Question 1. Describe superolateral surface of cerebrum.
Answer:
Cerebrum:
- Cerebrum is made of two cerebral hemispheres which are incompletely separated from each other by the median longitudinal fissure
External features:
- Each cerebral hemisphere has the following external features
- Three surfaces
- Superolateral
- Inferior
- Medial
- Four borders
- Superomedial
- Inferolateral
- Medial orbital
- Medial occipital
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
- Three poles
- Frontal pole
- Occipital
- Temporal
- Four lobes
- Frontal
- Parietal
- Occipital
- Temporal
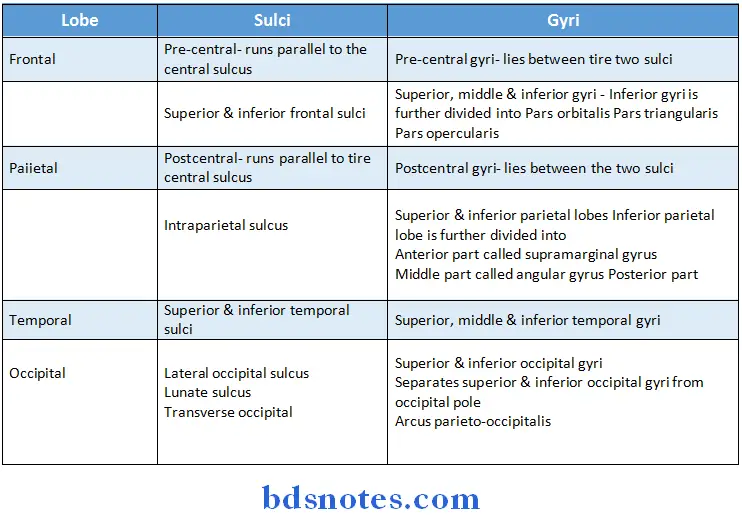
- These lobes are best appreciated on the superolateral surface of cerebrum
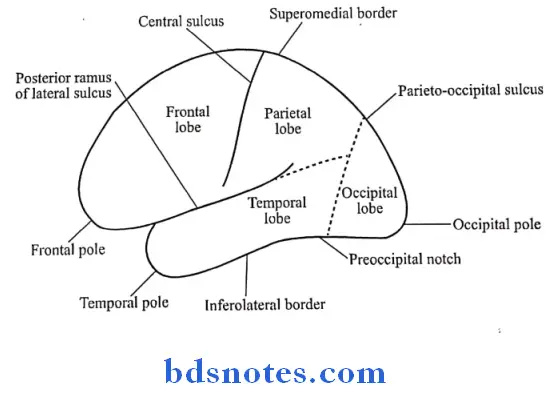
Superolateral surface:
Question 2. Describe the gross features, relations, blood supply & constituent fibres of corpus callosum (or) Parts of corpus callosum
Answer:
Corpus Callosum:
- It is the largest commissure of the brain
- It connects the two cerebral hemispheres
Gross Features:
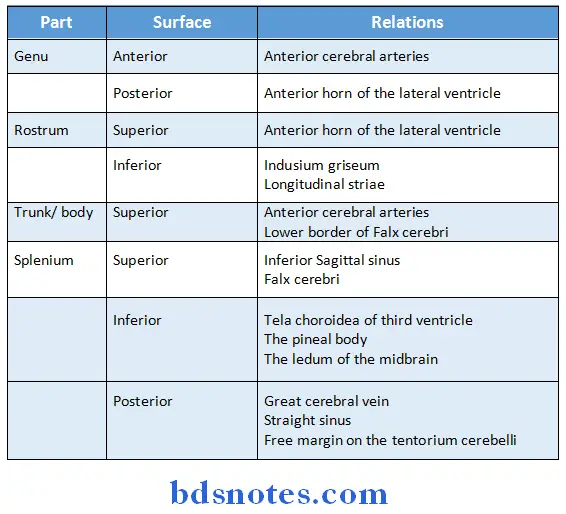
- Parts of corpus callosum
- Genu
- It is the anterior end
- It lies 4 cm behind the frontal pole
- Rostrum
- It is directed downwards & backwards from the genu
- Trunk or body
- It is the middle part between the genu & Splenium
- Its superior surface is convex from before backwards & concave from side to side
- Its inferior surface is concave from before backwards & convex from side to side
Attachments: - It provides attachment to the septum pellucidum & the fornix
- Splenium
- It is the posterior end forming the thickest part of the corpus callosum
- It lies 6 cm in front of the occipital pole
- Genu
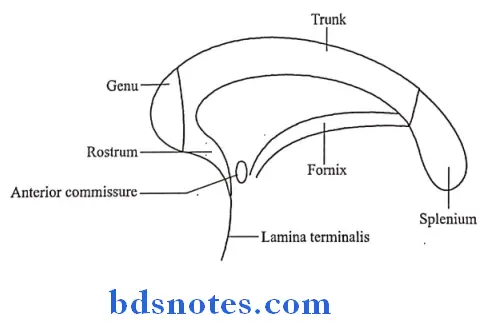
Relations:
Fibres:
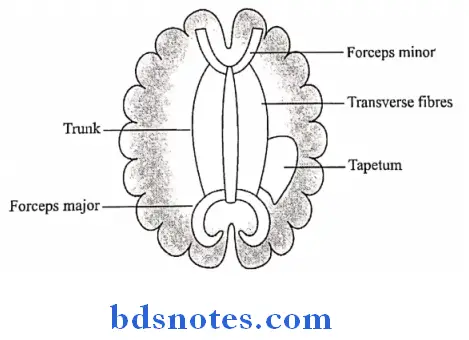
1. Forceps minor
- It is made up of fibres of the genu that connect the two frontal lobes
2. Forceps major
- It is made up of fibres of the Splenium connecting the two occipital lobes
3. Tapetum
- It is formed by some fibres from the trunk & Splenium
- It forms the roof & lateral wall of the posterior horn & the lateral wall of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle
4. The Rostrum connects the orbital surfaces of the two frontal lobes
Question 3. Corpus callosum
Answer:
- It is largest commissure of the brain
- It connects the two cerebral hemispheres
Parts:
- Genu
- It is the anterior end
- It lies 4 cm behind the frontal pole
- Rostrum
- It is directed downwards and backwards from the genu
- Trunk or body
- It is the middle part between genu and splenium
- Its superior surface is convex from before backwards and concave from side to side
- Its inferior surface is concave from before backwards and convex from side to side
- Splenium
- It is the posterior end forming the thickest part of the corpus callosum
- It lies 6 cm in front of the occipital lobe
Fibres:
- Forceps minor
- Made up of fibres of the genu that connect the two frontal lobes
- Forceps major
- Made up of fibres of the splenium connecting the two occipital lobes
- Tapetum
- Formed by some fibres from the trunk and splenium
- Forms the roof and lateral wall of the posterior horn and the lateral wall of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle
- The rostrum connects the orbital surfaces of the two frontal lobes
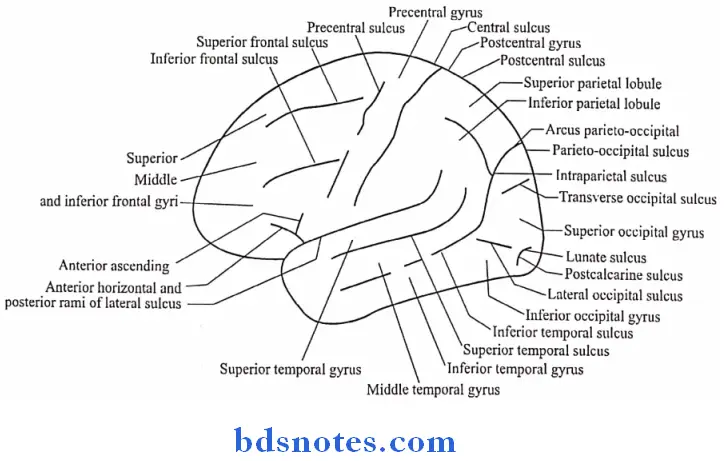
Question 4. Central sulcus
Answer:
Course:
- It begins at the superomedial border of the hemisphere a little behind the midpoint between the frontal & occipital poles
- It runs on the superolateral surface obliquely downwards & forwards & ends a little above the posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus
Question 5. Name the nuclei of cerebellum
Answer:
- Grey matter of cerebellum consists of four pairs of nuclei
- Nucleus dentatus – it is neocerebellar
- Nucleus globosus
- Nucleus emboliformis- paleocerebellar
- Nucleus fastigii- it is archicerebellar
Question 6. Name any four tracts passing through inferior cerebellar peduncle
Answer:
Afferent Tracts:
- Posterior spinocerebellar
- Cuneocerebellar
- Olivo cerebellar
- Parolivo cerebellar
- Reticulo cerebellar
- Anterior external arcuate fibres
- Striae medullares
- Trigemino cerebellar
Efferent Tracts:
- Cerebellovestibular
- Cerebelloolivary
- Cerebelloreticular
Question 7. Choroid plexus
Answer:
- The tela choroidea of fourth ventricle with vascular fringes is covered by secretory ependyma to form choroid plexus
- It consists of
- Vertical limb
- Lies next to midline
- Both sides limbs lie side by side to form T-shaped structure
- This projects into subarachnoid space
- Horizontal limb
- Extends into lateral recesses
- Vertical limb
Arterial supply:
- Posterior inferior cerebellar arteries
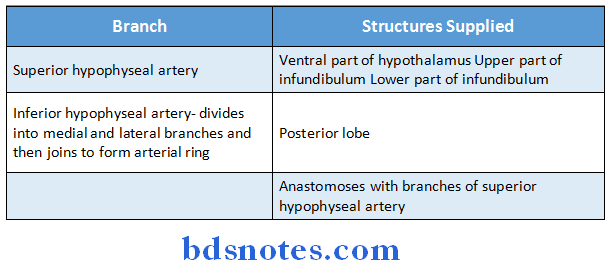
Question 8. Name arteries supplying pituitary gland
Answer:
- Pituitary gland is supplied by branches of internal carotid artery
Question 9. Name muscles supplied by spinal accessory nerve
Answer:
Muscles supplied by spinal accessory nerve are:
- Sternocleidomastoid
- Trapezius
Question 10. Name all cranial nerves
Answer:
- I – Olfactory nerve
- II – Optic nerve
- III – Oculomotor nerve
- IV – Trochlear nerve
- V – Trigeminal nerve
- VI – Abducent nerve
- VII – Facial nerve
- VIII – Vestibulocochlear nerve
- IX – Glossopharyngeal nerve
- X – Vagus nerve
- XI – Accessory nerve
- XII – Hypoglossal nerve
Question 11. Multipolar neuron
Answer:
- Multipolar neuron is a neuron having multiple processes
- Most of the neurons of man are of this type
- Example: all motor and internuncial neuron
Question 12. Parts of internal capsule
Answer:
Parts of Internal Capsule:
1. Anterior limb
- Lies between the head of the caudate nucleus and lentiform nucleus
2. Genu
- It is bend between anterior and posterior limb
3. Posterior limb
- It lies between thalamus and lentiform nucleus
4. Sublentiform part
- Lies below lentiform nucleus
5. Retrolentiform part
- Lies behind lentiform nucleus
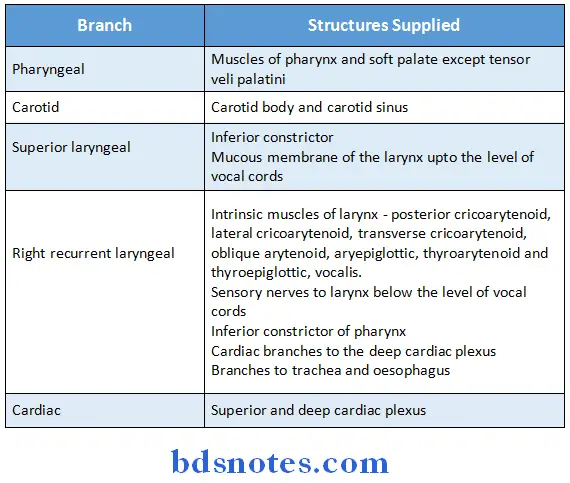
Question 13. Name the branches of vagus in neck.
Answer:
Branches of vagus in neck
Question 14. Give any four muscles supplied by hypoglossal nerve.
Answer:
- Muscles supplied by hypoglossal nerve
- Extrinsic muscle of tongue – styloglossus, genioglossus, hyoglossus
- Intrinsic muscles of tongue superior longitudinal, inferior longitudinal, transverse and vertical muscles
Question 15. Name the muscles supplied by oculomotor nerve.
Answer:
- Muscles supplied by oculomotor nerve
- Superior rectus of eyeball
- Inferior rectus of eyeball
- Medial rectus of eyeball
- Inferior oblique muscle
- Part of levator palpebrae superioris
Question 16. Neuro biotaxis
Answer:
- Neurobiotaxis is the tendency for a neuron to grow and develop towards the neuron or tissue it will innervate.

Leave a Reply