Fungal Infections Of Oral Cavity
Question.1. Enumerate fungal lesions of oral cavity. Describe clinical features, histopathology and investigation of oral candidiasis.
Or
Write note on moniliasis.
Or
Describe in brief moniliasis.
Or
Write short note on candidiasis.
Or
Write short note on oral candidiasis.
Answer. Enumeration of fungal lesion of oral cavity
Fungal lesions affcting oral tissues are:
- Candidiasis
- Coccidioidomycosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Blastomycosis
- Paracoccidioidomycosis
- Sporotrichosis
- Chromomycosis and phaeomycotic abscess
- Aspergillosis
- Cryptococcosis
- Zygomycosis
- Mycetoma.
- Candidiasis is a disease caused by the fungus called as Candida albicans.
- Oral involvement is probably most common manifestation.
Read And Learn More: Oral Pathology Question And Answers
Etiology
- Hormonal disturbances
- Local or systemic steroid therapy
- Xerostomia
- Poor oral hygiene
- Denture wearing
- Heavy smoking
- Prolong antibiotic therapy.
- Nutritional deficiency, e.g. vitamin A and vitamin B6.
Clinical Features
- Common sites are roof of mouth, retromolar area and mucobuccal fold.
- It is more common in women.
- Prodromal symptom is rapid onset of bad taste. Spicy food causes discomfort.
- There is presence of inflmmation, erythema and painful eroded areas may be associated with this disease.
- White patches of candidiasis are easily wiped out with wet gauge which leaves erythematous area or atrophic area.
- Deeper invasion by the organism leaves an ulcerative lesion upon removal of patch.
1. Acute Pseudomembranous Candidiasis
- Common sites are roof of mouth, retromolar area and mucobuccal fold.
- It is more common in women.
- Prodromal symptom is rapid onset of bad taste. Spicy food causes discomfort.
- There is presence of inflmmation, erythema and painful eroded areas may be associated with this disease.
- White patches of candidiasis are easily wiped out with wet gauge which leaves erythematous area or atrophic area.
- Deeper invasion by the organism leaves an ulcerative lesion upon removal of patch.
2. Acute Atrophic Candidiasis
- It can be seen anywhere in the oral cavity but most commonly site involved are tongue as well as the tissue underlying prosthesis.
- It appears as an erythematous area.
- Patient complains of burning sensation in lesional area along with vague pain.
3. Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis
- Male predilection is seen.
- Most common in heavy smokers.
- Oral sites involved are tongue, cheek and lips.
- There is presence of fim and white leathery plaques.
- Lesion cannot be rubbed with the lateral pressure.
- Lesion is whitish or creamy whitish in color. Borders of the lesion are vague.
Histopathology
- Epithelium show increase thickness of parakeratin at lesional area in conjunction with elongation of rete ridges.
- Small collection of neutrophils, i.e. microabscess is seen in parakeratin layer and superficial spinous layer.
- Hyphae or mycelia and yeast cells are seen in parakeratin layer of epithelium.
- There is presence of chronic inflammatory infiltrate cells such as lymphocytes and plasma cells immediately subjacent to infected epithelium.
Treatment
- Topical and systemic administration of nystatin is done.
- In immunosuppressed patients systemic administration of amphotericin B and fluconazole is given.
- Improvement of oral hygiene is essential.
Question.2. Write short note on acute pseudomembranous candidiasis.
Or
Write short note on oral thrush.
Answer. It is commonly known as “oral thrush”.
- Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis appears as a smooth, thick, creamywhite or allow, soft and friable plaque on the oral mucosa.
- Plaque can be easily wiped of by gentle scraping, which leaves an erythematous, raw, bleeding surface in the underlying area.
- Lesions may occur at any mucosal site and vary in size ranging from small areas to confluent plaques.
- Plaque consists of fungal organisms, keratotic debris, inflammatory cells, desquamated epithelial cells and firin, etc.
- Oral thrush commonly occurs among children, debilitated elderly persons and AIDS patients.
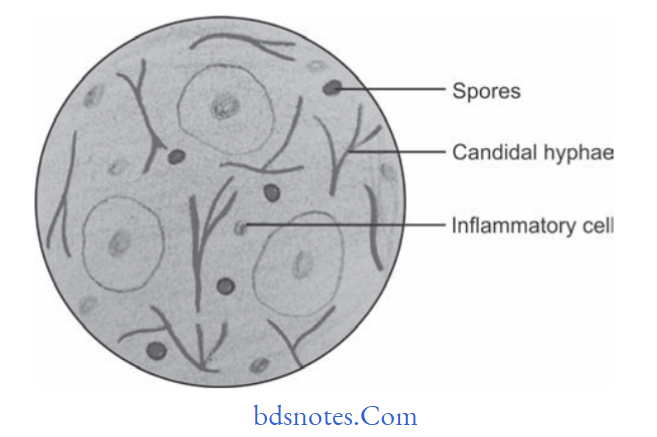
Histopathology
- Hyperplastic epithelium with superficial necrotic and desquamating para keratinized layer.
- Hyperplastic epithelium is infitrated by candidal hyphae and yeast cells along with PMNs.
- Often there is separation between the superficial pseudomembrane and the deeper layers of epithelium.
- Candidal hyphae often appear as a weakly basophilic thread-like structure.
- Lamina propria is infiltrated by chronic inflammatory cells,i.e. lymphocytes and plasma cells.
Treatment
- Antifungal drugs, i.e. nystatin, amphotericinB should be given.
- Proper oral hygiene should be maintained.
Question.3. Write short note on burning mouth syndrome.
Answer.
- Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a painful, frustrating condition often described as a scalding sensation in the tongue, lips, palate, or throughout the mouth. Although BMS can affect anyone, it occurs most commonly in middleaged or older women.
- BMS often occurs with a range of medical and dental conditions, from nutritional deficiencies and menopause to dry mouth and allergies. But their connection is unclear, and the exact cause of burning mouth syndrome cannot always be identified with certainty.
Signs And Symptoms
Moderate to severe burning in the mouth is the main symptom of BMS and can persist for months or years.
For many people, the burning sensation begins in late morning, builds to a peak by evening, and often subsides at night.
Some feel constant pain; for others, pain comes and goes. Anxiety and depression are common in people with burning mouth syndrome and may result from their chronic pain.
Other symptoms of burning mouth syndrome include:
- Tingling or numbness on the tip of the tongue or in the mouth
- Bitter or metallic changes in taste
- Dry or sore mouth.
Causes
There are a number of possible causes of burning mouth syndrome, including:
- Damage to nerves that control pain and taste
- Hormonal changes
- Dry mouth, which can be caused by many medicines and disorders such as Sjögren’s syndrome or diabetes
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Oral candidiasis, a fungal infection in the mouth
- Acid reflex
- Poorly-fitting dentures or allergies to denture materials
- Anxiety and depression.
Diagnosis
A review of your medical history, a thorough oral examination,and a general medical examination may help identify the source of your burning mouth. Tests may include:
- Blood work to look for infection, nutritional deficiencies,and disorders associated with
- BMS such as diabetes or thyroid problems
- Oral swab to check for oral candidiasis
- Allergy testing for denture materials, certain foods, or other substances that may be causing your symptoms.
Treatment
Treatment should be tailored to your individual needs.
Depending on the cause of your BMS symptoms, possible treatments may include:
- Adjusting or replacing irritating dentures
- Treating existing disorders such as diabetes, Sjögren’s syndrome, or a thyroid problem to improve burning mouth symptoms.
- Recommending supplements for nutritional defiiencies
- Switching medicine, where possible, if a drug you are taking is causing your burning mouth.
- Prescribing medications to:
- Relieve dry mouth
- Treat oral candidiasis
- Help control pain from nerve damage
- Relieve anxiety and depression.
When no underlying cause can be found, treatment is aimed at the symptoms to try to reduce the pain associated with burning mouth syndrome.
Question.4.Give classifiation of candidiasis and enumerate its laboratory tests.
Answer.
Classifiation of Candidiasis by Axell Et Al 1997
- Primary oral candidiasis:
- Acute form:
- Pseudomembranous candidiasis
- Erythematous candidiasis
- Chronic form:
- Hyperplastic candidiasis
- Erythematous candidiasis
- Pseudomembranous candidiasis
- Candida-associated lesion:
- Denture stomatitis
- Angular stomatitis
- Median rhomboid glossitis
- Acute form:
- Keratinized primary lesion super-infected with candida:
-
- Leukoplakia
- Lichen planus
- Lupus erythematosus
-
- Secondary candidiasis:
- Candidal endocrinopathy syndrome.
Laboratory test for Candidiasis
- Fragments of plaque material are smeared on a microscopic slide, macerated with 20% potassium hydroxide, and examined for typical hyphae.
- Gram-stained smears from lesions or exudates show budding Gram-positive cells.
- Sample can also be cultured on Sabouraud’s broth and ordinary bacteriological culture. Colonies appear as creamy white, smooth, and with yeasty odor.
- Candida albicAns alone forms chlamydospores on cornmeal agar culture at 20°C.
- A rapid method of identifying Candida albicAns is based on its ability to form germ tubes within 2 hours when incubated in human serum at 37°C.
- By PAS method of staining candidal hyphae and yeasts should be recognized.
- PAS method stains the carbohydrates of fungal cell walls and organisms are identified by bright magenta color. Hyphae are 2 µm in diameter, vary in length and may show branching.
Question.5. Write short note on chronic atrophic candidiasis.
Answer. It is also known as denture-induced stomatitis.
It is a clinical manifestation of erythematous candidiasis.
Candida albicans is present in the lesion.
Clinical Features
- Lesion is present under complete or partial denture.
- Most commonly seen in females in palate.
- Patient complains of soreness and dryness of mouth.
- Lesion shows patchy distribution and is associated with speckled curd-like white lesion.
- Tissue of palate becomes bright red, edematous and granular.
- Redness of mucosa is limited till the area covered by denture.
Treatment
Clotrimazole and nystatin ointments are applied after meal and at bed time 3 to 4 times.

Leave a Reply