Ethyl And Methyl Alcohols
Question 1. Explain The Pharmacological Basis For Ethyl Alcohol Used In Methyl Alcohol Poisoning.
Answer:
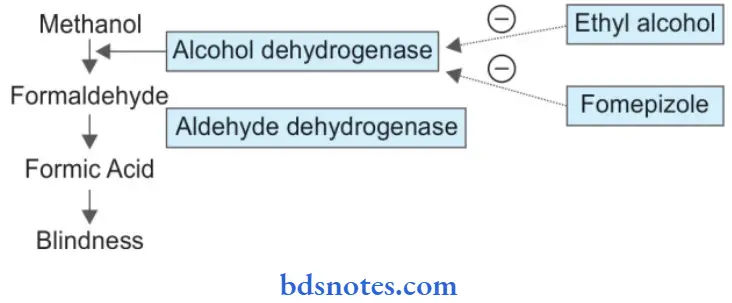
Methyl alcohol is metabolized to formaldehyde and then to formic acid by the action of the enzymes alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase respectively.
The accumulation of formaldehyde and formic acid is responsible for the features caused by methyl alcohol poisoning.
Formaldehyde and formic acid cause nerve damage and their effects on the retina and optic nerve can result in blindness.
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question And Answers
Ethyl alcohol competes with methanol for metabolism by alcohol dehydrogenase and thus retards the methanol metabolism. This reduces the formation of formic
acid thereby decreasing the risk of blindness.
Another approach used now to reduce methanol metabolism is the administration of an alcohol dehydrogenase inhibitor, fomepizole.
Its advantage over ethyl alcohol administration is its longer half-life, IV administration, and absence of inebriating action.

Leave a Reply