Forensic Odontology
Question.1.Write short note on sex differences in tooth morphology and jaw anatomy.
Answer.
Sex Differences In Tooth Morphology
- Amongst teeth, mandibular canines show greatest dimensional difference with larger teeth in males than in females.
- Mesiodistal width of mandibular canines was significantly greater in males than in females.
- Girls are more prone to caries as compared to boys because tooth erupt at an early age.
Sex Differences In Jaw Anatomy
- In males jaw bone is large, having broad ascending ramus while in females it is small, narrow ascending ramus.
- In males condyles of jaw bone are large while in females they are small.
- In males shape of chin is square while in females it is rounded/pointed.
- Gonial angle is less obtuse and flres in males while it is more obtuse and does not fire in females.
- Body height of jaw bone in males is high while it is low in females.
Read And Learn More: Oral Pathology Question And Answers
Question.2. Write short note on chelioscopy.
Or
Write short note on lip prints.
Answer. External surface of the lip has many elevations and depressions forming a characteristic pattern called lip prints, examination of which is referred to as coloscopy.
- This is unique for individuals like the fingerprints.
- Lip prints can constitute material evidence left at a crime scene much like fingerprints.
- Lip prints provide direct link to the suspect.
- Use of lipstick was essential to leave behind color traces of lip prints.
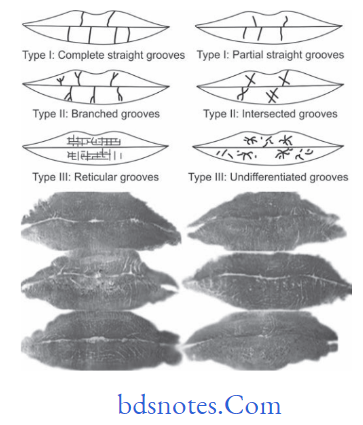
Classification of Lip Prints
By Tsuchihashi
- Type I Clear cut vertical grooves that run across entire lip
- Type I’- Similar to Type I but do not cover entire lip
- Type II Branched grooves
- Type III Intersected grooves
- Type IV Reticular grooves
- Type V Grooves that cannot be morphologically diffrentiated
- A combination of these grooves may be found on any given set of lips.
- To simplify recording lips are divided into quadrants similar to dentition, i.e. a horizontal line dividing the upper and lower lip and a vertical line dividing right and left sides. By noting the type of groove in each quadrant the individual’s lip print pattern may be recorded.
Question.3. Write short note on Bite marks.
Answer. Bite marks are defied as “A mark caused by the teeth either alone or in combination with other mouth parts”. -MacDonald.
Classification of Bite Marks
MacDonald’s Classification
He had given an etiological classification
- Tooth pressure marks: Marks on tissue due to ‘direct application of pressure by teeth’. Incisal and occlusal surfaces
produce these marks. - Tongue pressure marks: If suffient amount of tissue is taken in mouth tongue presses the tissue against rigid areas, i.e. lingual surface of teeth as well as palatal rugae. Marks left over skin are called as suckling.
- Tooth scrape marks: They occur due to scraping of teeth over bittn material. They are caused by anterior teeth
Importance Of Bite Marks
- They provide accurate identification since alignment of teeth is specifi in each individual.
- Bite marks are contaminated by saliva and consist of amylin, ptyalin and blood group which help in determination of individuals in criminal cases.
Bite Mark Collection
Collection of Bite Mark from Victim
Various methods are:
- Case demographics: All the information related to case is selected such as name, age, address, etc.
- Visual examination: Visually examine the shape, size,color, contour, texture and other features of bite marks and document all of them.
- Photography: Photographs should be taken as quickly as possible. They provide permanent record of bite marks.
- Impressions: Impressions of bittn area is made by vinyl polysiloxane.
- Saliva swab: Saliva act as a source of DNA. It should be collected carefully and is preserved to match the DNA with suspect.
Collection of Bite Mark from Suspect
- Photographs of suspect’s teeth should be taken.
- Impressions of maxillary and mandibular arch should be taken.
- Saliva swabs from buccal vestibule should be taken.
Bite Marks Analysis
It is done by:
- Metric analysis in conjunction with pattrn association.
- Direct method: In which suspect’s models are directly placed over bite mark.
- Indirect method: Incisal and occlusal edges of suspect’s teeth are traced on clear acetate and superimposed on bite mark photographs.
- Adobe photoshop software.
- 3D/CAD supported photogrammetry.
Conclusion of bite marks analysis
- Definite biter: Presence of reasonable medical certainty which indicate that bite mark is produced by suspect’s dentition.
- Probable biter: There is some degree of specificity to suspect’s teeth by sufficient number of matching points.
- Possible biter: Suspect’s teeth could make the bite mark and there are no characteristic matches for certainty. Similarity
of class characteristics is seen. - Not the biter: Bite marks and suspect’s dentition is not consistent.
Question.4. Write short note on dental DNA methods.
Answer. Following are the dental DNA methods:
- Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)
Typing: It is used for analyzing the variable lengths of DNA fragments that result from digesting a DNA sample with a special kind of restriction enzyme called “restriction endonuclease” which sections DNA at a specific sequence pattrn known as a restriction endonuclease recognition site. RFLP requires relatively large amounts of DNA.
Hence,cannot be performed with the samples degraded by environmental factors, and also takes longer time to get the results. - STRs typing: These are described as short stretches of DNA that are repeated at various locations throughout the human genome and this technology is used to evaluate specific regions (loci) within nuclear DNA.
Each person has some STRs that were inherited from father and some from mother, but however no person has STRs that are identical to those of either parent.
The uniqueness of an individual’s STRs provides the scientific marker of identity and hence is helpful in forensic identifiation and paternity testing.
STR can be used for identifiation of bodies in the mass disasters and old skeletal remains. - Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) analysis: Long intervals between the time of death and examination of tissues complicate the genetic identification with nuclear DNA and sometimes only bone and teeth may be available for analysis.
Teeth provide an excellent source for high molecular weight mtDNA that offer several unique advantages for the identification of human remains.
mtDNA is a powerful tool for forensic identification as it possesses high copy number, maternal inheritance, and high degree of sequence variability. - Ychromosome analysis: DNApolymorphisms on the human Y chromosome are valuable tools for understanding human evolution, migration and for tracing relationships among males.
Majority of the length of the human Y chromosome is inherited as a single block in linkage from father to male offspring as a haploid entity.
Hence, Y chromosomal DNA variation has been mainly used for investigations on human evolution and for forensic purposes or paternity analysis. - Xchromosome STR: Chromosome X specifi STR is used in the identifiation and the genomic studies of various ethnic groups in the world.
Since the size of Xchromosome STR alleles is small, generally including 100–350 nucleotides, it is relatively easy to be amplifid and detected with high sensitivity.
Xchromosome STR (XSTR) markers are a powerful complimentary system especially in defiiency paternity testing. Toothrelated jaw bone diseases can be divided in cysts and odontogenic tumors.
Reactive bone diseases, firo-osseous lesions, giant cell lesions, and bone tumors are taken together as the main second group.
Question.5. Write short note on forensic odontology.
Answer. Forensic odontology is that branch of dentistry which in the interest of justice deals with the proper handling and examination of dental evidence and with the proper evaluation and presentation of dental fidings.
Federation Dentaire Internationale (FDI)
Scope Of Forensic Odontology
- Identification: It helps in personal identification, i.e.individually or in mass disasters. This is done also through comparison of antemortem and postmortem dental information.
- Age assessment: This is done for assessing the age of person.
- Record preparation: Correct handling as well as examination of presentation of dental evidence in civil and criminal legal cases. These records make the foundation on which]
- Identifiation ofbite marks: It is involved in identifiation of bite marks in criminal cases.
- Child abuse: For detection of child abuse or human abuse too.
- Lip print: For comparison and identifiation of suspect, lip prints are examined.
- Legal aspect: In cases with dental traumatology.
Parameters to be Compared in Forensic Dentistry
- Teeth
- Prosthetic appliances, i.e. bridges, partials, crowns, false teeth
- Shape, form (morphological) peculiarities
- Genetic anomalies.

Leave a Reply