Drugs Used In Dentistry Question And Answers
Question 1. Write short note on corticosteroids.
Answer. There are two types of corticosteroids, i.e.
- Glucocorticoids.
- Mineralocorticoids.
Glucocorticoids
Corticosteroids Classification
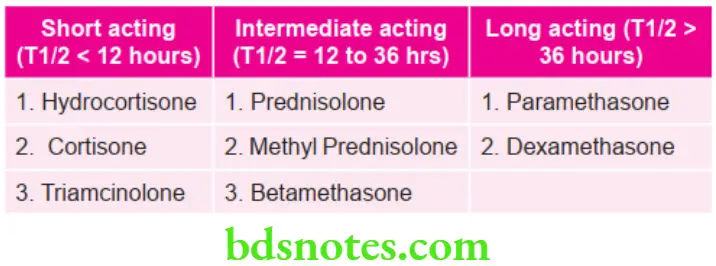
Corticosteroids Mechanism of Action
- Glucocorticoid enters the cell and bind with its receptor.
- This corticoreceptor complex move inside the nucleus of the cell.
- The complex bind to the chromatin so it causes transcription of mRNA, and hence causes protein synthesis.
Read And Learn More: Oral Medicine Question And Answers
Corticosteroids Actions
- It promotes glycogenesis, gluconeogenesis and decreases glucose utilization by peripheral tissues.
- They promote lipolysis.
- It increases renal excretion of calcium.
- It increases secretory activity of renal tubules.
- They maintain tone of arterioles and myocardial contractility.
- They are required for normal skeletal muscle activity.
- They suppress inflammatory response thus they decrease capillary permeability, exudation, central infiltration, phagocytic activity and thus, the sign of inflammation are reduced.
- They increase rate of destruction of lymphoid cells, increase RBCs, platelets, neutrophils and decreases lymphocyte, eosinophils, basophil.
- In CNS, glucocorticoids produce mild euphoria.
- In stomach, glucocorticoids increase gastric acid and pepsin secretion.
Corticosteroids Uses
- In acute and chronic adrenal insufficiency.
- In rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
- In rheumatic fever and acute gout.
- In severe allergic reaction.
- In bronchial asthma, aspiration, pneumonia, pulmonary edema.
- In skin diseases such as eczema.
- In malignancies such as acute lymphatic leukemia, Hodgkin’s lymphoma and other adrenal malignancies.
- In ulcerative colitis, septic shock.
Corticosteroids Adverse Effects
- In hyperglycemia, they cause precipitation of diabetes and glucosuria.
- They cause muscular weakness.
- They cause thinning of skin, fragile skin and purple striae hirsutism.
- They cause Cushing’s habitus in which there is moon face, narrow mouth and obesity of trunk with thinning of legs.
- They increase susceptibility to infection, i.e. TB and opportunistic infection may flare up.
- They cause delayed healing of wound and surgical incisions.
- They causes peptic ulcer.
- They causes osteoporosis, glaucoma and growth retardation in children.
- At high doses, they causes psychiatric disturbance.
- They causes suppression of hypothalamopituitary axis.
Corticosteroids Mineralocorticoids
The important natural mineralocorticoid is aldosterone, fludrocortisone and desoxycorticosterone.
Corticosteroids Uses
- In treatment of Addison’s disease.
- Hypoaldosteronism, diabetes mellitus.
- Severe postural hypotension.
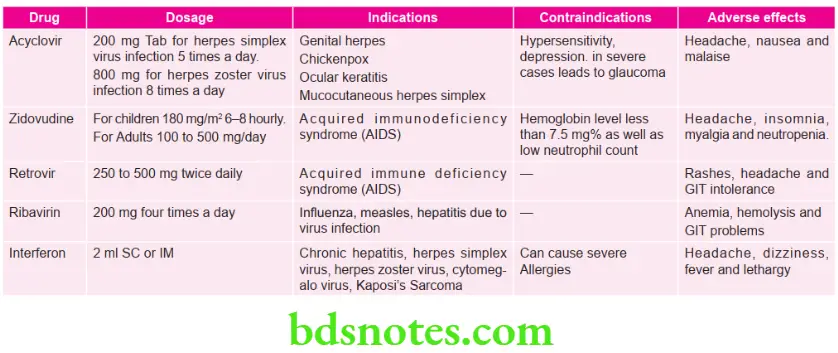
Question 2. Write short note on anti-viral drugs.
Answer. Anti-viral drugs are used to treat the viral diseases.
Anti-Viral Drugs Classification
- Anti-herpes virus: Idoxuridine, Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, Famciclovir, Ganciclovir.
- Anti-retrovirus:
- Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Zidovudine, Didanosine, Zalcitabine, Stavudine, Lamivudine, Abacavir.
- Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Nevirapine, Efavirenz, Delavirdine
- Protease inhibitors: Ritonavir, Indinavir, Nelfinavir, Saquinavir, Amprenavir, Lopinavir
- 3-Anti-Influenza virus: Amantadine, Rimantadine
- Non-selective anti-viral drugs: Ribavirin, Lamivudine, Adefovir dipivoxil, Interferon-α
Question 3. Write short note on amoxicillin.
Answer. It is an anti-microbial drug.
It is a penicillin drug which is effective against gram positive and gram-negative organisms.
Amoxicillin Mechanism of Action
Amoxicillin acts by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. It inhibits cross-linkage between the linear peptidoglycan polymer chains that make up a major component of the cell walls of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Amoxicillin Dosage
It is given in oral form as TDS dosage of about 200–500 mg. It can also be given parenterally i.e. IV or IM
Amoxicillin Drug Interaction
Amoxicillin should not be given with aminoglycosides because out of the two drugs, the one which is given earlier inactivate action of other drug.
Amoxicillin Uses
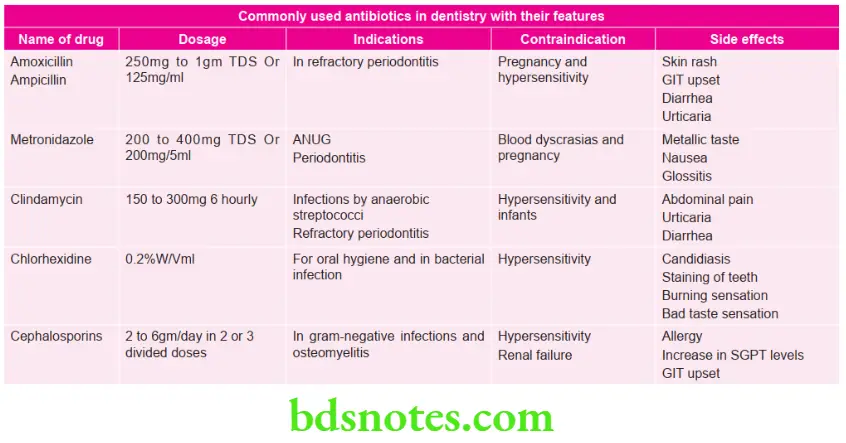
- It is used in refractory periodontitis.
- It is used to treat lyme disease.
- It is used to treat urinary tract infections caused by E. coli, Streptococci, etc.
- It is used to treat typhoid, sub acute bacterial endocarditis and Gonorrhea.
Question 4. Write short note on corticosteroids in dentistry.
Answer. Following are the uses of steroids in dentistry:
- Oral lichen planus: Prednisolone or methyl prednisolone is the choice of drug given in autoimmune disease like lichen planus. Its minimum effective dose in lichen planus is 15 to 20 mg daily. Treatment should be given for 6 weeks and the dose is then tapered to another 6 weeks. One recommended regimen is to start the drug ranging from 40 to 80 mg/day for 14 days as a single dose and maintenance dose is 60 to 80 mg/day on alternate days and this should be continued till remission. Topical therapy should be initiated from the second week to prevent the long term systemic therapy.Aphthous stomatitis: Here prednisolone and betamethasone syrup both are to be used via rinse and swallow method. Here first goal is the stop current attack and secondly attempt should be taken to break the cycle of recurrence to achieve atleast the temporary period of remission. Burst therapy should be given 40 mg of prednisolone taken one hour after rinsing in morning for 5 days, this is followed by 20 mg every other day for additional week along with the oral rinse of 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide aqueous suspension. 5 mL of suspension is swished 4 times daily for 2 to 3 minutes and then expectorated.
- Pemphigus and pemphigoid: Pulse intravenous corticosteroids along with oral immunosuppressant drug i.e. cyclophosphamide or azathioprine is given. Methyl prednisolone should be given in pulse therapy as 250 to 1000 mg for 1 to 3 hours for 3 days or equivalent doses of dexamethasone should be given for 1 to 5 days.
- Erythema multiforme: Mild to moderate lesions and also the severe lesions of erythema multiforme should be treated by short course of systemic glucocorticosteroid. Here 40mg of prednisolone should be given per day for a week and then it is tapered.
- Lupus erythematosus: In systemic lupus erythematosus oral lesions are treated by high potency topical corticosteroids or intralesional corticosteroid injections. Systemically low dose prednisolone 10 to 20 mg/day or 20 to 40 mg on alternate day should be given.
- Cranial arteritis: Prednisolone should be given as 40 to 60 mg/day and steroid should be tapered as the signs of disease get reduced. This is usually followed by maintenance dose for 1 to 2 years.
- Shock: Hydrocortisone 100 mg should be given as the part of therapy.
- Endodontics: After root canal treatment, triamcinolone acetonide can be given to reduce the inflammation.
- Perioperative corticosteroids in dentoalveolar surgery: Most commonly used steroids are dexamethasone, methylprednisolone acetate. Corticosteroids suppress the tissue mediators of inflammation, decreases transudation of fluids and edema, inhibitory action of prostaglandins is also present. Many of the patients experience mood altering effect from steroids which helps in coping with postoperative sequelae.
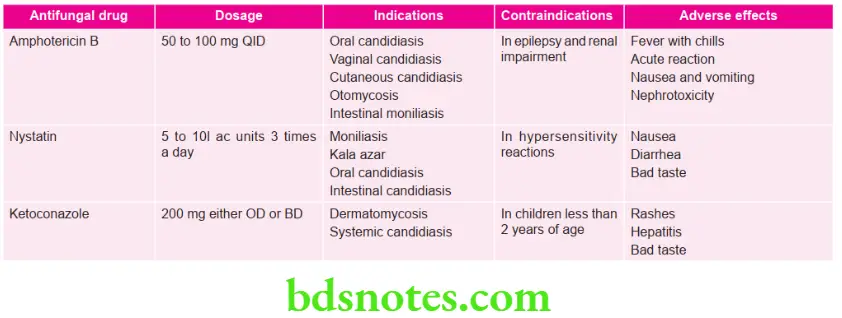
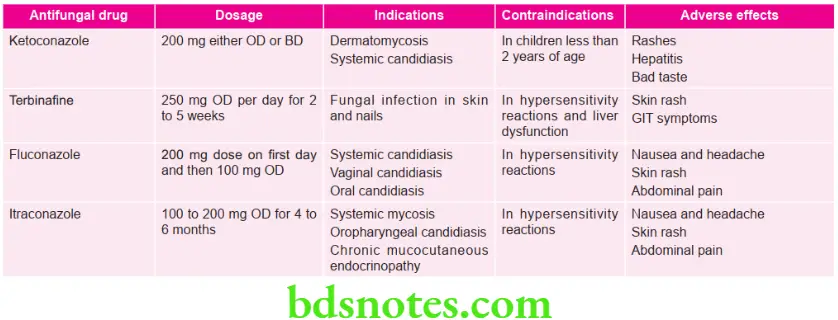
Question 5. Write short note on antifungal agents.
Or
Write short answer on antifungal drugs in oral medicine.
Answer. Antifungal agents are used in treatment of fungal diseases.
Antifungal Agents Classification
- Antibiotics:
- Polyenes: Amphotericin B, nystatin, natamycin, hamycin
- Heterocyclic benzofuran: Griseofulvin
- Antimetabolite: Flucytosine
- Azoles
- Imidazoles (Topical): Clotrimazole, meconazole, Oxiconazole (Systemic): Ketoconazole
- Triazoles (Systemic): Fluconazole, itraconazole, Voriconazole
- Allylamine: Terbinafin
- Other topical agents: Benzoic acid, sodium thiosulphate, butenafine, undecylenic acid, quiniodochlor, ciclopiroxolamine
Question 6. Write short note on antibiotics.
Answer. Antibiotics are the chemical substances which are produced by the microorganisms that suppress the growth of other microorganisms and may eventually destroy them.
Antibiotics Types
Antibiotics are of two types, i.e.
- Bacteriostatic: Antibiotics which inhibits growth of bacteria
- Bactericidal: Antibiotics which destroy bacteria
Antibiotics Indications
- For therapeutic purposes:
- In patients where host response is reduced by diseases such as diabetes mellitus, malnutrition, alcoholism.
- In patients with acute severely rapidly spreading infection
- In odontogenic infections, osteomyelitis, soft tissue wounds, etc.
- For prophylactic purposes:
- For postoperative wound infections
- Before preoperative procedures
Antibiotics Useful in Orofacial Infections
- Penicillin
- Cephalosporin
- Erythromycin
- Clindamycin
- Metronidazole
- Aminoglycoside
- Newer beta-lactam antibiotics, i.e. Carbapenem and monobactams
- Fluoroquinolones, i.e. Ciprofloxacin

Leave a Reply