Enamel
Question 1. Describe the physical and chemical properties of enamel.
Answer:
Physical properties:
1. Enamel Colour
- Enamel is translucent.
- Its color varies from yellowish-white to grayish white
- Yellowish-white teeth have thin, translucent enamel.
- Greyish teeth have more opaque enamel.
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
2. Enamel Thickness:
- A maximum thickness of about 2 – 2.5 mm is seen on the cusps of the molars and premolars.
- Thin at the neck of the teeth.
- Maximum thickness is also observed over supporting cusps.
3. Enamel Hardness:
- Due to its mineral content, it is extremely hard. It enables it to withstand the mechanical forces applied.
- Its hardness is about 350 KHN.
4. Enamel Specific gravity:
- The specific gravity of enamel is 2.8
5. Modulus of elasticity:
- It is higher at the surface.
6. Enamel Density:
- Decreases from surface to deeper regions.
7. Enamel Conductivity:
- Enamel is a nonelectrical conductive material.
- It is an insulator at room temperature.
8. Enamel Resistance:
- Temperature resistance range from 5 to 13 Hz
- Electrical resistance range from 105 to 105 ohm.
9. Enamel Permeability:
- Enamel acts as a semipermeable membrane.
- It permits complete or partial passage of certain molecules.
Enamel Chemical properties:
- The enamel consists of approximately 96% mineral and 5% organic material and water.
- The inorganic content of enamel is a crystalline calcium phosphate – hydroxyapatite.
- various ions- strontium, magnesium, lead, and fluoride may be incorporated into the enamel crystals.
- The susceptibility of these crystals to dissolution by acid provides the chemical basis for dental caries.
- The organic material consists of proteins – 2 main groups are seen.
- Amelogenins – 90% of proteins.
- Hydrophobic.
- Low molecular weight proteins.
- Rich in proline, histidine, glutamine, leucine.
- Nonamelogenins – 10% of proteins.
- High molecular weight proteins.
- Rich in glycine, aspartic acid and serine.
Question 2. Describe the structure of enamel (or) Describe the histology of enamel.
Answer:
Structure of enamel:
- Enamel mainly consists of
- Enamel rods or prisms.
- Interprismatic cementing substance
- Rod sheath.
1. Enamel rods or prims:
- They are long, slender cylindrical structures.
Enamel Number:
- It varies.
- 5 million – in lower lateral incisors
- 12 million – in upper first molars.
Course:
- It has a wavy course.
- It extends from the dentin enamel junction to the surface of the tooth.
Enamel Size:
- The length is greater than the thickness of the enamel.
- Size is 5 pm in breadth, 9 pm in length, and diameter averages 4 pm
- However, the diameter increases from the dentin enamel junction towards the enamel surface at a ratio of about 1:2.
Enamel Outlines:
- Arcade outlines are seen near DEJ.
- Keyhole-shaped outlines are seen at the enamel surface.
Direction:
- Perpendicular to the surface of the dentin.
- Vertical – near the cusp tip.
- Horizontal – at cervical in primary teeth.
- Apically oriented – at the cervical area in permanent teeth.
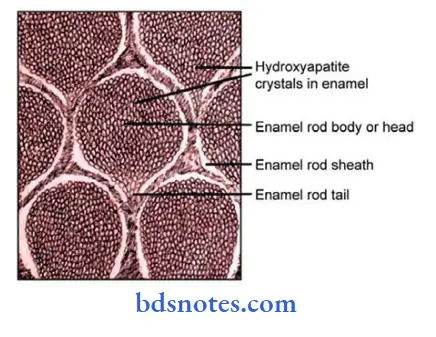
2. Interprismatic region:
- It surrounds each rod
- Its crystals are oriented in a direction different from those making up the rod.
- It is usually less titan 1 micron in width.
3. Rod sheath:
- The boundary between rod and interrod enamel is delimited by a narrow space containing organic material known as rod sheath.
- The rod sheath occurs because of the greater space that exists between the ends of the crystals of the interrod region as these crystals meet at sharp angles.
Several other structures are present:
1. Incremental lines of retail:
- They are a series of dark lines extending from the dentin enamel junction toward the tooth surface.
- They reflect incremented growth of the enamel.
- In the cervical parts, they run obliquely while from the DEJ to the surface they deviate occlusal.
2. Neonatal line:
- It is an enlarged stria of Retzius that apparently reflects the great physiologic changes occurring at birth.
3. Dentino enamel junction:
- It is the junction between two hard tissues enamel and dentin.
- It is a scalloped line.
- The convexities of the scallops are directed towards the dentin.
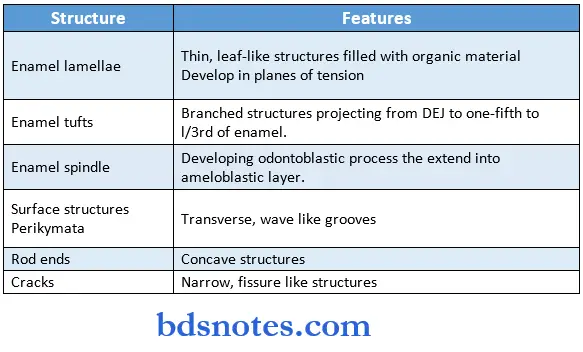
4. Enamel lamellae:
- They consist of linear, longitudinally oriented defects filled with organic material.
5. Enamel tufts:
- They project from the DEJ for a short distance into the enamel.
- They appear to be branched and contain a greater concentration of enamel proteins.
6. Enamel spindles:
- They seem to originate from the odontoblastic process.
7. Suiface structures:
Perikymata:
- They are transverse, wave-like grooves.
- They are continuous around a tooth and usually lie parallel to each other and to the CEJ.
Rod ends:
- They are concave and vary in depth and shape.
- They are shallowest in the cervical area and deepest near incisal and occlusal edges.
Crocks:
- They are narrow, fissure-like structures that are seen on almost all surfaces.
- They are the outer edges of lamellae.
Question 3. Describe hypocalcified areas of enamel.
Answer:
Hypocalcified areas of enamel:
1. Enamel lamellae:
- They extend for varying depths from the enamel surface.
- They are thin, leaf-like structures filled with organic material.
- They may develop in planes of tension.
- The inner parts of the lamella consist of an organic cell detritus and the outer parts consist of a double layer of cuticle.
Hypocalcified Areas of Enamel Types:
- Type 1:
- Lamellae are composed of poorly calcified rod segments.
- It is restricted to the enamel.
- Type 2:
- Lamellae consist of degenerated cells.
- They are restricted to dentin.
- Type 3:
- Lamellae arise in erupted teeth where the cracks are filled with organic material.
- It is more common than other types.
- They are restricted to dentin.
- Significance:
- They are sites of weakness
- They act as pathways for caries-producing bacteria.
2. Enamel tufts:
- They are branched structures projecting from DEJ to one-fifth to one-third of enamel.
- They consist of hypocalcified enamel rods and interprismatic substances and a greater concentration of enamel proteins.
- They are abundantly in horizontal sections.
- They may be likened to geologic faults.
3. Enamel spindle:
- Before the formation of enamel, some developing odontoblastic processes extend into the ameloblastic layer and become rapped to form enamel spindles.
- They reveal the crystals of dentin and enamel intermix.
- They are best seen in longitudinal sections.
- They are directed at a right angle to dentin.
- They are hypo-mineralized or partially-mineralized structures.
- They are found mainly in cusp tip regions.
4. Hypocalcified Areas of Enamel Surface structures:
Perikymata:
- They are transverse, wave-like grooves
- They are continuous around a tooth and usually lie parallel to each other and to the CEJ.
- They are more in the CEJ and gradually decrease near the occlusal or incisal edge of a surface.
- The course is irregular in the cervical region.
- They are external manifestations of the striae of retail.
Rod ends:
Refer to the Previous Question.
Cracks:
Refer to the Previous Question.
Question 4. Write about enamel organs.
Answer:
Enamel organ:
originates from the stratified epithelium of the primitive oral cavity, which consists of 4 layers.
1. Outer enamel epithelium:
- It consists of a single layer of cuboidal cells.
- It is separated from Hie surrounding connective tissue of the dental sac by a delicate basement membrane.
- During enamel formation, cells of the outer enamel epithelium develop villi, cytoplasmic vesicles, and a large number of mitochondria indicating active transport of materials.
- The capillaries in contact with it show very thin walls for providing active transport.
- Prior to enamel formation, the outer enamel epithelium is maintained only in the cervical parts of the enamel organ.
- At the highest convexity of the organ, the cells of the outer enamel epithelium become irregular in shape.
2. Stellate reticulum:
- It forms the middle part of the enamel organ.
- It consists of start-shaped cells with long processes.
- The neighboring cells are separated by wide intercellular spaces while they are connected with each other and with the cells of other layers by desmosomes.
Stellate reticulum Functions:
- It is elastic and resistant.
- It acts as a buffer against physical forces.
- It permits only a limited flow of nutritional elements.
- The size of the stellate reticulum reduces in thickness to decrease the distance between the capillaries of the dent sac and ameloblasts.
3. Stratum intermedium:
- It consists of two or three rows of flat polyhedral cells.
- It is situated between the stellate reticulum and the inner enamel epithelium.
- Its cells consist of desmosomes and long fibrils.
Stratum intermedium Functions:
- It plays a role in the production of enamel.
- It controls fluid diffusion into and out of the ameloblasts.
4. Inner enamel epithelium:
- It consists of tall, columnar cells that differentiate into ameloblasts.
- It is derived from the basal cell layer of the oral epithelium.
- Its cell differentiation occurs earlier in the region of the incisal edge or cusps than in the cervical area.
Cervical loop:
- At the border of the wide basal opening of the enamel organ, the inner enamel epithelium reflects onto the outer enamel epithelium.
- This is called a cervical loop.
- In it, cells gradually increase in size.
- After the crown formation, the cells of the cervical loop give rise to Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath.
Question 5. Describe the life cycle of ameloblasts.
Answer:
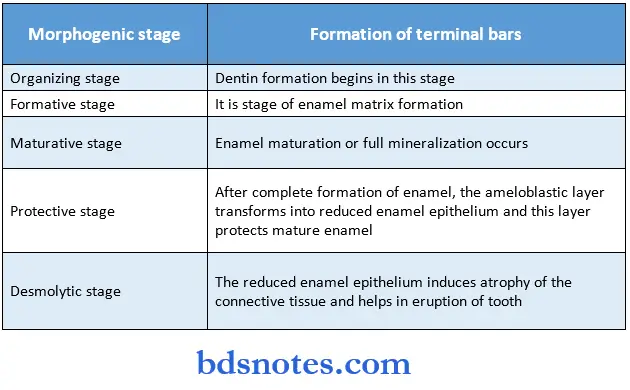
Life-cycle of ameloblasts:
- There are six stages in the life cycle of ameloblasts.
1. Morphogenetic stage:
- Cells of the dental epithelium are separated from the dental papilla by a basement membrane.
- The cells of the inner dental epithelium are cuboidal or low columnar.
- The nucleus is large and centrally located.
- The Golgi apparatus is poorly developed and present in the proximal portion of the cells.
- Mitochondria and other organelles are scattered throughout the cell.
- Ameloblasts interact with the adjacent mesenchymal cells, determining the shape of the dentin enamel junction and the crown.
- The terminal bars are points of close contact between cells.
2. Organizing stage:
- The inner enamel epithelium interacts with the adjacent connective tissue cells, which differentiate into the odontoblast.
- The cells elongate and their nuclei shift proximally towards the stratum intermedium.
- The Golgi complex increases in volume and migrates distally from its proximal position.
- Thus, ameloblast becomes a polarised cell, with the majority of its organelles situated in the cell body distal to the nucleus.
- During the terminal phase of this stage, dentin formation by the odontoblasts begins.
- After dentin formation, the ameloblasts are cut off from their original sources of nourishment.
- They are then supplied by tire capillaries that surround and may even penetrate tire outer enamel epithelium.
3. Formative stage:
- The first layer of dentin is formed.
- Epithelial cells come into close contact with the connective tissue of the pulp, and dentin formation begins.
- Enamel matrix begins to form.
- During it, ameloblasts retain the same length and arrangement.
- Blunt cell processes develop on the ameloblast surfaces, which penetrate tire basal lamina and enter tire prevention.
4. Maturative stage:
- After most of the enamel matrix is formed in the occlusal or incisal area, enamel maturation begins.
- But during this, the enamel matrix is still forming at the tire cervical area.
- During this stage, ameloblasts reduce in size and are closely attached to the enamel matrix.
- They contain microvilli at distal extremities.
- The cells of the stratum intermedium assume a spindle shape.
5. Protective stage:
- By this stage, the enamel is completely developed and fully calcified.
- The cells of stratum intermedium and outer enamel epithelium form reduced enamel epithelium. Functions of reduced enamel epithelium:
- Protect the mature enamel.
- Separate it from the connective tissue until the tooth erupts.
- This prevents the development of anomalies.
6. Desmolytic stage:
- The reduced enamel epithelium proliferates and causes atrophy of the connective tissue to separate it from the oral epithelium.
- This results in the fusion of reduced enamel epithelium and oral epithelium.
- Epithelial cells secrete enzymes that destroy connective tissue fibers by hemolysis.
Question 6. Describe in detail amelogenesis.
Answer:
Amelogenesis:
- Amelogenesis is the process of enamel formation on teeth.
- This involves a two-step process.
- It produces a partially mineralized enamel.
- The second step involves a significant influx of additional minerals.
-
- Removal of organic material and water to attain greater than 96% mineral content.
- Amelogenesis is described in 3 functional stages and 6 phases.
1. Presecretory stage:
- Morphogenetic phase:
- The crown shape is determined.
- Cells of the dental epithelium are separated from the dental papilla by a basement membrane.
- The cells of the inner dental epithelium are cuboidal with a large nucleus.
- The Golgi apparatus is poorly developed and present in the proximal part of cells.
- Mitochondria are scattered throughout the cell.
- Differentiation phase:
- Cells of the inner dental epithelium differentiate into ameloblasts.
- These cells elongate and their nuclei are shifted proximally.
- The cell organelles migrated distally from its proximal portion, and thus polarity of the cell changes.
- Tome’s process develops as a distal extension, against which enamel is formed.
- Production of enamel proteins starts.
- Adjacent ameloblasts are aligned closely with each other through junctional complexes.
2. Secretory stage:
- Ameloblasts elaborate and organize the entire enamel thickness.
- Enamel proteins are packed into membrane-bound secretory granules.
- These granules migrate to the Tome’s process.
- The content of these granules is released against the newly formed mantle dentin along the surface of the process to form an initial layer of enamel.
- Ameloblasts migrate away from the dentin surface and develop a distal portion of Tome’s process.
- This portion penetrates into the enamel beyond the initial layer.
- Formation of interrod and enamel rod occurs.
3. Maturation stage:
- Transitional phase:
- It involves.
- Oral Histology
- Reduction in height of the ameloblasts
- Decrease in their volume and organelle content
- Ameloblasts undergo apoptosis.
Maturation proper:
- Ameloblasts cause the removal of water and organic material from enamel
- Introduces organic material into the enamel.
- Ruffle-ended ameloblasts secrete bicarbonate ions.
- This alkalizes the enamel fluid to prevent reverse demineralization and maintain pH.
- Ruffle-ended ameloblasts also promote the pumping of calcium ions into the maturing enamel.
- Interstitial fluids that leak from smooth-ended contribute to the neutral pH of enamel fluid.
Protective phase:
- During this phase, the newly formed enamel surface is protected until the time of tooth eruption.
Question 7. Write briefly about the mineralization of enamel.
Answer:
Mineralization of enamel:
- There occurs the immediate formation of crystallites within enamel proteins secreted first against mantle dentin.
- It is followed by its elongation against the ameloblast membrane at sites where enamel proteins are released.
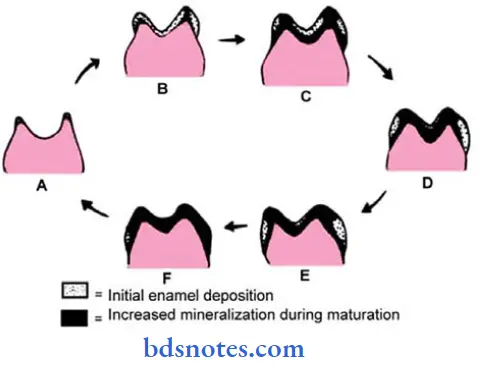
- Mineralization of enamel takes place in two stages.
- In the first stage, about 25-30% of mineralization occurs.
- Immediate partial mineralization occurs in the matrix segments and tire interprismatic substance.
- No matrix vesicles or unmineralized matrix is seen.
- The first mineral forms are crystalline apatite
- This is converted into hydroxyapatite.
- Maturation.
- It is a stage of gradual completion of mineralization.
- The maturation process progresses from crown height to the cervical area and forms the dentinal end of the rods to the surface.
- Growth of the crystals occurs.
- Tuftelin, an enamel protein participates in the nucleation of enamel crystals.
- Other enamel proteins bind the specific surfaces of the crystal and inhibit further deposition.
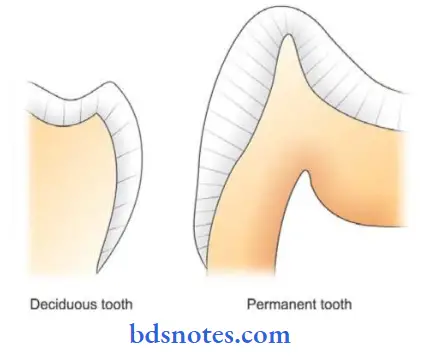
- The rate of formation of enamel is 4 pm/ day.
- It is more in permanent teeth than in deciduous teeth.
- The crystal further increases in size even after tooth eruption due to ion exchange with saliva.
- The organic matrix is gradually thinned out and widely spaced.
- Loss in the volume of the organic matrix is caused by the withdrawal of a substantial amount of protein as well as water.
- The mineralization of enamel differs from that of other tissues.
- The difference is as follows.
- In the first stage, about 25-30% of mineralization occurs.
Question 8. Enamel rods.
Answer:
- They are long, slender mineralized structures of enamel.
- They have a clear, crystalline appearance permitting light to pass through them.
Cross-sectional views:
- It resembles fish scales.
- Under the light microscope, they occasionally appear hexagonal,
- Sometimes they appear round or oval.
Enamel rods Number:
- It varies from
- 5 million in the lower lateral incisors to
- 12 million in the upper first molar.
Enamel rods Size:
- The diameter of the rods averages 4 pm, breadth is 5 pm, and length 9 pm
- The rods in the cuspal area are longer than in the cervical area.
- The diameter of the rod increases from the DEJ towards the enamel surface in the ratio of 1:2.
- Its length is greater than the thickness of the enamel.
Enamel rods Clinical Consideration:
- Each rod is surrounded by rod sheaths and separated by interred substances.
- When cut longitudinally, sections pass through the heads or bodies of one row of rods and tails of adjacent rows.
- The change in the direction of rods is responsible for the appearance of Hunter-Schreger bands.
- Permanent tooth
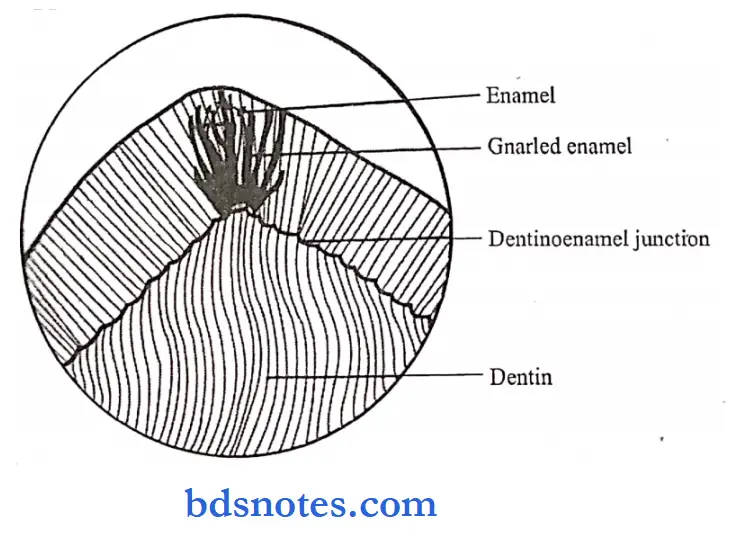
Question 9. Gnarled enamel.
Answer:
On the axial surfaces of teeth, the rods are usually straight and parallel to each other.
- But over the cusps of teeth, the rods are straight and parallel for a short distance from the surface, but at the DEJ, the rods appear twisted around each other in a complex arrangement known as gnarled enamel.
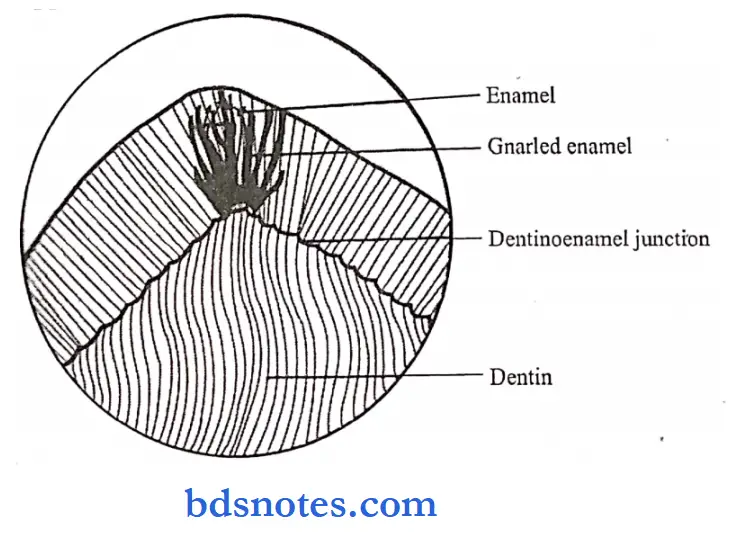
Gnarled enamel Significance:
- Gnarled enamel is a functional adaptation of enamel rods in the cuspal area where excessive load is applied.
- It indicates that the ameloblast has initially an irregular course during early amelogenesis.
Question 10. The formative phase of ameloblast.
Answer:
- The formative phase is the third stage in the life cycle of ameloblast.
- It occurs after the formation of the first layer of dentin.
- The dentin is necessary for the enamel matrix formation.
- During this stage, ameloblasts retain the same length and arrangement.
- But changes occur in the organization and number of cytoplasmic organelles.
- Development of blunt cell process on the ameloblast surfaces occurs.
- This process penetrates the basal lamina and enters the presentation.
- Dentin formation occurs due to the differentiation of odontoblasts.
- This occurs due to close contact of the epithelial cells with the connective tissue of the pulp.
- It is followed by the maturative stage.
- During it, most of the enamel matrix has been formed in the occlusal or incisal area.
- But it still continues in the cervical area.
- Next, morphological changes occur even in the ameloblast as they closely attach to the enamel matrix.
Question 11. Enamel lamellae and enamel tufts.
Answer:
Enamel tufts:
- They are called enamel tufts as they appear as tufts of grass in cross-section.
- They consist of hypocalcified enamel rods and interprismatic substances.
- They even contain a great concentration of enamel proteins – the major is 13.17 kd protein.
- They are ribbon-like structures with their inner end arising in dentin.
- They are abundantly seen in horizontal and longitudinal sections.
Extend:
- They extend from DEJ up to about 1/5* to 1/3th of the enamel thickness.
- They extend in the direction of the long axis of the crown.
Significance:
- They are functional adaptations to the spatial conditions in the enamel.
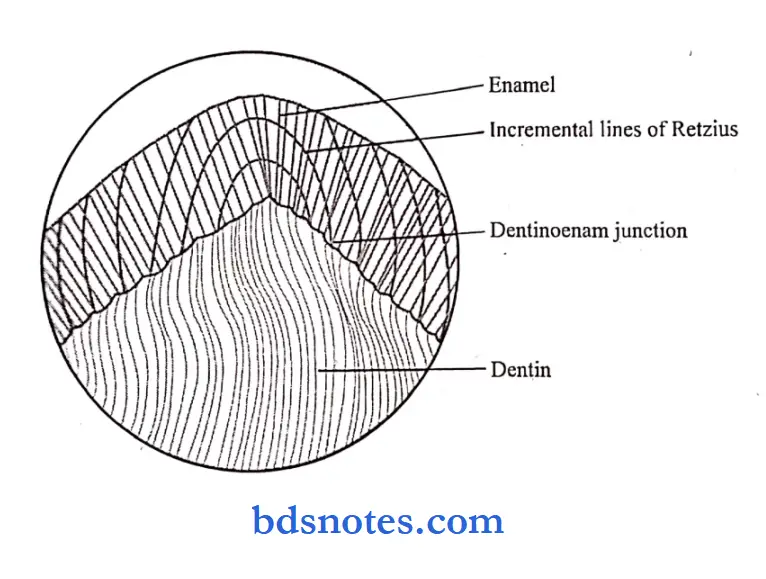
Question 12. Incremental lines in enamel.
Answer:
- They are seen as a series of dark lines extending from DEJ toward the tooth surface.
- While in cross-section they appear as concentric rings.
- They reflect oppositional or incremental growth of the enamel layer.
- As the crown becomes bigger, new cohorts of cells are added cervically to compensate for the increase in size.
- The demarcation between the enamel produced by these cohorts appear as a line of Retzius.
- In longitudinal sections, they surround the tips of dentin and in the cervical parts they run an oblique course.
- From the DEJ to the enamel surfaces, they deviate occlusal.
- They are hypo-mineralized structures
- They reflect variations in structure and mineralization that occur during the growth of the enamel.
- The evenly spaced lines represent 6-11 days of rhythm in enamel formation while other lines are due to stress.
- Broadening of the incremental lines occurs in abnormal conditions arising due to metabolic disturbances.
- Incremental lines of Retzius Dentinoenam junction
Question 13. Describe the enamel cuticle.
Answer:
Enamel cuticle:
- The primary enamel cuticle is a membrane that covers the entire crown of the newly erupted tooth,
- It is removed by mastication and other mechanical forces.
Enamel cuticle Histology:
- This remembrance is a basal lamina present beneath the epithelium.
- It is seen as a wavy course.
- It is secreted by the ameloblasts after the completion of enamel formation.
- It is secreted after the epithelial enamel organ retracts from the cervical region during tooth development.
Enamel cuticle Function:
- The Enamel cuticle protects the enamel surface from the resorptive activity of the adjacent vascular tissue prior to tooth eruption.
Enamel cuticle Fate:
- Once the enamel cuticle is removed by mastication is replaced by a pellicle.
- This pellicle covers the newly erupted teeth and is secreted by the salivary proteins.
- It can be removed off easily from the enamel surface but is reformed within hours.
- Within a day or two, after the formation of the pellicle, micro-organisms are colonized over it to form bacterial plaque.
Question 14. Physical and chemical properties of enamel
Answer:
Enamel Physical Properties:
- Color
- Translucent
- Color varies from yellowish-white to greyish white
- Thickness
- Maximum thickness is seen on the cusps of molars and premolars
- Thin at the neck region
- Hardness – 350 KHN
- Specific gravity – 2.8
- Modulus of elasticity – higher at the surface
- Density – decreases from surface to deeper regions
- Conductivity
- Insulator at room temperature
- Resistance
- Temperature resistance – 5-13 Hz
- Electrical resistance – 10 15 to 10 5 ohm
- Permeability
- It acts as a semipermeable membrane
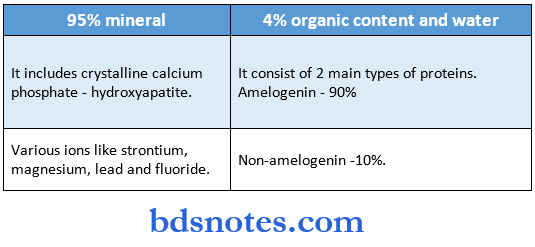
Enamel Chemical properties:
- The enamel consists of approximately 96% mineral and 5% organic material and water
- The inorganic content of enamel is a crystalline calcium phosphate-hydroxyapatite
- Various ions – strontium, magnesium, lead, and fluoride are incorporated into it
- The susceptibility of these crystals to dissolution by acid provides the chemical basis for dental caries
- The organic material consists of proteins – 2 main groups are seen Amelogenin
- Nonamelogenin
Question 15. Hypocalcified structures of enamel
Answer:
- Enamel lamellae
- They extend for varying depths from the enamel surface
- They are thin, leaf-like structures filled with organic material
- They may develop in planes of tension
- Types:
- Type A
- Consist of poorly calcified rod segments
- Restricted to enamel
- Type B
- Consist of degenerated cells
- They are restricted to the dentin
- Type C
- These fare lamellae arising in erupted teeth
- They are restricted to the dentin
- Enamel tufts
- Enamel tufts are tuft structures arising from dentin-enamel junction towards the enamel surface
- Enamel spindles
- They are mesenchymal in origin.
- They are formed by extensions of odontoblast processes into enamel before calcification.
- Surface structures
- Perikymata
- The small ridges and perikymata seen on the surfaces of canines are a result of normal development.
- They are shallow furrows on the enamel surfaces where the striae of Retzius end.
- Rod ends
- They are concave and vary in depth and shape
- Cracks
- They are narrow, fissure-like structures that are seen on almost all surfaces
- Perikymata
Question 16. Ameloblast
Answer:
- Enamel is laid down only by ameloblasts
- Ameloblast is a cell from which tooth enamel is formed.
- Synthesis of enamel matrix proteins occurs in it.
- The life cycle of ameloblast
Question 17. Enamel hypoplasia
Answer:
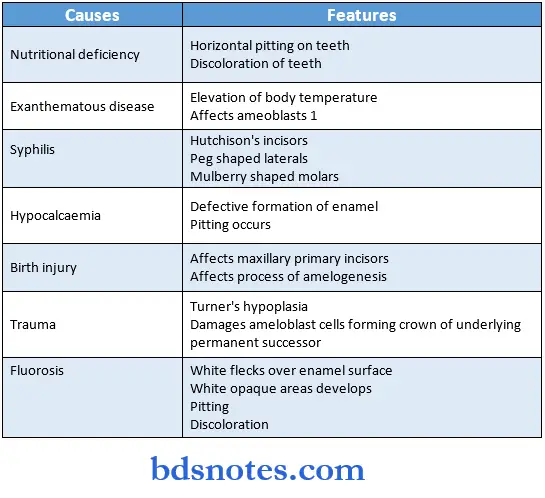
- It is defined as an incomplete or defective formation of the organic enamel matrix of teeth
Enamel hypoplasia Types and causes:
- Congenital – hereditary
- Environmental causes for enamel hypoplasia
Question 18. Gnarled enamel.
Answer:
- It shows the intertwining of enamel rods over the cuspal areas of the molars and premolars.
- It is a functional adaptation of rods to excessive load.
- It represents the irregular initial course of ameloblast during early amelogenesis.
Question 19. Enamel lamellae.
Answer:
- They are thin, leaf-like structures filled with organic material.
- They may develop in planes of tension and act as pathways for caries-producing bacteria.
Enamel lamellae Types:
1. Type 1:
- Composed of poorly calcified rod segments.
2. Type 2:
- Consist of degenerated cells.
3. Type 3:
- Arise in erupted teeth where the crack are filled with organic material
Question 20. Dentinoenamel junction.
Answer:
- It is the junction between two hard tissues enamel and dentin.
- It is a scalloped line with convexities directed toward the dentin.
- In the dentin enamel junction, the crystals of dentin and enamel are mixed with each other.
- It is a series of ridges.
- It is more pronounced in areas of excessive masticatory load i.e., in the occlusal area.
- It is a hypermineralized zone of about 30 jam thick.
- It is most prominent before the completion of mineralization.
Question 21. Enamel spindles.
Answer:
- Before the formation of enamel, some developing odontoblastic processes extend into the ameloblastic layer and become trapped to form enamel spindles.
- They reveal the crystals of dentin & enamel intermix.
- They are best seen in the longitudinal section.
- They are hypo-mineralized or partially mineralized structures.
Enamel spindles Site:
- Mainly found in cusp tip regions.
Enamel spindles Extend:
- From odontoblastic process into enamel epithelium
Enamel spindles Direction:
- Right angle to the surface of dentin.
Question 22. Age changes of enamel.
Answer:
1. Surface of enamel:
- Attrition of occlusal surfaces and proximal contact points.
- Loss of vertical dimension of the crown
- Loss of rod ends and perikymata
- Facial and lingual surfaces lose their structure more rapidly than proximal surfaces.
- Anterior teeth lose their structure more rapidly than posterior teeth.
2. Color:
- Teeth darken with age due to the addition of organic material to enamel from the environment.
3. Permeability:
- Enamel becomes less permeable with age.
- The crystal increases in size and acquires more ions with age.
- This decreases the pores between them causing a reduction in permeability.
4. Caries incidence:
- There is an apparent reduction in the incidence of caries.
- This is due to a progressive increase in the fluoride content of the enamel.
Question 23. Nasmyth’s membrane.
Answer:
- It is a membrane that covers the entire crown of the newly erupted tooth.
- It is easily removed by mastication and other mechanical forces.
- It is also called a primary enamel cuticle.
- It resembles the basal lamina.
- It is secreted by the ameloblasts after the completion of enamel formation.
Nasmyth’s membrane Function:
- It protects the enamel surfaces from the resorptive activity of the adjacent vascular tissue prior to tooth eruption.
Question 24. Chemical composition of enamel.
Answer:
Question 25. Enamel.
Answer:
- Enamel is a hard, mineralized tissue that covers the anatomical crowns of teeth.
- It is an epithelial-derived protective covering of teeth.
- The cells that are responsible for enamel formation are called ameloblasts.
- Enamel consists of 96% mineral and 4% organic material and water.
- Enamel is extremely hard which enables it to withstand mechanical forces.
- It is translucent and varies in color.
- It chiefly consists of enamel rods, rod sheaths, and cementing interprismatic substance.
Question 26. Ameloblast.
Answer:
- Ameloblast is the cells responsible for the formation of enamel.
- It covers the entire surface of the enamel as it forms.
- But they are lost as tire tooth emerges into the oral cavity.
- These elongated cells are attached to each other by junctional complexes and to cells in stratum intermedium by desmosomes.
Ameloblast Size:
- 4 – 5 jam in diameter.
- 40 pm high.
- Function:
- Ameloblasts secrete matrix proteins.
- They are responsible for creating and maintaining an extracellular environment favorable to mineral deposition.
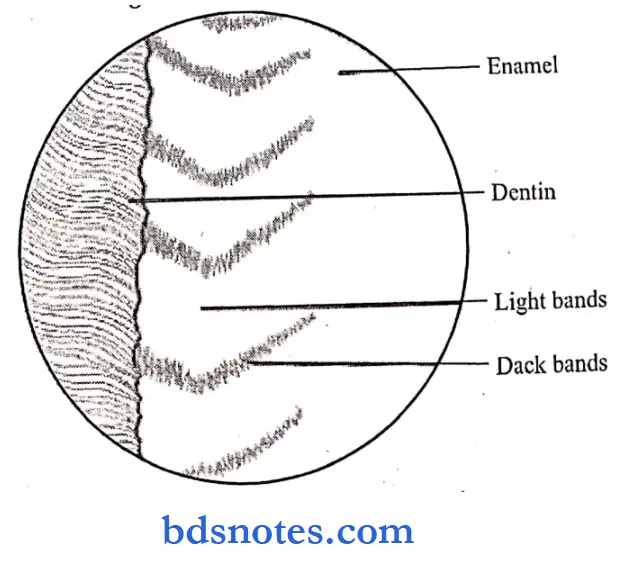
Question 27. Hunter and Schreger bands.
Answer:
- They are an optical phenomenon produced by changes in direction between adjacent groups of rods.
- They are found in the inner two third of the enamel.
- They appear as dark and light alternating zones that can be reversed by altering the direction of incident light.
- It reveals the difference in the orientation of groups of rods within these zones.
- They originate at the dentino enamel border.
- They minimize the risk of cleavage in the axial direction under the influence of occlusal forces.
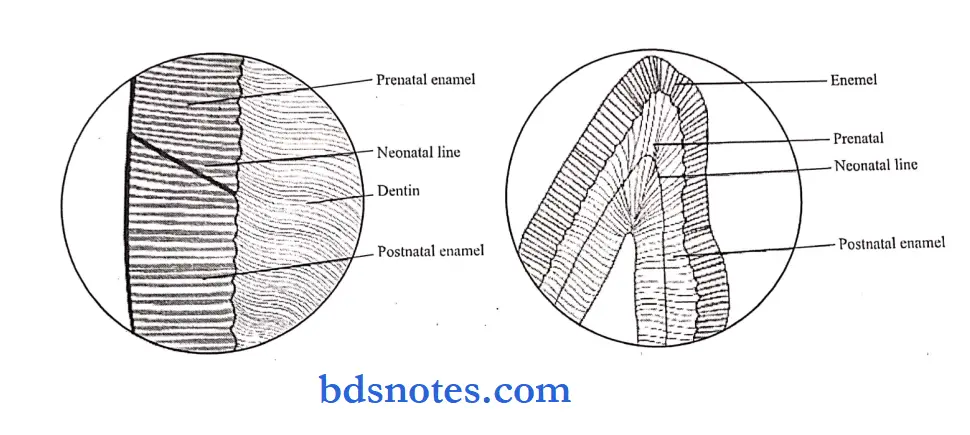
Question 28. Neonatal line.
Answer:
- It is an enlarged stria of the retzius that apparently reflects the great physiologic changes occurring at birth.
- It is seen as a brown line separating enamel formed and mineralized before birth and enamel mineralized after birth.
- Deciduous teeth and a permanent 1st molar are formed.
- Partly before birth and partly after birth, hence, a neonatal line is present in these teeth.
- They are more frequently absent in boys than girls suggesting boys are less dentally mature.
- Their location varies in preterm and post-term births.
Question 29. Pellicle.
Answer:
- The surface of the enamel of newly erupted teeth is covered by a pellicle, n It is secreted by the salivary proteins.
- It can be removed easily after the tooth is mechanically polished, n But it is reformed within hours.
- Within a day or two, after its formation, microorganisms are colonized over it to form dental plaque.
Question 30. Tomes process.
Answer:
- The projections of ameloblasts in the enamel matrix are known as the tomes process.
- They show a ‘picket fence’ arrangement.
- They contain secretory granules, rough endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondrial.
- It appears during the prcsccretory phase of amelogenesis.
When enamel formation begins, the tomes process comprises only a proximal portion. - Later on, ameloblasts migrate away from the dentin surface and develop the distal portion of the tome’s process.
- After the development of both portions, the secretion of enamel proteins becomes staggered.
Question 31. Hypocalcified structures of enamel.
Answer:
Question 32. Enamel knot, cord, and niche
Answer:
Enamel Knot:
- They are clusters of non-dividing epithelial cells present in molar cap stage tooth germ
- It consists of cells that do not divide but promote the division of adjacent epithelial cells
- Each tooth germ has a single primary enamel knot at the cap stage which disappears and a secondary knot appears It represents a signaling center for tooth morphogenesis Enamel Cord:
- Temporal nested patterns in the enamel knot that extend between the inner and outer dental epithelium are called enamel cords.
Enamel Niche:
- The Enamel organ appears to have a double attachment to the dental lamina through strands.
- These strands enclose a funnel-shaped depression containing connective tissue. This is known as the enamel niche
Question 33. Enamel cuticle
Answer:
- It is a delicate membrane covering the newly erupted teeth
Enamel cuticle Formation:
- Secreted by ameloblasts when the Enamel organ is retracted from the cervical region Enamel formation is complete
Enamel cuticle Functions:
- Protects the surface of enamel from the resorptive activity of adjacent tissue prior to the eruption
Enamel cuticle Fate:
- Removed by mastication
- Replaced by pellicle

Leave a Reply