of the base and catalyst in the cartridge, the mixing tip is placed in the front of the machine.
- On pressing the button on the top, the machine automatically mixes the base and catalyst by the movement of the plungers pushing against the collapsible plastic bags.
- Here in this system the internal spiral is motor drive that rotates. A uniform, thorough mixing can be accomplished even for higher viscosity materials.
- In this system benefit is of uniform mixing and the speed of mixing and the disadvantage is the equipment is expensive.
- Only addition silicones and polyethers are available in these systems.
Question 10. Write a short note on imbibition and syneresis.
Or
What is syneresis and imbibition.
Or
Write short note on syneresis and imbibition.
Or
Write a brief on syneresis and imbibition.
Answer:
Syneresis:
- Syneresis is defied as expression of fluid onto surface of gel structure, this process allows hydrocolloid impression to achieve equilibrium through stress relaxation.
- During syneresis small droplets of exudate are formed on the surface of hydrocolloid and the process occurs irrespective of the humidity of surrounding atmosphere.
- They can be alkaline or acidic depending on the composition of gel.
- It is less in hydrocolloids, i.e. alginate and agar which contain a high concentration of dispersed medium.
- Gel shrinks during syneresis and alters original dimension of impression. So the cast which is made get altered in its dimensions.
Imbibition:
- Imbibition is defined as the process of water sorption.
- If a hydrocolloid gel is placed in water it will absorb water by the process known as imbibition.
- Gel gets swelled during imbibition and thereby alters the original dimensions. So the cast which is made from that will be smaller in dimension.
- Irreversible hydrocolloids will continue to undergo imbibitions if they are placed under the water. They imbibe until the water content is much greater than that of the original gel.
Importance: Syneresis and imbibition can result in dimensional changes and therefore inaccurate cast. To avoid this, hydrocolloid impression should be poured immediately.
Question 11. Write a short note on gel structure.
Answer:
A gel is a semisolid and is produced from a sol during the process of gelation by the formation of the first or chains or micelles of the dispersed phase which become interlocked to the given characteristic jelly-like consistency. Within the gel, the first branch and intermesh to form a “brush heap structure”. The dispersion medium is held in the interstices between the fibrils by capillary attraction or adhesion.
Gelation may be brought about in one of two ways:
- Lowering the temperature, for example, Agar
- By a chemical reaction, for example, Alginate
Gel strength depends on:
- The density of the fibrillar structure—Greater the concentration, greater will be the number of micelles and hence the greater the brush heap density.
- Filler particles become trapped in the fibrillar network and their size, shape, and density determine their effectiveness. Addition of filers also increases the viscosity of sol.
Question 12. Give ideal requirements of an impression material
Answer:
Ideal Requirements of an Impression Material:
- Have a pleasant taste, odor, and aesthetic color.
- Not contain any toxic or irritating ingredients.
- Have an adequate shelf-life for storage and distribution.
- Be economic.
- Be easy to use with the minimum equipment.
- Have adequate setting characteristics that meet clinical requirements.
- Possess a satisfactory consistency and texture.
- Have an adequate strength so that it will not break or tear while removing from the mouth.
- Possess elastic properties with freedom from permanent deformation after strain.
- Exhibit dimensional stability.
- Be compatible with the die and cast materials.
Question 13. Write a short note on impression disinfection.
Answer:
Disinfection of impression is a concern because of viral diseases such as hepatitis B, AIDS, and herpes simplex.
The viruses can contaminate the gypsum mould and present a risk to dental laboratory and operating personnel. As impression is removed from the mouth, it is disinfected before pouring the cast to prevent cross-contamination.
- As per protocol of Centers for disease control and Prevention, hydrocolloid impressions should be immersed in household bleach, iodophors or synthetic phenols.
- As the impression is taken out from mouth, it is thoroughly rinsed and then disinfectant is sprayed over the impression.
- Now the impression is wrapped in a disinfectant-soaked towel, and is sealed for 10 minutes.
- As disinfection get complete impression is thoroughly rinsed with water to remove remnants of disinfectant which can affect surface of cast when gypsum is poured.
- For disinfecting the elastomeric impression materials recommended disinfectant solutions except for polyether are 2% glutaraldehyde, chlorine compounds, complex phenolic and phenolic glutaraldehyde compounds.
- As polyethers are hydrophilic their disinfectant protocol is same as hydrocolloids.
- Impressions are disinfected for 10 minutes in 2% glutaraldehyde and for 3 minutes in
chlorine compounds.
Question 14. Describe in detail about condensation silicone.
Answer:
Condensation Silicone:
It is also known as conventional silicones.
Composition of Condensation Silicone:
![]()
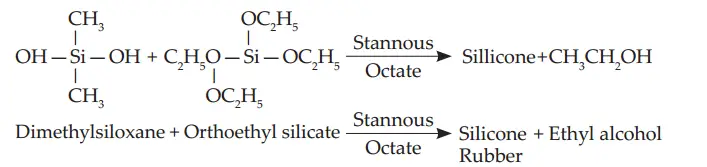
Setting Reaction of Condensation Silicone:
It is a condensation reaction. Polymerization occurs as a result of cross-linkage between the ortho-ethyl silicate and terminal hydroxy group of dimethylsiloxane to form a three-dimensional network. Ethyl alcohol is the by-product of the reaction which evaporates causing contraction of set condensation silicone impression. Reaction is exothermic with temperature rise of 1°C.
Properties of Condensation Silicone:
It has pleasant color and odor.
- Its setting time is 6 to 9 minutes, while the mixing time is 45 seconds.
- It is non-toxic but direct skin contact should be avoided.
- Excellent reproduction of surface details.
- Dimensional stability is comparatively less because of high curing shrinkage (0.4 to 0.65).
- Tear strength (3000) g/cm is lower than the polysulfides.
- It is stiffer than polysulfide.
- It is hydrophobic so field should be dried before making the impression.
- It can be plated with silver/copper.
- Shelf-life is slightly less than polysulfide.
Advantages of Condensation Silicone:
- It does not consist of bad odor of polysulphides.
- Basic advantages of elastomeric impression materials are present.
Disadvantages of Condensation Silicone:
- Shelf life is limited.
- As by-products are formed after the chemical reaction, the impression cannot be kept for an extended period of time.
- Due to the evaporation of ethyl alcohol dimensional stability is affected.
Manipulation of Condensation Silicone:
Following are the methods of manipulating condensation silicone, i.e.
- Hand mixing
- Static auto mixing system.
1. Hand Mixing:
- High viscosity material, i.e. put is usually supplied in small tubs with different colored scoops for identification and dispensing.
- Equal quantities of both the pastes are taken.
- Mixing is done by hand by kneading the material together to obtain a uniform mix without any streaks.
- Manufacturers also supply in base and catalyst in separate tubes with a much smaller diameter opening for catalyst,to enable dispensing equal lengths of base and catalyst,
though the volume being different. - For condensation silicone, the quantity of reactor paste needed is very little.
- So the base and reactor pastes are extruded on a mixing pad with an unequal length of base and catalyst on a paper pad and manipulated by a stiff bladed spatula in a circular motion for 45 seconds till the mix is free from streaks.
2. Static Automixing System:
- These days many of the materials are now dispensed by an extruder gun with a mixing tip.
- The base and catalyst are stored or supplied in separate cylinders of the plastic cartridge.
- The extruder gun contains two plungers on which these cylinders are placed.
- Now the base and catalyst are forced through the mixing tip.
- It consists of a stationary plastic internal spiral that brings together the correct volume of both base and catalyst, and dispenses it premixed.
- Apply the mixed material directly over the prepared teeth and/or on the impression tray.
- The advantages of the mixing tip include dispensing of the correct ratio of base and catalyst and uniform mixing without the incorporation of air bubbles.
- Condensation silicones are available in these systems.
- It is stiffr than polysulfide.
- It is hydrophobic.
Question 15. Compare and contrast reversible hydrocolloid from irreversible hydrocolloid impression materials with regard to their chemistry and properties.
Or
Write the difference between irreversible and reversible hydrocolloids.
Or
Compare agar-agar and alginate impression material.
Answer:
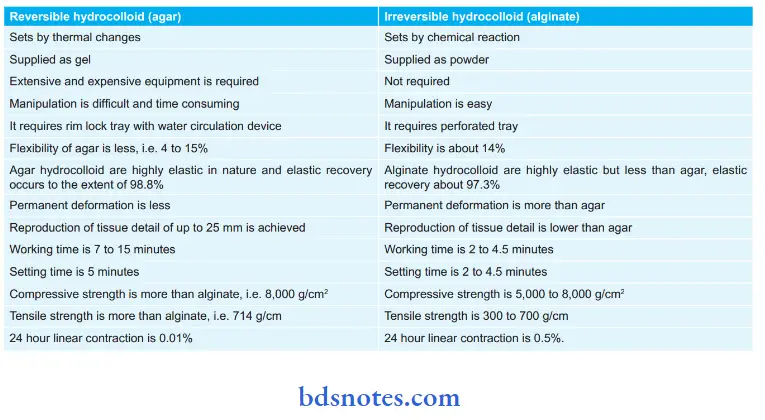
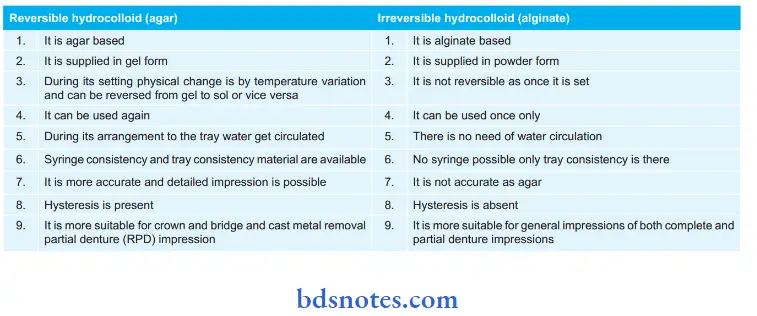
Difference between irreversible and reversible hydrocolloid:
Question 16. Write a short note on dust-free alginate.
Answer:
- Dust-free alginate is the newer alginate without silica particles.
- It is coated with glycol which makes the particles so heavier on puffy or at the time of manipulation the alginate particles does not blow in the air.
- By coating alginate particles with glycol, helps in balancing the composition and maintaining the standards of the composition.
- This type of alginate does not cause any health hazards because no silica particles are present in it.
- The shrinkage of dust-free alginate is less.
- They reproduce good surface details.
They are available in different types of colors and flavors:
- These types of alginate are available with changes in colors which guide and help the dentist as well as are attractive to the patients.
- Their water powder (w/p) ratio is less as compared to older alginate.
- They are available in two types such as fast setting alginate and slow-setting alginate.
- They are more elastic or fragile than older alginate, their tensile strength is also higher than the older alginate also.
Question 17. Write in detail about properties and uses of alginate.
Answer:
Properties of Alginate (ADA Specification No. 18):
- Taste and Odor: Alginate has a pleasant taste and smell. A variety of colors, odors, and tastes are added to make it pleasant.
- Flexibility: It is 14% at stress of 12.2 N. Lower W/P ratio results in lower flexibility.
- Elastic and Elastic Recovery: Alginate hydrocolloids are highly elastic and about 97.3% elastic recovery occurs. So, permanent deformation is more for alginate.
- Reproduction of Tissue Detail: Detail reproduction is lower as compared to agar hydrocolloids.
- Strength:
- Compressive strength — 5,000 – 8,000 g/cm2 or 0.5 to 0.9 MPa.
- Tear strength — 350 – 700 g/cm2 Or 0.4 to 0.7 KN/m.
- Dimensional Stability: Alginate has poor dimensional stability due to evaporation, syneresis and therefore cast should be poured immediately.
- Adhesion: Alginate does not adhere well to the tray. Good adhesion is important for accuracy of impression. Retention to the tray is achieved by mechanical locking features in tray.
- Biological Properties: Silica particles present in the dust which rises from the cane after fluffy alginate powder is a possible health hazar
Shelf-life and Storage:
Alginate material deteriorates rapidly at elevated temperature and humid environment. That is why:
- Material is stored in cool, dry environment.
- Lid of bulk package is replaced after every use to minimize moisture contamination.
- Stock only for 1 year.
Question 18. Enumerate various impression materials used in dentistry.
Answer:
Enumeration of Various Impression Materials Used in Dentistry:
1. Rigid impression materials
- Impression plaster
- Impression compound
- Zinc oxide eugenol impression paste
- Impression waxes
2. Elastic impression materials
- Hydrocolloids
- Agar, i.e. reversible hydrocolloid
- Alginate, i.e. irreversible hydrocolloid
- Elastomeric impression materials
- Polysulphide
- Condensation polymerizing silicones
- Addition polymerizing silicones
- Polyether
Question 19. Discuss in detail the disinfection procedure for irreversible hydrocolloid material.
Answer:
Disinfection procedure for irreversible hydrocolloid material:
As the impression is removed from the mouth, it is disinfected before pouring the cast to prevent cross-contamination. As per the protocol of Centers for disease control and Prevention, hydrocolloid impressions should be immersed in household bleach, iodophors, or synthetic phenols.
As impression is taken out from the mouth, it is thoroughly rinsed and then disinfectant is sprayed over the impression. Now the impression is wrapped in a disinfectant-soaked towel and is sealed for 10 minutes. As disinfection get a complete impression is thoroughly rinsed with water to remove remnants of disinfectant which can affect the surface of the cast when gypsum is poured
Question 20. Classify elastomeric impression materials. Describe the composition and setting reaction of addition and condensation silicone material. Enumerate differences between them.
Or
Classify elastomeric impression materials. Describe the composition and setting reaction of addition and condensation silicone material.
Answer:
Classification of Elastomeric Impression Material:
1. On the basis of their chemistry
- Polysulfide
- Condensation polymerizing silicones
- Addition polymerizing silicones
- Polyether.
2. On the basis of their viscosity (ISO 4823: 2015)
- Type 0 — Putt consistency (very heavy)
- Type 1 — Heavy bodied consistency (tray consistency)
- Type 2 — Medium bodied consistency (regular-bodied)
- Type 3 — Light bodied (syringe consistency).
3. On the basis of wettability or contact angle
- Hydrophilic, if their contact angle is from 80°–105°
- Hydrophobic, if their contact angle is from 40°–70°.
Differences between Condensation and Addition Silicone:
![]()
Composition of Addition Silicone:
- Base
- Poly (methyl hydrogen siloxane)
- Other siloxane prepolymers
- Fillers (amorphous silica or fluorocarbon)
- Palladium-hydrogen absorber
- Retarders.
- Accelerator
- Divinyl polysiloxane
- Other siloxane prepolymers
- Platinum salt—catalyst
- Fillers.
Setting Reaction of Addition Silicone:
It is an additional reaction. In this, the base polymer is terminated with vinyl groups and is cross-linked with silane. The reaction is activated by platinum salt. There are no by-products as long as there is a balance between the vinyl siloxane and silane siloxane. If unbalanced, hydrogen gas is produced causing air bubbles in stone models. To avoid this palladium is added to absorb hydrogen
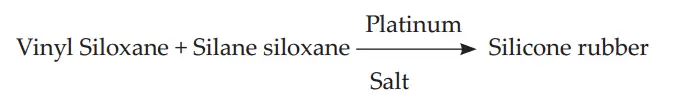
Composition of Condensation Silicone:
![]()
Setting Reaction of Condensation Silicone:
It is a condensation reaction. Polymerization occurs as a result of cross-linkage between the ortho-ethyl silicate and the terminal hydroxyl group of the dimethylsiloxane to form a 3D network. Stannous octoate acts as the catalyst. The reaction is exothermic.
The ethyl alcohol formed as a byproduct evaporates gradually from the set rubber leading to shrinkage.

Question 21. Write a short note on polysulfide.
Answer:
Polysulfide is also known as mercaptan or Thiokol
Composition of Polysulfide:
Setting Reaction of Polysulfide:
As base and accelerator pastes are mixed, they undergo both polymerization by oxidation of terminal SH groups and the cross-linking of pendant SH groups. Reaction occurs between polymer with free mercaptan, i.e.–SH groups, and the oxidizing agent lead dioxide, which lengthens and cross–links the chain through the reaction of terminal and pendant –SH group. The whole reaction is exothermic which increases the temperature from 3°C to 5°C and the formation of water as a by-product.
Mercaptan + Lead dioxide → Polysulfie + Water
Properties of Polysulfide:
- It has unpleasant odor and color. It stains linen and is messy to work with.
- These materials are extremely viscous and sticky. Mixing is difficult.
- It has a long setting time of 12.5 minutes.
- Excellent reproduction of surface detail.
- Dimensional stability: The curing shrinkage is high and continuous even after settling. It has the highest permanent deformation among the elastomers, i.e. 3 to 5%.
- It has high tear strength (4,000 g/cm).
- It has good flexibility (7%) and low hardness.
- It is hydrophobic so the mouth should be dried before making an impression.
- It can be electroplated more with silver than copper.
- Shelf-life is good, i.e. 2 years.
Advantages of Polysulfide :
- Excellent reproduction of surface detail as fine as 0.025 mm wide
- It can be electroplated more with silver than copper
- The shelf-life is good (2 years)
- It has good flexibility (7%)
- It has high tear strength (4,000 g/cm) thus making it more resistant to tearing even when the impression is in thin section.
Disadvantages of Polysulfide:
- Unpleasant odor and color.
- These materials are extremely viscous and sticky. Mixing is difficult.
- It has long setting time which adds to the patient’s discomfort.
- Dimensional unstability: It has high permanent deformation. The curing shrinkage is high, and loss of byproduct (water) also causes shrinkage.
- Staining is present due to lead dioxide.
Manipulation of Polysulfide:
- High-viscosity material, i.e. putt is usually supplied in small tubs with different colored scoops for identification and dispensing.
- Equal quantities of both pastes are taken.
- Mixing is done by hand by kneading the material together to obtain a uniform mix without any streaks.
- Manufacturers also supply base and catalyst in separate tubes with a much smaller diameter opening for a catalyst to enable dispensing equal lengths of base and catalyst, though the volume is different.
- For polysulphides mixing of low-viscosity material is accomplished by taking equal lengths of base and catalyst on a paper pad and manipulating by stiff bladed spatula in a circular motion for 45 seconds till the mix is free from streaks.
Question 22. Write the differences between reversible and irreversible hydrocolloids.
Or
Write the difference between irreversible and reversible hydrocolloids.
Or
Compare agar-agar and alginate impression material.
Answer:
An impression is defined as “an imprint or negative likeness of the teeth and/or edentulous areas where the teeth have been removed, made in a plastic material which becomes relatively hard or set while in contact with these tissues. Impressions may be made of full complements of teeth, of areas where some teeth have been removed, or in mouth from which all teeth have been removed.
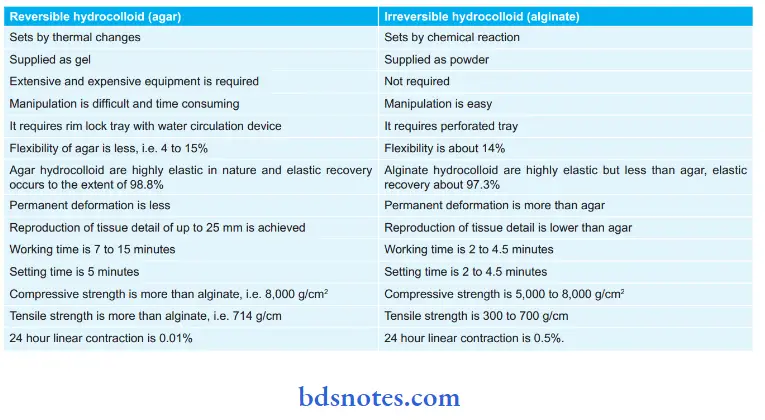
Difference between Reversible and Irreversible Hydrocolloid:
Question 23. Write in detail about factors controlling setting time and properties of ZOE impression paste.
Answer:
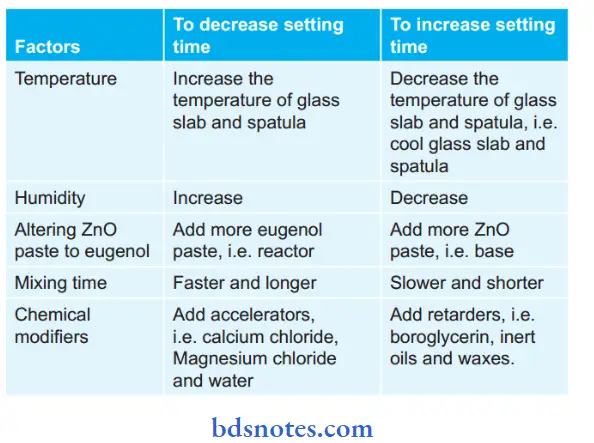
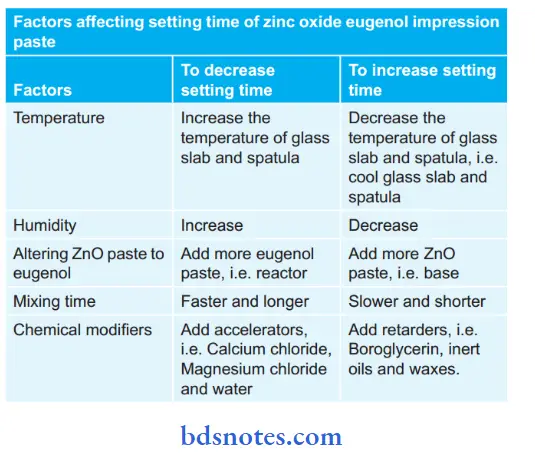
Factors Controlling Setting Time of ZOE Impression Paste
Factors affecting the setting time of zinc oxide eugenol impression paste are as follows:
Question 24. How will you change the setting time of ZOE paste?
Answer:
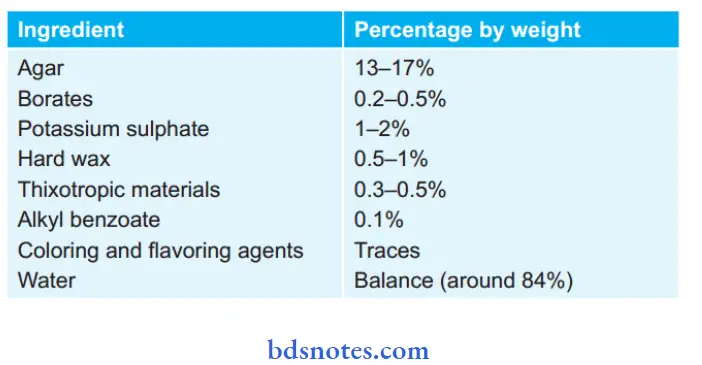
Question 25. What is the composition of Agar – Agar
Answer:
The reversible hydrocolloid impression material is agar.
Composition :
Question 26. Discuss the addition silicone impression material in detail.
Or
Give composition, chemical reaction, and properties of addition silicone impression material.
Or
Write short note on additional silicone.
Or
Write short note on polyvinyl siloxane impression material.
Answer:
Addition Silicone:
Addition silicone is also known as polyvinyl siloxane.
Composition of Addition Silicone:
- Base
- Poly (methyl hydrogen siloxane)
- Other siloxane prepolymers
- Fillers (amorphous silica or fluorocarbon)
- Palladium hydrogen absorber
- Retarders.
- Accelerator
- Divinyl polysiloxane
- Other siloxane prepolymers
- Platinum salt—catalyst
- Fillers
Setting Reaction of Addition Silicone:
It is an additional reaction. In this, the base polymer is terminated with vinyl groups and is cross-linked with silane. The reaction is activated by platinum salt. There are no by-products as long as there is a balance between the vinyl siloxane and silane siloxane. If unbalanced, hydrogen gas is produced causing air bubbles in stone models. To avoid this palladium is added to absorb hydrogen.
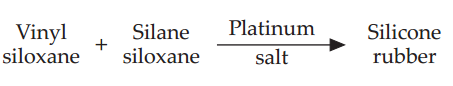
Properties of Addition Silicone:
- Its odor and color is pleasant.
- It can lead to allergic reactions.
- Reproduction of surface details is excellent.
- The setting time is 5 to 9 minutes. The mixing time is 45 seconds.
- Working time is extended by chilling the tubes.
- Dimensional stability is good. Curing shrinkage is low (0.17%) and permanent deformation is very low, i.e. 0.05 to 0.3%.
- Tear strength is good, i.e. 3,000 g/cm.
- Material is hydrophobic so care should be taken while pouring impression.
- It can be electroplated from silver or copper
- Flexibility is low. Extra spacing should be provided in the impression tray. Care should be taken at the time of removing stone cast from the impression to avoid breakage.
- Its shelf-life ranges from 1 to 2 years.
Advantages of Addition Silicone:
- Most dimensionally stable impression material.
- These impressions can be kept for 7 days after taking an impression.
- They are available in various consistency so can be used in various clinical situations.
Disadvantages of Addition Silicone:
- They are inherent and have hydrophobic nature.
- A rounded margin with loss of detail in impression is caused by moisture contamination of the prepared tooth.
- Sulfur contamination from latex gloves inhibit setting reaction of additional silicones.
- As residual hydrides in set material react with moisture present in atmosphere and evolve hydrogen gas, due to this cast cannot be poured readily.
- It should be poured after 30 minutes for gypsum casts and only after 24 hours for epoxy dies.
Manipulation of Addition Silicone:
An equal length of base and accelerator is extruded onto the mixing pad side by side without touching. The accelerator paste is then incorporated into the base paste. Mixing is done using a tapered stiff bladed spatula. A streak-free mix is obtained in 45 seconds.
Question 27. Write a brief on reversible hydrocolloids.
Answer:
A reversible hydrocolloid is also known as agar. It is an elastic impression material.
Classifiation of reversible hydrocolloid:
Based on the viscosity (ISO 21563:2013)
- Type 1: Heavy bodied (for use as tray material)
- Type 2: Medium-bodied (for use as tray or syringe material)
- Type 3: Light bodied (for syringe use only)
- Type 4: Light-bodied for agar-alginate combination technique.
The function of Ingredients:
- Agar: Basic constituent for tray material.
- Borate: Provide strength to gel.
- Potassium sulphate: Counteract retarding effect of borate and ensure proper setting of cast and die.
- Hard wax: Act as filer, and provides strength, viscosity, and rigidity.
- Thixotrophic material: Acts as a plasticizer.
- Alkyl Benzoate: Preservative
- Coloring and flavoring: For patient comfort and acceptance.
- Water: As dispersion medium.
Uses of reversible hydrocolloid:
-
- For cast duplication
- For full mouth impressions without deep undercut.
- For FPD impressions.
- As tissue conditioner.
Advantages of reversible hydrocolloid:
- Preparation of accurate dies is possible.
- Good elastic properties reproduce most undercut areas.
- Good recovery from distortion.
- Saliva in the mouth creates no problem.
- Well-tolerated by the patient.
- It is economical.
- Can be reused.
Disadvantages of reversible hydrocolloid:
- The flow of material is not good
- Electroplating cannot be done
- During insertion, patient experienced thermal discomfort
- Only a single model is poured
- Special and expensive instruments are required
- The impression should be poured immediately.
Question 28. Classify compare elastic impression materials.
Answer:
Elastic Impression Materials:
- Hydrocolloids or aqueous elastic impression material
- Agar, i.e. reversible hydrocolloid
- Alginate, i.e. irreversible hydrocolloid
- Elastomeric impression materials or non-aqueous elastic impression materials
- Polysulphide
- Condensation polymerizing silicones
- Addition polymerizing silicones
- Polyether
Comparison of Elastomeric Impression Materials:
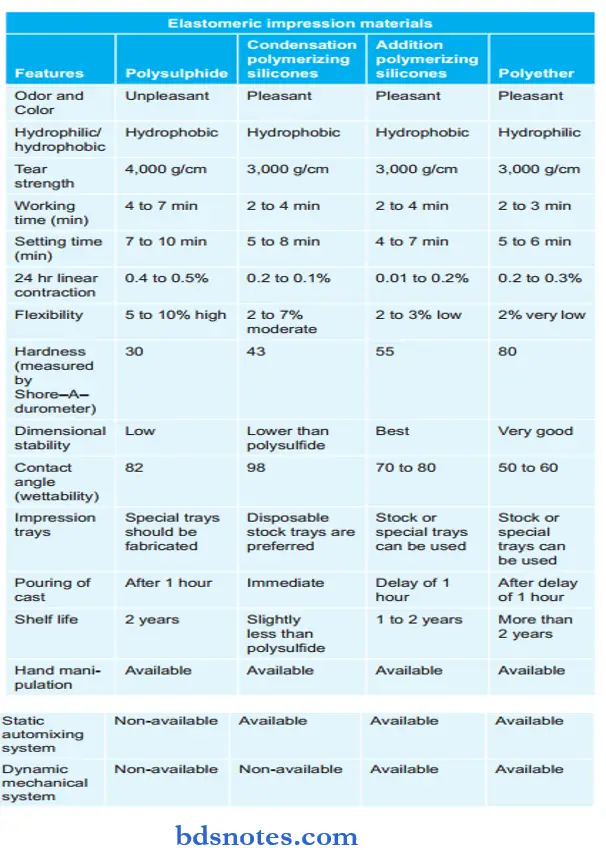
Impression compound is a rigid reversible impression material that sets due to physical change. On applying heat it softens and on cooling it becomes hard.
- Type I—Impression compound.
- Type II—Tray compound.
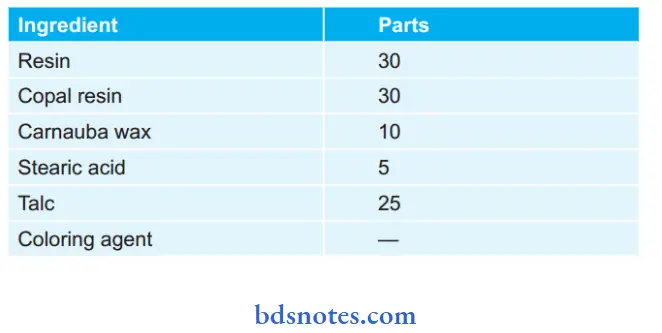
Plasticizers: Various compounds such as shellac, stearic acid, and gutt-percha are added to improve plasticity and workability. Fillers such as talc increase the strength of matrix material
Properties of Elastomeric Impression Materials
- Fusion Temperature: When the impression compound is heated in a water bath, it softens at 39°C, on continued heating above 43.5°C material start to soften and flow to a plastic mass which is manipulated. All impressions should be made above this temperature.
- Thermal Properties:
- It has low thermal conductivity and is a poor conductor of heat.
- The coefficient of thermal expansion is high due to the presence of resin and wax. Linear contraction from mouth to room temperature is 0.3%.
- Flow: During impression making good flw is necessary. Soft material flows in tissue contour. As the impression compound hardens its flow is stopped.
Applications of impression compound.
- For type I:
- Making a primary impression in the edentulous mouth.
- For the impression of full crown preparation where gingival tissues should be displaced.
- In border molding.
- For type II:
- For checking undercut in inlay preparation.
- For making special tray.
Advantages of impression compound.
- Material can be reused a number of times if an error occurs.
- If any portion remains inaccurate, it should be remade without making a complete impression.
- By filming the surface of impression material accuracy can be improved.
- The material got its own body to support itself mainly in peripheral portion.
- The material should not collapse completely if tray is unable to support it.
Disadvantages of impression compound.
- Due to high viscosity details recorded are fewer.
- While taking impressions soft tissues get compressed.
- It has poor dimensional stability due to which it gets distorted.
- If undercuts are present it is difficult to remove.
- It gets overextended mainly in peripheries.
Question 30. Difference between Addition Silicone And Condensation Silicone
Answer:
The difference in Setting Reaction of Addition and Condensation Silicone:
![]()
Question 31. Write a short note on the wet field technique.
Answer:
The wet field technique is the alternative technique of applying syringe material of reversible hydrocolloid material, i.e. agar
- In this technique area that has to be recorded is bathed in warm water and syringe material is deposited only on the occlusal or incisal surface of teeth.
- Tray material gets seated.
- The hydraulic pressure of viscous tray material forces the fluid syringe hydrocolloid down in the areas which are to be recorded.
- This motion displaces the syringe material, blood, and debris throughout the sulcus.
- The impression should be removed with the sudden snapping motion.
Question 32. Write a short note on the silicone rubber base impression material.
Answer:
There are two types of silicone rubber base impression material present based on the type of polymerization reaction occurring during its setting.
The materials are:
- Condensation silicones
- Addition silicones
Question 33. Write the Classification of zinc oxide eugenol impression pastes.
Answer:
A dental impression is defined as a negative record of the tissues of the mouth.
Classification of Zinc Oxide Eugenol Impression Paste:
ADA specification No. 16
- Type I or hard
- Type II or soft.
Question 34. Write a short note on the lamination technique.
Answer:
The lamination technique is also known as the agar-alginate combination technique.
- In this technique, a syringe type of agar is loaded in a cartridge, and alginate of the regular type is mixed and placed on a stock tray.
- The syringe agar is injected around the preparation.
- The cooled alginate is seated on the top of the agar.
- Alginate sets in about 3 minutes and agar gels within this time as a result of being cooled by the alginate.
- During setting of alginate and gelling of agar, a bond forms between them. When the tensile strength is between 600 to 1100 g/cm the bond is better.
- The impression is removed in about 4 minutes. The surface of the impression is in agar and the base of the impression is in alginate.
- Accuracy is good for an agar-alginate impression
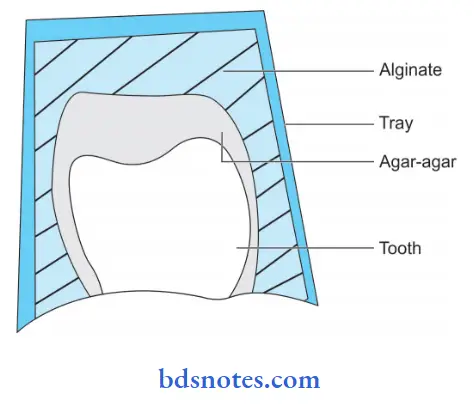
Advantages of the Lamination technique:
- The syringe of agar produces better results than alginate.
- Fewer air bubbles
- Water-cooled trays are not needed so it is more convenient.
- It sets faster than the regular agar technique.
Question 35. Write a short note on polyether rubber base impression material.
Answer:
It is a polyether-based polymer which is introduced in Germany in the late 1960s. It was developed in an attempt to combine the good mechanical properties of polysulfides with the dimensional stability of silicones.
Composition of polyether rubber base:
- Base paste
- Polyether polymer—80 to 85%
- Colloidal silica—acts as the filer
- Glycolether or phthalate—plasticizer
- Reactor or accelerator paste
- Aromatic sulfonate ester—crosslinking agent
- Colloidal silica—filer
- Phthalate or glycol ether—plasticizer.
Setting Reaction of polyether rubber base
It is cured by the reaction between aziridine rings which are at the end of branched polyether molecules. The main chain is a copolymer of ethylene oxide and tetrahydrofuran. Crosslinking is brought about by the aromatic sulphonate ester via the imine end groups. The reaction is exothermic. No by-product is formed.
Polyether + Sulfonic ester → Crosslinked rubber
Properties of polyether rubber base:
- Its taste and odor are pleasant.
- It can lead to skin reactions due to the presence of sulfonic ester. Thorough mixing is done before making an impression.
- Its setting time is 6 to 8 minutes, mixing is done quickly, i.e. in 30 seconds. Heat decreases the setting time.
- Dimensional stability is good. Curing shrinkage is low, i.e. 0.24%.
- Permanent deformation is low, i.e. 0.8 to 1.6%.
- Polyether absorbs water and can change dimension, so prolonged contact with water and humid climate is not recommended.
- The material is stiff and it is difficult to remove it from undercuts so additional spacing is required.
- Tear strength is good, i.e. 3,000 g/cm.
- Since the material is hydrophilic, moisture in the impression field is not critical.
- It has best compatibility with stone among all elastomers.
- Its shelf-life is excellent, i.e. more than 2 years.
- It can be electroplated with silver or copper.
Manipulation of polyether rubber base
Following are the methods of manipulating polyether rubber base impression material, i.e.
- Hand mixing
- Static auto-mixing system
- Dynamic mechanical system
1. Hand Mixing:
- High-viscosity material, i.e. putt is usually supplied in small tubs with different colored scoops for identification and dispensing. Equal quantities of both pastes are taken.
- Mixing is done by hand by kneading the material together to obtain a uniform mix without any streaks.
- Manufacturers also supply base and catalyst in separate tubes with a much smaller diameter opening for catalyst to enable dispensing equal lengths of base and catalyst,
though the volume being different. - In polyether rubber base impression material the quantity of reactor paste needed is very little. So the base and reactor pastes are extruded on the mixing pad with unequal length without touching each other.
- The required amount of thinner when supplied is added to the base and accelerator depending on the viscosity needed. Reactor paste is incorporated into the base paste. Mixing is done by using a tapered stiff bladed metal or plastic spatula. A streak free mix is obtained in 45 seconds.
2. Static Automixing System:
- These days many of the materials are now dispensed by an extruder gun with a mixing tip.
- The base and catalyst are stored or supplied in separate cylinders of the plastic cartridge.
- The extruder gun contains two plungers on which these cylinders are placed.
- Now the base and catalyst are forced through the mixing tip.
- It consists of a stationary plastic internal spiral that brings together the correct volume of both base and catalyst and dispenses it premixed.
- Apply the mixed material directly over the prepared teeth and/or the impression tray.
- The advantages of the mixing tip include dispensing of the correct ratio of base
and catalyst, and uniform mixing without the incorporation of air bubbles. - Polyethers are available in these systems.
3. Dynamic Mechanical System:
- It is also known as an automated mixing system.
- It consists of a separate mixing machine with cartridges for the base and catalyst and a plastic mixing tip.
- The base and catalyst are supplied in collapsible plastic bags.
- After housing of the base and catalyst in the cartridge, the mixing tip is placed in the front of the machine.
- On pressing the button on the top, the machine automatically mixes the base and catalyst by the movement of the plungers pushing against the collapsible plastic bags.
- Here in this system, the internal spiral is the motor drive that rotates.
- A uniform, thorough mixing can be accomplished even for higher-viscosity materials.
- In this system, the benefit is of uniform mixing and the speed of mixing and the disadvantage is the equipment is expensive.
- Polyethers are available in these systems.
Question 36. Write a short note on disinfectants used for impression materials.
Answer:
Disinfectants used for impression material are as follows:
- Impression compound: Iodophors, sodium hypochlorite (1:10 dilution).
- ZOE impression: Iodophors, sodium hypochlorite (1:10 dilution).
- Polyether: Iodophors, sodium hypochlorite (1:10 dilution).
- Silicone and polysulphide: Iodophors, sodium hypochlorite, synthetic phenols.
- Wax bites: Iodophors.
Disinfection of impressions is done by immersing the impressions in a plastic bag containing disinfectants or by spraying the impression surface and leaving it for 15 minutes. Polyether and hydrocolloids should be immersed only for 10 minutes. Remove the impressions and rinse in running water, remove excess water, and pour the cast.
Question 37. Write a short note on the composition of alginate.
Answer:
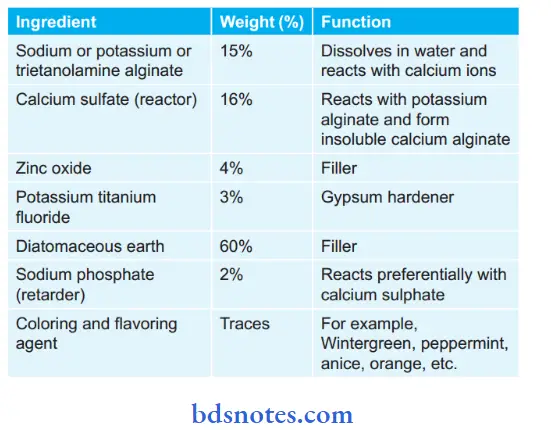
Composition of Alginate:
Question 38. Write a short note on diatomaceous earth.
Answer:
Diatomaceous earth is filer in various dental impression materials such as alginate, agar, zinc oxide eugenol impression paste, and impression compound.
- Diatomaceous earth is composed of remains of minute planktonic algae that were deposited millions of years ago and whose skeletons become calcified.
- 60% Diatomaceous earth is added in the alginate powder to increase the stiffness as well as strength of alginate gel.
- It also provides a smooth texture and aids in the formation of a sol by dispersing alginate powder particles when mixed with water.
- When the powder in the alginate can is fluffed to break loose the particles, diatomaceous earth which is made up of fie porous silica particles will become airborne when the lid is removed.
- Long-term exp of inhalation of this diatomaceous earth which consists of porous fie silica particles can cause silicosis or pulmonary hypersensitivity.
Diatomaceous earth is also used in catalyst paste of zinc oxide eugenol impression material.
- Here it provides proper consistency of the mix.
- 0.3 to 0.5% diatomaceous earth act as a filer in agar and control viscosity, rigidity, and strength.
- 50% diatomaceous earth in impression compound acts as a filter and increases the strength, reduces flow at mouth temperature, and decreases coefficient of thermal expansion.
- Kieselguhr a form of diatomaceous earth is used as a mild abrasive and polishing agent.
Question 39. Write in detail about the manipulation and properties of silicone rubber base impression material.
Answer:
Silicone Rubber Base Impression Materials:
There are two silicone rubber base impression materials, i.e.
- Condensation silicone
- Addition silicone
Manipulation of Silicone Rubber Base Impression Materials:
Following are the methods of manipulating silicone rubber base impression materials, i.e.
- Hand mixing
- Static auto mixing system
- Dynamic mechanical system
1. Hand Mixing:
- High viscosity material, i.e. putt is usually supplied in small tubs with different colored scoops for identification and dispensing.
- Equal quantities of both pastes are taken.
- Mixing is done by hand by kneading the material together to obtain a uniform mix without any streaks.
- Manufacturers also supply base and catalyst in separate tubes with a much smaller diameter opening for catalyst to enable dispensing equal lengths of base and catalyst, though the volume is different.
- For addition, silicone mixing of low-viscosity material is accomplished by taking equal lengths of base and catalyst on a paper pad and manipulating by stiff bladed spatula
in a circular motion for 45 seconds till the mix is free from streaks. - For condensation silicone, the quantity of reactor paste needed is very little.
- So the base and reactor paste is extruded on a mixing pad with unequal lengths of base and catalyst on a paper pad and manipulated by stiff bladed spatula in a circular motion for 45 seconds till the mix is free from streaks.
2. Static Automixing System:
- These days many of the materials are now dispensed by an extruder gun with a mixing tip.
- The base and catalyst are stored or supplied in separate cylinders of the plastic cartridge.
- The extruder gun contains two plungers on which these cylinders are placed.
- Now the base and catalyst are forced through the mixing tip, which consists of a stationary plastic internal spiral that brings together the correct volume of both base and catalyst and dispenses it premixed.
- Apply the mixed material directly over the prepared teeth and/or the impression tray.
- The main benefits of the mixing tip includes dispensing of the correct ratio of base and catalyst and uniform mixing without the incorporation of air bubbles.
- Both addition and condensation silicones are available in these systems.
Dynamic Mechanical System:
It is also known as an automated mixing system.
- It consists of a separate mixing machine with cartridges for the base and catalyst and a plastic mixing tip.
- The base and catalyst are supplied in collapsible plastic bags.
- After housing of the base and catalyst in the cartridge, the mixing tip is placed in the front of the machine.
- On pressing the button on the top, the machine automatically mixes the base and catalyst by the movement of the plungers pushing against the collapsible plastic bags.
- Here in this system, the internal spiral is a motor drive that rotates. A uniform, thorough mixing can be accomplished even for higher-viscosity materials.
- In this system, benefit is of uniform mixing and the speed of mixing, and the disadvantage is the equipment is expensive.
- Additional silicones are available in these systems.
Properties of Condensation Silicone:
- It has pleasant color and odor.
- Its setting time is 6 to 9 minutes, while the mixing time is 45 seconds.
- It is non-toxic but direct skin contact should be avoided.
- Excellent reproduction of surface details.
- Dimensional stability is comparatively less because of high curing shrinkage (0.4 to 0.65).
- Tear strength (3,000) g/cm is lower than the polysulfides.
- It is stiffer than polysulfide.
- It is hydrophobic, so field should be dried before making an impression.
- It can be plated with silver/copper.
- Shelf-life is slightly less than polysulfide.
Properties of Addition Silicone:
- Its odor and color is pleasant.
- It can lead to allergic reactions.
- Reproduction of surface details is excellent
- The setting time is 5 to 9 minutes. The mixing time is 45 seconds.
- Working time is extended by chilling the tubes.
- Dimensional stability is good. Curing shrinkage is low (0.17%) and permanent deformation is very low, i.e. 0.05 to 0.3%
- Tear strength is good, i.e. 3,000g/cm.
- Material is hydrophobic so care should be taken while pouring impression.
- It can be electroplated from silver or copper
- Flexibility is low. Extra spacing should be provided in the impression tray.
- Care should be taken at the time of removing stone cast from the impression to avoid breakage.
- Its shelf-life ranges from 1 to 2 years.
Question 40. Write a short answer on the disinfection of dental materials.
Answer:
Disinfection of dental materials should be done to prevent the cross-infections.
- Following are the various disinfecting materials for disinfecting dental materials are:
- Impression compound: Iodophors, sodium hypochlorite (1:10 dilution).
- ZOE impression: Iodophors, sodium hypochlorite (1:10 dilution).
- Polyether: Iodophors, sodium hypochlorite (1:10 dilution).
- Silicone and polysulphide: Iodophors, sodium hypochlorite, synthetic phenols.
- Wax bites: Iodophors.
Disinfection of Various Dental Materials:
- For disinfection of resin prosthesis recommended method is by disinfecting with sodium hypochlorite (1:10 solution).
- This is done by placing of the prosthesis in a zipped plastic
bag with disinfectant for 15 minutes. - As the hydrocolloid impression is taken out from the mouth, it is disinfected before pouring the cast to prevent cross-contamination.
- CDC protocol recommends that hydrocolloids should be immersed in household bleach, i.e. sodium hypochlorite, iodophors, or synthetic phenols.
- The impression should be thoroughly rinsed in water after removal from the mouth, then an impression is sprayed liberally with disinfectant and is wrapped in a disinfectant-soaked towel, and is sealed for 10 minutes. As disinfection is over, it is rinsed thoroughly in water.
- For disinfecting the elastomeric impression materials recommended disinfectant solutions except for polyether are 2% glutaraldehyde, chlorine compounds, complex phenolic, and phenolic glutaraldehyde compounds.
- As polyethers are hydrophilic their disinfectant protocol is the same as hydrocolloids.
- Impressions are disinfected for 10 minutes in 2% glutaraldehyde and for 3 minutes in chlorine compounds.
- If the impression is not disinfected before pouring the cast, it is necessary to disinfect the stone cast. Disinfectants, i.e.
- 5% phenol or 2% glutaraldehyde is mixed with water when the cast is poured.
- Alternatively, models and casts are disinfected by immersion in 1:10 dilution of sodium hypochlorite for 30 minutes or with the spray of iodophor.

Leave a Reply