Hematinics
Question 1. Comment On Hematinics In Anemias.
Answer:
Hematinics are the agents required for the formation of blood and are used in the treatment of anemia.
- Besides treating the cause anemias are treated by giving the drugs hematinics which mainly include iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid.
- Iron: Iron is absorbed mostly in the duodenum in the ferrous form. After absorption, iron can either be stored as ferritin or it is transported with transferrin to be utilized in the formation of blood. Iron is used for prophylaxis or treatment of iron deficiency anemia (microcytic hypochromic anemia).
It can be given by oral or parenteral route. The parenteral route (IV, IM) is indicated only when oral iron is not tolerated, not absorbed, or along with erythropoietin. The rate of hematopoietic response with parenteral iron is not faster than that with optimal doses of oral iron therapy.
Major adverse effects of oral iron that result in poor compliance are gastrointestinal problems like epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, and metallic taste. These are related to elemental iron content in the iron preparation.
Parenteral iron preparations are iron–dextran and iron–sorbitol–citrate. The former can be given either by IV or IM routes whereas the latter should not be used intravenously. The major problem with parenteral iron is pain at the injection site and pigmentation of the skin.
- Iron: Iron is absorbed mostly in the duodenum in the ferrous form. After absorption, iron can either be stored as ferritin or it is transported with transferrin to be utilized in the formation of blood. Iron is used for prophylaxis or treatment of iron deficiency anemia (microcytic hypochromic anemia).
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question And Answers
-
- Folic Acid: Dietary folic acid is reduced to dihydrofolic acid (DHFA) and then to tetrahydrofolic acid (THFA), which is methylated to form methyl tetrahydrofolate. Later compound is the main form in which it is transported in the blood.
Deficiency of folic acid results in mega-holoblastic anemia that is indistinguishable from that due to vitamin B12 deficiency. The main use of folic acid is in the treatment of megaloblastic anemia.
It is also indicated in pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects in the fetus. Leucovorin (folinic acid) can be used to prevent the toxicity of methotrexate.
- Folic Acid: Dietary folic acid is reduced to dihydrofolic acid (DHFA) and then to tetrahydrofolic acid (THFA), which is methylated to form methyl tetrahydrofolate. Later compound is the main form in which it is transported in the blood.
-
- Vitamin B12: Cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin are the two major forms present in the diet. It is present in animal foods (liver, kidney, meat, cheese, egg yolk, etc.) and the only vegetable source is legumes (microorganisms in the nodules synthesize it).
Deficiency of vitamin B12 leads to megaloblastic anemia which is indistinguishable from folic acid deficiency. Vitamin B12 is used for the treatment of megaloblastic anemia and for correcting neurological abnormalities (methylcobalamin is used).
If the cause of megaloblastic anemia is not known, folic acid alone should not be given because it will correct the blood picture of anemia but neurological defects due to vitamin B12 deficiency may be aggravated.
- Vitamin B12: Cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin are the two major forms present in the diet. It is present in animal foods (liver, kidney, meat, cheese, egg yolk, etc.) and the only vegetable source is legumes (microorganisms in the nodules synthesize it).
Question 2. Write The Drug Treatment Of Anemia.
Answer:
Drug Treatment Of Anemia
Drug treatment of anemia involves many of its causes:
- Increased blood loss: Due to increased blood loss as in menorrhagia, gastric ulceration, etc. there is a deficiency of iron which is fulfilled by taking the oral therapy of ferrous sulfate, ferrous gluconate, ferrous fumarate, or by parenteral therapy of iron dextran, iron sorbitol complex IM only.
- Increased blood requirement as in pregnancy and growing children: During this iron deficiency anemia is caused and is corrected by taking an oral dose of ferrous fumarate, ferrous gluconate, and ferrous sulfate or by a parenteral dose of iron dextran or iron Sorbitol as IM injection.
- Impaired red cell formation due to deficiency of essential factors, i.e.
- Vitamin B12: Due to a deficiency of vitamin B12 pernicious anemia is caused which is corrected by taking cyanocobalamin or hydroxocobalamin as IM or deep SC.
- Folic acid: Due to the deficiency of folic acid megaloblastic anemia is caused which is cured by taking oral or parenteral administration of folic acid.
- Drug-induced anemias:
- By long-term use of certain drugs, i.e. aspirin and other NSAIDs, due to chronic loss of blood. Microcytic, hypochromic anemia is caused which is treated by oral and parenteral administration of iron.
- By use of phenacetin, primaquine hemolytic anemia is caused which is treated by taking iron orally or parenterally.
Question 3. Comment On Iron Therapy.
Answer:
Iron therapy takes place either orally or parenterally.
Oral Therapy
- Indications: It is indicated when:
- Prophylactically to prevent anemia when there is an increased requirement.
- To treat iron deficiency anemia.
- Drugs used: In oral therapy, the most commonly used drugs are ferrous sulfate, ferrous gluconate, and ferrous fumarate.
Parenteral Therapy
- Indications: It is indicated when there are:
- Failure of absorption orally as in malabsorption syndrome.
- Inability to tolerate oral iron.
- When a patient is not relied on to take oral iron.
- When daily loss of iron is more than intake.
Drugs used: During parenteral therapy, iron dextran is given as IM/IV and iron sorbitol complex is given as IM only.
- Ferrous sucrose and ferric carboxymaltose should be given IV.
Question 4. Compare And Contrast Ferrous Sulphate And Iron Dextran.
Answer:
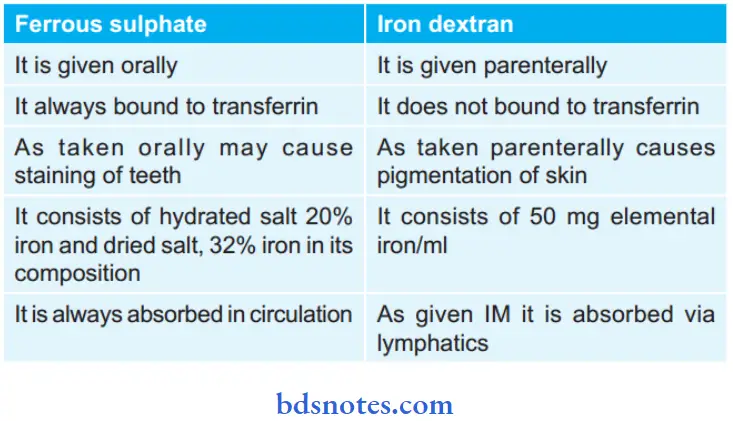
Question 5. Comment On Oral Iron Names In Git Absorption.
Answer:
Oral iron names in GIT absorption:
- Ferrous sulfate which consists of hydrated salt 20% iron and dried salt 32% iron and is better absorbed by the intestine. For example, folate 200 mg Tab.
- Ferrous gluconate contains 12% iron and is available in the market as ferrocenium 300 mg and 400 mg Tab.
- Ferrous fumarate contains 33% iron and is present in the market as NORI-A 200 mg Tab.
- Colloidal ferric hydrochloride is present as neoferum 200 mg Tab.
- Carbonyl iron consists of highly purified metallic iron.
- Other forms of iron present in oral formulations are ferrous succinate, iron choline citrate, iron calcium complex, and ferrous aminoate are better absorbed in GIT and produce less bowel upset.
Question 6. Write On Injectable Iron Preparations, Name, Indications, And Toxicity.
Answer:
Name of injectable iron preparations
- Iron sorbitol citric acid complex (Jectofer)
- Iron dextran complex (Imferon)
- Ferric carboxymaltose and ferrous sucrose.
Injectable Iron Indications
- When oral iron is not tolerated due to high bowel upset.
- When there is a failure in the absorption of oral iron due to malabsorption, chronic inflammation, etc.
- When there is non-compliance with oral iron.
- In the presence of severe deficiency with chronic bleeding.
- Along with erythropoietin oral iron is not absorbed at the time parenteral iron is administered.
Injectable Iron Toxicity
- Toxicity is mainly in infants and children.
- It is very rare in adults
- Manifestations are vomiting, abdominal pain, hematemesis, diarrhea, lethargy, cyanosis, dehydration, acidosis, convulsions, finally shock, cardiovascular collapse, and death.
Question 7. Write Down The Drug Treatment Of Iron Poisoning.
Answer:
Following is the drug treatment for iron poisoning:
- Induce vomiting or perform gastric lavage with sodium bicarbonate solution to render iron insoluble.
- Desferrioxamine is the choice of drug which is given IM 0.5–1 gm repeated 4 to 12 hourly.
- If desferrioxamine is not available DTPA or calcium edentate is given.
- Fluid and electrolyte balance is maintained.
- Diazepam IV can be given to control convulsions.
Question 8. Write Short Note On Iron Preparations And Side Effects Of Iron Therapy.
Answer:
Iron preparations are of two types, i.e. oral and parenteral.
Iron Oral Preparation
- Ferrous sulfate contains 20% hydrated salt and 32% elemental iron.
- Ferrous gluconate consists of 12% elemental iron
- Ferrous fumarate consists of 33% elemental iron
- Colloidal ferric hydroxide consists of 50% elemental iron
- Carbonyl iron consists of highly purified metallic iron.
Other Forms
- Ferrous succinate consists of 35% elemental iron
- Ferrous gluconate consists of 5% elemental iron
- Ferric ammonium citrate (scale iron)
- Iron hydroxide poly maltose
- Ferrous aminoate consists of 10% elemental iron.
Indications Of Oral Preparation
In iron deficiency anemia
Side Effects Of Oral Iron Therapy
- Epigastric pain
- Heartburn
- Nausea and vomiting
- Staining of teeth
- Metallic taste
- Constipation
Iron Parenteral Preparation
- Iron dextran (imferno): Colloidal solution containing 50 mg elemental iron/ml. It can be given IM or IV
- Iron sorbitol citric acid complex (Jectofer): 50 mg iron/ml. It is given IM only
- Ferrous sucrose and ferric carboxylase: They should be given IV
Indications Of Parenteral Preparation
- It is indicated when oral iron is not tolerated
- In cases where there is the failure of absorption of iron
- In non-compliance
- In iron deficiency anemia.
Side Effects Of Parenteral Iron Therapy
- Pain at the site of IM injection
- Pigmentation of skin
- Sterile abscess
- Fever, headache, joint pain, flushing, palpitation, chest pain, and dyspnea.
- Anaphylactoid reaction.
Question 9. Write Short Note On Oral Iron Preparations.
Answer:
Oral iron preparations are indicated in the treatment of iron deficiency anemia.
Names Of Oral Iron Preparations
- Ferrous Sulphate contains 20% Hydrated salt and 32% elemental iron
- Ferrous gluconate consists of 12% elemental iron
- Ferrous fumarate consists of 33% elemental iron
- Colloidal ferric hydroxide consists of 50% elemental iron
- Carbonyl iron consists of highly purified metallic iron.
Other forms:
-
- Ferrous succinate consists of 35% elemental iron
- Ferrous gluconate consists of 5% elemental iron
- Ferric ammonium citrate (scale iron)
- Iron hydroxide poly maltose
- Ferrous aminoate consists of 10% elemental iron
Side Effects Of Oral Iron Therapy
- Epigastric pain
- Heartburn
- Nausea and vomiting
- Staining of teeth
- Metallic taste
- Constipation.

Leave a Reply