Epidemiology Of Malocclusion
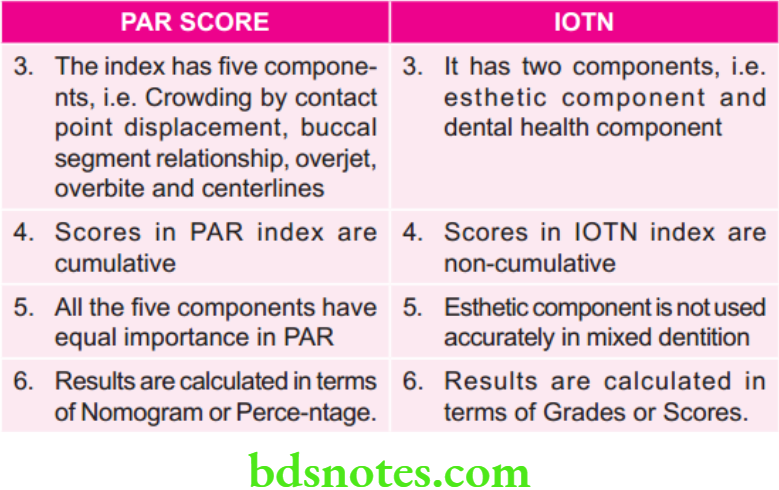
Question 1. Briefly differentiate between PAR score and IOTN.
Answer.

Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Question And Answers
Question 2. List common orthodontic indices.
Answer. Following are the orthodontic indices:
- Massler and Frankel index (1951): It counts the number of teeth displaced or rotated. Assessment by this index is qualitative.
- Malalignment index (1959): It was given by Vankirk and Pennell. It measures the tooth displacement and rotation. Assessment by this index is quantitative.
- Handicapping labiolingual index (1960): It was given by Draker. It measures traumatic deviations, clef palate, overjet, overbite, anterior open bite, mandibular protrusion and labiolingual spread.
- Occlusal feature index (1961): It was given by Poulton & Aaronson. It measures vertical overbite, horizontal overjet and lower anterior crowding cuspal interdigitation.
- Malocclusion severity (1960-1961): It measures seven weighted and defied criterias, i.e. anterior open bite, overjet, overbite, congenitally missing maxillary incisors, posterior crossbite, fist permanent molar relationship and tooth displacement. As per this index six malocclusion syndromes were given by Grainger, i.e.
- Positive overjet and anterior open bite
- Positive overjet, positive overbite, distal molar relationship and posterior crossbite with maxillary teeth buccal to mandibular teeth
- Negative overjet, mesial molar relationship and posterior crossbite with maxillary teeth lingual to mandibular teeth
- Congenitally missing maxillary incisors
- Tooth displacement
- Potential tooth displacement.
- Occlusal index (1966): It measures nine weighted and defined criterias, i.e. molar relationship, overjet, overbite, congenitally missing maxillary incisors, posterior cross bite, posterior open bite, midline relation, maxillary median diastema and tooth displacement. As per this index seven malocclusion syndromes were given by Summers, i.e.
- Overjet and overbite
- Distal molar relation, overjet, overbite, posterior cross-bite, midline deviation and midline diastema
- Congenitally missing maxillary incisors
- Tooth displacement
- Posterior open bite
- Mesial molar relation, overjet, overbite, posterior crossbite, midline deviation and midline diastema
- Mesial molar relation, mixed dentition analysis and tooth displacement.
Various scoring schemes as well as forms are given as per the different stages of dentition development, i.e. deciduous dentition, mixed dentition and permanent dentition.
- Handicapping malocclusion assessment index (1968): It was given by Salzmann. The measurements consists of three parts:
- Intra-arch deviation: Missing teeth, crowding, rotation and spacing
- Inter-arch deviation: Overjet, overbite, crossbite and open bite
- Six handicapping dentofacial deformities: Facial and oral cleft lower lip palatal to maxillary incisors, occlusal interference, functional jaw limitation, facial asymmetry and speech impairment.

Leave a Reply