Multiple Choice Questions In Dental Materials
Question 1. Rheology is the study of
- Stress and strain
- Flow of matter
- Color
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Flow of matter
Read And Learn More: Dental Materials Question And Answers
Question 2. Tarnish is
- Surface discoloration on 1 metal
- Deterioration of 1 metal
- Fracture of 1 metal
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Surface discoloration on a metal
Question 3. The pH of calcium hydroxide cement ranges from
- 7 – 8
- 9 – 12
- 3 – 5
- 5 – 7
Answer: 3. 3 – 5
Dental Mcqs With Answers
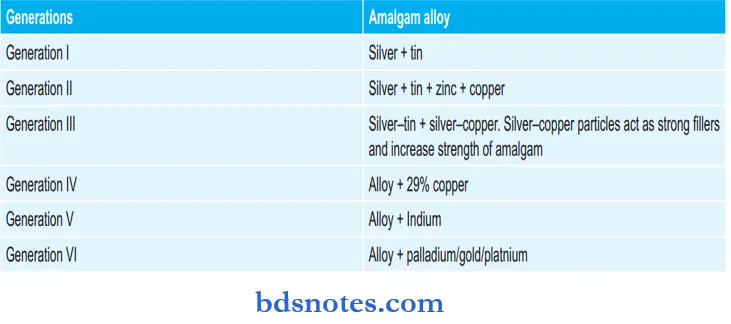
Question 4. Quaternary dental amalgam alloy is
- Silver-tin-copper-indium
- Silver-tin-copper-iridium
- Silver-tin-copper palladium
- Silver-tin-copper platinum
Answer: 1. Silver-tin-copper-indium
Question 5. As per William’s classification, particle size of microfine composite can be described as
- > 3 µm
- 5 – 100 nm
- < 3 µm
- 0.04 µm
Answer: 4. 0.04 µm
Question 6. Elastomeric impression materials are generally hydrophobic except
- Polysulfide
- Addition silicone
- Polyether
- Condensation silicone
Answer: 3. Polyether
Question 7. Recommended W/P ratio for dental plaster
- 0.45 – 0.50
- 0.22 – 0.24
- 0.28 – 0.30
- 0.50 – 0.75
Answer: 1. 0.45 – 0.50
Question 8. Which zone of blow torch flame is used for fusion of casting alloy
- Oxidizing zone
- Mixing zone
- Combustion zone
- Reducing zone
Answer: 4. Reducing zone
Question 9. Firing temperature of medium-fusing dental porcelain ranges from
- 850 to 1100°3
- 1101 to 1300°3
- 1300 to 1400°3
- 700 to 8500°3
Answer: 2. 1101 t0o 1300°3
Dental Mcqs With Answers
Question 10. The fusion temperature of impression compound is
- 55 – 60°3
- 60 – 65°3
- 43 – 50°3
- 35 – 40°3
Answer:
Question 11. ______has the highest temperature which is used for soldering purpose
- Acetylene
- Hydrogen
- Natural gas
- Oxygen
Answer: 1. Acetylene
Question 12. Which of the following impression material is not rigid?
- Impression compound
- Wax
- Zinc oxide eugenol paste
- Agar
Answer: 4. Agar
Question 13. Secondary caries is found to be less when cavity restoration is done with
- Zinc phosphate cement
- Glass ionomer cement
- Gold inlay
- Silver amalgam
Answer: 2. Glass ionomer cement
Question 14. Which metal acts as 1 oxygen scavenger
- Copper
- Silver
- Zinc
- Palladium
Answer: 3. Zinc
Question 15. Which of the following is not an investment material?
- Silica bonded
- Copper bonded
- Phosphate bonded
- Gypsum-bonded
Answer: 2. Cooper bonded
Dental Mcqs With Answers
Question 16. The fusion temperature of impression compound occurs
- Before mouth temperature
- At skin temperature
- At room temperature
- Above mouth temperature
Answer: 3. At room temperature
Question 17. Stiffness is
- The degree of elastic deformation
- The resistance to elastic deformation
- Capacity to absorb mechanical energy
- The amount of expansion in thermal condition
Answer: The resistance to elastic deformation
Question 18. Which of the following phase is eliminated in a high copper amalgam?
- γ1 phase
- γ2 phase
- β phase
- η phase
Answer: 2. γ 2 phase
Question 19. The sprue former should be attached to the wax pattern
- At the thinnest point
- At the point of greatest bulk
- On occlusal surface
- None of the above
Answer: 2. At the point of greatest bulk
Question 20. The commonly used solution for electroplating of impressions with silver is
- Silver nitrate
- Silver sulfate
- Silver amalgam
- Copper sulfate
Answer: 4. Copper sulfate
Question 21. The human eye is sensitive to wavelengths from
- 200 – 400 nm
- 400 – 600 nm
- 400 – 700 nm
- 600 – 900 nm
Answer: 3. 400 – 700 nm
Dental Mcqs With Answers
Question 22. An example of a reversible hydrocolloid is
- Alginate
- ZOE paste
- Polyether
- Agar
Answer: 4. Agar
Question 23. Loss of gloss from the surface of the mixed mass of dental plaster or stone indicates
- lnitial setting time
- Final setting time
- Lack of water
- Does not indicate anything
Answer: 1. Initial setting time
Question 24. Material added in investment material to withstand high temperatures without decomposing is
- Binder
- Modifier
- Refractory material
- Die material
Answer: 3. Refractory material
Question 25. Polymer-monomer ratio by volume for denture base resin is
- 3:1 by volume
- 2:1 by volume
- 1:1 by volume
- 3:2 by volume
Answer: 1. 3:1 by volume
Question 26. ln 18-8 stainless steel the percentage of chromium is
- 8%
- 18%
- 18.8%
- It does not contain chromium
Answer: 18%
Question 27. Which alloy is called shape memory alloy?
- Titanium-molybdenum alloy
- Cobalt-chromium alloy
- Nickel-titanium alloy
- Nickel-chromium alloy
Answer: 3. Nickel-titanium alloy
Dental Mcqs With Answers
Question 28. Sticky wax is an example of
- Pattern waxes
- Impression waxes
- Processing waxes
- Resin waxes
Answer: 3. Processing waxes
Question 29. The exuding of fluid from the gel which is commonly seen in hydrocolloid impression materials is called
- Syneresis
- Evaporation
- Condensation
- lmbibition
Answer: 1. Syneresis
Question 30. The inhibitor used in liquid component of powder liquid type dentine acrylic resin to prevent premature polymerization is
- Benzoyl peroxide
- Hydroquinone
- N, N-dimethyl-toluidine
- Glycol dimethacrylate
Answer: 2. Hydroquinone
Question 31. What does the etching of intact enamel with phosphoric acid produce?
- An increase in surface area
- 1 decrease in surface area
- No change in surface area
- Decrease in chemical bonding capacities
Answer: 1. An increase in surface area
Question 32. Should amalgam be burnished after it has been carved
- No, it brings mercury to the surface of margin
- No, it might destroy the crystal structure
- Yes, it continues condensation at the margins
- Yes, it makes the surface looks shiny
Answer: 3. Yes, it continues condensation at the margins
Question 33. Casting flux should be used
- To prevent contamination of the gold from the asbestos linear
- To prevent too rapid melting of gold
- Its only with gold that has been previously cast
- To prevent oxidation of the metal during melting
Answer: 4. To prevent oxidation of the metal during melting
Question 34. In order to melt gold optionally which part of the flame should be used
- Reducing zone
- Oxidizing zone
- Liquidus zone
- Any part of the flame will do
Answer: 1. Reducing zone
Dental Materials Mcqs
Question 35. A hydrocolloid impression stored in water for thirty minutes will exhibit imbibition. 1 cast poured into such an impression will
- Be dimensionally smaller cross-arch than the impression arch
- Be a dimensionally larger cross-arch than the impressed arch
- Be dimensionally the same cross-arch as the impressed arch
- Be acceptable for a diagnostic cast
Answer: 2. Be dimensionally larger cross-arch than the impressed arch
Question 36. An acceptable portion of the water of 100 g of most laboratory artificial stones to pour diagnostic casts is
- 22 mL
- 28 mL
- 34 mL
- 40 mL
Answer: 1. 22 mL
Question 37. The most important part of an impression
- Impression material used
- The co-operation of the patient
- The efficiency of the dental assistant
- The tray.
Answer: 2. Co-operation of the patient
Question 38. Which die material gives the most dimensionally accurate die?
- Improved stone
- Silver amalgam
- Electrodeposited silver
- Epoxy
Answer: 1. Improved stone
Question 39. Which die material is the material of choice for hydrocolloids
- Improved stone
- Electrodeposited silver
- Silicophosphate
- Epoxy resin
Answer: 1. Improved stone
Question 40. Perforated stock trays for making irreversible hydrocolloid impressions of partially edentulous arches may have advantages over non-perforated trays. Which of the following are such advantages?
- The mechanical interlocking of the impression material to the tray minimizing dissolution
- Less displacement of tissues
- Easier to border mould the impression
- Less difficult to clean the tray of impression material
Answer: 1. Mechanical interlocking of the impression material to the
Question 41. Dental plaster is also known as
- α hemihydrate
- γ hemihydrate
- β hemihydrate
- ε hemihydrates
Answer: 3. β hemihydrate
Question 42. The photoinitiator in light-cure composite resin is
- Camphorquinone
- Visible light
- N, N-dimethyl-toluidine
- Silanes
Answer: 1. Camphorquinone
Dental Materials Mcqs
Question 43. If two pieces of metal are joined by 1 third the metal, it is called
- Welding
- Soldering
- Crazing
- Sensitization
Answer: 2. Soldering
Question 44. Corrosion resistance in stainless steel wire is provided by
- Iron
- Nickel
- Chromium
- Cobalt
Answer: 3. Chromium
45. Which of the below impression materials is not elastomeric impression material?
- Polyether
- Polysulphide
- Condensation silicon
- Irreversible hydrocolloid
Answer: 4. Irreversible hydrocolloid
Question 46. Packing of denture base resin should be done in
- Dough stage
- Stringy stage
- Wet sand stage
- Rubbery stage
Answer: 1. Dough stage
Question 47. The change in length per unit length of 1 material for a 1°C change in temperature is called
- Thermal diffusivity
- Thermal conductivity
- Coefficient of thermal expansion
- Specific heat
Answer: 3. Coefficient of thermal expansion
Question 48. The light use for curing composite resin is
- Blue light
- Red light
- Green light
- Yellow light
Answer: 1. Blue light
Question 49. The etchant used for acid-etch technique for composite resin is
- 37% phosphoric acid
- 37% sulfuric acid
- 37% hydrochloric acid
- 32% citric acid
Answer: 1. 37% phosphoric acid
Question 50. Zinc oxide eugenol impression paste sets by the process of
- Polymerization
- Chelation
- Condensation
- Addition
Answer: 2. Chelation
Dental Materials Mcqs
Question 51. One of the most important advantages of 1 truly elastic impression material would be its capacity for
- Close adaptation to soft tissues
- Withdrawal without permanent distortion
- Reproduction of surface details
- Refraction of gingival tissues
Answer: 2. Withdrawal without permanent distortion
Question 52. Increasing the temperature of the gauging water for alginate will cause the resultant sol to gel
- Faster
- Slower
- Stronger
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Faster
53. The main difference between powders of regular dental plaster and dental stone is
- Chemical composition
- Solubility in water
- Particle shape and size
- Mixing time
Answer: 3. Particle shape and size
Question 54. The hygroscopic technique is associated with which of the following materials?
- Investment
- Amalgam
- Hydrocolloid
- Self-cured resin
Answer: 1. Investment
Question 55. The stiffness of 1 dental gold alloy is determined by its
- Proportional limit
- Modulus of elasticity
- Ultimate tensile strength
- Flow
Answer: 2. Modulus of elasticity
Question 56. The catalyst employed in self-cured resin is
- Hydroquinone
- Methyl methacrylate
- 1 tertiary amine
- Benzoin methyl ester
Answer: 3. 1 tertiary amine
Question 57. Polymerization of methyl methacrylate monomer is accompanied by 1 volumetric shrinkage of
- 7 %
- 21%
- 0.5%
- 1%
Answer: 2. 21%
Question 58. Corrosion of amalgam restoration is usually caused by
- Sulfur
- Oxygen
- Chlorides
- Overtrituration
Answer: 2. Oxygen
Question 59. An acceptable proportion of water to 100 g of improved stone, i.e. diestone is
- 20 mL
- 22 mL
- 24 mL
- 28 mL
Answer: 2. 22 mL
Dental Materials Mcqs
Question 60. Alginates are
- Sol
- Gel
- Hydrocolloid
- Colloid
Answer: 3. Hydrocolloid
Question 61. During amalgamation, trituration is done to
- Dissolve the alloy in mercury
- Coat the alloy particles with mercury
- Remove excess mercury from amalgam
- Dissolve Hg in alloy
Answer: 2. Coat the alloy particles with mercury
Question 62. The gold alloys used for casting contain at least _______ percent of precious metal according to ADA specifiation no. 5.
- 55
- 65
- 75
- 85
Answer: 1. 55
Question 63. The average particle size of powdered gold is
- 10 µm
- 15 µm
- 30 µm
- 0.1 mm
Answer: 2. 15µm
Question 64. Which of the following do polycarboxylate and GIC have in common?
- Polysiloxane
- Phosphoric acid
- Polyacrylic acid
- Ion leachable glass
Answer: 3. Polyacrylic acid
Question 65. The cavity varnish applied reduces postoperative sensitivity in amalgam restoration by
- Decreasing conduction of heat to pulp
- Minimizing marginal leakage around the restoration
- Altering the chemical composition of restoration materials
- Preventing penetration of corrosion products into dentinal tubules
Answer: 4. Preventing penetration of corrosion products into dentinal tubules
Question 66. The frozen slab technique is applicable to:
- Zinc polycarboxylate
- Polymer reinforced cement
- Zinc phosphate
- Glass ionomer cement
Answer: 3. Zinc phosphate
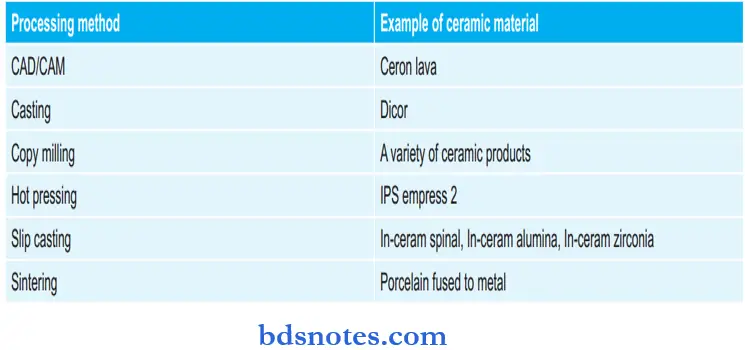
Question 67. Dicor restoration is
- Two colored restoration
- Heat pressed ceramics
- Castable ceramics
- None of these
Answer: 3. Castable ceramics
Question 68. The most toxic form of mercury is
- Methyl and ethyl mercury
- Mercury vapor
- Inorganic mercury forms
- Mercury sulfide
Answer: 1. Methyl and ethyl mercury
Dental Materials Mcqs
Question 69. The major disadvantage of polysulphide impression material in clinical practice is
- Poor biocompatibility
- Poor tear strength
- It is radiolucent
- It stains clothes and has an unacceptable odor.
Answer: 4. It stains clothes and has an unacceptable odor.
Question 70. Retarder in zinc oxide eugenol is:
- CaCl2
- Zinc acetate
- Alcohol
- Glycerine
Answer: 4. Glycerine
Question 71. Carbon in 18-8 austenitic steel
- Increases hardness
- Decreases hardness
- Has no specific function
- Is an unwanted impurity
Answer: 1. Increases hardness
Question 72. In auto polymerizing resin the polymerization occurs by
- Microwave energy
- Heat
- Chemical initiation
- Light
Answer: 3. Chemical initiation
Question 73. Osseointegration means
- Direct bone-to-implant contact
- Formation of fibrous band like PDL around the implant
- Both 1 and 2
- None of these
Answer: 1. Direct bone-to-implant contact
Question 74. Gillmore and Vicat needle test determine
- Setting time of gypsum product
- Working time of gypsum product
- Setting expansion of gypsum products
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Setting time of gypsum product
Question 75. A sprue is attched to
- Margin of pattern
- Thickest portion of pattern
- Thinnest portion of pattern
- None of these
Answer: 2. Thickest portion of pattern
Question 76. Orthodontic brackets can be made from
- Gold
- Stainless steel
- Ceramic
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 77. Glass ionomer cement is used as
- Luting agent
- Restorative material
- Pit and fissure sealant
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 78. Heating the gold castings in acid to remove impurities is called
- Pickling
- Annealing
- Etching
- None of these
Answer: 1. Pickling
Question 79. The tendency of 1 material to deform under intermittent masticatory pressure is called
- Malleability
- Tensile stress
- Impact stress
- Creep
Answer: 4. Creep
Question 80. The gelation temperature of hydrocolloid should be
- 20°3 to 27°3
- 27°3 to 37°3
- 37°3 to 45°3
- 45°3 to 52°3
Answer: 3. 37°3 to 45°3
Dental Materials Mcqs
Question 81. How soon after 1 moisture contamination does a zinc-containing amalgam alloy start expanding?
- 24 hours
- 1 – 2 days
- 3 – 5 days
- 7 days
Answer: 3. 3 – 5 days
Question 82. The sprue in the wax pattern should be placed
- At right angle
- At a 45° angle
- At obtuse angle
- It depends upon the type of wax pattern
Answer: 2. At a 45° angle
Question 83. The material used in its pure form in dentistry is
- Composite
- Silver
- Gold
- Amalgam
Answer: 3. Gold
Question 84. The effect of zinc oxide eugenol on pulp
- Is Irritating
- Encourages pulpal fibrosis
- Is sedating
- Has no effect
Answer: 3. Is sedating
Question 85. Which one of the following dental cement accelerates the formation of reparative dentin?
- Eugenol
- Calcium hydroxide
- Zinc oxide
- Silica
Answer: 2. Calcium hydroxide
Question 86. The setting time of Zn PO4 cement can be retarded by
- Mixing more powder to liquid
- Mixing powder to liquid, checked by water
- Slower addition of powder to liquid
- Faster addition of powder to liquid
Answer: 3. Slower addition of powder to liquid
Question 87. Dispersion of crystalline phase to strengthen ceramics results in
- Dispersed porcelain
- Glazed porcelain
- Aluminum porcelain
- All the above
Answer: 3. Aluminum porcelain
88. Green strength with reference to plaster means:
- Dry strength
- Compressive strength
- Strength of dental stone due to green color
- Wet strength
Answer: 4. Wet strength
Question 89. Dustless alginate is produced by
- Reducing diatomaceous earth
- Adding heavy metal salts
- Coating with a dihydric alcohol
- Altering matrix
Answer: 3. Coating with a dihydric alcohol
Dental Materials Mcqs
Question 90. The brush heap structure is found in
- ZnO impression material
- Agar
- Condensation silicone
- Polyether
Answer: 2. Agar
Question 91. Chromium in 18-8 stainless steel is
- Imparts corrosion resistance
- Stabilizes the austenitic phase
- Both of the above
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Imparts corrosion resistance
Question 92. Shape memory and pseudoelasticity are the features of
- Ni-Ti alloy
- Elgiloy
- Stainless steel
- Tungsten-molybdenum alloy
Answer: 1. Ni-Ti alloy
Question 93. The process of exuding of fluid from the gel surface is called
- Syneresis
- Hysteresis
- imbibition
- Diapedesis
Answer: 1. Syneresis
Question 94. The stress that tends to resist twisting motion is called
- Compressive stress
- Tensile stress
- Shear stress
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Shear stress
Question 95. Which of the following elements has anti cariogenic properties
- Zinc phosphate
- Glass ionomer
- Calcium hydroxide
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Glass ionomer
Question 96. Among the following the most suitable for Class I and Class II restorations is
- Traditional
- Microfilmed
- Hybrid
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Hybrid
Question 97. In porcelain fused to metal, the bond is
- Mechanical
- Chemical
- Oxide layer formation
- Chemical-mechanical
Answer: 4. Chemical-mechanical
Question 98. Wrought metal is
- When metal is worked in a cold state
- When metal is heated and then cooled
- When Cu is added to 1 metal
- When more than two metals are mixed in 1 molten state
Answer: 1. When metal is worked in a cold state
Question 99. Setting time of zinc-phosphate cement can be increased by
- Reducing power liquid ratio
- Increasing speculation time
- Decreasing the temperature of the glass slab
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Dental Materials Mcqs
Question 100. Pinhole and subsurface porosity is caused by
- Entrapment of gas during solidification
- Shortage of metal during solidification
- Inadequate pressure during existing
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Entrapment of gas during solidification
Question 101. Which of the following material is elastic?
- Impression compound
- Core
- Agar-Agar
- Zinc eugenol impression paste
Answer: 3. Agar-Agar
Question 102. Which of the following materials can be electroplated without the risk of distortion?
- Polysulphide
- Condensation silicone
- Addition silicone
- Hydrocolloids
Answer: 1. Polysulphide
Question 103. Stiffness refers to
- Resistance to elastic deformation
- Degree of elastic deformation
- Expendability of heating
- Shrin kage on cooling
Answer: 1. Resistance to elastic deformation
Question 104. Dental amalgam alloys and mercury are mixed in ratio of
- 1:2
- 2:1
- 1:1
- 1:3
Answer: 3. 1:1
Question 105. Most common drawback of amalgam restoration is
- Porosity
- Marginal breakdown
- Contraction on settng
- Contraction array from margins
Answer: 2. Marginal breakdown
Question 106. The cement which does not irritate the pulp tissue is:
- Calcium hydroxide
- Silicate
- Glass ionomer cement
- Resin cement
Answer: 1. Calcium hydroxide
Question 107. Activating compound for visible light curing system:
- Hydroquinone
- Benzoin methyl ether
- Potassium oxide
- Camphorquinone
Answer: 4. Camphorquinone
Question 108. Regarding glass ionomer
- The powder is methyl methacrylate
- This powder is an aluminosilicate glass
- To relax mercury
- The powder is calcium hydroxide
Answer: 2. This powder is an aluminosilicate glass
Question 109. With respect to acid-etching
- It creates a microscopically rough surface
- It creates macroscopically rough surface
- It contains hydrofluoric acid
- Following etching the etchant should be washed with phosphoric acid
Answer: 1. It creates a microscopically rough surface
110. The major disadvantage of polysulphide impression material is
- Poor biocompatibility
- Radiolucent
- Rigidity
- It stains cloth and unacceptable odor
Answer: 4. It stains cloth and unacceptable odor
Dental Materials Mcqs
111. When solid gets wet completely, then contact angle is
- 90°
- 0°
- 0° to 90°
- 90°
Answer: 2. 0°
112. Wash or corrective impression is done by
- Impression plaster
- Impression paste
- Alginate
- Rubber base impression material
Answer: 2. Impression paste
Question 113. The main ingredient in dental plaster is
- Calcium sulfate hemihydrate
- Calcium phosphate
- Calcium anhydrate
- Calcium sulfate dihydrate
Answer: 1. Calcium sulfate hemihydrate
Question 114. Acrylic (cold cure):
- Melts at 100°3
- Softens at 100°3
- Still requires heat for polymerization
- Produces heat during polymerization
Answer: 4. Produces heat during polymerization
Question 115. According to ADA specification No.1, the minimum compressive strength for silver amalgam filing after 1 hour should be
- 80 MPa
- 140 MPa
- 260 MPa
- 510 MPa
Answer: 1. 80 MPa
Question 116. Investment material used for cobalt-chromium alloy is
- Gypsum-bonded
- Phosphate bonded
- Silica bonded
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Phosphate bonded
Question 117. Most biocompatible material in oral cavity is
- Platinum
- Palladium
- Titanium
- Gold
Answer: 3. Titanium
Question 118. The chief advantage of zinc phosphate cement is
- Good compressive strength
- Film thickness
- Lack of irritation
- Low solubility
Answer: 2. Film thickness
Question 119. Asbestos liner is used in 1 casting ring to
- Facilitate venting of the mold
- Retard the heating of the investment
- Permit expansion of the mold
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Dental MCQS
Question 120. Modulus of elasticity means
- Rigidity or stiffness of the material
- Ability to be stretched with permanent deformation
- Ductility of 1 material
- Malleability of the metal
Answer: 1. Rigidity or stiffness of the material
Question 121. Which of the following is the safest and most reliable method of regulating setting time of gypsum products?
- Altering the water/powder ratio
- Controlling temperature of water to be used for mixing
- Speed of hand manipulation
- Adding salt in mixing
Answer: 2. Controlling temperature of water to be used for mixing
122. Young’s modulus defies what
- Elastic limit
- Resilience
- Stiffness
- Flexibility
Answer: 3. Stiffess
123. The strength of the porcelain decreases due to
- Overfishing
- Entrapped air bubbles
- Sudden cooling
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
124. Denture base resins are packed in the mould during
- Sandy stage
- Dough stage
- Sticky stage
- Rubbery stage
Answer: 2. Dough stage
Question 125. In self-activated resin the polymerization occurs by
- Microwave energy
- Heat
- Chemical initiator
- Light
Answer: 3. Chemical initiator
Question 126. 1 common mechanism of failure of ceramics is
- Propagation of cracks
- Ductile failure
- Creep
- None of the above
Answer: 4. None of the above
Question 127. Which of the following is not a criterion for an ideal restorative material of choice?
- Biocompatible
- Permanent bond to tooth structure
- Match the natural appearance of tooth structure
- Degenerate in 1 short period of time
Answer: 4. Degenerate in 1 short period of time
Question 128. Which of the following is a thermoplastic material?
- Alginate
- Agar-agar
- Addition silicone
- Zinc oxide eugenol
Answer: 2. Agar-agar
Dental MCQS
129. Tarnish and corrosion is a property of
- Resin
- Wax
- Cement
- Metals
Answer: 4. Metals
130. Denture teeth are made up of
- Acrylic resin
- Porcelain
- All of the above
- None of the above
Answer: 3. All of the above
131. The setting expansion of casting investment is approximately
- 0 to 0.1%
- 0.1 to 0.5%
- 0.5 to 1%
- 1 to 6%
Answer: 2. 0.1 to 0.5%
Question 132. The most importantmanipulated variable with gypsum products is
- Water temperature
- Correct water/powder ratio
- Speculation time
- Vacuum mixing
- Use of special liquid
Answer: 2. Correct water/powder ratio
Question 133. The most common agent for etching enamel is
- 10% polyacrylic acid
- 37% phosphoric acid
- 10% phosphoric acid
- 37% polyacrylic acid
- 8% oxalic acid
Answer: 2. 37% phosphoric acid
Question 134. The optimum bulk of alginate impression material to reduce distortion and to obtain the most accurate reproduction of 1 patient’s oral tissue is
- 1 – 2 mm
- 2 – 4 mm
- 4 – 6 mm
- 6 – 8 mm
- As thin as possible
Answer: 3. 4 – 6 mm
Question 135. Impression plaster is an example of which type of gypsum product?
- Type I
- Type II
- Type III
- Type IV
Answer: 1. Type I
Question 136. Why is it necessary to wait 24 hours to complete polymerization of a custom acrylic tray?
- To allow the tray to achieve maximum dimensional stability
- To allow the tray to achieve maximum strength
- To allow the tray to achieve maximum rigidity
- All the above
Answer: 1. To allow the tray to achieve maximum dimensional stability
Dental MCQS
Question 137. The two basic stresses in dental material are
- Axial and shear
- Compression and axial
- Tension and compression
- Shear and horizontal
Answer: 3. Tension and compression
Question 138. The polymerization shrinkage of polymethyl methacrylate is
- 7%
- 14%
- 21%
- 35%
- None of the above
Answer: 5. None of the above
Question 139. The main advantage of using polyvinyl siloxane as an impression material in field prosthodontics is It is hydrophilic
- Long working time
- Low cost
- Dimensional stability
- Easier to pour than other impression materials
Answer: 4. Easier to pour than other impression materials
Question 140. Which of the following is 1 hydrophilic impression material?
- Alginate
- PVS
- Polyether
- Condensation silicone
- Polysulphide
Answer: 1. Alginate
Question 141. Griffi’s microcracks are seen in
- Dental ceramics
- Dental composites
- Denture base resins
- Waxes
Answer: 1. Dental ceramics
Question 142. Brazing is a metal joining procedure that requires 1 melting temperature
- More than 450°
- Less than 450°3
- 450°3
- None
Answer: 1. More than 450°
Question 143. Terra alba is
- Calcium sulfate
- Set gypsum particles that act as an accelerator
- None of the above
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Set gypsum particles that act as an accelerator
MCQs In Dental Materials
Question 144. Fillers in composite resin
- Increase polymerization shrinkage
- Decrease polymerization shrinkage
- Have no effct
- Are not added
Answer: 2. Decrease polymerization shrinkage
Question 145. What is the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of inlay wax:
- 360 × 10-6/°3
- 360 × 10-5 /°3
- 350 × 10-6/°3
- 350°
Answer: 3. 350 × 10-6 /°3
Question 146. LD50 is known as
- Median lethal dose
- Mid-lethal dose
- Average lethal dose
- 50% dose
Answer: 1. Median lethal dose
Question 147. ADA specification no. for gypsum and die materials is
- 26
- 25
- 11
- 12
Answer: 2. 25
Question 148. Leucite is
- Magnesium silicate
- Silica potash
- Potassium aluminum silicate
- Aluminum silicate
Answer: 3. Potassium aluminum silicate
Question 149. Camphoroquinone in composite resins is
- Accelerator
- Photoinitiator
- Amine activator
- Inhibitor
Answer: 2. Photoinitiator
Question 150. Inhibitor of composite resins is
- Butylated hydroxytoluene 0.01%
- Butylatedtoluene 0.1%
- Propyltoluene 0.01%
- All above
Answer: 1. Butylated hydroxytoluene 0.01%
Question 151. Which of the following properties of dental material is time-dependent?
- Creep
- Resilience
- Elastic limit
- Ultimate strength
Answer: 1. Creep
MCQs In Dental Materials
Question 152. The term given to the phenomena of moisture absorption by an alginate impression is
- Imbibition
- Syneresis
- Hysteresis
- Gelation
Answer: 1. Imbibition
Question 153. Perforated impression trays are used for
- Alginate
- Zinc oxide eugenol
- Agar-agar
- Impression compound
Answer: 1. Alginate
Question 154. Type III dental gypsum is
- Class II stone
- Density
- Class I stone or hydro cal
- Model or lab plaster
Answer: 3. Class I stone or hydro cal
Question 155. Which of the cement is most kind to pulp?
- Polycarboxylate
- GIC
- Silicate
- Resin cement
Answer: 1. Polycarboxylate
Question 156. Die is
- Impression of a single tooth
- Impression of whole teeth
- Replica of a single tooth
- Replica of whole teeth
Answer: 3. Replica of a single tooth
Question 157. The principal application of zinc phosphate cement is
- In final cementation
- As temporary cementation
- As 1 temporary filling material
- It has less occlusal wear
Answer: 1. In final cementation
Question 158. Sprue in wax pattern should be placed at
- 90° angle
- 45° angle
- Obtuse angle
- Depend on wax pattern
Answer: 2. 45° angle
Question 159. The component in very minor quantity in stainless Steel that change the properties to 1 maximum level is
- Carbon
- Molybdenum
- Chromium
- Nickel
Answer: 1. Carbon
Question 160. The process of changing the rubber base product or liquid polymer to a rubber-like material is generally known as
- Boiling
- Condensation
- Vulcanization
- Chain lengthening
Answer: 3. Vulcanization
MCQs In Dental Materials
Question 161. The crystals of CaSO4 dihydrate are
- Crystallites
- Spherulites
- Rhomboids
- Colloids
Answer: 2. Spherulites
Question 162. Crazing occurs in
- Denture base resins
- Impression materials
- Plaster of Paris
- Waxes
Answer: 1. Denture base resins
Question 163. Rheology is the study of
- Deformation and the flow of matter
- Creep
- Water
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Deformation and the flow of matter
Question 164. Bis-GMA is:
- Bisphenol 1 — glycidyl methacrylate
- Bisphenol 1 — glycol methacrylate
- Bisphenol 1 — glycol acrylate
- Bisphenol 1 — glycidyl acrylate
Answer: 1. Bisphenol 1—glycidyl methacrylate
Question 165. Non-crystalline form of silica is/are
- Fused silica only
- Quart fused silica
- Cristobalite only
- Tridymite only
Answer: 1. Fused silica only
Question 166. Ceramic has
- High compressive and low tensile strength
- Low compressive and high tensile strength
- High compressive and high tensile strength
- Low compressive and low tensile strength
Answer: 1. High compressive and high tensile strength
Question 167. Ideally, soldering procedure is done at a temperature
- Less than 450°3
- More than 450°3
- 450°3
- 1450°3
Answer: 2. More than 450°3
Question 168. Set gypsum is:
- CaSO4 hemihydrate
- CaSO4 dihydrate
- CaSO4 monohydrate
- CaSO4
Answer: 2. CaSo4 dihydrate
MCQs In Dental Materials
Question 169. Gold foil filing in dentistry done by hammering or pressure is an example of
- Soldering
- Brazing
- Hot welding
- Cold welding
Answer: 4. Cold welding
Question 170. The process of dehydration of gypsum is
- Heating
- Calcination
- Precipitation
- Dehydration
Answer: 2. Calcination
Question 171. The process of absorbing water which leads to expansion of alginate is known as
- Syneresis
- Imbibition
- Sublimation
- Sintering
Answer: 2. Imbibition
Question 172. The type of calcium hemihydrate in dental stone is
- Alpha
- Beta
- Delta
- Gamma
Answer: 1. Alpha
Question 173. Type of calcium hemihydrate in dental plaster is
- Alpha
- Beta
- Delta
- Gamma
Answer: 2. Beta
Question 174. The setting reaction of 1 g of calcium hemihydrates yields how much calories
- 3100
- 3600
- 3900
- 4100
Answer: 3. 3900
Question 175. For orthodontic casts, which of the following material is used
- Impression plaster
- Model plaster
- Dental stone
- High strength stone
Answer: 2. Model paper
Question 176. Term gummy smile indicates that when the gingival display is:
- >5 mm
- >3 mm
- >4 mm
- <3 mm
Answer: 2. > 3mm
Question 177. The cement which has antibacterial properties is
- Glass ionomer
- Polycarboxylate
- Zinc oxide eugenol
- Resin cement
Answer: 2. Polycarboxylate
Question 178. Maximum opening of mouth in human being is
- 30 to 40 mm
- 40 to 50 mm
- 50 to 60 mm
- 60 to 70 mm
Answer: 2. 40 to 50 mm
Question 179. The most common drawback of amalgam restoration is
- Secondary expansion
- Porosity
- Marginal breakdown
- Contraction on setting
Answer: 3. Marginal breakdown
Question 180. Overgrowth of intraoral tissue caused by chronic irritation usually an overextended denture flnge is present in
- Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
- Epulis stratum
- Ferrule
- Abfraction
Answer: 2. Epulis fisuratum
Question 181. The burning sensation on the mandibular ridge is due to pressure on
- Mandibular ridge
- Molar area
- Incisor area
- Mental foramen
Answer: 4. Mental foramen
Question 182. Clicking of denture teeth is due to which of the following?
- Reduced VDO
- Excessive VDO
- Porcelain teeth
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3
Question 183. Angular cheilosis, glossitis, edema, and papillary atrophy are due to deficiency of which of the following?
- Vitamin 1
- Vitamin 2
- Vitamin 3
- Vitamin 4
Answer: 2. Vitamin 2
Question 184. An elastomeric impression material that has an exothermic setting reaction with water as 1 by-product is
- Polyether
- Polysulphide
- Addition silicone
- Condensation silicon
Answer: 2. Polysulphide
MCQs In Dental Materials
Question 185. Which of the following hemostatic agent is used in retraction cord causes tissue necrosis?
- Epinephrine
- Potassium aluminum sulfate
- Aluminum chloride
- Zinc chloride
Answer: 4. Zinc Chloride
Question 186. Maximum stress before fracturing is known as:
- Strength
- Ultimate tensile strength
- Yield strength
- Modulus
Answer: 1. Strength
Question 187. An impression material that sets in a cross-linking polymerization reaction and gives of the by-product ethanol is
- Polyether
- Polysulphide
- Condensation silicone
- Addition silicone
Answer: 3. Condensation silicone
Question 188. The best provisional restoration material is
- PMMA
- PEMA
- Bis–acryl
- All of the above
Answer: 1. PEMA
Question 189. Activating compound for visible light curing system
- Hydroquinone
- Camphoroquinone
- Benzoin methyl ether
- Potassium oxide
Answer: 2. Camphoroquinone
Question 190. When the solid wets completely, the contact angle is
- 90°
- 0°
- >90°
- <90°
Answer: 2. 0°
Question 191. Inelastic impression material is
- Impression compound
- Alginate
- Agar
- Polyether
Answer: 1. Impression compound
Question 192. ADA specification no. for gypsum products are describe under:
- 1
- 4
- 12
- 25
Answer: 2. 4
Question 193. In heat-cure denture base resin, the monomer is
- Methyl methacrylate
- Ethyl methacrylate
- Methylethyl methacrylate
- Polymethyl methacrylate
Answer: 1. Methyl methacrylate
Question 194. Ni-Ti alloys have
- Shape memory
- Hyper rigidity
- Corrosion resistance
- Weldable properties
Answer: 1. Shape memory
Question 195. Waxes used in dentistry for
- Primary impression
- Corrective impression
- Impression of a single tooth
- None
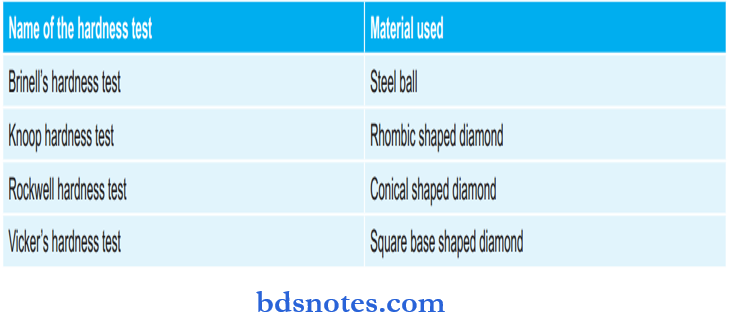
Answer: 2. Corrective impression
Question 196. ZnO eugenol paste hardens by
- Chemical reaction
- Cold
- Heat
- Pressure
Answer: 1. Chemical reaction
Question 197. Setting expansion is advantageous in
- Casts
- Models
- Investment
- Dies
Answer: 3. Investement
Question 198. Which of the following test is 1 microhardness test
- Brinell
- Knoop
- Shore A
- Rockwell
Answer: 2. Knoop
Question 199. The most rigid elastomer is
- Polyether
- Polysulphide
- Addition silicone
- Condensation silicone
Answer: 1. Polyether
Question 200. 4th state of matter is
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas
- Colloid
Answer: 4. Colloid
Question 201. The strength of gypsum is dependent on
- Carbon content
- Silica content
- Gypsum
- Copper
Answer: 2. Silica content
Question 202. The most commonly used titanium alloy for dental and medical purposes is
- Ti-6Al4V
- Ti-5Al4V
- Ti-5Al5V
- Ti-6Al6V
Answer: 1. Ti – 6Al4V
Question 203. Cavity varnishes have
- Average bonding to tooth
- Low bonding to tooth
- Excellent bonding to tooth
- No bonding to tooth
Answer: 4. No bonding to tooth
Question 204. Flux used in dental ceramics
- Alumina
- Silica
- Kaolin
- Boric oxide
Answer: 4. Boric oxide
Question 205. Stainless steel orthodontic wire can be hardened by
- Tempering
- Work hardening
- Age hardening
- Precipitation hardening
Answer: 2. Work Harding
Question 206. Acid-etching is done for
- 30 seconds
- 60 seconds
- 90 seconds
- 120 seconds
Answer: 1. 30 seconds
Question 207. The latest method of curing denture base resin is
- Heat
- Visible light
- Chemicals
- Lasers
Answer: 2. Visible Light
Question 208. Dr. Taggart is associated with
- Discovery of ceramics
- Lost wax technique
- Acid-etch technique
- Bleaching procedure
Answer: 2. Lost wax technique
Question 209. The non–metal which conducts electricity
- Graphite
- Carbon
- Acrylic
- Porcelain
Answer: 1. graphite
Question 210. ADA specification no. of impression compound is
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 3. 3
Question 211. Which of the following material is a hydrocolloid?
- Agar
- ZOE paste
- Polyether
- Impression
- Plaster
Answer: 1. Agar
Question 212. A surface phenomenon that results in surface deterioration is
- Pitting
- Tarnish
- Corrosion
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Tarnish
Question 213. Which of the following cement accelerates the formation of reparative dentin
- ZOE cement
- Calcium hydroxide cement
- Zinc phosphate cement
- Silicate cement
Answer: 2. calcium hydroxide cement
Question 214. The water/powder ratio of dental stones is
- 0.40 to 0.75
- 0.45 to 0.50
- 0.28 to 0.30
- 0.22 to 0.24
Answer: 3. 0.28 to 0.30
Question 215. The percentage of phosphoric acid in etchant is
- 27%
- 37%
- 47%
- 57%
Answer: 2. 37%
216. The use of wrought base metal alloy is
- Clasps for RPD
- Root canal files
- Orthodontic wires
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
217. 4th state of matter is
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas
- Colloid
Answer: 4. Colloid
Question 218. At which stage of polymerization packing is done?
- Sandy
- Stringy
- Dough
- Rubbery
Answer: 3. Dough
Question 219. Crocus cloth is:
- Emery
- Garnet
- Pumice
- Rouge
Answer: 4. Rouge
Question 220. Which of the following material has the highest coefficient of thermal expansion?
- Dental amalgam
- Acrylic resin
- Dental ceramic
- Inlay wax
Answer: 4. Inlay wax
Question 221. The slope of the stress/strain is referred to as
- Proportional limit
- Young’s modulus
- Resilience
- Poisson’s ratio
Answer: 2. Youngs’s modulus
Question 222. Which part of flame should be used for melting the alloy?
- Mixing zone
- Reducing zone
- Combustion zone
- Oxidizing zone
Answer: 2. reducing zone
Question 223. ADA specification no. for gypsum products is
- 10
- 15
- 20
- 25
Answer: 4. 25
Question 224. Moisture contamination of amalgam leads to
- Marginal breakdown
- Shrinkage
- Delayed expansion
- Increase stresses
Answer: 3. Delayed expansion
Question 225. Which of the following material is the die material
- Type IV gypsum product
- Type V gypsum product
- Epoxy resin
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 226. The boiling point of methyl methacrylate is
- 100°3
- 100.8°3
- 110°3
- 110.8°3
Answer: 2. 100. 8°3
Question 227. The loss of gloss for dental plaster occurs approximately at
- 5 minutes
- 9 minutes
- 10 minutes
- 19 minutes
Answer: 2. 9 minutes
Question 228. Silica is added in the investment material to act as
- Coloring agent
- Oxidizing agent
- Reducing agent
- Refractory agent
Answer: 4. Refractory agent
Question 229. Which of the following material cannot be used as 1 duplicating material?
- Alginate
- Agar
- Addition silicone
- ZOE impression paste
Answer: 1. Alginate
Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. Water powder ratio of dental plaster ___________
Answer: 0.45 to 0.50
Question 2. Impression technique in which both agar and alginate are used to make impression ___________
Answer: Laminate technique
Question 3. Hydrophilic elastomeric impression material is ___________
Answer: Polyether
Question 4. Investment material used for gold coating is ___________
Answer: Gypsum
Question 5. Activatorpresentinself-cure acrylic resin ___________
Answer: Tertiary amine
Question 6. Fineness of 18 carat gold is___________
Answer: 750 fie
Question 7. Percentage of phosphoric acid used in acid-etching is___________
Answer: 37%
Question 8. Restoration done using a combination of GIC and composite is called ___________
Answer: Compomer
Question 9. Tin oxide is used to polish ___________
Answer: Amalgam and enamel
Question 10. Mixing time of GIC is ___________
Answer: 45 seconds
Question 11. Type I gypsum product is ___________
Answer: Impression plaster
Question 12. The most common initiator used in heat-cured acrylic resin is ___________
Answer: Benzoyl peroxide
Question 13. Last stage of addition polymerization ___________
Answer: Termination
Question 14. Maximum flow permitted for Type B inlay wax at 37°C is ___________
Answer: 1%
Question 15. Liquid bottle of acrylic resin turns milky due to ___________
Answer: Initiation of polymerization
Question 16. The minimum percentage of gold used for direct filing is ___________
Answer: 22 carat
Question 17. The coefficient of thermal expansion of inlay wax is ___________
Answer: 250–300 ppm/°C
Question 18. Main constituent of root canal sealant is ___________
Answer: Calcium hydroxide
Question 19. The pH of calcium hydroxide is ___________
Answer: 9.2–11.7
Question 20. Clinical significance of smearlayeris that ___________
Answer: It lowers dentin permeability
Question 21. Type IV gypsum product is ___________
Answer: High-strength stone or improved stone or die stone
Question 22. The extent to which an adhesive wets the surface of an adherend may be determined by measuring the ___________ angle.
Answer: Contact
Question 23. Stage of polymerization during which polymer chain ceases to grow ___________
Answer: Termination
Question 24. ___________is used to measure both settng and working times.
Answer: Vicat penetrometer
Question 25. Relative lightness or darkness of color is ___________
Answer: Value
Question 26. Highly siliceous material of volcanic activity ___________
Answer: Pumice
Question 27. The coarser form of Kieselguhr is called ___________
Answer: Diatomaceous earth
Question 28. Tartar control agent is tetra potassium ___________
Answer: Pyrophosphate
Question 29. Hybrid ionomer is ___________
Answer: Glass ionomer’
Question 30. Zinc causes delayed ___________
Answer: Expansion
Question 31. Recommended W/P ratio for Type IV gypsum product is ___________
Answer: 0.24
Question 32. Compressive strength of amalgam restoration of 1 hour generally is ___________
Answer: 80 MPa
Question 33. Liquids that show lower viscosity as shear rate increases are known as ___________
Answer: Pseudoplastic flids
Question 34. Linear shrinkage of heat-cure resin is ___________
Answer: 0.5%
Question 35. Preconditioning treatment of metal cast is done by ___________
Answer: 5% ammonium hydroxide
Question 36. Acid-etching was developed by ___________
Answer: Dr. Michael Buonocore
Question 37. The weakest phase of amalgam is ___________
Answer: Tin-mercury gamma—2 phase
Question 38. The amount (%) of dental stone in gypsum-bonded investment is ___________
Answer: 25–45%
Question 39. Film thickness of glass ionomer luting agent should not be more than ___________
Answer: 20–25 µm
Question 40. Size of filer particles in microfiled composite is ___________
Answer: 0.04 µm
Question 41. The role of magnesium chloride in zinc oxide eugenol impression paste is to ___________
Answer: Accelerate
Question 42. Gillmore needle is used to test___________
Answer: Initial and final setting of plaster of paris
Question 43. Particle size in microfiber composite resin is___________
Answer: 0.01 to 0.1µ
Question 44. The ability of an orthodontic wire to spring back to its original shape is called ___________
Answer: Resilience
Question 45. Best material for duplicating cast is___________
Answer: Agar-agar
Question 46. Mixingofamalgamalloyandmercuryiscalled ___________
Answer: Dental amalgam
Question 47. Invest material used for cobalt-chromium alloy is___________
Answer: Phosphate-bonded
Question 48. PorcelainbindswithmetalinPFMcrownby___________ bond.
Answer: Chemicomechanical
Question 49. ImpressionofpreparationforFPDismadeby ___________
Answer: Low-viscosity elastomeric impression material
50. Moisture contamination of an amalgam can lead to___________
Answer: Delayed expansion
Viva-Voce Questions
Question 1. Who is known as the father of dentistry?
Answer: Pierre Fauchard
Question 2. Name the forces which hold atoms together.
Answer: Cohesive
Question 3. Name the primary bonds which are simple chemical type and resulting from mutual attraction of positive and negative charges.
Answer: Ionic bonds
Question 4. When the two substances of unlike molecules are brought in intimate contact with each other then the molecule of one substance attacts other. What is this known as.
Answer: Adhesion
Question 5. How much is the ideal angle of wetting?
Answer: 0°
Question 6. Which is the study of flow?
Answer: Rheology
Question 7. What is resistance to motion by liquids known as?
Answer: Viscosity
Question 8. What is force unit per area?
Answer: Stress
Question 9. Define heat of vaporization.
Answer: It is defined as the amount of energy that is needed for the transformation of boiling liquid into vapor.
Question 10. What is the latent heat of fusion?
Answer: It is defined as the amount of energy released when liquid freezes.
Question 11. Define melting temperature.
Answer: It is defined as amount of energy that is required for the transformation of solid in liquid state.
Question 12. Define sublimation.
Answer: It is defined as the process in which some liquids are transformed directly into gas phase
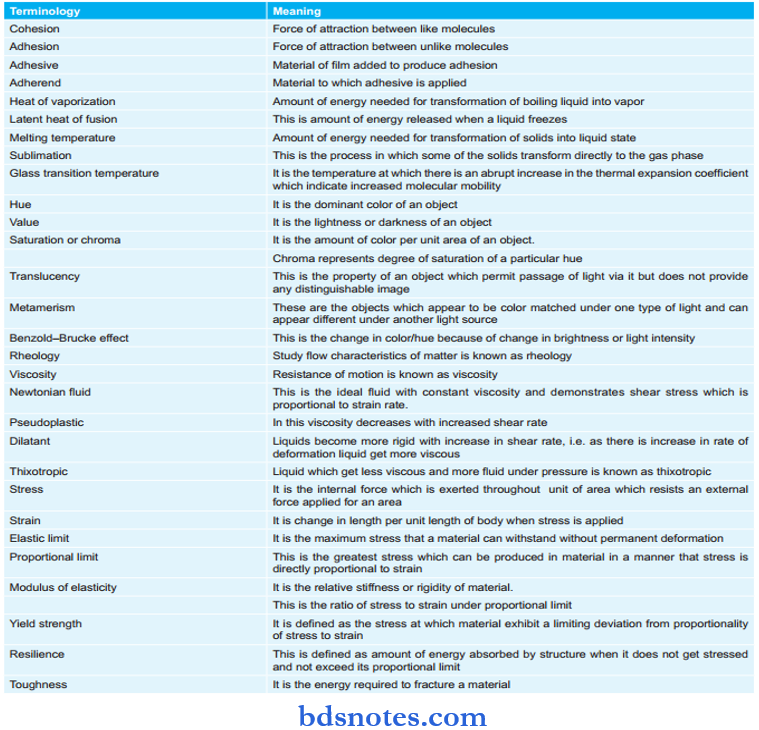
Question 13. Define cohesion.
Answer: It is defined as the force of attraction between like molecules.
Question 14. Define adhesion.
Answer: It is defined as force of adhesion between unlike molecules.
Question 15. What is adhesive?
Answer: It is the material added to produce adhesion.
Dental Materials MCQs With Answers
Question 16. What is adherence?
Answer: The material to which adhesive is applied is known as adherened.
Question 17. Define glass transition temperature.
Answer: Temperature at which there is an abrupt increase in the thermal expansion coefficient indicating the increased molecular mobility.
Question 18. Define hue.
Answer: Hue is defined as the specific color produced by a specific wavelength of light.
Question 19. Define value.
Answer: Value or brilliance is defined as the lightness or darkness of an object.
Question 20. Define saturation.
Answer: Saturation or chroma is defined as the amount of color per unit area of an object.
Question 21. Define translucency.
Answer: It is defined as the property of an object which permits the passage of light through it and does not give any distinguishable image.
Question 22. Define metamerism.
Answer: It is the phenomenon in which objects which appear to be color matched under one type of light may appear differently in another light source.
Question 23. What is Benzold–Brucke effct?
Answer: This is the color or hue due to a change in brightness or light intensity.
Question 24. What is fluorescence?
Answer: It is the energy that a tooth absorbs and which is converted into light with longer wavelength and becomes a light source.
Question 25. What is stress?
Answer: Stress is defined as force per unit area.
Question 26. Define strain.
Answer: It is defied as a change in length per unit length of body when stress is applied.
Question 27. What is the elastic limit?
Answer: It is defined as the maximum stress which a material can withstand without permanent deformation.
Question 28. What is the proportional limit?
Answer: It is the greatest stress which may be produced in the material in such a way that stress is directly proportional tostrain.
Question 29. What is the modulus of elasticity?
Answer: It is defined as the ratio of stress to strain within a proportional limit.
Question 30. What is yield strength?
Answer: It is the defied as strength during which material exhibits a limiting deviation from proportionality of stress to strain.
Question 31. Define resilience.
Answer: It is defined as amount of energy that is absorbed by a structure when it is stressed not to exceed the proportional limit.
Question 32. Define brittleness.
Answer: Brittleness is defined as the inability of the material to sustain plastic deformation before fracture occurs.
Question 33. What is Ductility?
Answer: It is defined as the ability of a material to withstand permanent deformation under tensile load without rupture.
Dental Materials MCQs With Answers
Question 34. What is malleability?
Answer: It is defined as the ability of a material to withstand permanent deformation under compressive load without rupture.
Question 35. What is flexibility?
Answer: It is defined as the strain which occurs when the material is stressed to its proportional limit.
Question 36. Name some methods for measuring hardness.
Answer: Methods for measuring hardness are: microhardness test, i.e. Rockwell and Brinnel hardness, microhardness test, i.e. Vicker’s hardness and Knoop hardness, Shore test, Moh’s hardness test, Barcoal hardness test
Question 37. Which material has the highest linear coefficient of thermal expansion of dental materials?
Answer: Dental wax.
Question 38. What is gelation?
Answer: It is defined as the transformation from sol to gel.
Question 39. What is sand in a water system known as?
Answer: Suspension.
Question 40. How much is the gelation temperature for agar?
Answer: 37°C
Question 41. Name the process by which the gel absorbs the water.
Answer: Gelation
Question 42. Which material is commonly used for preliminary impressions?
Answer: Alginate
Question 43. What is a dust-free alginate?
Answer: Dustless alginates consist of polyethylene or polypropylene glycol. These agents stop the fie particles to release from the alginate powder.
Question 44. How much is the water/powder ratio of alginate?
Answer: 40 mL of water to 15 g of powder
Question 45. Name the agents used to produce a smooth surface of impression.
Answer: Surfactants
Question 46. Name the storage media for agar impression.
Answer: 2% potassium sulfate and 100% relative humidity
Question 47. From where the agar is extracted?
Answer: Seaweed
Question 48. Name the retarder used in the setting of gypsum.
Answer: Borax
Question 49. What is the liquefication and gelation temperature for agar?
Answer: Liquefiation temperature is 70 to 100°C and gelation temperature is 37 to 50°C
Question 50. How much is the maximum tolerant temperature of oral cavity?
Answer: 55°C
Question 51. Which material is used to make duplicating dyes?
Answer: Agar
Question 52. What is the laminate technique?
Answer: This technique combines agar and alginate. In this technique, chilled alginate replaces the tray agar.
Question 53. What is chromalginate?
Answer: Chromalginates are the color-changing alginates.
Question 54. Which is the first dental elastomer?
Answer: Polysulphide
Question 55. Name the filler and plasticizer in the polysulphide impression material.
Answer: The filler is titanium dioxide and the plasticizer is dibutyl phthalate
Question 56. What is vulcanization?
Answer: It is the cross-linking process which involves sulfie mercaptan materials. Polysulphide materials are called as vulcanizing materials or mercaptan materials
Question 57. Which is the most biologically inert material?
Answer: Silicone
Question 58. Name the compound which acts as scavenger for released hydrogen gas in addition to silicones.
Answer: Platinum
Question 59. What does the penetrometer assess?
Answer: Both working time and setting time
Question 60. What does single tooth impressions known as?
Answer: Tube impression
Question 61. In which impression material autocatalytic reaction is seen?
Answer: ZOE paste
Question 62. Name the material used to improve flow and mixing characteristics of the impression compound.
Answer: Canada balsam
Question 63. Name the principle constituent of dental plaster and dental stone.
Answer: Dental Investment
Question 64. Name the hemihydrate which has fibrous aggregate of fine crystals with pores.
Answer: β-hemihydrate
Question 65. Name the hemihydrate which is characterized by its sponginess and irregular shape.
Answer: α-hemihydrates
Question 66. What is the water/powder ratio of dental plaster and dental stone?
Answer: The water/powder ratio for dental plaster is 0.6 and for dental stone is 0.28
Question 67. For what purpose loss of glass test is done?
Answer: For the initial set of dental plaster
Question 68. Name the retarders used for gypsum.
Answer: Glue and gelatin
Question 69. What is wet strength or green strength?
Answer: It is the strength that is obtained when excess water is present than required for the hydration of hemihydrates which is left out in the specimen.
Question 70. Name the tests which evaluate initial set and fial set of plaster of Paris.
Answer: Initial tests are loss of gloss tests and Initial Gillmore needle test. The final tests are the Vicat needle test and the Final Gillmore needle test.
Question 71. What should be needed to start the addition polymerization?
Answer: Free radicals
Question 72. In a chemically activated induction system in denture base resins which component acts as an activator and which component act as initiator.
Answer: Tertiary amine act as activator and benzoyl peroxide act as an initiator
Question 73. In light activating system which agent acts as activator?
Answer: Photons
Question 74. How much is the wavelength of the light-activated system is required to trigger the reaction?
Answer: 470 nm
Question 75. Name the compounds added to the resin to reduce its fusion temperature.
Answer: Plasticizers
Question 76. Which is the cross-linking agent added to the liquid in poly (methyl methacrylate) dentures?
Answer: Glycol dimethacrylate
Question 77. Name the inhibitor added to polymerized methyl methacrylate.
Answer: Hydroquinone
Question 78. Which are the most popular separating agents?
Answer: Water-soluble alginates
Question 79. What is the advantage of microwave polymerization?
Answer: Polymerization occur speedly
Question 80. What is the disadvantage of fluid resin technique?
Answer: There is the decrease in the overall vertical dimension
Question 81. Why localized polymerization shrinkage occur?
Answer: It occurs due to insufficient mixing of polymer and monomer
Question 82. Which are the short-term soft liners or tissue conditioners?
Answer: Chemically activated materials
Question 83. Which are the most recently used materials in maxillofacial prostheses?
Answer: Polyurethane polymers
Question 84. What is the major disadvantage of quart containing composite?
Answer: They cause difficulty in polishing
Question 85. Which are the most commonly used coupling agents?
Answer: γ methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane
Question 86. Which is the most commonly used inhibitor in resin systems?
Answer: Butylated hydroxyl toluene
Question 87. Which are the optical modifiers in composites?
Answer: Titanium dioxide and aluminum oxide
Question 88. Which is the composite of choice in the anterior teeth mainly in the non-stress-bearing areas?
Answer: Microfiled composite
Question 89. Name the instruments to be used with composites.
Answer: Teflon or plastic instruments
Question 90. Which LASER is best for curing the composites?
Answer: Argon LASER
Question 91. How much percentage of phosphoric acid is used in the acid-etching technique?
Answer: 37%
Question 92. Name the alloys which exhibit complete liquid solubility but limited solid solubility.
Answer: Eutectic alloy
Question 93. Name the peritectic alloy used in dentistry.
Answer: Silver–tin system
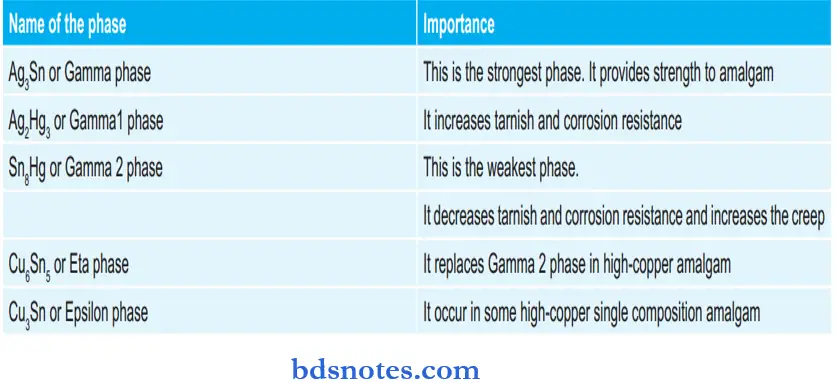
Dental Materials MCQs With Answers
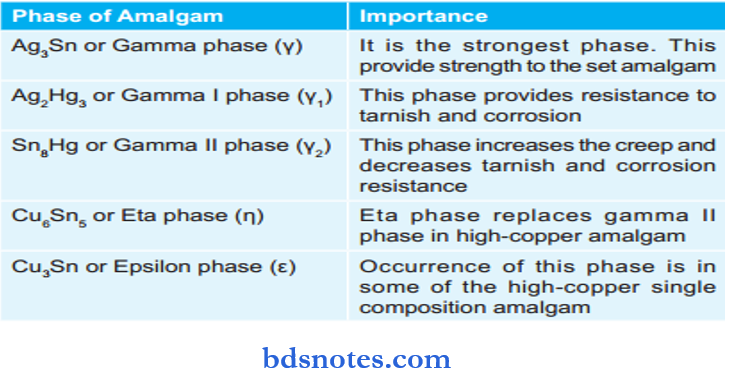
Question 94. Name various phases of amalgam and their importance.
Answer:
Question 95. Which type of hypersensitivity reaction occurs due to mercury allergy?
Answer: Combs Type IV hypersensitivity reaction
Question 96. What is tarnish?
Answer: It is the surface discoloration of metal or even a slight loss on alteration on surface finish or luster.
Question 97. Which compound plays a significant role in tarnish?
Answer: Sulfur
Question 98. Which are the types of alloys immune to sulfide tarnishing?
Answer: Base metal
Question 99. Which amalgam is associated with delayed expansion?
Answer: Zinc containing amalgam
Question 100. Name the gas developed in delayed expansion.
Answer: Hydrogen gas
Question 101. What is the main function of zinc in amalgam?
Answer: It acts as a deoxidizer
Question 102. Which is the weakest phase in the amalgamation reaction?
Answer: Sn8Hg or Gamma II phase
Question 103. Which is the strongest phase in the amalgamation reaction?
Answer: Ag3Sn or Gamma phase
Question 104. Name the main tarnish product of amalgam.
Answer: Ag2S
Question 105. Name the amalgam which has the highest compressive strength after 1 hour and 2 days period.
Answer: Single composition
Question 106. In which type of amalgam highest condensation pressure is required?
Answer: Lathe-cut
Question 107. Which are the most common corrosion products found with traditional amalgam alloys?
Answer: Oxides and chlorides of tin
Question 108. As mercury restoration is done pain after 24 hours of restoration is due to.
Answer: Hyperocclusion or cracked tooth
Question 109. How much is the maximum safe level of mercury during occupational exposure?
Answer: 50 micrograms per cubic mm.
Question 110. As mercury restoration is done pain after 4 to 5 days of restoration is due to:
Answer: Delayed expansion
Question 111. Which is the most malleable metal?
Answer: Gold
Question 112. Which is the oldest gold product?
Answer: Gold foil
Question 113. What does ammonia-treated gold foil known as?
Answer: Non-cohesive gold foil
Question 114. What is the role of platinum in gold foil?
Answer: It increases hardness and wear resistance.
Question 115. How much is the solidification shrinkage of gold alloy?
Answer: 1.25 to 1.65%
Question 116. What does karat refers to the parts of pure gold in how much parts of an alloy?
Answer: 24
Question 117. What is the use of mat gold?
Answer: Mat gold builds the internal bulk of restoration.
Question 118. What do you meant by 22-karat gold?
Answer: It means the gold alloy consists of 22 parts of pure gold and 2 parts of other metals.
Question 119. What do you mean by stepping?
Answer: It is the process in which each increment of gold is stepped by placing the condenser point at the adjacent positions as force is provided. Stepping causes each piece to compact over the whole surface so that voids do not get bridged.
Question 120. What is encapsulated gold powder or granulated gold?
Answer: At fist the powdered gold is mixed with wax and pellets are formed, these are than wrapped with gold foil. This is called as encapsulated gold powder.
Question 121. To which of the alloys is ‘greening’ associated?
Answer: Palladium silver alloy
Dental Materials MCQs With Answers
Question 122. What is greening shrinkage?
Answer: It is seen in silica-bonded investments because of drying of colloidal silica gel.
Question 123. Which metals produce passivating effect?
Answer: Chromium, aluminum, and titanium
Question 124. What is tempering?
Answer: It is the process of heat treating that increases the toughness of iron-based alloys
Question 125. What is sensitization?
Answer: When 18-8 stainless steel is heated to 400 to 900°C, chromium combines with carbon, and the resultant compound is chromium carbide due to which the corrosion resistance property of stainless steel is reduced.
Question 126. What is stabilization of stainless steel?
Answer: To remove sensitization titanium is added to stainless steel and as titanium gets readily precipitated and form titanium carbide which is more corrosion resistant. This is known as stabilization of steel.
Question 127. What is Elgiloy?
Answer: It is Co – Cr – Ni
Question 128. What is grain refinement?
Answer: It is the process of reduction of grain size in solid metal by adding an element or compound to molten metal and cooling at particular rate.
Question 129. What do you mean by equiaxed?
Answer: It means that all three dimension of grain are similar.
Question 130. Which material is commonly used as an antireflux?
Answer: Graphite
Question 131. What are the uses of martensitic steel?
Answer: It is used in the manufacturing of surgical and cutting instruments
Question 132. What are the uses of austenitic steel?
Answer: It used for manufacturing orthodontic wires, endodontic instruments, and crowns used in pediatric dentistry.
Question 133. Which is the most main ingredient in inlay wax?
Answer: Paraffin wax
Question 134.For smoothening and making the paraffin wax resistant to cracking what is added?
Answer: Gum Damar
Question 135. Which wax has low thermal conductivity and high coefficient of thermal expansion?
Answer: Inlay wax
Question 136. Which compound has elastic memory?
Answer: Dental wax
Question 137. By which dental material green shrinkage is associated with?
Answer: Ethyl-bonded investment
Question 138. If the size of the sprue former is small which type of porosity occurs?
Answer: Localized shrinkage porosity
Question 139. At what angle the sprue pattern is spread?
Answer: 45°
Question 140. How much is the maximum investment thickness between the end of mold cavity and the end of investing ring?
Answer: 6 mm
Question 141. What is pickling?
Answer: Pickling is the process which removes surface oxides from gold castings.
Question 142. Which is the best pickling solution used for the gypsum casting investments?
Answer: 50% HCl
Question 143. Why do fis and spines occur on the casting?
Answer: Rapid heating
Question 144. What is the process of removing the smear layer is known as?
Answer: Conditioning
Question 145. If type II GIC gets combined with admixed amalgam alloy what it is known as?
Answer: Miracle mix
Question 146. Name the cement which is least irritating to the tissues.
Answer: Zinc oxide eugenol cement
Question 147. Name the technique which uses the advantages of glass ionomer cement and provides esthetics of composite restoration.
Answer: Sandwich technique
Question 148. Name the first cement which undergoes adhesive bonding with tooth structure.
Answer: Zinc polycarboxylate
Dental Materials MCQs With Answers
Question 149. Which cement has the highest floride content?
Answer: Silicophosphate cement
Question 150. What do you mean by ion leachable glass?
Answer: Powder of traditional glass ionomer cement is known as ion-leachable glass. Ion leachable glass is calcium -floro – aluminum – silicate glass.
Question 151. Which is the oldest luting cement?
Answer: Zinc phosphate cement
Question 152. Name the cement which causes injury to the pulp.
Answer: Silicate cement
Question 153. Which is the least irritating dental cement?
Answer: Zinc oxide eugenol cement
Question 154. What is chemical tempering?
Answer: It is the exchange of larger potassium ions for small sodium ions.
Question 155. What is thermal tempering?
Answer: In this process quenching of the particular compound is done when it is hot and present in its molten state.
Question 156. What is added in ceramics to gain opacity?
Answer: Titanium oxide.
Question 157. What is leucite?
Answer: Feldspar when melted forms a crystalline phase known as leucite.
Question 158. What is sintering?
Answer: This is the process of filing the ceramic so particles of powder sinter together to form a prosthesis.
Question 159. What is abrasive binding?
Answer: Abrasive binding is the clogging of the abrasive instrument with debris.
Question 160. What is abrasive dressing?
Answer: This is the procedure that removes clogged debris from the abrasive instrument.
Question 161. What do you mean by IPS empress?
Answer: This is a leucite-based ceramic and have 35% leucite by volume. It is used for making anterior veneers.
Question 162. What do you mean by IPS empress II?
Answer: This is lithium disilicate-based ceramic. It is used as core build-up ceramic for crowns and bridges.
Question 163. What is glazing?
Answer: It is the process which provides a smooth and glossy surface, improves esthetics, and helps in maintain hygiene.
Question 164. What is cramming?
Answer: It is the process of microscopic plate-like crystal nucleation and growth of crystalline material in the glass matrix.
Question 165. What is brazing?
Answer: In this process metal parts are joined together by melting filer material between these two metal parts at a temperature below the solidus temperature of the metal being joined. Fusion temperature of the filer is greater than 450°C.
Question 166. What is soldering?
Answer: In this process metal parts are joined together by melting filer material between these two metal parts at a temperature below the solidus temperature of the metal being joined. The fusion temperature of the filer is lesser than 450°C.
Question 167. What is welding?
Answer: It is the method of joining two parts of metal pieces by either applying pressure or applying heat or both.
Question 168. What is pre- and post-soldering?
Answer: Joining two metals before porcelain veneering is known as soldering while joining two metals after porcelain veneering is known as post soldering
Question 169. Name the commonly used dental soldiers.
Answer: Gold solder and silver solder
Question 170. What is flux?
Answer: Flux is an agent which removes the oxide coating on parent metal and protects metal surface from oxidation during the soldering procedure.
Question 171. What is antireflux?
Answer: This agent is used to limit the flow of molten solder over metals being joined.
Question 172. Which is the most commonly used heat source for melting the solder?
Answer: Gas oxygen torch
Additional Formation
Various Terminologies:
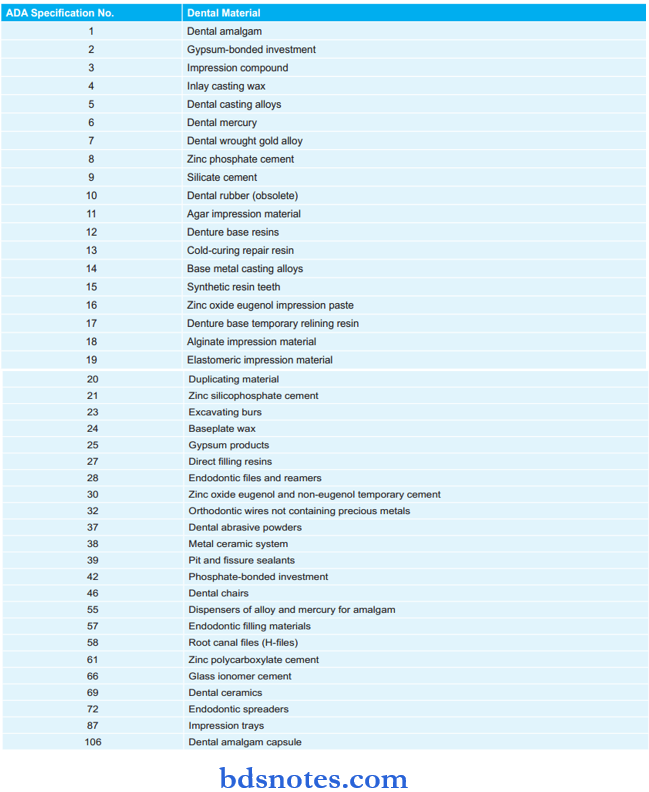
ADA Specification NUmbers Of Various Dental Materials:
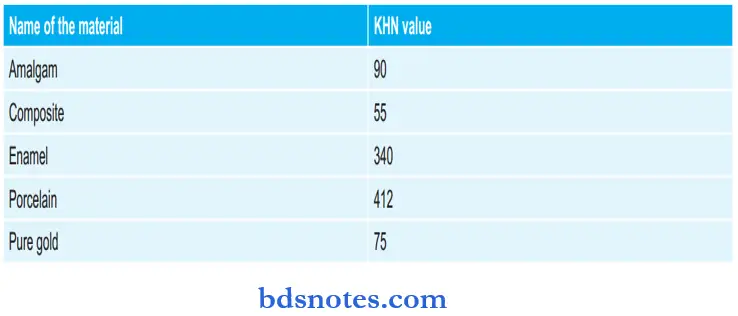
Various Hardness Tests And of Thermal Expansion of Various Materials:
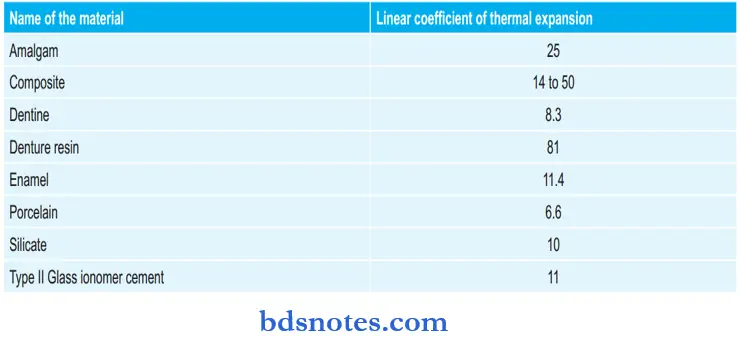
Linear Coefficient Of Thermal Expansion Of Various Materials:
KHN Values Of Various Materials:
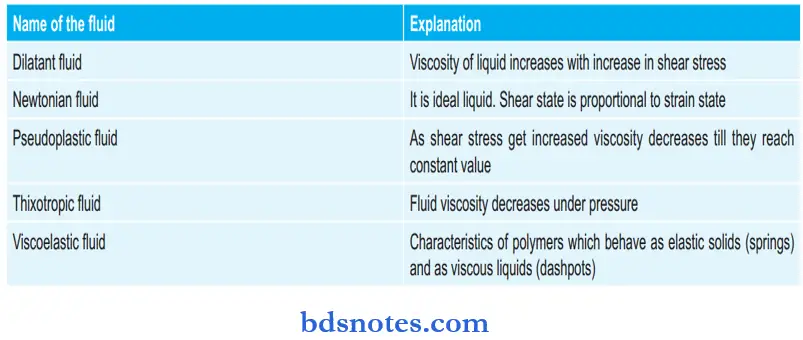
Various Types Of Fluids:
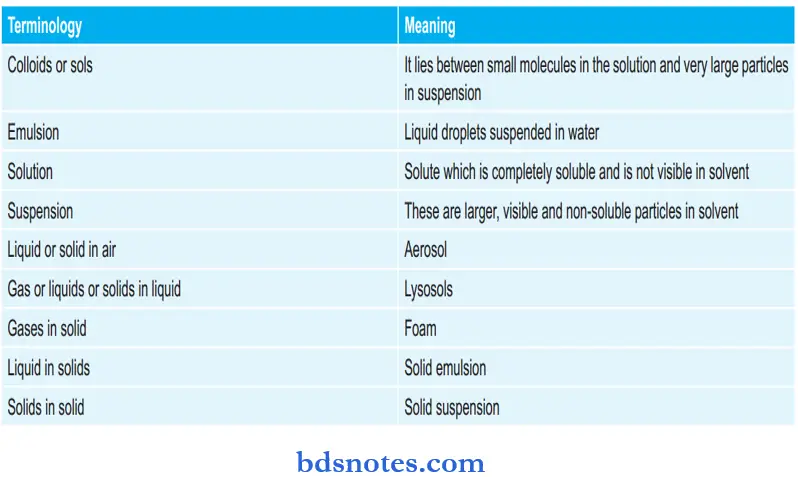
Various Terminologies:
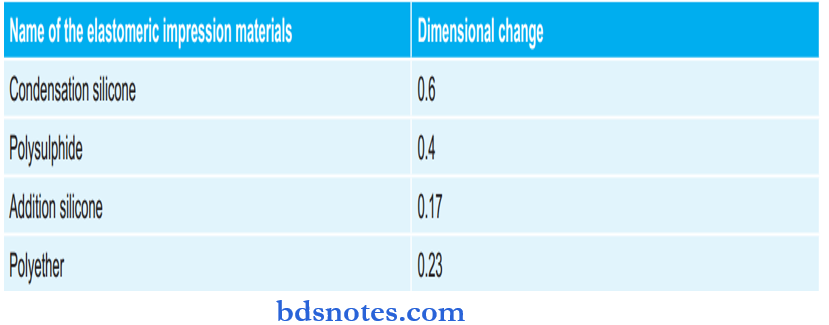
Elastomeric Impression Materials And Numerical Values Of Their Dimensional Change
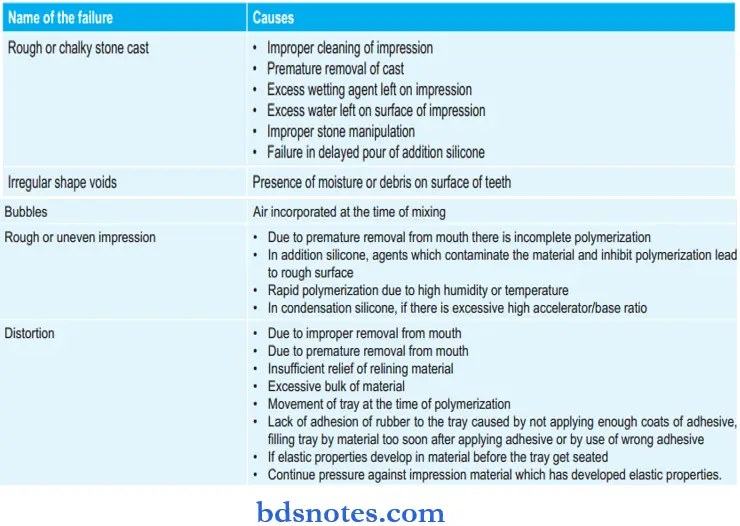
Failures Of Non – aqueous Elastomeric Impression Materials:
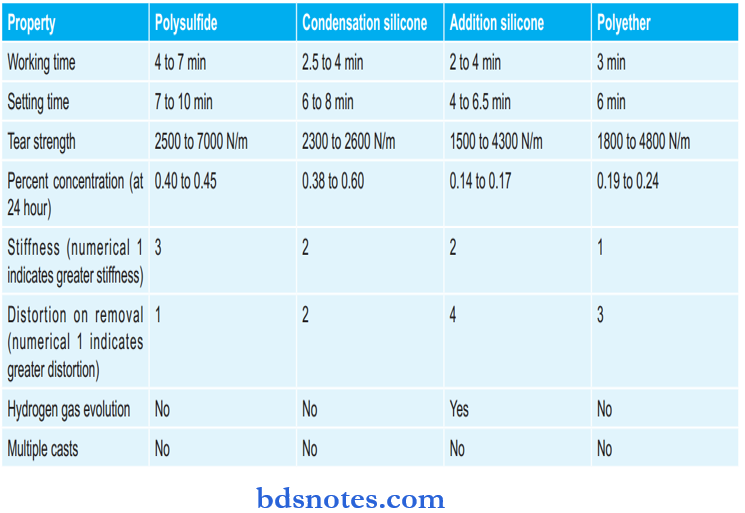
Various Properties Of Elastomeric Impression Materials:
Increasing OrderOf Permanent Deformation In Elastomeric Impression Materials:
Addition silicone < Condensation silicone <Polyther<Polysulfide.
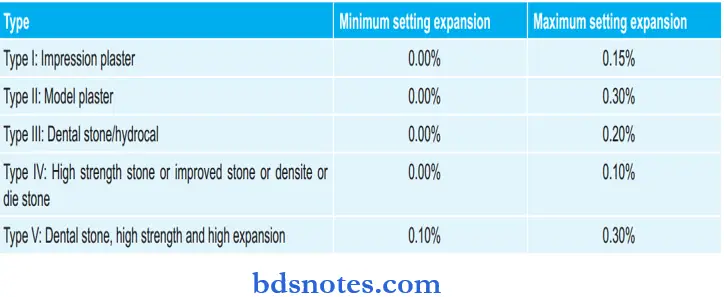
Types Of Gypsum Products With Their Setting Expansion:
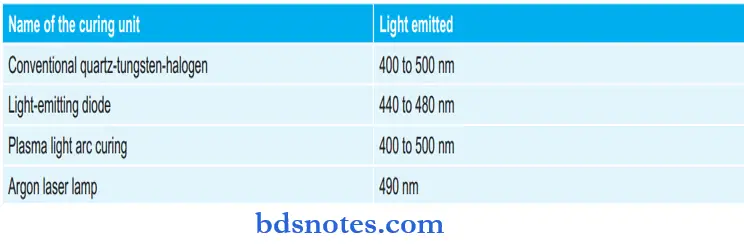
Name of the Curing and Light Emitted by them:
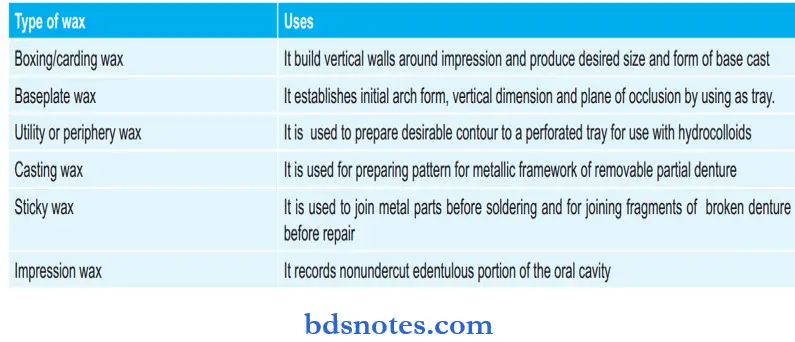
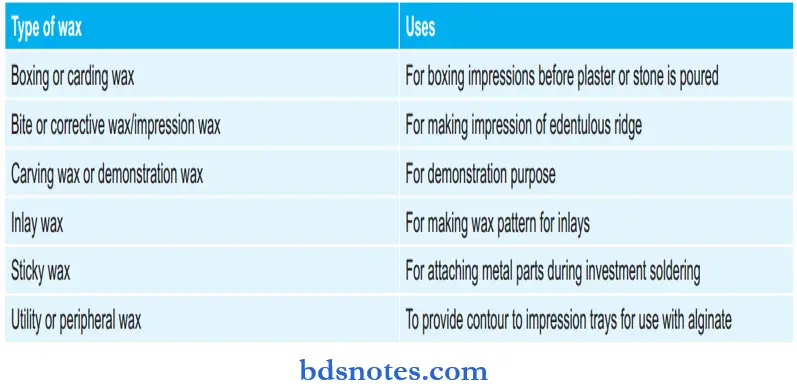
Types of wax and their uses:
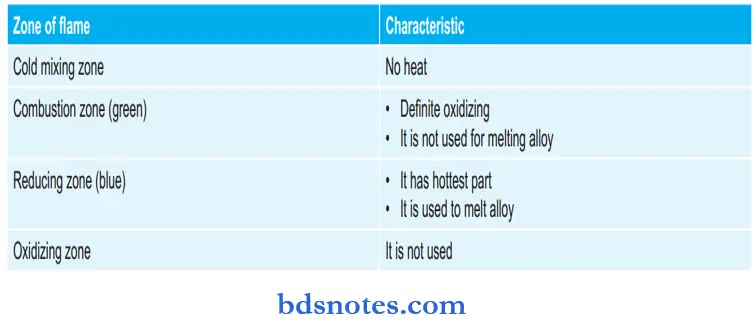
Various Zones of Flame:
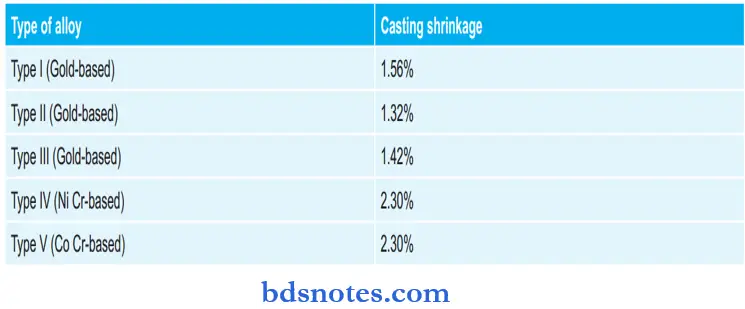
Various Casting Alloys with their Linear Solidification Shrinkage:
Various Metals And Their Properties :
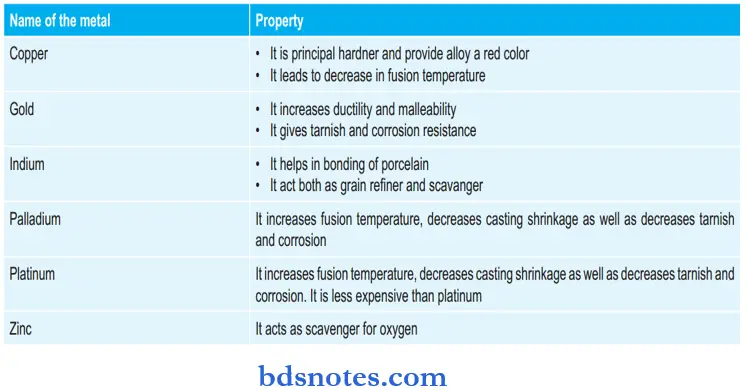
Various Alloys and their Constituents:
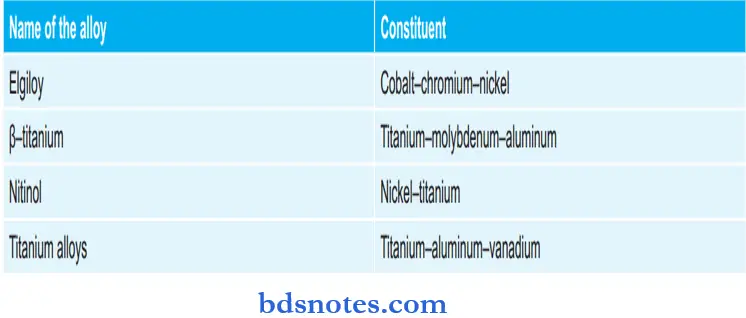
Coefficient Of Thermal Expansion Of Various Materials:
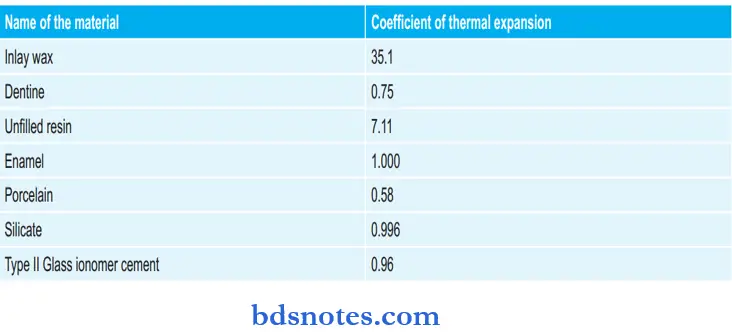
Various Pigment Oxides and their Shades to Natural Tooth:
Various Processing Methods and Ceramic Material Used:
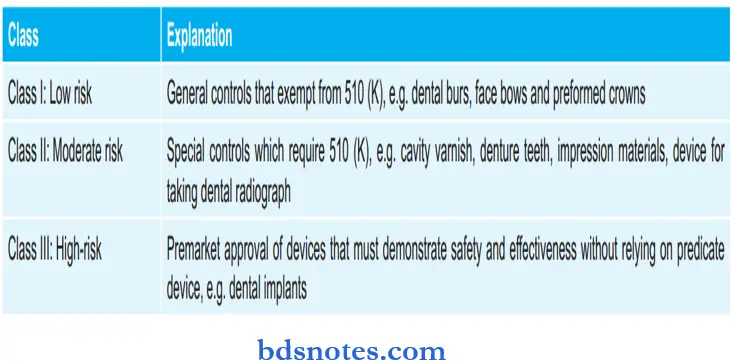
US FDA Classification of Devices in Three Possible Risk-Based Classes:
Various Generations of Amalgam:
Various Phases of Amalgam and their importance:
Increase in Order Strenght of Various Amalgam Alloys:
Low – copper <Admix alloy < Single composition
Types of Waxes and their Uses:
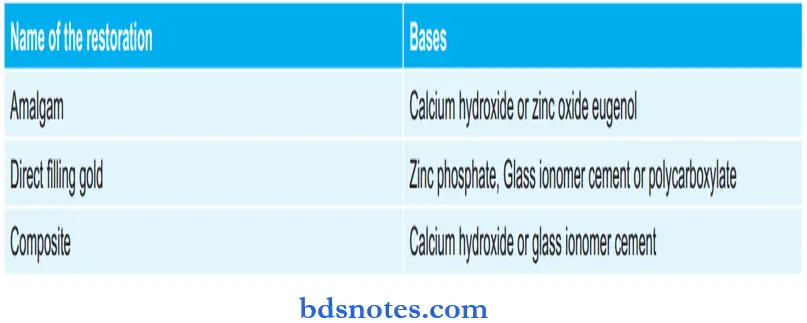
Various Restorations and Bases used with them:
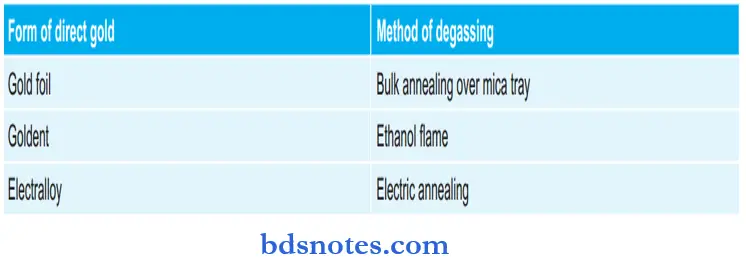
Form of direct gold and its method of degassing:

Leave a Reply