Lymphatic System
Question 1: What is the lymphatic system?
Answer. The lymphatic system is a closed system of vessels which drains colloid tissue fluid to the blood vascular system by an alternative route; hence, it is considered an auxiliary system to the venous system.
It essentially consists of a series of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. It actually drains tissue fluid made up of macromolecules of proteins, fat droplets, bacteria, etc., which cannot be drained by veins. It also helps to protect the body from harmful agents such as bacteria and viruses.
Lymph Node Histology
Question 2: Enumerate the components of the lymphatic system and list its functions.
Answer. Components Of The Lymphatic System
- Lymph vessels
- Peripheral lymphoid organs, for example, lymph nodes and spleen
- Central lymphoid organs, for example, bone marrow and thymus
- Epitheliolymphoid system, for example, MALT (GALT and BALT)
- Lymphocytes, for example, B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes
Functions Of The Lymphatic System
- Helps the venous system to drain the colloidal components of the tissue fluid
- Helps in the absorption of digested fat
- Filters particulate matters and noxious agents (bacteria, etc.) of lymph
- Produces lymphocytes
- Produces antibodies (immune substances)
- In pathological conditions, it provides channels for the spread of infection and cancer cells
Question 3: What are lymph capillaries and explain how they differ from blood capillaries?
Answer. The lymph capillaries begin blindly in the tissue spaces and form intricate networks. They differ from blood capillaries in the following ways:
- They are larger in size and more regular and permeable to bigger molecules (i.e. macromolecules).
- They form pathways for the absorption of colloidal tissue fluid with macromolecules such as proteins and particulate matter from tissue spaces.
Lymph Node Histology
Question 4: Enumerate the sites where lymph capillaries are absent.
Answer.
- Epidermis
- Hair
- Nails
- Cornea
- Articular cartilages
- Splenic pulp
- Spinal cord
- Brain
- Bone marrow
Question 5: Enumerate the factors that facilitate the drainage of lymph.
Answer.
- Filtration pressure in tissue spaces is generated by the filtration of fluid from blood capillaries.
- Contraction of surrounding muscles compressing the lymph vessels.
- Pulsations of arteries adjoining the lymph vessels.
- Respiratory movements and negative intrathoracic pressure.
- Contraction of smooth muscles in the wall of the lymph vessels.
Question 6: Write a short note on the lymph node.
Answer.
Lymph Node: The lymph nodes are oval or reniform bodies situated in the course of lymph vessels. The size of lymph nodes varies from a pinhead to a large bean. They have a slight depression on one side called hilum.
The blood vessels enter and leave the node at the hilum of the node. Several afferent lymph vessels enter the periphery of the lymph node, while only a single efferent lymph vessel emerges at the hilum.
Read And Learn More: Selective Anatomy Notes And Question And Answers
Their normal colour is greyish pink. They are usually found in groups and depending on their location they are generally divided into two groups: superficial group of lymph nodes and deep group of lymph nodes.
Note: The lymph nodes are the only lymphoid organs that possess both afferent and efferent lymph vessels.
Structure Of Lymph Node
The lymph node consists of two major components:
- connective tissue framework and
- parenchyma.
- The connective tissue component forms:
- Capsule
- Trabeculae
- Reticular stroma
- The parenchyma forms:
- Cortex
- Paracortex
- Medulla
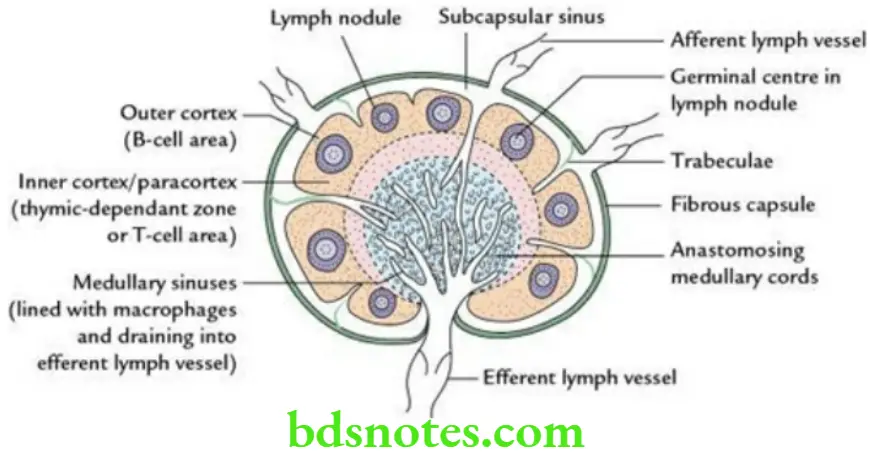
- The capsule is made up of connective tissue (mainly collagen fibres) and sends prolongations (trabeculae) within the body of lymph nodes. Beneath the capsule lies the subcapsular sinus, which receives afferent lymph vessels.
- The cortex (the outer peripheral part of the lymph node) contains lymphatic nodules. The lymph nodules mainly consist of B lymphocytes. The central parts of the lymph nodules contain germinal centres made up of rapidly dividing, lightly stained cells the lymphoblasts.
- The paracortex (the inner part of the cortex) consists mainly of T lymphocytes and is called a thymic-dependent zone.
- The medulla (the inner central part of the lymph node) consists of a network of anastomosing medullary cords with intervening medullary sinuses.
- The medulla contains mature B lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages.
Lymph Node Histology
Question 7: Enumerate the functions of the lymph nodes.
Answer.
Functions Of The Lymph Nodes
- Act as filters for lymph, thus preventing entry of foreign particles, pathogens, etc. into the bloodstream.
- Macrophages in the sinuses of the lymph nodes engulf foreign particles.
- Trap the antigens by phagocytes.
- Produce mature B and T lymphocytes.
- Provide a site for interaction between antigen-laden phagocytes and lymphocytes to produce an immune response – both cellular and humoral.
- Produce antibodies.

Leave a Reply