Digital Radiography
Question 1. Write short note on digital radiography.
Answer. The term digital radiography refers to a method of capturing a radiographic image using a sensor, breaking it into electronic pieces and presenting and storing the image using a computer.
Not limited to intraoral images, panoramic and cephalometric image may also be obtained.
Digital Radiography Indications
- Detect disease, lesion and conditions of teeth and surrounding structures.
- To confirm the detected diseases.
- To evaluate growth and development.
- To document the condition of a patient.
- To illustrate changes secondary to caries, periodontal disease or trauma.
- To provide information during dental procedure such as root canal instrumentation and surgical placement of implants.
Read And Learn More: Oral Radiology Question And Answers
Three Methods to obtain digital image
Direct digital imaging
Sensor is placed directly in patient’s mouth and exposed to radiation this sensor captures the image, and they transmits the image to a computer monitor in seconds.
Indirect digital imaging
Rinsing X-ray film is digitalized using CCD camera, which scan the image and converts the image and then display it on computer, screen.
Storage Phosphor imaging
- Wireless digital radiography system.
- A reversible imaging plate coated with phosphors is used.
- These plates are flexible and fi into mouth.
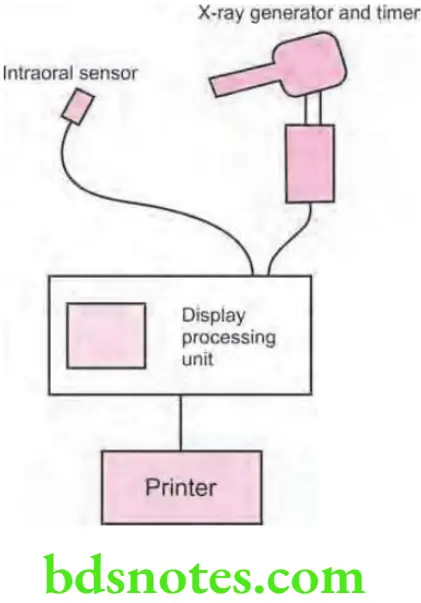
Equipment
- X-radiation source.
- Intraoral senses.
- Digital image display.
Digital Radiography Advantages
- Superior gray scale resolution
- Easy reproducibility
- Reduced exposure to radiation
- Increased speed of image viewing
- Lower equipment and film cost.
- Increased efficiency.
- Enhancement of diagnostic image.
Digital Radiography Disadvantages
- Initial set-up is costly.
- Image quality is still a source of debate.
- Sensor size—these are thicker than intraoral fims and therefore no patient compliant.
- Infection control, the sensor has to be covered adequately in a disposable plastic wrapper.
- Legal issues, because the original digital image can be manipulated, it is debatable whether digital radiographs can be used as evidence in lawsuits.
Question 2. Write short note on advantages and limitations of digital radiography.
or
Write short note on advantages and disadvantages of digital radiography.
Answer. Purpose of digital radiography is to generate images that can be used in diagnosis and assessment of dental disease.
Digital Radiography Advantages
- Superior gray scale resolution
- Easy reproducibility
- Reduced exposure to radiation
- Increased speed of image viewing
- Lower equipment and fim cost.
- Increased effiency.
- Enhancement of diagnostic image.
- Excellent quality image with no loss of quality commonly associated with conventional chemical processing.
- Image processing, enlargement and reconstruction for specifi diagnostic purpose is possible.
- With the aid of the computer, detection of defects and three-dimensional visualization of dental structures based on radiographic data is possible.
- Effective patient education tool
Digital Radiography Limitations/disadvantages
- Initial set-up is costly.
- Image quality is still a source of debate.
- Sensor size—these are thicker than intraoral fims and therefore no patient compliant.
- Infection control, the sensor has to be covered adequately in a disposable plastic wrapper.
- Legal issues, because the original digital image can be manipulated, it is debatable whether digital radiographs can be used as evidence in lawsuits.
Question 3. Write short note on radiovisiography (RVG).
or
Write short note on RVG
Answer. RVG was invented by Dr Frances Mouyens.
- Dr Mouyens invented a way to employ fier optics to narrow down a large X-ray image onto a smaller size that could be sensed by a Charge Coupled Device (CCD) image sensor chip.
- The RVG system is capable of rapidly displaying a digital radiographic image on a monitor which results in a lower patient radiation.
- The “Radio” component is the conventional X-ray generator with a timer, capable of very short exposure time, along with image receptor.
- The “Visio” portion converts the output signal from a CCD to a digital format and displays it on a monitor.
- The “Graphy” component consists of data storage unit connected to a video printer.
- The most significant advantages of digital imaging, therefore, are computer-aided image interpretation and image enhancement, in addition to the obvious options of standardized image archiving and image retrieval.
- The CCD is a solid-state detector composed of an array of X-ray or light sensitive pixels on a pure silicon chip.
- Apixel or picture element consists of a small electron well into which the X-ray or light energy is deposited upon exposure.
- The individual CCD pixel size is approximately 40 μ with the latest versions in the 20μ range. The rows of pixels are arranged in a matrix of 512 x 512 pixels.
- There are two types of digital sensor array designs: area and linear.
- Area arrays are used for intraoral radiography, while linear arrays are used in extraoral imaging. Area arrays are available in sizes comparable to size 0, size 1, and size 2 fims, butthe sensors are rigid and thicker thanradiographic fim and have a smaller sensitive area for image capture.
- The sensor communicates with the computer through an electrical cable.
- Area arrays CCDs have two primaryformats: Fiberoptically coupled sensors and direct sensors.
- Fiberoptically coupled sensors utilize a scintillation screen coupled to a CCD. When X-rays interact with the screen material, light photons are generated, detected, and stored by CCD.
- Direct sensor CCD arrays capture the image directly without the intermediate scintillation layer. When exposed to radiation, the covalent bonds between silicon atoms are broken, producing electron whole pairs.
- The number of electron whole pairs that are formed is proportional to the amount of exposure that an area receives. The electrons are then attracted towards the most positive potential in the device, where they create “charge packets”.
- Each packet corresponds to one pixel.
- The charge pattern formed from the individual pixel in the matrix represents the latent image.
- The image is read by transferring each row of pixel charges from one pixel to the next in a “bucket brigade” fashion. As a charge reaches the end of its row, it is transferred to a read out amplifier and transmitted as a voltage to analog-to-digital convertor located within or connected to the computer.
- Voltages from each pixel are sampled and assigned a numeric value representing a gray level.
Radiovisiography Clinical applications
- Dental caries detection
- Intrabony defects
- Periapical pathologies detection
- Detection of root fractures
- Detection of root canal length
- Application in mentally retarded/developmentally disabled individuals
- In Telemedicine
Question 4. Write short answer on image receptors.
Answer. Term image receptor refer to any medium used to capture an image, including fim, charge coupled devices (CCDs), complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensors or storage phosphor plates.
These are also known as image sensors.
Principle for making the projection radiographs is same for each of these receptor types.
Types of image Receptors
- Conventional or Radiographic films
- Direct action or packet film
- Indirect action film used in conjunction with intensifying screens in a cassette
- Digital
- Solid state sensors i.e. CCD and CMOS
- Phosphor plates i.e. PSP
Image Receptors Radiographic films
- In dentistry, radiographic film is used as image receptor and is still widely used.
- Radiographic films are of two types:
- Direct action: It is sensitive primarily to the X-ray photons.
- Indirect action or screen fim: This is sensitive to the light photons which are emitted by adjacent intensifying screens. They respond to the shorter exposure of X-rays, enabling the lower dose of radiation to be given to the patient.
Technology on Which digital image Receptors Work
Digital image receptors use diffrent technologies and come in diffrent sizes and shapes.
Mainly two types of technologies are used i.e.
- Solid state technology: Solid state detectors are charged couple devices (CCDs), complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensors and flt panel detectors. These all have in common certain physical properties and have ability to generate digital image in computer without any external device. In dentistry, intra-oral solid state detectors are known as sensors.
- Photostimulable phosphor technology: It consists ofa phosphor coated plate in which the latent image is formed by the X – ray exposure. Latent image get converted to digital image by scanning device via stimulation by laser light. This technology is referred to as storage phosphor on basis of notion that the image formation is temporarily stored in phosphor. Image plate is the term used to differentiate them from film and solid state detectors.
Various image Receptors and their clinical applications



Leave a Reply