Dental Materials Miscellaneous
Question 1. Describe blood supply and lymphatic drainage of the tongue.
Answer:
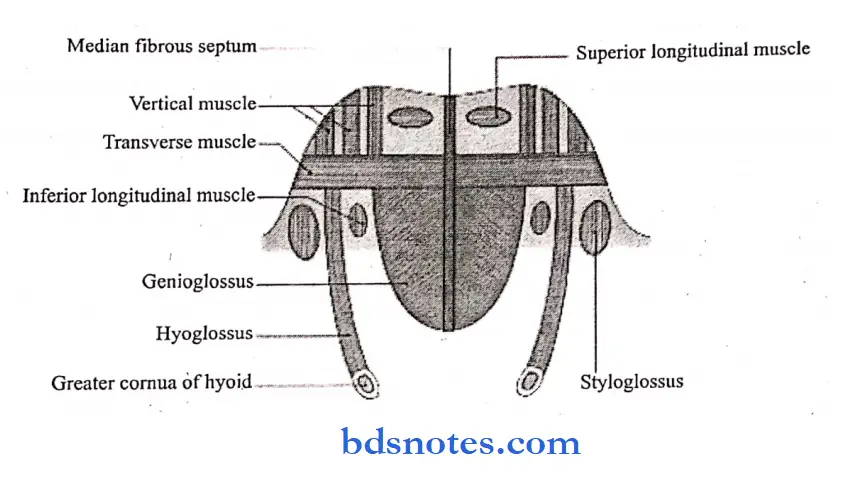
Muscles of the tongue:
1. Intrinsic muscle:
- Superior longitudinal:
- It lies beneath the mucous membrane.
- It shortens the tongue and makes it dorsum concave.
- Inferior longitudinal:
- It is a narrow band lying close to the inferior surface of the tongue between the genioglossus and the hyoglossus.
- It shortens the tongue and makes its dorsum convex.
- Transverse:
- It extends from the median septum to the margins.
- It makes the tongue narrow and elongated.
- Vertical:
- It is found at the borders of the anterior part of the tongue.
- It makes the tongue broad and flattened.
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
2. Extrinsic muscle:
- Genioglossus – connects the tongue to the mandible
- Hyoglossus connects the tongue to the hyoid bone
- Styloglossus connects the tongue to the styloid process
- Palatoglossus – connects the tongue to the palate.
Arterial supply:
- Lingual artery – a branch of the external carotid artery
- Tonsillar branch of the facial artery
- Ascending pharyngeal branch of the external carotid.
Venous drainage:
- Deep lingual vein.
- This ends in the internal jugular vein.
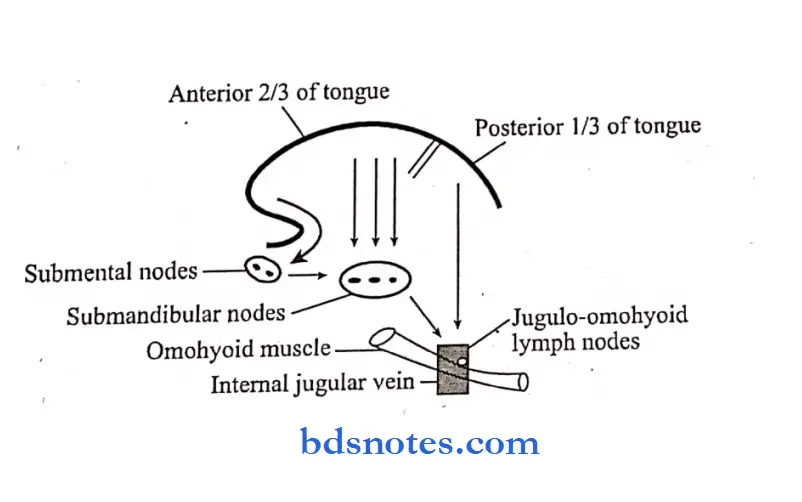
Lymphatic drainage:
- Tip of the tongue – to submental nodes
- Anterior rd of the tongue – to submandibular nodes
- Posterior rd of the tongue – to jugular -omohyoid nodes
- Posterior most part – upper deep cervical lymph nodes.
Question 2. Functions of tooth
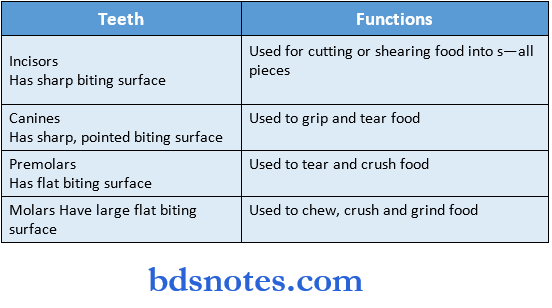
Answer:
- Functions of tooth Chewing Food needs to be broken and chewed before entering the digestive system so that our body can easily absorb nutrients from them
- Functions of Tooth Speech Teeth help to pronounce accurately
- Functions of tooth Esthetic Teeth help to look good
- Preserve space for permanent teeth Deciduous teeth provide room for permanent teeth
Question 3. Pain pathway
Answer:
Pain pathway for fast pain:
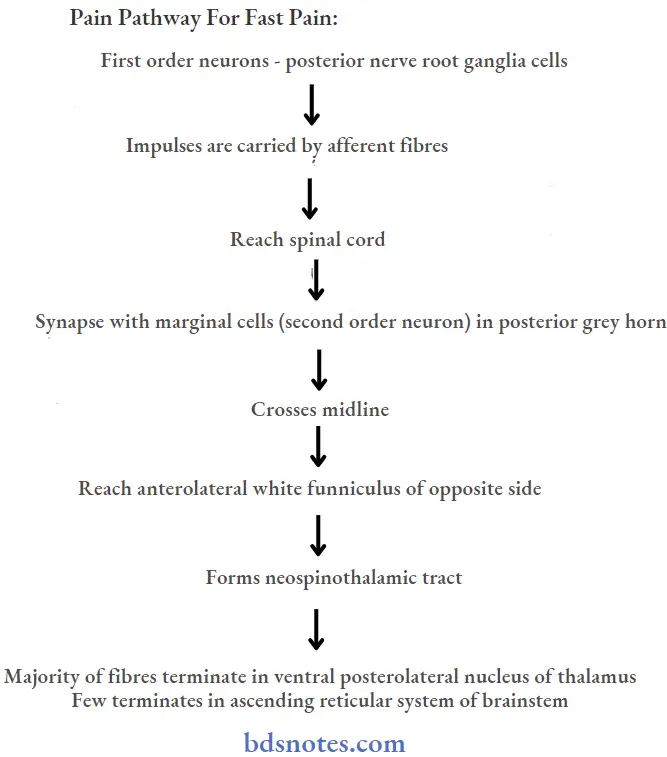
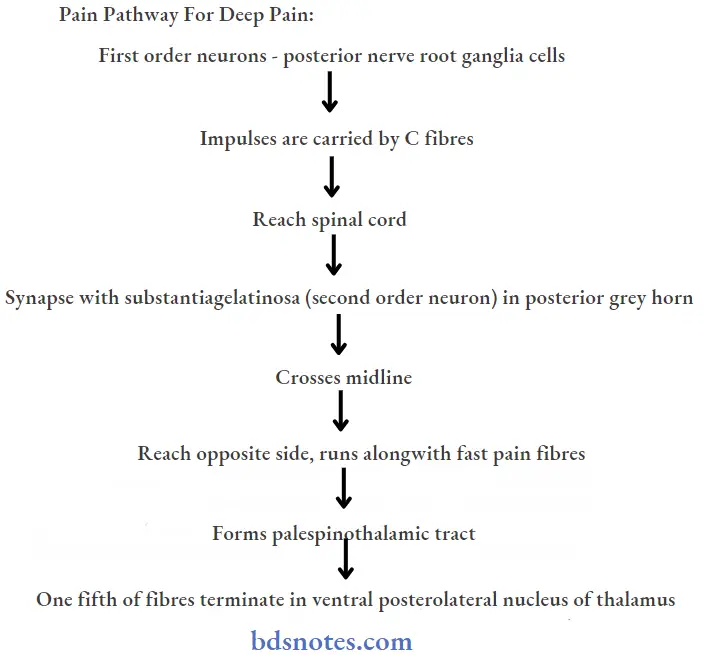
The remaining terminates in:
- Reticular formation of the brainstem
- Tectum of brainstem
- Grey matter around the aqueduct of Sylvius
- Terminating sites forms third order neuron
Question 4. Nerve supply to the tongue.
Answer:
1. Motor nerves:
- Palatoglossus muscle – by the cranial root of the vagus nerve
- All other muscles – hypoglossal nerve.
2. Sensory nerves:
- General sensation – lingual nerve.
- A taste sensation for anterior 2/3rd except vallate papillae chorda tympani.
- General sensation and taste for the posterior 1/3rd including circumvallate papillae – glossopharyngeal Posterior most part of the tongue vagus nerve.
Question 5. Pathways of taste.
Answer:
First-order neurons:
- Taste fibers of the facial nerve (VII), glossopharyngeal (IX) nerve, and vagus (X) nerve run, into the nucleus of tractus solitarious (NTS) in the medulla.
- The cell bodies of the second-order neurons are located in NTS and their axons ascend to join the medial lemniscus and terminate with V nerve fibers in the posteroventral nucleus of the thalamus.
- The third-order neurons arise and end in the inferior part of the ipsilateral postcentral gyrus.
Question 6. Tuberculum impair.
Answer:
- The medial ends of the two mandibular processes are separated by a midline swelling.
- This is called tuberculum impar.
- Immediately behind it, the epithelium proliferates to form a down growth (thyroglossal duct) from which the thyroid gland develops.
- The site of this downgrowth is subsequently marked by a depression called foramen caecum.
- The anterior two-thirds of the tongue is formed by the fusion of the tuberculum impar and the two lingual swellings.
Question 7. Submerged teeth.
Answer:
- They are ankylosed deciduous teeth usually located in the mandibular posterior region.
- They occur since the occlusal table of the retained smaller-sized tooth is located below the occlusal plane of the rest of the teeth in the arch.
- It is merely a deciduous tooth.
- It may occur because of the congenital absence of an underlying permanent tooth.
- Normally the surrounding permanent teeth which have erupted earlier, lock the submerged deciduous molar in its original position.
Question 8. Super numerary teeth.
Answer:
- The presence of any extra tooth in the dental arch in addition to the normal series of teeth is called supernumerary teeth.
- It may develop from
- Accessory tooth bud
- Splitting of the normal tooth bud
- It is more common in the maxilla.
Super numerary teeth Types:
- Mesiodens
- Distomolars
- Paramolars
- Extra lateral incisors.
Question 9. Infantile swallowing.
Answer:
- It is limited to breastfeeding.
- During it, the tongue is positioned over the lower gum pad protruding between the lower lip and nipple.
- Through it, milk is directed to the pharynx by the peristaltic movement of the tongue and mylohyoid.
- Passage of milk occurs between buccal pillars and lateral channels of the pharynx.
- It is transformed to mature swallowing.
Question 10. Freeway space
Answer:
- During rest position, space exists between the upper and lower teeth
- This is called freeway space
Freeway space Value:
- It should be 2-4 mm
Freeway space Significance:
- If it increases, the vertical dimension at occlusion reduces and becomes inefficient
- If it decreases, the vertical dimension at occlusion increases to a great extent
Question 11. Odland bodies
Answer:
- It is a small organelle formed in the upper spinous and granular cell layer
- It is a coating granule, glycolipid in nature
- It has an internal lamellated structure
- Its contents get discharged into the intercellular space forming an intercellular lamellar material that contributes to the permeability barrier
- This barrier is formed between granular and cornified cell layers

Leave a Reply